Chapter 15 - The Special Senses
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Describe the sound conduction pathway to the fluids of the internal ear
Sound Detection → Hearing is the reception of an air sound wave that is converted to a fluid wave that ultimately stimulus mechanosensitive cochlear hair cells that end impulses to the brain for interpretation
Anatomy of the Cochlea
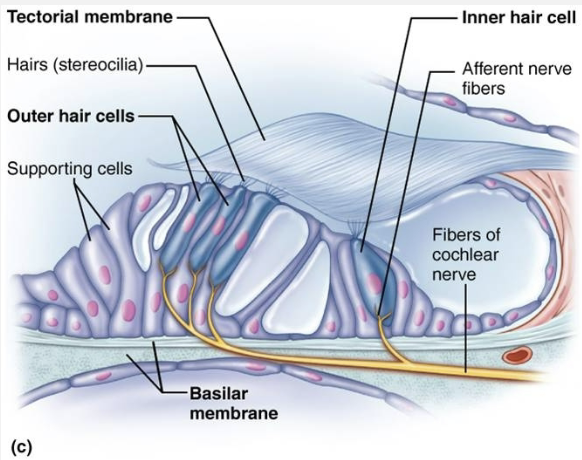
Auditory Pathway
Tympanic membrane
Sound waves enter external acoustic meatus and strike tympanic membrane, causing it to vibrate
The higher the intensity, the more vibration
Auditory ossicles
Transfer vibration of eardrum to oval window
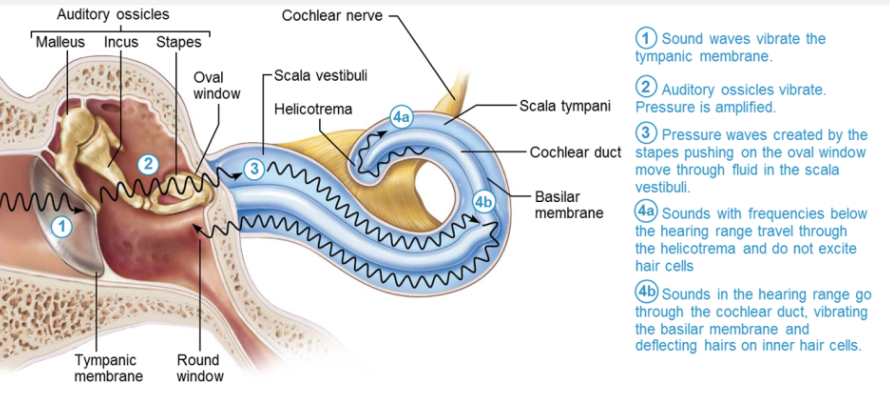
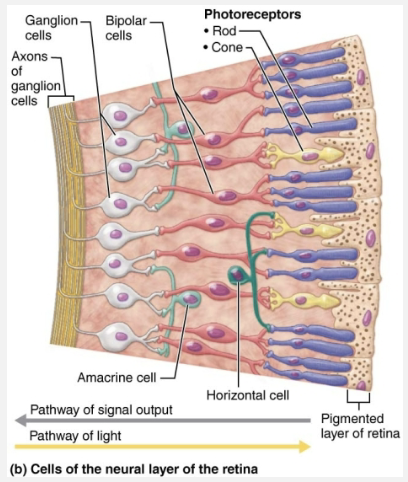
Describe the structure of the Retina
Retina → Originates as an out-pocketing of brain
Contains:
Millions of photoreceptors cells that transduce light energy
Neurons
Glial cells
Delicate two layered membrane
Outer pigmented layer
Inner neural layer
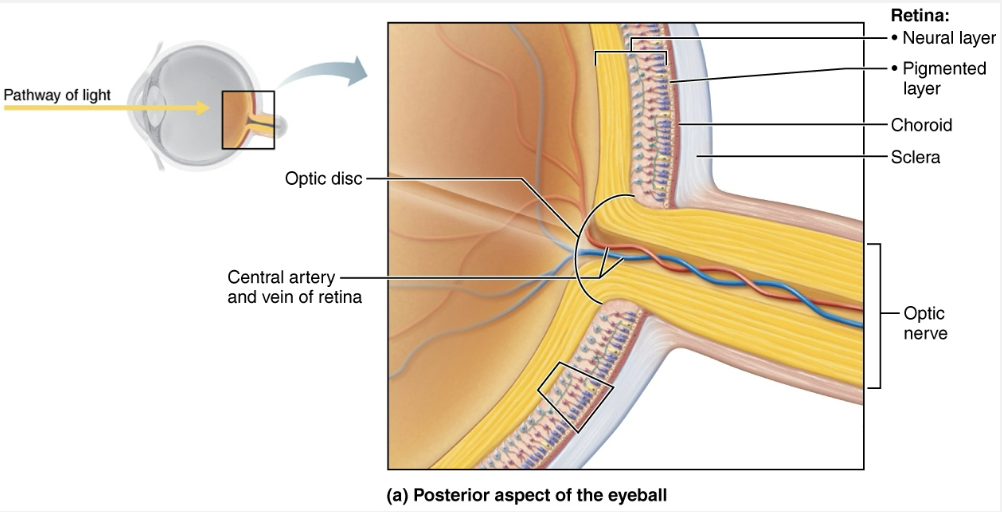
Two Membrane Layers of the Retina
Outer pigmented layer
STRUCTURE
Single-cell-thick lining next to choroid
Extends anteriorly, covering ciliary body and iris
FUNCTION
Absorbs light and prevents its scattering
Phagocytizes photoreceptor cell fragments
Stores vitamin A
Inner neural layer
STRUCTURE
Transparent layer
Composed of three main types of neurons
Photoreceptors
Bipolar neurons
Ganglion cells
FUNCTION
Signals spread from photoreceptors to bipolar cells to ganglion cells
Ganglion cell axons exit eye as optic nerve
Optic Disc
Site where optic nerve leaves eye
Lacks photoreceptors, so referred to as blind spot
Type Types of Photoreceptors
Modified neurons
Rods
Dim light, peripheral vision receptors
More numerous and more sensitive to light than cones
No color vision or sharp images
Numbers greatest at periphery
Cones
Vision receptors for bright light
React more quickly than rods
High-resolution color vision
Light
Packets of energy (photons or quanta) that travel in wavelike fashion at high speeds
Color that eye perceives is a reflection of that wavelength
EX: Grass is green because it absorbs all colors EXCEPT green
EX: White reflects all colors, and black absorbs all colors
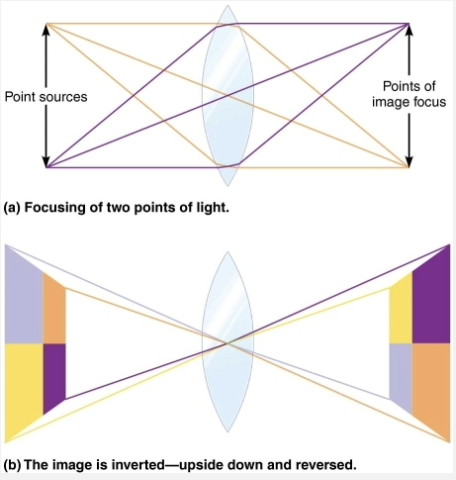
Refraction and Lenses
Refraction → Bending of light rays
Due to change in speed of light when it passes from one transparent medium to another and path of light is at an oblique angle
EX: from liquid to air
Lenses → Can also refract light because they are curved on both sides
Convex: Thicker in center than at edges
Bend light passing through it → so that rays converge at focal point
Image formed at focal point is upside-down and reversed from left to right
Concave: Ticker at edges than in center
Disperse light, preventing light from being focused
Describe the Pathway of Light though the Eye
Pathway of light entering eye
Cornea
Aqueous humor
Lens
Vitreous humor
Entire neural layer of retina
Photoreceptors
Light is refracted three times along path:
Entering cornea
Entering lens
leaving lens
Lens is able to adjust its curvature to allow for fine focusing
Can focus for distant vision and for close vision
Explain Color blindness and Astigmatism
Color blindness → Lacks one or more cone pigments
Inherited as a X-linked condition, so more common in males
The most common type is red-green, in which either red cones or green cones are absent
Depending on which cone is missing, red can appear green, or vice versa
Relay on different shades to get cues of color
Taste
Sensory organ for taste
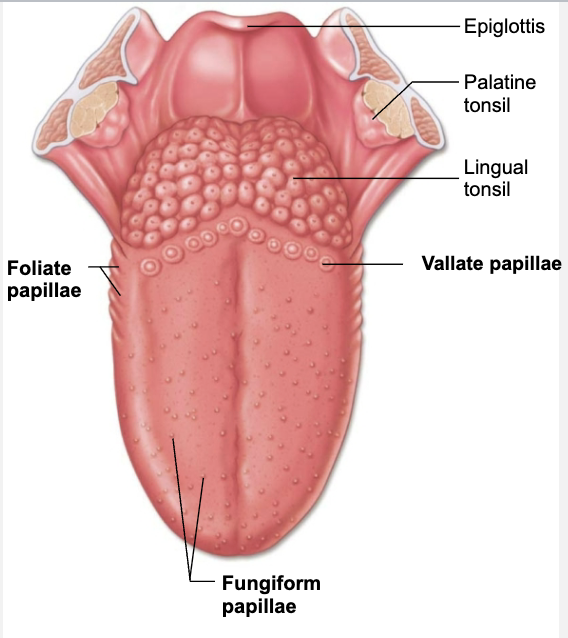
Most of 10,000 taste bunds are located in papillae, peg-like projection of tongue mucosa
Describe Structure and Function of 3 Types of Taste Buds
Fungiform papillae
Tops of these mushroom-shaped structures house most taste buds
Scatted across tongue
Foliate papillae
On the side walls of tongue
Vallate papillae
Largest taste bund with 8-12 forming “V” at back of tongue
Two types of Epithelial cells on each Taste Bud
Gustatory epithelial cells
Taste receptor cells have microvilli called gustatory hairs that project into taste pores, bathed in saliva
Sensory dendrites coiled around gustatory epithelial cells send taste signals to brain
Three types of gustatory epithelial cells
One releases serotonin
Others lack synaptic vesicles
But one releases ATP as neurotransmitter
Basal epithelial cells
Dynamic stem cells that divide every 7-10 days
List the five basic taste sensation
Sweet
Sugars
Saccharin
Alcohol
Some amino acids
Some lead salts
Sour
Hydrogen ions in solution
Salty
Metal ions (inorganic salts)
Sodium chloride tastes saltiest
Bitter
Alkaloids such as quinine and nicotine
Caffeine
Non-alkaloids; aspirin
Umani
Amino acids glutamate and aspartate
EX: beef or cheese taste
Monosodium glutamate
Physiology of Taste
Be dissolved in saliva
Diffuse into taste pore
Contact gustatory hairs
Influence of Other Sensations on Taste
Taste is 80% smell
If nose is blocked, foods taste bland
Mouth also contains thermoreceptors, mechanoreceptors, and nociceptors
Temperature and texture enhance or detract from taste
Spicy hot foods can excite pain receptors in mouth, which some people experience as pleasure
EX: hot chili peppers