AQA Combined science chemistry paper 2 higher
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
What is the equation for rate of reaction?
Mass / time
Vol/time
Mol/time
What factors can affect rate of reaction and how?
- Surface area- more particles exposed to reactants= greater chance of collision= rate increases .
- Temperature- Reactant particles have more energy= Move quicker= More collisions= Rate increases because particles have energy equal to/ greater than activation energy.
- Pressure/ concentration = More reactant particles per volume = crowded so greater chance of collision = rate increases.
- Catalyst= Reduces activation energy so rate increases.
What is a reaction vessel?
A container
Give an example of a catalyst
- Enzymes
- Iron
- Platinum
- Vanadium oxide
What is the collision theory?
The theory that chemical reactions only occur when reacting particles collide with eachother with sufficient energy.
What is the minimum ammount of energy that particles need to react called?
Activation energy.
What is the catalyst in a biological system?
Enzyme
On an energy graph, where would the reactants, activation energy, overall energy change and products be?
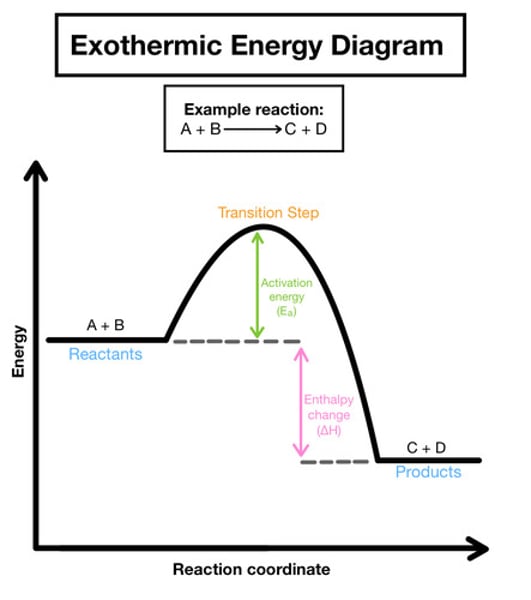
If reaction = exothermic are products below or above reactants
Products below reactants because they release energy rather than take in
If reaction= endothermic are products below or above the reactants?
Above reactants
What is a reversible reaction?
A reaction where the products can react together to form the original reactants
In a reversible reaction, what happens if one side is exothermic?
Other side is endothermic
What is dynamic equilibrium?
Equilibrium in a closed system that prevents escape of reactants and products where the reactions occur at exactly the same rate in each direction.
How can direction be changed of reversible reactions?
Due to changing conditions.
What is Le Chatelier's principle?
When a system at equilibrium has a change made to the conditions, it will respond to counteract that change.
What occurs during pressure increase if a system is at equilibrium?
Equilibrium moves to direction of fewer molecules of gas
What happens when concentration is changed to reactants or products at equilibrium?
- The system is no longer at equilibrium and the concentrations of all substances will change until equilibrium is reached again.
What is crude oil?
- A finite resource found in rocks
- Mixture of hydrocarbons.
Where does crude oil come from?
The remains of ancient biomass (mainly plankton) that was buried in mud.
What are hydrocarbons?
Alkanes. Contain only hydrogen and carbon.
What is the general formula for alkanes?
Cn H2n+2
What are the first 4 alkanes?
Methane, Ethane, Propane, Butane
How are hydrocarbons in crude oil seperated?
Into fractions using fractional distillation.
What can the fractions of fractional distillation produce?
- Fuels
- Feedstock for petrochemical industry
What fuels are produced from crude oil?
Petrol, diesel, kerosene, heavy fuel oil and liquified petroleum gases.
What useful materials are produced by the petrochemical industry?
Solvents, lubricants, polymers and detergents.
How does fractional distillation work?
- Hot crude oil enters near the bottom of a fractioning column, hot at bottom, cooler at top.
- Vapours from the oil rise through the column
- Vapours condense at boiling points.
- Liquids are led out of the column at different heights.

What is condensation?
Gas to liquid.
What is volatility?
How easily a compound evaporates
What is a fraction of crude oil?
A simpler more useful mixture containing hydrocarbons of similar length and similar boiling points.
What are short chain hydrocarbons?
Hydrocarbons with few carbon atoms
What are long chain hydrocarbons?
Hydrocarbons with lots of carbon atoms
What is fractional distillation?
The process of separating crude oil into groups of hydrocarbons with similar numbers of carbon atoms
What are the 3 stages of fractional distillation?
Evaporation, condensation, collection
Where is crude oil vapour put in a fractionating column?
At the bottom of the column and rises upwards
Short chain hydrocarbons have a _ boiling point
Low
What is the name for carbon containing compounds?
Organic compounds
What is the name for families of similar compounds containing carbon atoms?
Homologous series
What are the 2 changes in state that occur during fractional distillation?
Evaporation, condensation
Are short or long hydrocarbons more useful? Why?
Short. Cracking converts long hydrocarbins into short hydrocarbons. Less viscous and a lower boiling point,ignite easily and high volatility.
What is the word equation for complete combustion of a hydrocarbon?
hydrocarbon + oxygen --> carbon dioxide + water (+ energy)
During a combustion reaction, are the atoms in the hydrocarbon oxidised or reduced?
Oxidised
What is oxidation
Gain of oxygen
What are alkanes?
Saturated hydrocarbons that only contain single bonds
What are the fuels produced and uses from crude oil by fractional distillation?
Petrol, to run cars. Kerosene, to run planes. Diesel oil to run trucks. Heavy fuel oil, can be heating oil, fuel oil or lubricating oil.
What happens to the hydrocarbons as you go down the list? (methane, ethane, propane,butane.)
The size increases.
What is viscosity?
A liquid's resistance to flow, or thickness of fluid. High viscosity means it flows slowly, for example honey.
Describe the trend in viscosity in hydrocarbons., with reference to size.
As the size of the hydrocarbon molecules increases, the molecules get more viscous. So, long chain hydrocarbons flow more slowly, have a higher viscosity. Methane low viscosity, butane high.
What is flammability?
How easily a hydrocarbon combusts /burns.
Describe the trend in flammablity in hydrocarbons, with reference to size.
The flammability decreases. Short chain hydrocarbons are extremely flammable. Long chain hydrocarbons are hard to burn. As the size of the hydrocarbon molecules increases, the molecules get less flammable. Methane flammable, butane less flammable.
What can methane be used for due to its flammability?
A bunsen burner
What is boiling point?
The temperature where a liquid changes to a gas
What do all the first 4 alkanes have to do with eachother, referencing to boiling point?
All have a boiling point lower than room temperature, all are gases at room temperature.
Describe the trend in boiling point in hydrocarbons, referencing to size.
The boiling point increases as size increases. Long chain hydrocarbons have a high boiling point, hence why they condense at the bottom of the fraction. Methane lowest boiling point, butane highest.
In conclusion, what happens when the hydrocarbon size increases?
The viscosity increases, the boiling point increases and the flammability decreases.
Why do short chain hydrocarbons make good fuels? Reference to its properties.
They are highly flammable, have a low viscosity and a low boiling point.
What are alkanes and alkenes examples of ?
Homologous series of hydrocarbons
What does cracking mean?
Splitting up long chain hydrocarbons
Why do short chain hydrocarbons make good fuels?
They are flammable
What are most of the long chain alkane molecules produced from fractional distillation turned into?
Smaller, more useful alkane molecules by cracking.
What are the products of cracking used for ?
Fuels such as petrol for cars and paraffin for jet fuel.
What does cracking produce?
Alkanes and alkenes.
What is more reactive - alkanes or alkenes ?
Alkenes
What are alkenes used for?
To produce polymers and as starting materials to produce other chemicals
What is the test for alkenes?
Bromine water test
What colour is bromine water?
Bright orange
What happens when bromine water is added to an alkene?
The bromine reacts with the alkene to make a colourless compound, so the bromine water looses its colour.
What happens when bromine water is added to an alkane?
No reaction will happen and it will stay bright orange.
What are the two methods of cracking?
Catalytic cracking and steam cracking
What are the conditions for catalytic cracking?
- 550°C maximum temperature
- Use of a catalyst
What catalyst can be used for catalytic cracking?
- Aluminium oxide
What are the conditions for steam cracking?
- Over 880°C
-Steam
- No catalyst
What type of reaction is cracking?
Thermal decomposition
What is thermal decomposition?
The break down of molecules by heating them
Describe the process of catalytic cracking
The long chain hydrocarbon is heated to vaporize it, the vapor is then passed over the catalyst, the long chain molecules split apart on the surface of the catalyst.
Describe the process of steam cracking
The long chain hydrocarbon is heated to vaporize it, mixed with steam and heated to a very high temperature in order to split apart the long chain molecules
What are pure substances?
A single element or compound, not mixed with any other substance
How do you distinguish a pure substance?
- Pure substances will melt and boil at a fixed point, whereas mixtures will at a range of different temperatures
Is the diagram on the other side a mixture or pure substance?
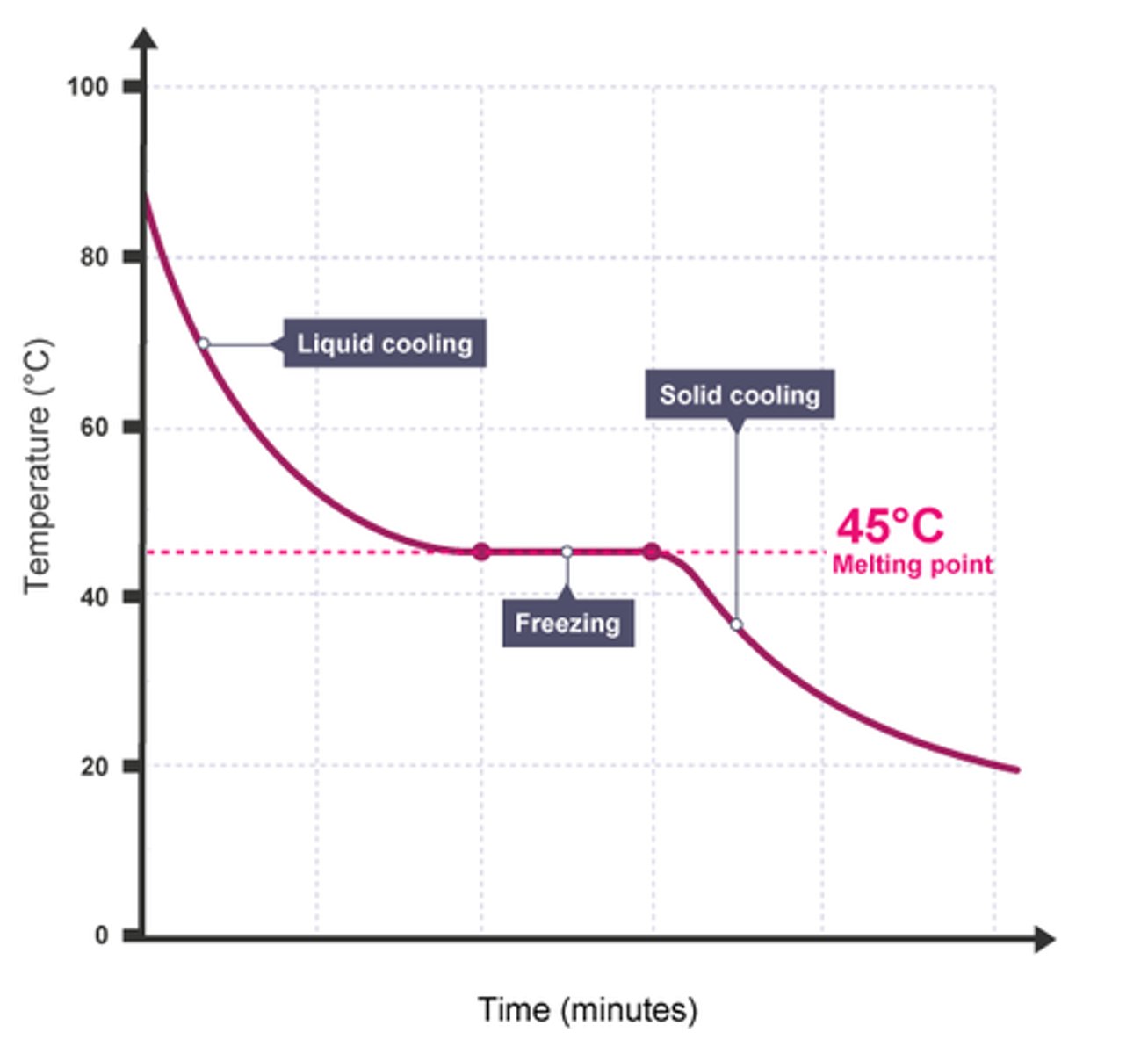
Is the diagram on the other side a mixture or pure substance?
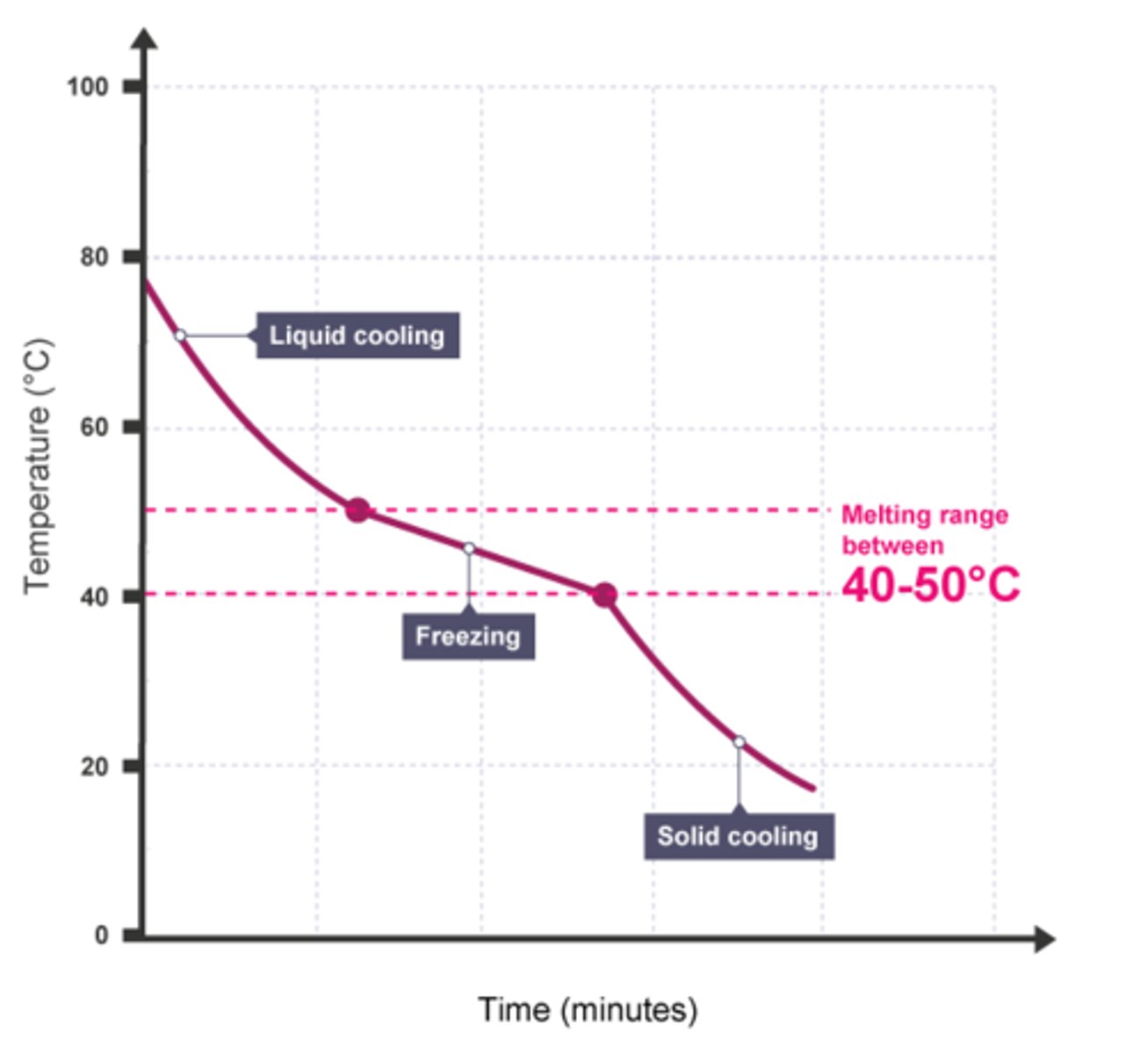
What is a formulation?
A mixture designed as a useful product
How is a formulation made?
By mixing the components in carefully measured quantities to ensure that the product has the required properties
Give some examples of formulations
Fuels, cleaning agents, paints, medicines, alloys, fertilizers and foods
What is chromatography?
A method used to separate the substances in a mixture
What is the method for chromatography?
See photo
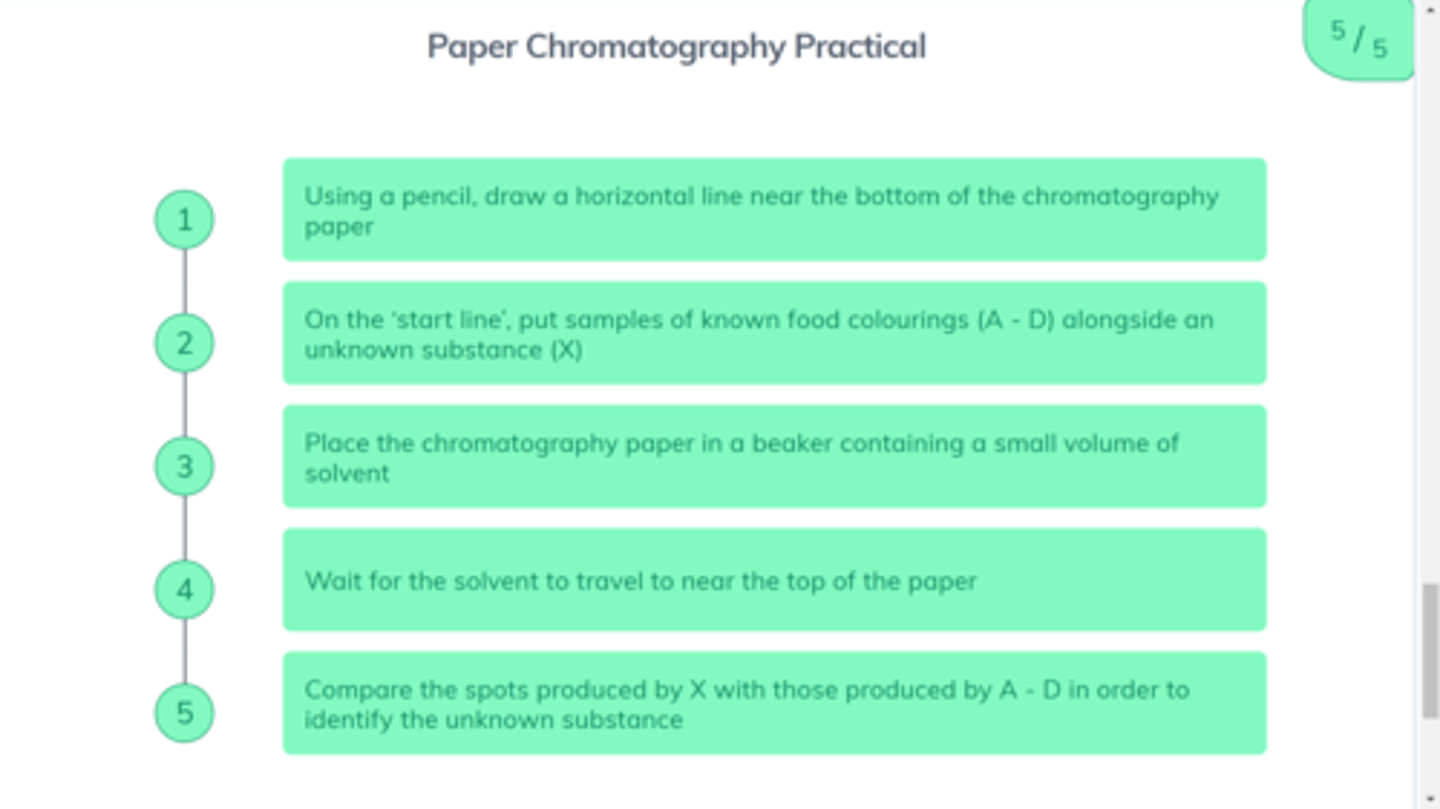
What are the two phases of chromatography?
- Mobile phase: where the molecules can move (liquid or gas)
- Stationary phase: where molecules can't move (solid or really thick liquid)
What is formed between the two phases of chromatography?
An equilibrium because the substances constantly move between mobile and stationary phase
What chemicals will move further in chromatography?
The chemicals that spend more time in the mobile phase rather than the stationary phase
How many spots will a pure substance form on chromatography paper?
One spot, because only one substance in sample
What component is the stationary phase in paper chromatography?
The paper
What component is the mobile phase in paper chromatography?
The solvent, eg. water, ethanol
What determines the amount of time the molecules sped in each phase?
- How soluble they are in the solvent
- How attracted they are to the paper
What does soluble mean?
Ability to be dissolved in a solvent (water, ethanol)
What molecules will travel furthest in chromatography?
Molecules with a higher solubility and less attraction to the paper. Will spend more time in the mobile phase
What can the solvent front determine?
Distance traveled by solvent
Memorise this chromatogram
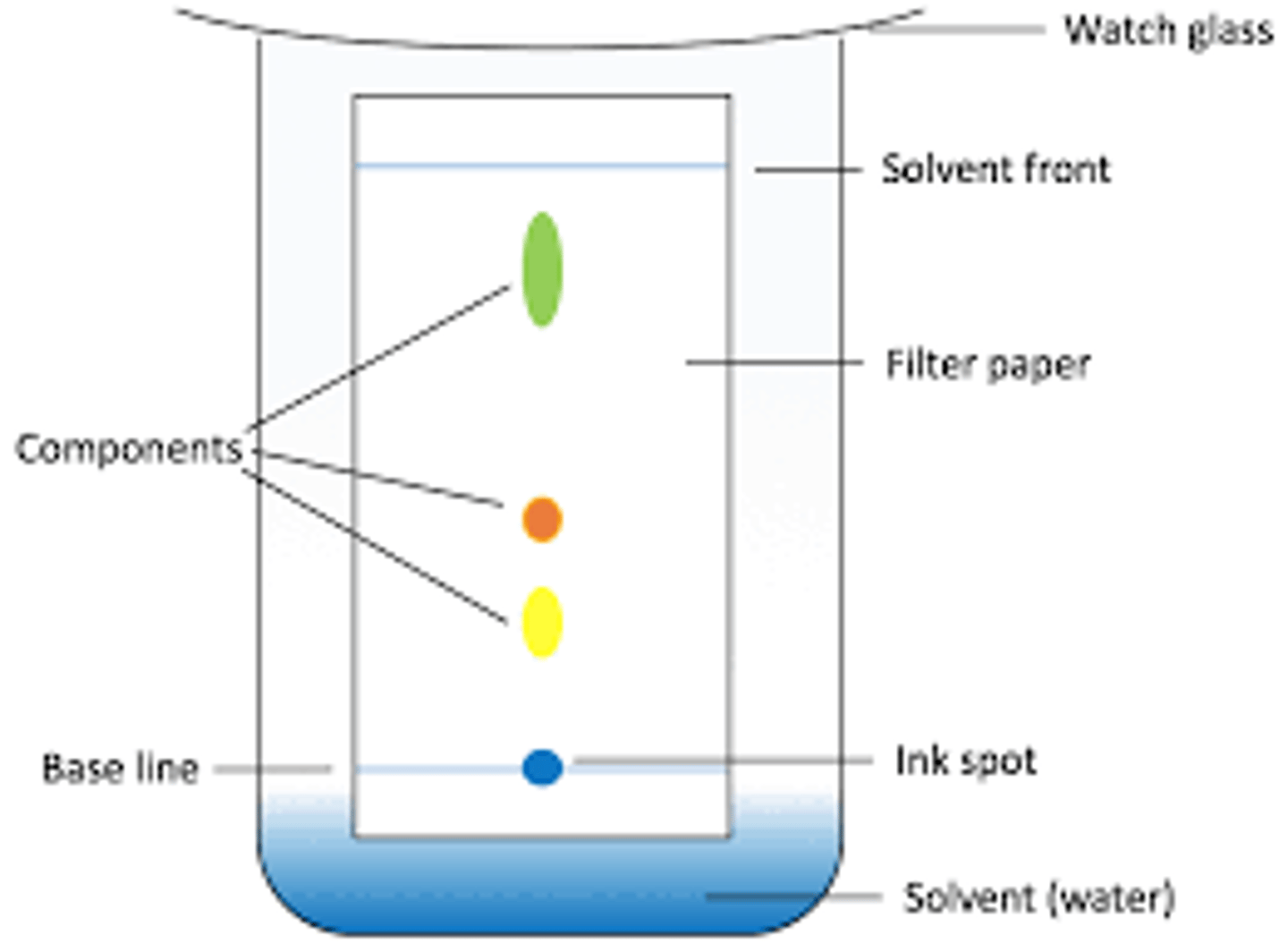
What is the Rf value formula?
distance travelled by substance / distance travelled by solvent
What is the distance travelled by the substance?
Distance from the baseline to the centre of the spot
How do you see if a certain substance is present in a mixture?
Run a pure sample of that substance alongside the mixture. If one of the spots of the mixtures match or if the Rf value is the same, the substance may be present
What happens if you change the solvent
The Rf value changes