Business Chapter 1 Gr 10
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Business
An organization that produces and/or sells goods and/or services to satisfy the needs and wants of consumers.
Producers
Individuals or companies that make goods or provide services.
Consumers
Individuals who buy goods and use services to fulfill their needs or wants.
Goods
Physical items that can be purchased and used, such as a computer or car.
Services
Non-tangible acts that provide benefits to consumers in exchange for payment, like haircuts or consultations.
Consumer Goods
Goods purchased directly by consumers to satisfy personal needs and wants.
Industrial Goods
Goods purchased by businesses for production purposes, such as flour for baking.
Ultimate Consumer
The individual who buys goods for personal use.
Industrial Consumer
A business that uses goods for its own operations, like a restaurant buying bread.
Factors of Production
Resources needed to produce goods and services, including human resources, natural resources, capital, and technology.
Profit
The income remaining after all costs and expenses are paid; calculated as Revenue - Expenses.
Expenses
The costs incurred in running a business, such as wages and materials.
Solvent
A business that can cover all its expenses but may not be making a profit.
Competition
The rivalry among businesses to attract consumers, influencing prices and quality.
Direct Competition
Businesses that offer similar goods or services to the same market.
Indirect Competition
Businesses that fulfill the same need in different ways.
Demand
The quantity of goods or services consumers are willing to buy at a specific price.
Law of Demand
As the price of a good/service decreases, the quantity demanded increases.
Supply
The quantity of goods or services that businesses are willing to provide at various prices.
Law of Supply
Higher prices typically lead to an increase in the quantity supplied.
Price
Determined by the interaction of supply and demand; influenced by production costs.
Obsolete
Items that are no longer in use or useful, such as VCRs or typewriters.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
physiological, safety, belongingness, ego, self- actualization
Decision-Making Model
A structured approach for businesses to solve problems and adapt to consumer needs and market changes.
Steps in the Decision-Making Model
Define the decision, identify alternatives, evaluate pros and cons, make a decision, and evaluate the decision.
a want
a non essential product to survival
a need
an essential product for survival
factors affecting demand
consumer’s income, increase in income level ( increases spending), decrease in income level ( decreases spending), change in expectation of future conditions, change in population
factors affecting supply
change in the number of producers, price of related goods, change in technology, change in expectation, change in cost of production
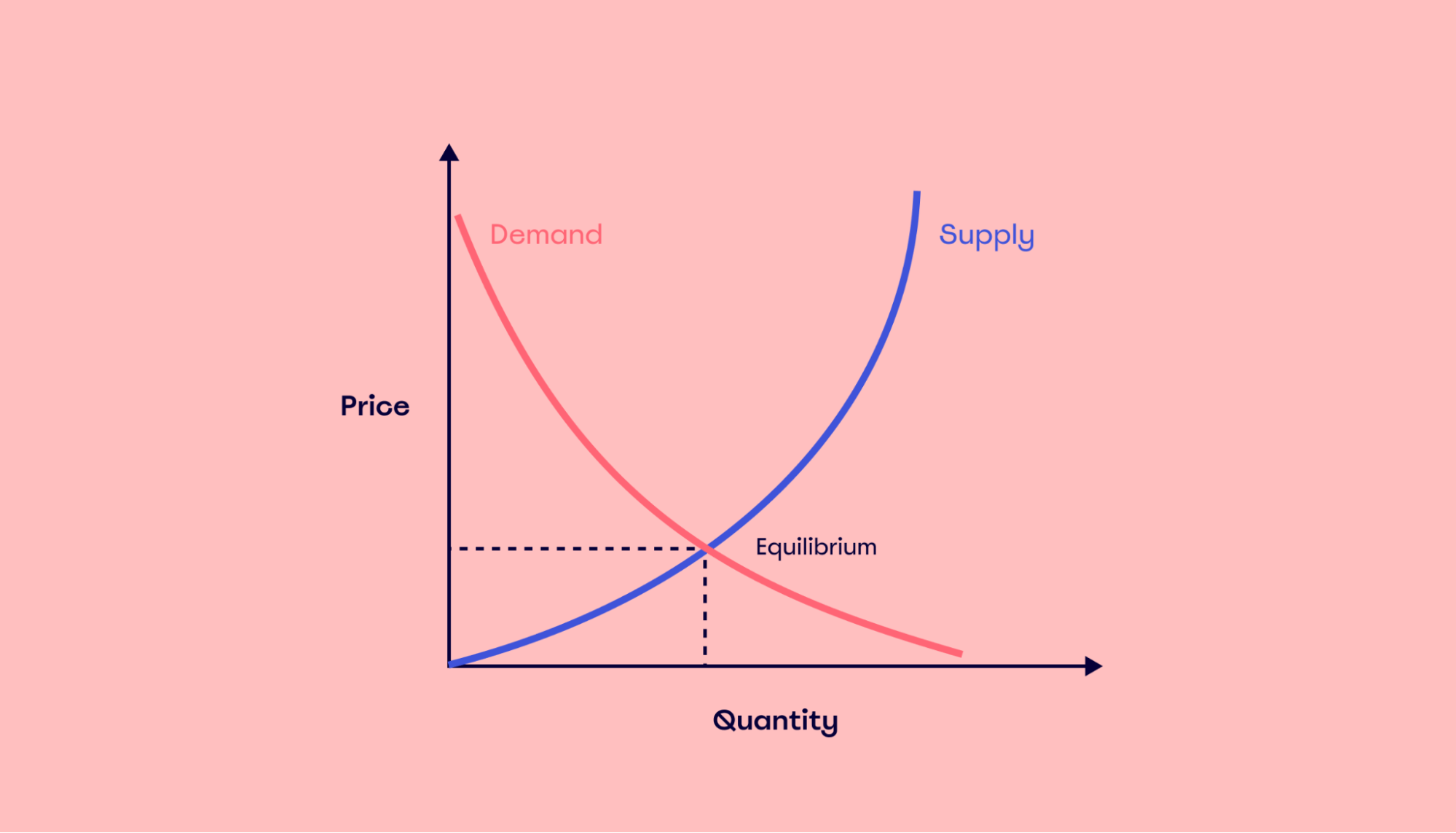
supply and demand curve
higher price higher supply, lower price higher demand
3 consumers benefits of competition
higher product quality, production and introduction of new products, lower prices
examples of innovation
cyclotron ( cancer treatment), beanless coffee, smart swim goggles with AR