Foundations of Psychology
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
Psychology
the scientific study of behavior and mental processes
Behavior
anything that you do that can be observed in response to different stimuli
Mental processes
internal experiences like thoughts, feelings, sensations, and perceptions that can be observed
Systematic study
Systematic collection and examination of data or empirical evidence to support or disprove hypotheses rather than depending on common sense
Scientific method
validity, replication, reliability for a good test
Hippocrates
Greek Physiologist who believed the mind or soul resided in the brain, mind-body dualism
Mind-body dualism
seeing mind and body as two different things that interact
Plato
Greek philosopher who believed that who we are and what we know are innate (nature)
Aristotle
Plato's student who believed that who we are and what we know are acquired from experience (nurture)
John Locke
believed that knowledge comes from observation, coined the term 'tabula rasa' (born knowing nothing-blank slate) nurture
Rene Descartes
believed that what we know is innate and focused on how the nervous system responds (nature)
Nature vs. nurture
debate about the extent to which behavior is inborn or learned through experience
Charles Darwin
came up with the theory of natural selection
Wilhelm Wundt
credited as the founder of scientific psychology, set up the first research Laboratory in Germany in 1879. created school of structuralism, which studied the elements of consciousness
Introspection
looking inward to identify how one feels, thinks, or acts. used in structuralism
William James
psychologist who focused on the function or purpose of behavioral acts (the why). started the school of functionalism and wrote the first psychology text book
Max Wertheimer
founded Gestalt Psychology, asserting that the whole is more than the sum of its parts
Eight approaches to psychology
Behavioral, psychoanalytic/psychodynamic, humanistic, biological, cognitive, evolutionary, socio-cultural, eclectic
Behavioral psychology
focuses on measuring and recording observable behavior. everyone could be taught to behave a certain way. pavlov, skinner, and watson. classical, operant, and oversive
Pavlov
studied dogs and rewards in behavioral psychology
Skinner
studied rats, reward and punishment in behavioral psychology
Watson
studied Baby Albert and associations in behavioral psychology
Psychoanalytic
focuses on unconscious internal conflicts to explain mental disorders
Sigmund Freud
developed the psychoanalytic approach and focused on unconscious desires
Psychodynamic
varied with Freud's ideas but kept with the roots of psychoanalysis. approved them with the proper scientific method
Humanistic
emphasizes the importance of people's feelings and views human nature as naturally positive and growth-seeking
Abraham Maslow
known for the hierarchy of needs in humanistic psychology
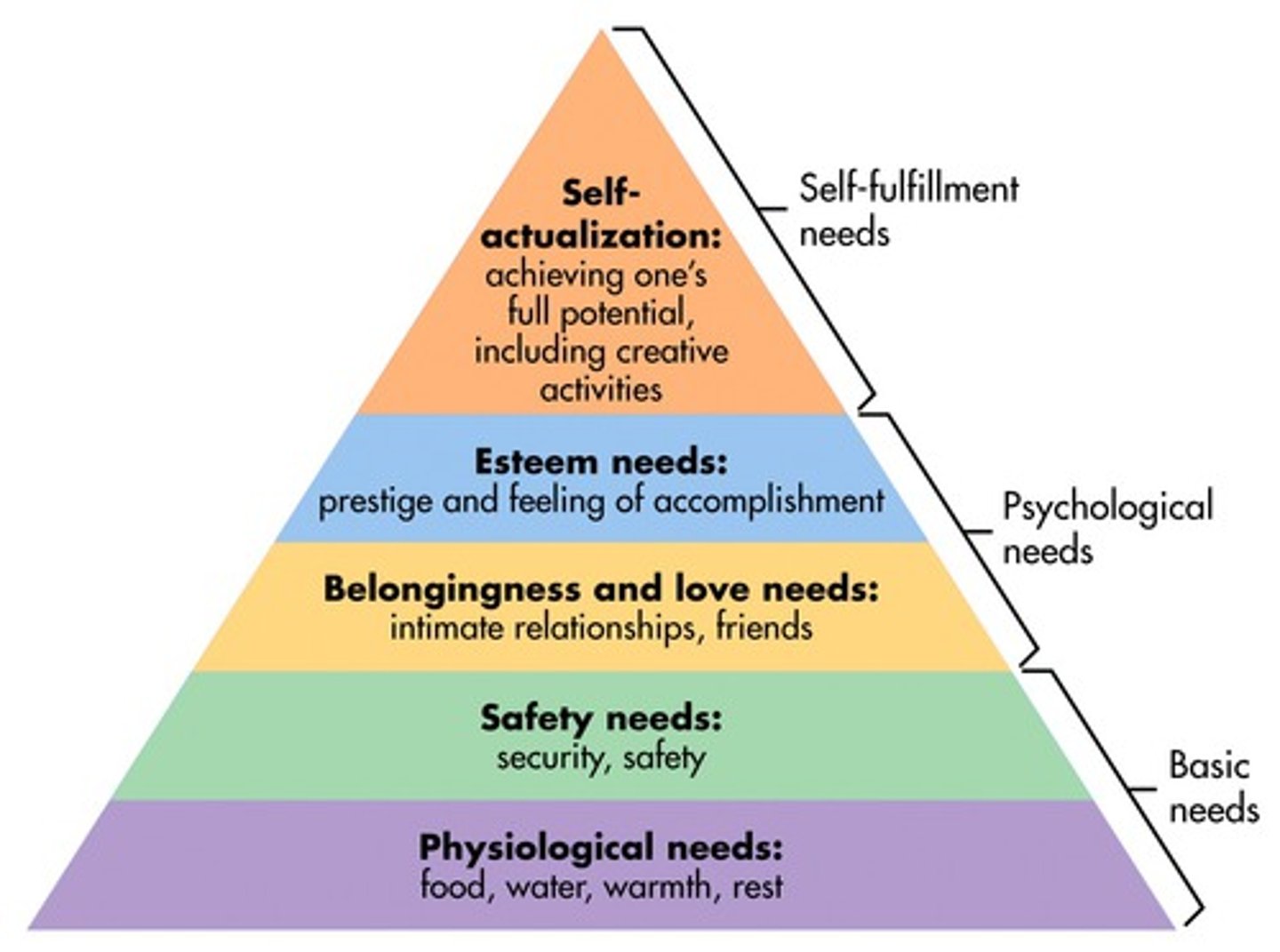
Carl Rogers
known for unconditional positive regard in humanistic psychology
Biological approach
examines how complex chemical and biological processes within the endocrine and Nervous systems are related to behavior
Cognitive
emphasizes the importance of receiving, storing, and processing information. how our mind processes and retains information
Evolutionary
attempts to explain behavior patterns as adaptations naturally selected to increase reproductive success
Socio-cultural
examines cultural differences in an attempt to understand, predict, and control behavior
Eclectic
the most widely used psychological approach today, using a combination of all approaches
Clinical Psychologists
evaluate and treat mental, emotional, and behavioral disorders
Counseling Psychologists
help people adapt to change or make changes in their lifestyle
Developmental Psychologists
study psychological development throughout a lifespan. Piaget and his study of children
Engineering Psychologists
do research on how people function best with machines
Educational Psychologists
focus on how effective teaching and learning take place
Forensic Psychologists
apply psychological principles to legal issues
biopsychologists
comes from the levels of analysis. concentrate on biological, psychological, and social factors
Industrial/Organizational Psychologists
aim to improve productivity and the quality of work life by applying psychological principles to the workplace
Neuro-psychologists
explore the relationship between brain/nervous systems and behavior
Psychometricians
focus on methods for acquiring and analyzing psychological data
Rehabilitation Psychologists
help clients with mental retardation, developmental disabilities, and disabilities resulting from neurological injury
School Psychologists
Assess and counsel students, consult with educators and parents, and perform behavioral interventions when necessary.
Social Psychologists
Focus on how a person's mental life and behavior are shaped by interactions with other people.
Sports Psychologists
Help athletes refine their focus on competition goals, increase motivation, and deal with anxiety and fear of failure.
Psychiatrists
Different from psychologists because they diagnose and prescribe medicine.
DSM
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual. Identifies attributes of specific disorders.
Hindsight Bias
The tendency to believe, after learning the outcome, that you knew it all along.
Overconfidence
The tendency to think we know more than we do.
Barnum Effect
The tendency for people to accept very general or vague characterizations of themselves and take them to be accurate.
Applied Research
Research used to serve a specific purpose with clear, practical applications.
Basic Research
Explores questions out of curiosity, aiming to explain, predict, and describe fundamental bases of behavior.
Hypothesis
Expresses a relationship between two variables in a study.
Independent Variable
Whatever is being manipulated in the experiment to bring about change.
Dependent Variable
Whatever is being measured in the experiment, dependent on the independent variable.
Operational Definitions
Explain how variables will be measured in 'real life' terms to ensure study validity and reliability. sleep deprived should say "x hours less sleep than your regular sleep cycle"
Sampling
Identifying the population to study and ensuring the sample is representative. Stratified means getting a random sample that is a good representation
Experimental Method
Involves manipulating variables to determine causal relationships in an experiment.
Confounding Variables
Variables that could cause changes in the dependent variable, not related to the independent variable.
Random Assignment
Assigning participants randomly into groups to control for confounding variables.
Hawthorne Effect
Changes in behavior due to awareness of being experiemented.
Experimenter Bias
Bias introduced by the experimenter, mitigated by double-blind procedures (neither participants nor administrator knows which group gets the placebo)
Placebo Effect
When a group feels an effect from a fake drug
Order Effects
Effects based on the timing of stimulus reception.
Correlational Method
Expresses relationships between variables but does not show causation. Positive is the same direction, negative is increasing and decreasing
Survey Method
A common type of study in psychology measuring correlations.
Naturalistic Observation
Observing subjects in their natural environment without manipulation. Gets rid of the Hawthorne effect, but you cant really prove cause and effect
Correlation Coefficient
A number measuring the strength of a relationship between variables. +1/-1, the closer it is to 0, the weaker it is
Case Studies
an individual or group is studied in depth in the hope of revealing universal principles
Statistics
Recording and analyzing study results using descriptive statistics and common language.
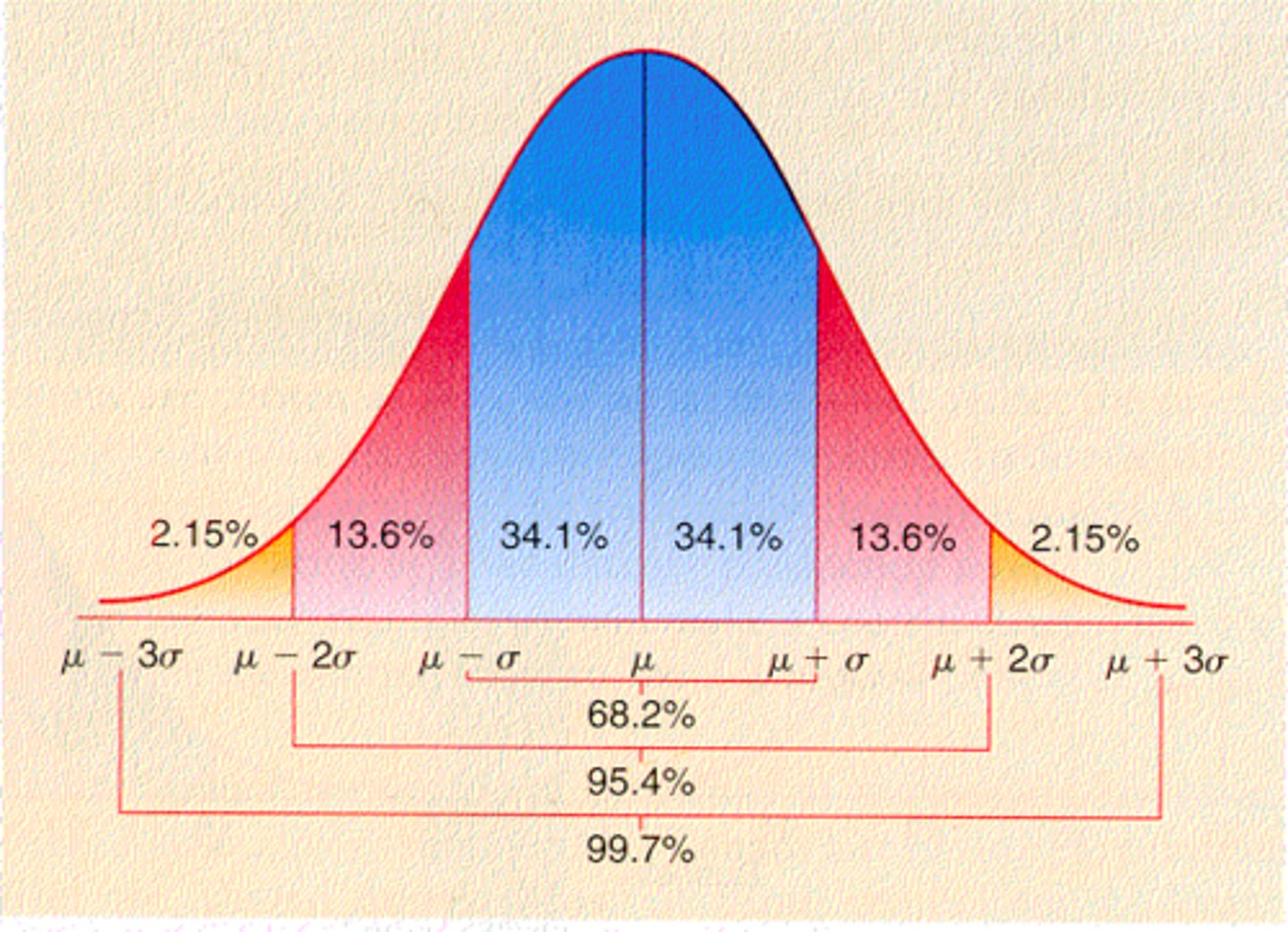
Normal Distribution
Distribution where the mean, median, and mode are the same.
Range
The difference between the biggest and smallest number in a set.
Standard Deviation
The variance of scores around the mean, indicating the spread of the distribution.
Z Scores
Measure the distance of a score from the mean, indicating its position in the distribution. + is above mean, - is below
Inferential Statistics
Used to determine if study findings can be applied to the larger population.
APA Ethical Guidelines for Research
Includes IRB for humans and animals, ensuring research is conducted ethically.
central tendancy
mean, median, mode
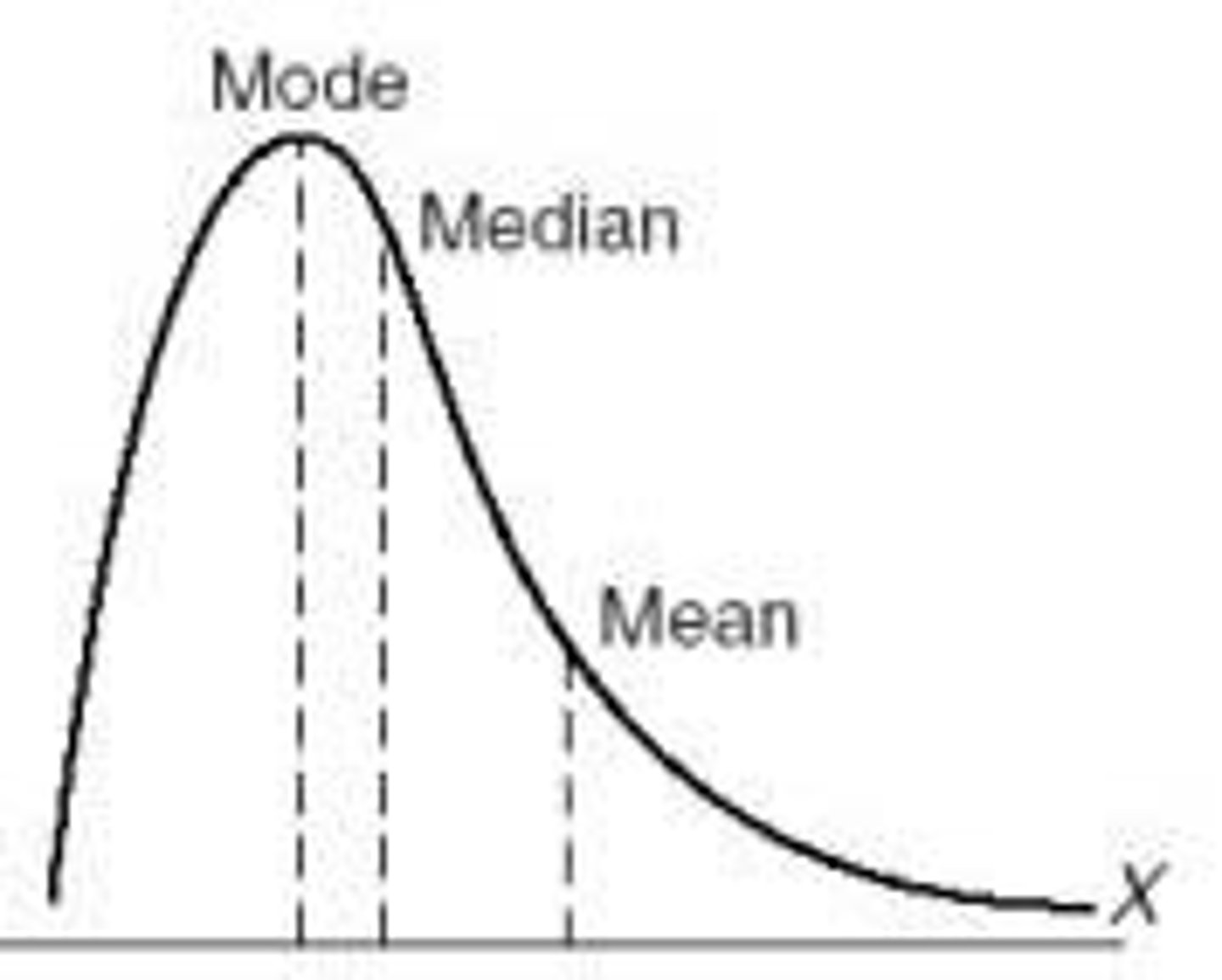
positive skew distribution
1 high schore, skews to the left
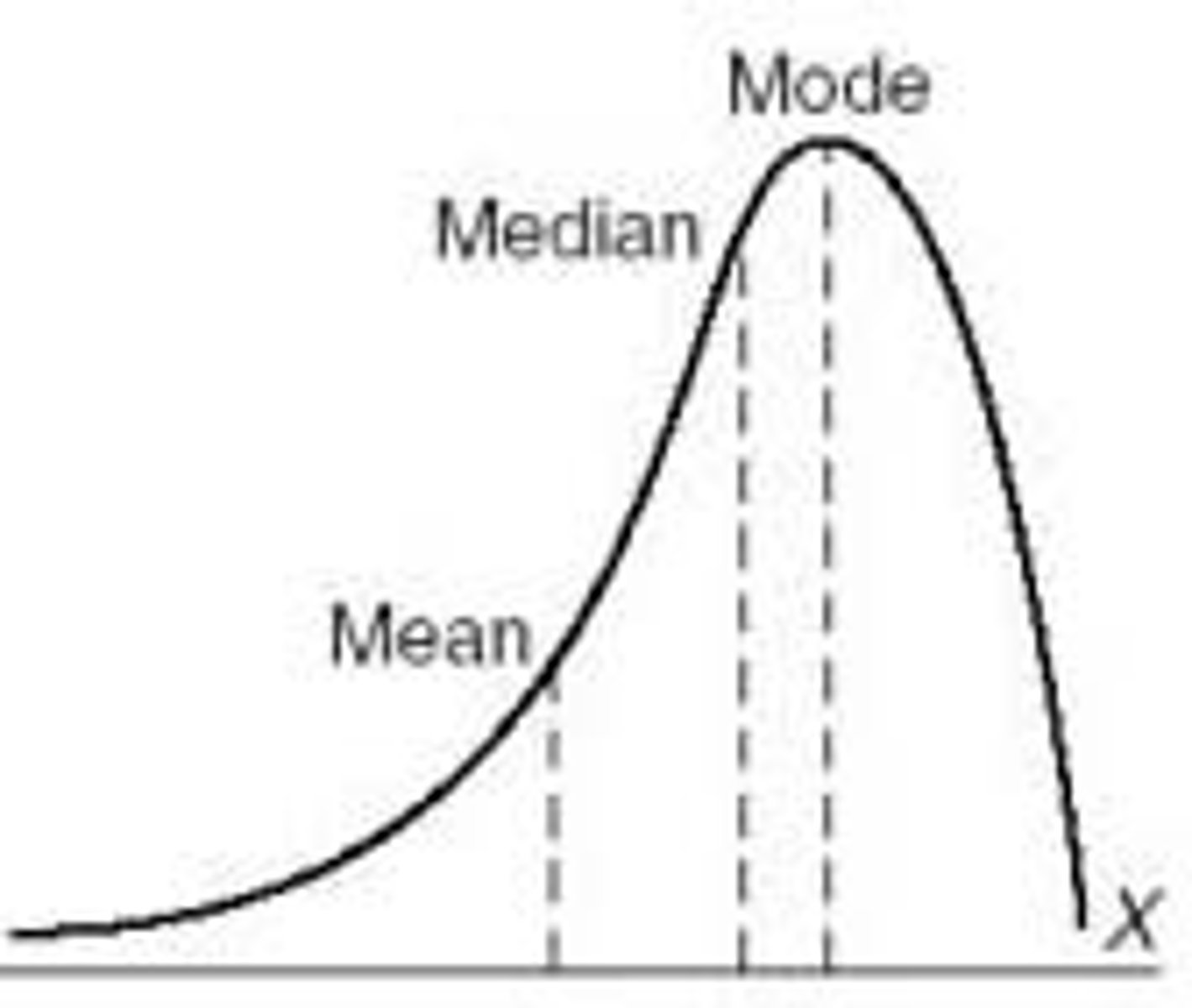
negative skew distribution
1 low score, skews to the right
p value
the probability of how likely it is that your data could have occurred under the null hypothesis(no statistical significance). 0.5= statistically significant so the null hypothesis would be rejected
Margaret Washburn
first woman to earn a Ph.D. in psychology
Mary Calkins
First female president of the APA