Portage Learning Anatomy & Physiology 2: Module 2 Exam
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
This layer of the meninges is tightly attached to the brain.
Pia mater (menix)
The _______ fissure separates the right and left cerebral hemispheres.
Median longitudinal
What is the purpose of the blood-brain barrier? Describe its maintenance from a cellular level.
The blood-brain barrier is a diffusion barrier which prevents most particles from entering the central nervous system tissue, keeping the brain and spinal cord separate from general blood circulation. The blood-brain barrier is formed by the relatively impermeable brain capillaries, due to the glial cells astrocytes. Maintenance of the blood-brain-barrier is important to provide a stable chemical environment for the nervous system.
All the following are functions of the hypothalamus except:
A. Maintain homeostasis
B. Controls the pituitary gland
C. Links the nervous and endocrine systems
D. Relays sensory impulses to the cerebrum
D
What is the largest portion of the brain?
A. Cerebellum
B. Cerebrum
C. Corpus collosum
D. Cingulate gyrus
B
This region of the brain acts to coordinate multiple sources of sensory information.
A. Primary sensory cortex
B. Primary motor cortex
C. Association area
D. Precentral gyrus
E. Postcentral gyrus
C
A patient is having difficulty understanding language but is still able to speak fluently. The patient's dermatomes are intact. Which area of the brain is most likely damaged?
A. Broca’s area
B. Wernicke’s area
C. Occipital lobe
D. Parietal lobe
E. Primary sensory cortex
B
Describe how memories are stored and retrieved in the brain. Include a specific brain region.
Memories are not stored in one specific area within the brain but instead are stored throughout the cerebral hemispheres. The hippocampus acts as a memory center to help with memory storage and retrieval. The involvement of the limbic system explains why emotionally charged events result in our most vivid memories.
Which statement is false concerning the brainstem?
A. The midbrain portion of the brainstem is continuous with the spinal cord.
B. The pons helps to regulate breathing.
C. The midbrain contains the superior and inferior colliculi.
D. The medulla contains reflex centers to regulate vasoconstriction.
A
Which of the following is false concerning the cerebellum?
A. The gray matter is external while the white mater is internal.
B. The cerebellar peduncles are located posteriorly.
C. The anterior lobe receives information from the body trunk.
D. The vermis coordinates arm movements.
B
Alzheimer's disease impacts which region(s) of the brain?
A. Occipital lobe
B. Frontal lobe
C. Parietal lobe
D. Hippocampus
E. All the above
E
Which of the following is false concerning a CVA?
A. An ischemic stroke is also known as a “brain bleed”.
B. A TIA is a form of an ischemic stroke.
C. Stroke survivors may regain some lost functions through therapy.
D. A hemorrhagic stroke is due to a broken blood vessel.
A
A patient is unable to extend his fourth and fifth digits when asked to open his hand. What is most likely the cause?
A. CVA in the frontal lobe
B. Carpal tunnel syndrome
C. Ulnar nerve damage
C. Anterior spinal cord injury
C
Label the following spinal cord regions in the diagram below:
1: _____________________
5: _____________________
6: _____________________
9: _____________________
11: ____________________
1: Posterior (Dorsal) column
5: Anterior median fissure
6: Posterior (Dorsal) horn
9: Dorsal root
11: DRG (Dorsal Root ganglion)
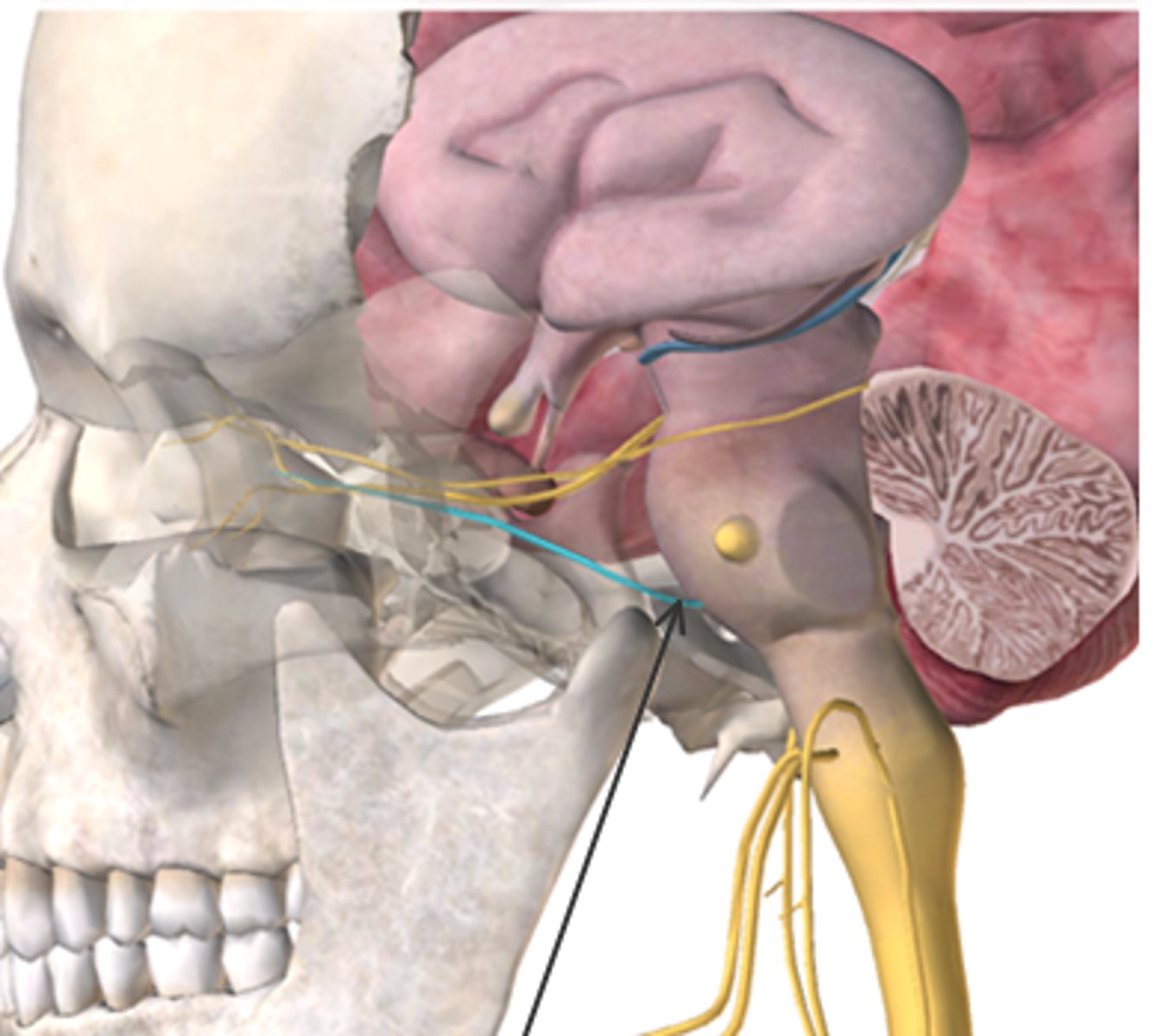
What cranial nerve is highlighted in blue (also indicated by the arrow) in the figure below?
A. Optic
B. Oculomotor
C. Trochlear
D. Abducens
E. Spinal Accessory
D
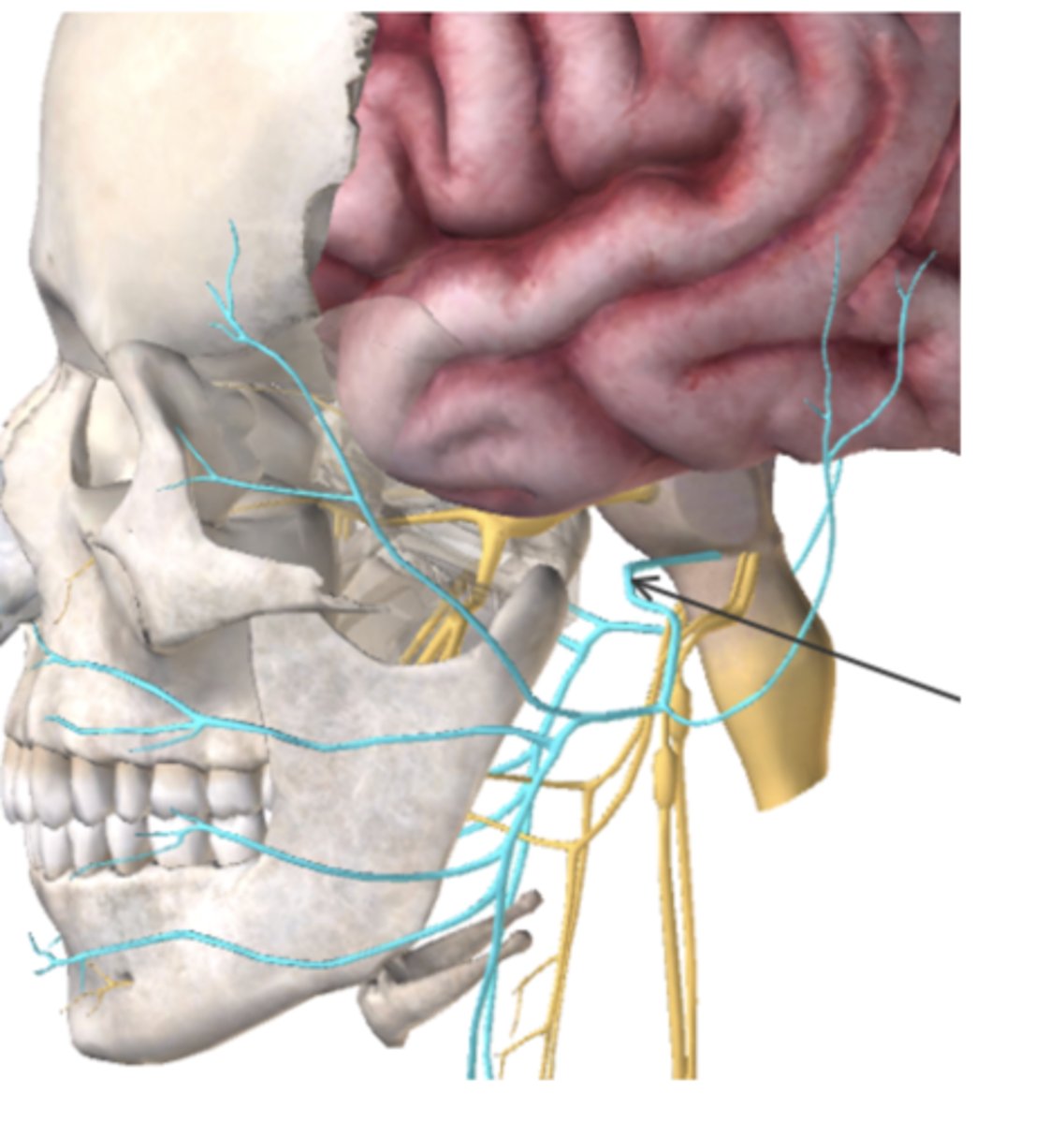
What type of nerve is the cranial nerve below and what does it control? (Highlighted in blue, also indicated by the arrow)
A. Mixed: Sensation of digestive tract and Regulation of heart rate
B. Motor: Tongue movement
C. Sensory: Hearing/balance
D. Mixed: Facial muscles and Taste
D
Which of the following is true about the trigeminal nerve?
A. The mandibular branch receives sensory information from taste buds.
B. The ophthalmic branch controls eye movements.
C. The maxillary branch receives information from the upper lip.
D. The maxillary branch controls the muscles of mastication.
C
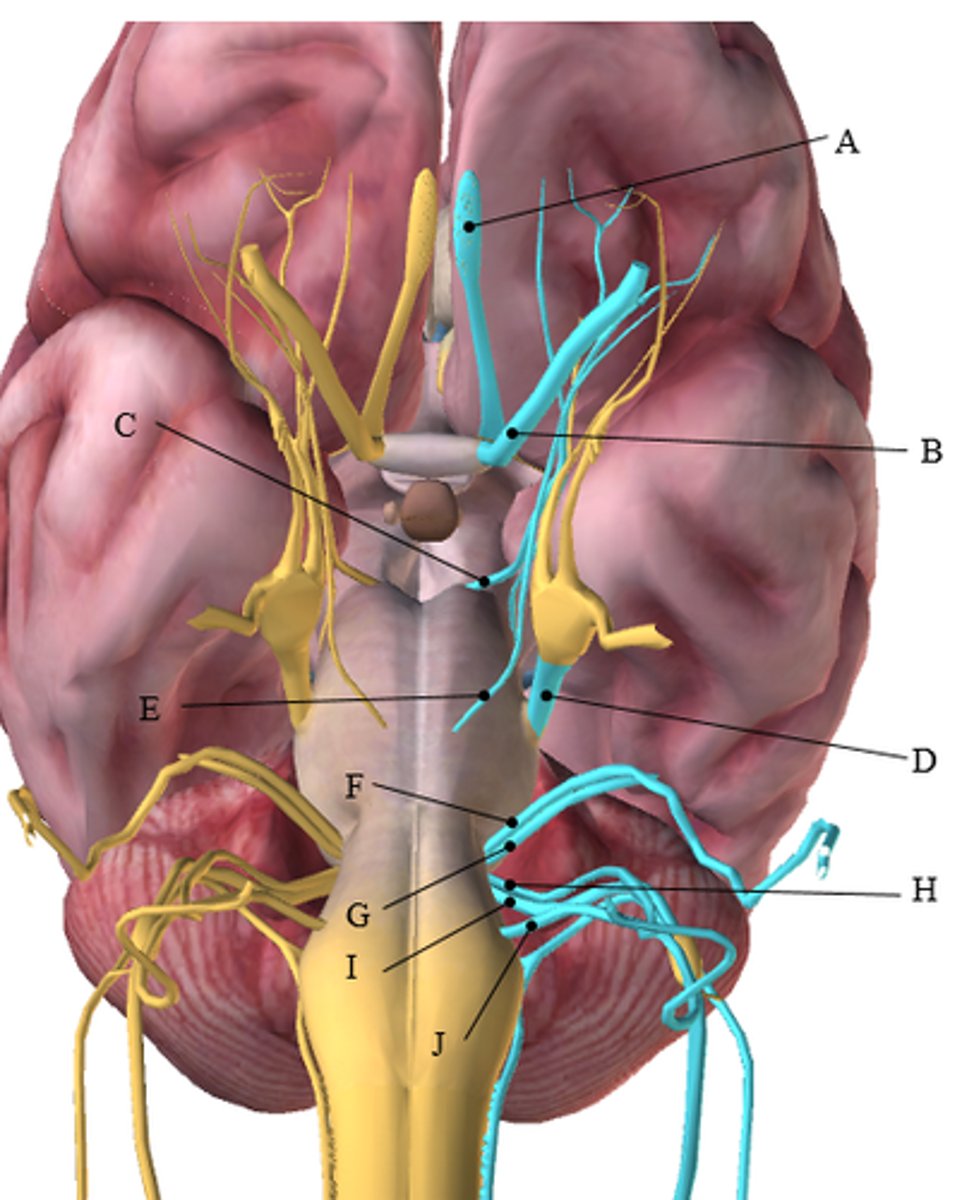
Use the figure below to answer the following questions. Answer by writing the letter (A-J) from the figure that corresponds with the correct cranial nerve.
This cranial nerve receives information from the retina.
This cranial nerve is responsible for the sensation of the digestive tract.
This cranial nerve controls movement of the eye laterally.
This cranial nerve receives sensory information for hearing.
This cranial nerve is responsible for voluntarily moving the tongue.
1. B. (Optic)
2. I. (Vagus)
3. E. (Abducens)
4. G. (Vestibulocochlear)
5. J. (Hypoglossal
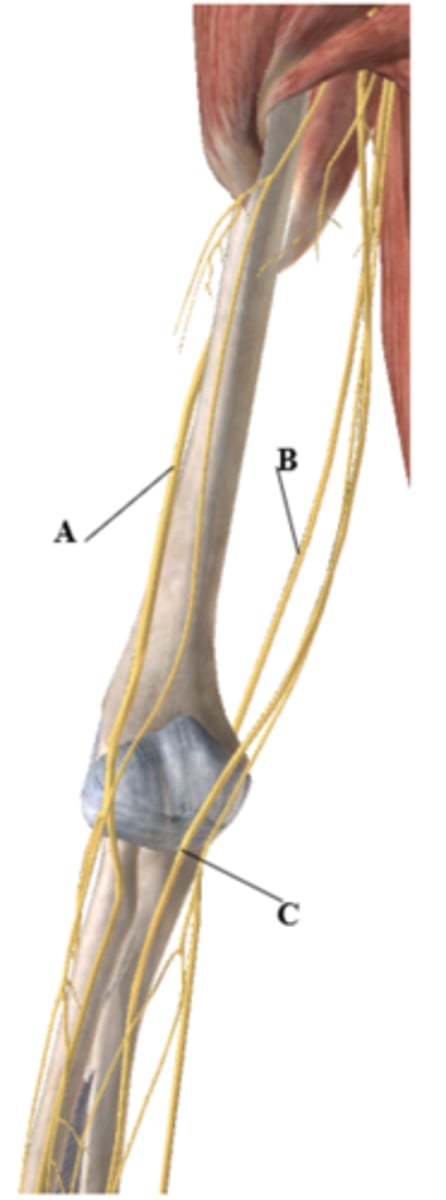
Label the nerves (A-C) in the figure below:
A: _________________
B: _________________
C: _________________
A-Radial
B- Ulnar
C- Median
The lumbar plexus is from spinal nerves:
A. T12-L04
B. L04- S04
C. C01-C05
D. L01-S01
A
A patient is on a ventilator post a car accident. What region of the spine is most likely damaged?
A. L01-L05
B. S01-S05
C. T01-T12
D. C03-C05
D
A patient damaged the radial nerve. What action is most likely limited?
A. Elbow flexion
B. Hip extension
C. Wrist flexion
D. Wrist extension
D
A patient has decreased sensation over the posterior surface of the thigh. What nerve is most likely damaged?
A. Femoral
B.Sciatic
C. Saphenous
D. Common fibular nerve
B
Which of the following is true concerning the brachial plexus?
A. Roots are located furthest from the spinal cord.
B. There are anterior and posterior divisions.
C. Divisions branch next into two cords: anterior and posterior.
D. The posterior cord forms the median nerve.
B
These contain the ganglia for the sympathetic nervous system that controls the effector organs in the trunk, head and limbs.
A. Sympathetic trunk ganglia
B. Celiac ganglion
C. Superiomesenteric ganglion
D. Inferior mesenteric ganglion
E. Ciliary ganglion
A
Which of the following is false concerning the parasympathetic nervous system?
A. Primarily contains cholinergic synapses.
B. It is also called the craniosacral division.
C.Acts to increase the heart rate.
D. Promotes the digestion of foods.
C
A patient comes into the ER following an accident. She is scared and starting to hyperventilate. You talk with her in a calm, reassuring manner as she receives medical care. You are trying to increase the activity in which division of her nervous system? Explain your answer.
You are trying to increase the activity of the parasympathetic nervous system as it is also sometimes called the “housekeeper system” because it promotes all the internal responses we associate with a relaxed state. The parasympathetic system also acts to slow the heart rate.
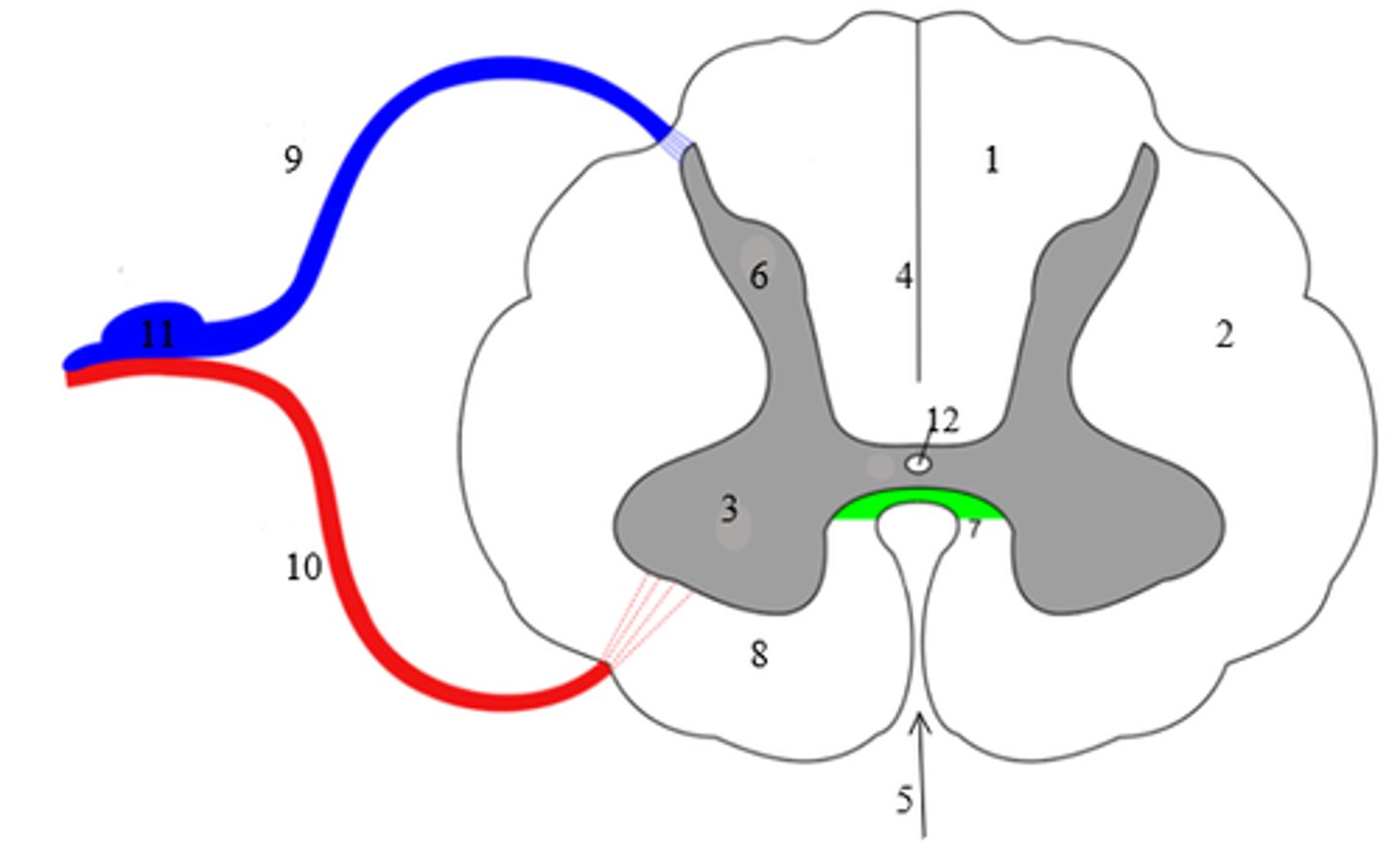
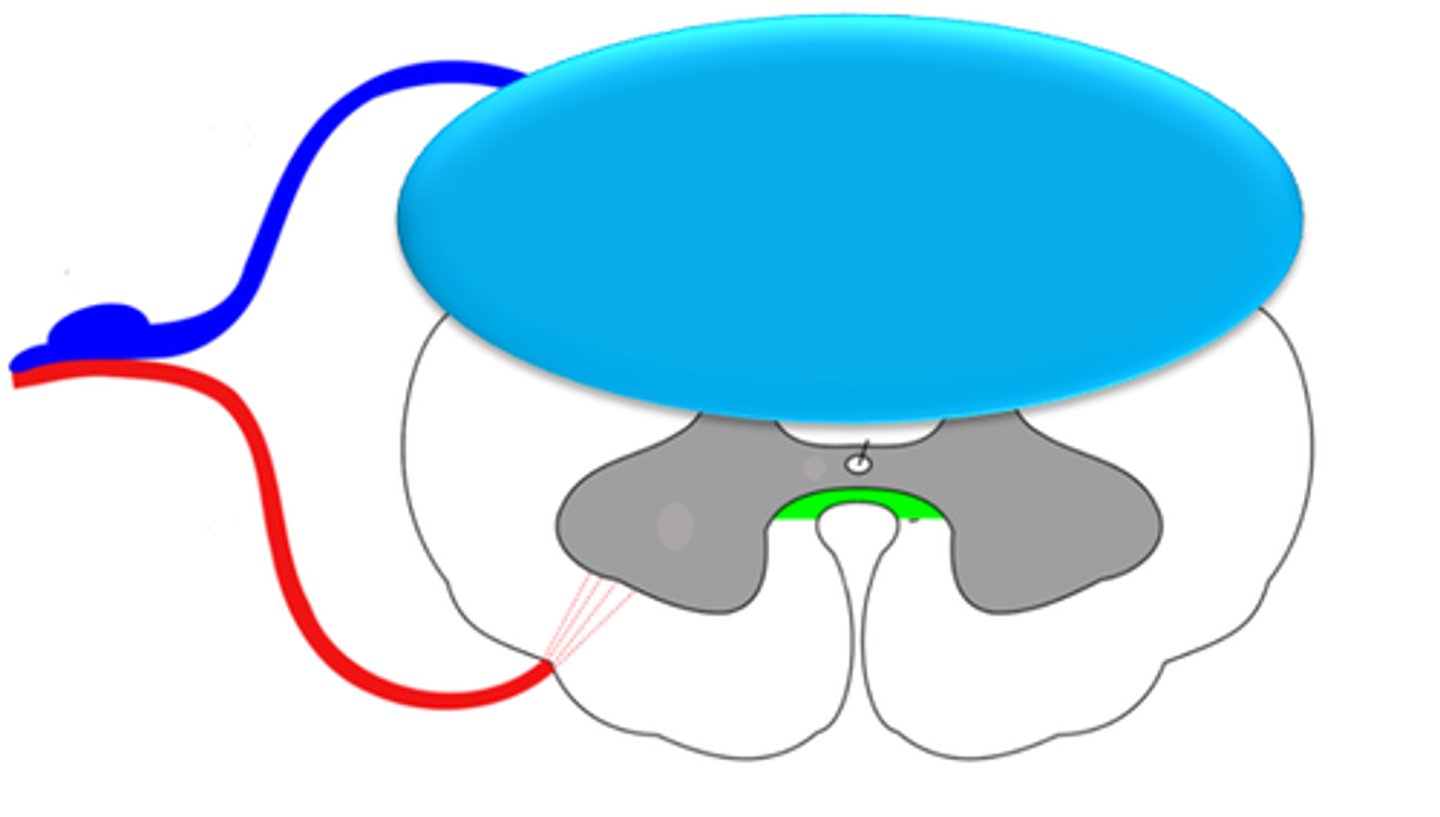
If someone sustains an injury to the area of the spinal cord, as shown below by the blue oval, would you be more likely to see paralysis or decreased sensation? Explain your answer.
You would be more likely to see decreased sensation because sensory neurons enter the spinal cord posteriorly.
One of your patients sustained a hemorrhagic CVA. You notice they have rigid movements when moving their arms. They also have difficulty forming a plan to move their body. What area of the brain is most likely impacted? Explain your reasoning.
The basal ganglia is responsible for executing a motor plan and to slow and control fine movements (creating the rigid movements).
Apraxia, or impaired motor planning. Apraxia results in rigid movements and difficulty executing a motor plan.