Chapter 11: Tropical Weather, Hurricanes, and Storm Prediction Techniques
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
Tropics
Broad belt around Earth
Tropical Wave
A type of atmospheric trough that forms in and around the Atlantic Ocean, characterized by an extended region of very low air pressure directed north to south and flowing from east to west over the tropics, resulting in cloud cover and thunderstorms.
Hurricanes
An intense storm that forms over tropical water.
Tropical Cyclone
All systems that originate over tropical water.
Tropical Storms
Cyclone with strong winds and intensity less than hurricanes.
Anatomy of a Hurricane
Intense storm of tropical origin with winds greater than 64 knots, featuring an eye and eyewall, and an organized mass of thunderstorms.
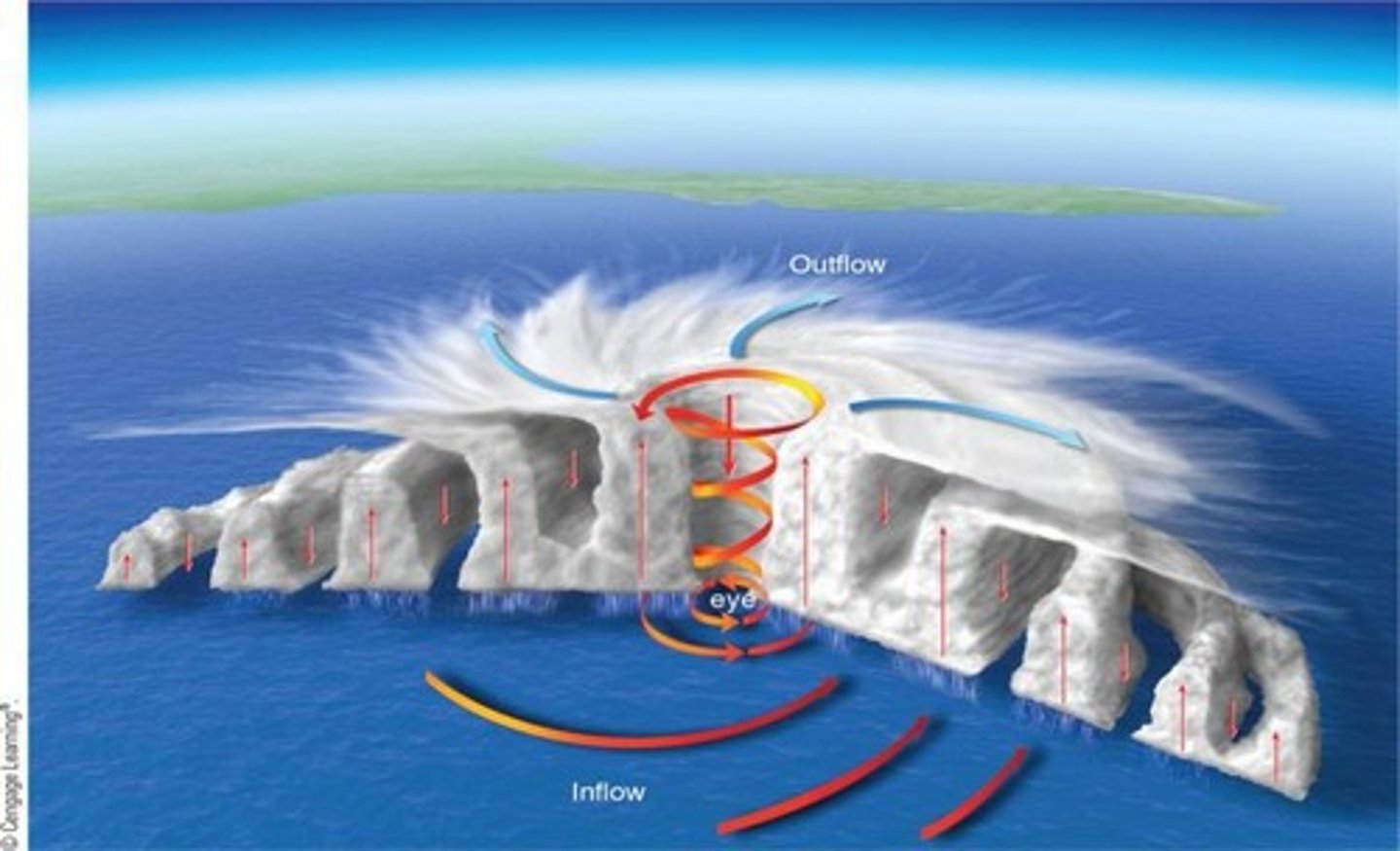
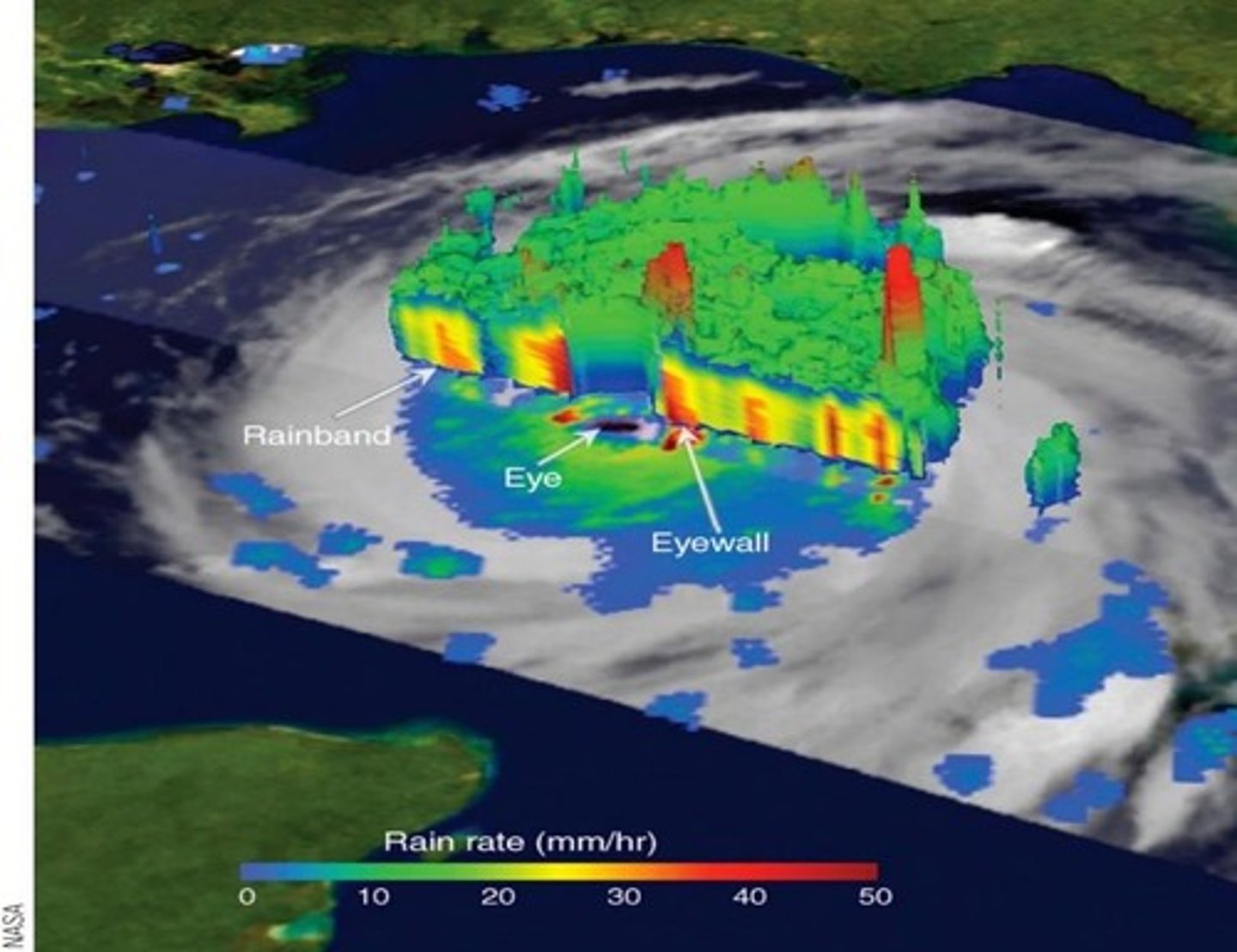
Eye of the Hurricane
The calmest part of the hurricane located in the center, usually 20-40 miles in diameter.
Conditions for Hurricane Formation
Light winds, high humidity through the troposphere, and high surface water temperature (≥80°F) over a vast area.
Hurricane Season (North Pacific)
May 15 to November 30.
Hurricane Season (North Atlantic)
June 1 to November 30.
Outflow in a Hurricane
The process where wind lifts up through the eye and flows out, feeding the development of more clouds and storms.
Storm Features
High winds, rain and hail, lightning, and tornadoes may be associated with thunderstorms in a hurricane.
Hurricane Katrina
A significant hurricane that affected the Gulf of Mexico on August 28, 2005.

Wind Convergence
A condition that supports hurricane formation.
Trade Wind Inversion
A condition that can inhibit storm formation.
Tropical Weather Systems
Includes non-squall clusters, squall lines, and tropical waves.
Winds in the Tropics
Generally blow from the E, NE, or SE.
Streamlines
Used by forecasters to analyze wind patterns instead of isobars.
Pin Hole Eye
A small eye associated with a powerful hurricane.
High Humidity in the Troposphere
A critical condition for hurricane formation.
Warm Surface Water
Surface water temperatures must be more than 80 degrees F for hurricane formation.
Cyclone
A general term for a system of winds rotating inward to an area of low atmospheric pressure.
Very warm surface waters
26.5°C over a large expanse of open ocean
The Developing Storm
Thunderstorms encircling a center of surface low pressure
Eyewall replacement
Dissipation of original eyewall and formation of a new one farther out from the eye
Hurricane Formation
Hurricanes form over tropical waters where the winds are light, the humidity is high in a deep layer extending up through the troposphere, and the surface water temperature is warm, typically 26.5°C.
Hurricane Dissipation
When hurricanes cross over colder water and lose their heat supply, they deteriorate quickly.
Hurricane Movement
General tracks: west, northwest, north, and northeast with considerable variation.
North Atlantic Hurricanes
Hurricanes that form in the tropical north Atlantic move westward/northwestward and often collide with Central or North America.
Eastern Pacific Hurricanes
Approximately nine hurricanes form each year in the eastern Pacific, forming off the coast of Mexico over the Northeast Pacific.
Naming Hurricanes
Before naming, hurricanes are identified according to latitude and longitude using alphabetical female names, alternating female and male names, and the Greek alphabet.
Devastating Winds
Hurricane approaching from the south with highest winds on the eastern side.
Storm Surge
Stronger winds on the eastern side will likely cause the highest storm surge and most damage.
Flooding
Flooding can occur due to storm surges associated with hurricanes.
Saffir-Simpson scale
Classifies hurricane strength based on central pressure, estimating possible damage of sustained winds and storm surge, ranging from 1 to 5.
Major hurricanes
Categorized as ≥3 on the Saffir-Simpson scale.
Super typhoons
Sustained winds over 130 knots are categorized as category 4 and are called super typhoons.
Hurricane-Spawned Tornadoes
About one-fourth of the hurricanes that strike the U.S. produce tornadoes, causing considerable damage.
Hurricane Fatalities
Up until 2005, the annual death toll from U.S. hurricanes averaged fewer than 50 persons over a span of about 30 years.
Hurricane Movement in North Atlantic
Most hurricanes swing away from land and move northward, parallel to the U.S. coastline.
Naming Hurricanes and Tropical Storms
A system that has evolved from latitude/longitude designations to alternating male/female names since 1978.
Retirement of storm names
The names of storms causing great damage are retired for at least 10 years.
Galveston hurricane, 1900
An estimated 8000 people lost their lives when a hurricane slammed into Galveston, Texas, making it the deadliest natural disaster in U.S. history.
New England hurricane, 1938
Slammed into Long Island with a forward motion of 61 knots / 70 mph, causing a 12-ft storm surge and wind gusts of 162 knots / 186 mph.
Camille, 1969
A Category 5 hurricane at landfall with central pressure of 909 mb, winds of 160 knots / 182 mph, and a storm surge of 23 ft.
Hurricane Andrew, 1992
Formed outside the tropics near 25°N, with winds increasing from 45 knots to 122 knots in 2 days, causing over $30 billion in damages.
Hurricane Katrina, 2005
The most damaging hurricane to ever hit the United States, with winds of 152 knots (175 mi/hr) and over 2000 deaths.
Hurricane Rita, 2005
Another Category 5 storm that struck New Orleans less than 1 month after Hurricane Katrina.
Hurricane Sandy, 2012
Lost hurricane status ~3 hours before landfall in New Jersey, causing the most deadly and damaging storm surge in over 70 years.
Hurricane Michael, 2018
Made landfall as a Category 5 hurricane, with a storm surge of 3 - 4 m (9 - 14 ft) and winds up to 140 knots (160 mph).
Hurricane watch
Issued 24 to 48 hours before a storm arrives when a hurricane poses a direct threat to an area.
Hurricane warning
Issued when a hurricane strike is certain.
Category 5 hurricane
A hurricane with sustained winds of 157 mph (252 km/h) or higher.
Central pressure
The atmospheric pressure at the center of a hurricane, measured in millibars (mb).
Wind gusts
Short bursts of high wind speeds, often measured in knots or mph.
Homes destroyed
Refers to the number of residences that were completely demolished by a hurricane.
Hurricane damage
The physical destruction caused by a hurricane, including damage to infrastructure, homes, and the environment.
Evacuate
To leave an area as soon as possible if your city recommends it during a Hurricane Warning.
Extreme denial
A state of refusing to accept the reality of a hurricane, which can be deadly.
Fatalistic paralysis
A state of inaction due to a belief that one cannot change the outcome, which can be deadly during a hurricane.
Hurricane Prediction Models
Computer models used by meteorologists to forecast hurricanes based on data from various sources.
Ensemble forecasting
A method used to predict hurricane paths by running several forecast models with slightly different weather information.
Numerical weather prediction models
Computer simulations that simplify how hurricanes and their surroundings are represented.
Dynamical models
Models that consider the thickness of warm ocean water ahead of the storm's course to forecast its severity.
Hurricane hunters
Aircraft that carry instruments directly into the storm and drop devices such as dropsondes.
Dropsonde
A device dropped from an aircraft that measures air temperature, humidity, and atmospheric pressure.
Ensemble forecast
A forecast based on running several models or simulations of the same model with different initial conditions.
Project STORMFURY
An attempt to modify hurricanes by seeding clouds to create rain and reduce winds, though its effectiveness is inconclusive.
Seeding with silver iodide
A method studied for modifying hurricanes, with uncertain effectiveness.
Oil or film on water
A proposed method to reduce evaporation and latent heat available to storms, though not yet proven effective.
Weather satellites
Satellites that provide data on wind and storm conditions from a bird's eye view.
Radar
Technology that peers into storms to unveil clouds and gather data.
Wind instruments
Devices on satellites that obtain wind information in and around a storm.
Reconnaissance aircraft
Aircraft used to gather data on hurricanes and their conditions.
Hurricane path
The predicted trajectory of a hurricane based on various forecasting models.
Storm instruments
Devices carried by hurricane hunters to collect data about storm conditions.
Cloud seeding
A method of attempting to modify weather by introducing substances into clouds.