Biology - DNA Translation and Mutation
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
___ is the process by which the information coded in DNA is used to make a specific protein.
The actual synthesis of proteins takes place on the ribosome, a cellular structure made up of rRNA.
Translation
What determines the shapes and types of proteins in an organism, and why are proteins important?
for example, proteins in muscle fibers enable muscle tissue to flex and move.
The specific sequence of nitrogenous bases in the organism's DNA determines the shapes and types of proteins.
___ are essential because they perform many functions in the cell, such as transporting materials, providing structural support, and facilitating chemical reactions.
Proteins
The shape and type of proteins also contribute to an organism’s ___, like how the proteins in curly hair differ from those in straight hair.
traits
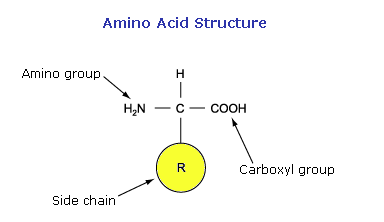
What are proteins made of?
Proteins are made of polypeptides, which are chains of amino acids.
How many types of amino acids are there?
There are 20 different types of amino acids.
What determines the shape of a polypeptide?
The shape of a polypeptide is determined by its sequence of amino acid side chains.
What determines how a protein functions?
The overall shape of the folded polypeptide determines how the protein functions.
___ takes place on the ribosome.
Protein synthesis
__ brings amino acids to the ribosome and lines up with mRNA to help form a polypeptide chain.
tRNA
During translation, the mRNA strand is used to form a ___ by bonding amino acids together with the help of tRNA.
polypeptide chain
__ provides the instructions that guide the assembly of amino acids into a polypeptide chain.
mRNA
mRNA determines the sequence of amino acids by using ___, which are sequences of three nitrogenous bases.
Each __ matches a specific amino acid, and tRNA brings the corresponding amino acids to form the polypeptide.
codons
___ are sequences of three nitrogenous bases on mRNA that code for specific amino acids.
Codons
___matches its nitrogenous bases with complementary codons on mRNA, bringing the corresponding amino acid to the ribosome to form the polypeptide chain.
tRNA
How do you determine the amino acid coded by the mRNA codon AAG?
To determine the amino acid for codon AAG, find the base "A" in the "1st Base" row, then locate the second "A" in the "2nd Base" column, and finally find "G" in the "3rd Base" row. The amino acid coded by AAG is lysine.
The amino acid coded by the mRNA codon AAG is ___
lysine
How is a protein’s function determined?
A protein’s function is determined by its shape, which is based on the sequence of amino acids. The sequence of amino acids comes from the mRNA sequence, which is copied from the DNA sequence.
A __ is a change in the nitrogenous base sequence of DNA. Mutations can have different effects—some can be harmful, some beneficial, and some may have no effect on an organism.
The impact of a ___ depends on how it alters the genetic code.
mutation
A base is removed from the nucleotide sequence.
original mRNA: G A C C G U C A G G
mutant mRNA: G A C C U C A G G
Deletion
A base is added to the nucleotide sequence.
original mRNA: G A C C G U C A G G
mutant mRNA: G A C C A G U C A G G
Addition
A base is replaced with a different base.
original mRNA: G A C C G U C A G G
mutant mRNA: G A C C U U C A G G
Substitution
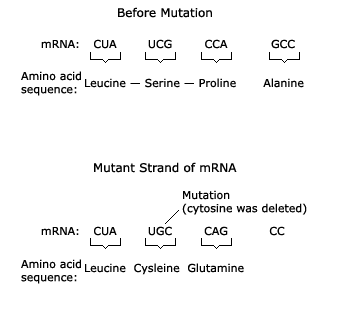
How can a mutation affect an organism?
A mutation can have different effects on an organism depending on how and where the nucleotide sequence changes
If the mutation alters the protein’s shape so it cannot function properly, it can harm the organism.
Harmful Mutation
If the mutation improves the protein’s function, it can benefit the organism.
Beneficial Mutation
Some mutations have no effect if they do not change the protein’s function.
Neutral Mutation
___ that shift the sequence of codons can lead to completely different proteins, which may have significant consequences.
Mutations
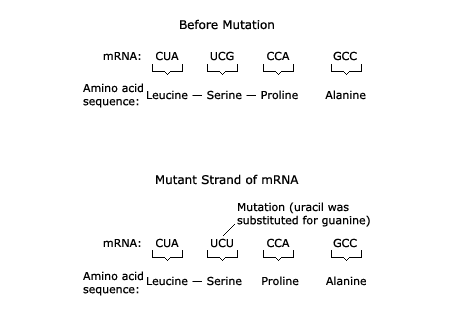
How can a mutation have no effect on an organism?
Some mutations have no effect because multiple codons can code for the same amino acid.
If a base is substituted but the new codon still codes for the same amino acid, the protein remains unchanged, and the mutation has no impact on the organism.
___ is the process of modifying an organism’s DNA using laboratory methods to benefit the organism or others.
Genetic engineering
Adding DNA from one organism into another to produce useful proteins.
Recombinant DNA
Inserting an organism’s DNA into an empty egg cell to create a genetically identical copy.
Cloning:
Mapping human DNA to identify genes and inherited mutations.
Human Genome Project