Injury Response Process
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Treating an injury with thermal, electrical, mechanical, or light energy, we...
Attempt to provide the optimal environment for healing to occur
Therapeutic Modality
a form of stress applied to the body for the purpose of eliciting an involuntary physiological response
Physical Stress Theory
describes how tissues react relative to the amount of stress they receive relative to normal
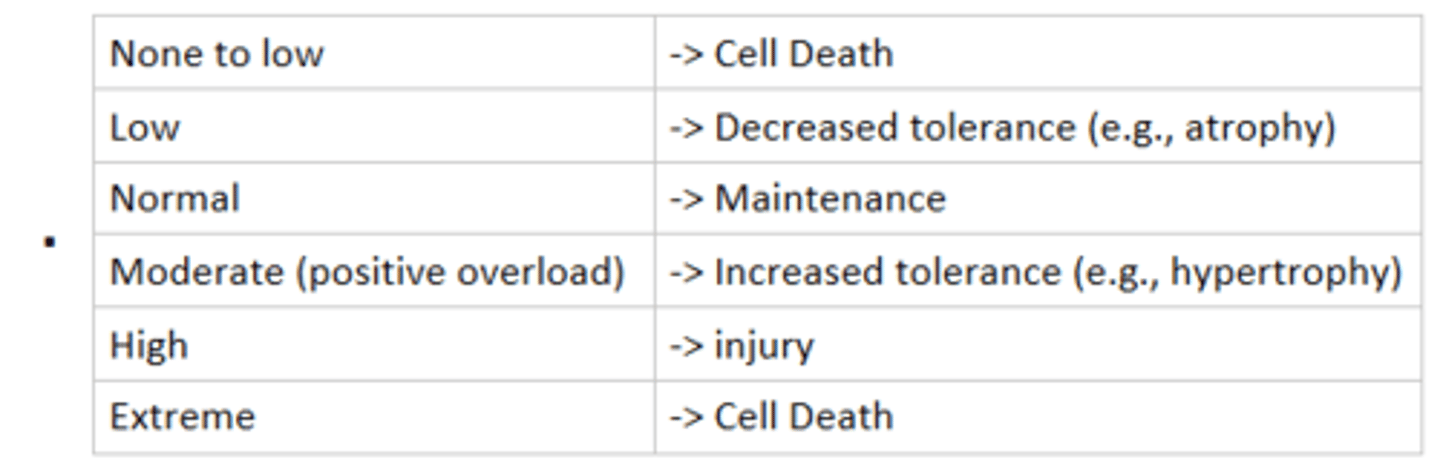
General Adaptation Syndrome (three stages of stress response)
alarm, resistance, exhaustion
Alarm Stage
Body's initial sudden reaction to a change in homeostasis
Resistance Stage
Body continues to adapt to the stressor by using homeostatic resources to maintain its integrity
- longest phase of the general adaptation syndrome, lasting many days, months, or years
Exhaustion Stage
Occurs when the body cannot withstand stresses
- stage may present as traumatic or overuse injuries (goal: stay out of this stage!)
Macrotrauma
acute injury (sprains, strains, fractures, etc)
Microtrauma
Repeated, relatively low-intensity forces can cause stress fractures, chronic inflammatory conditions, and muscle soreness
Wolff's law
bone adapts to the forces placed on it
Epithelial tissue (1st layer of skin)
- secretes and absorbs various substances and has the distinction of being devoid of blood vessels
- the skin's outer layer is formed by stratum corneum, a layer of flat, densely packed dead cells
Adipose Tissue
- consists of fat cells
- high water content
Muscle tissue
smooth, skeletal, cardiac
smooth muscle
Involuntary muscle found inside many internal organs of the body
cardiac muscle
Involuntary muscle tissue found only in the heart.
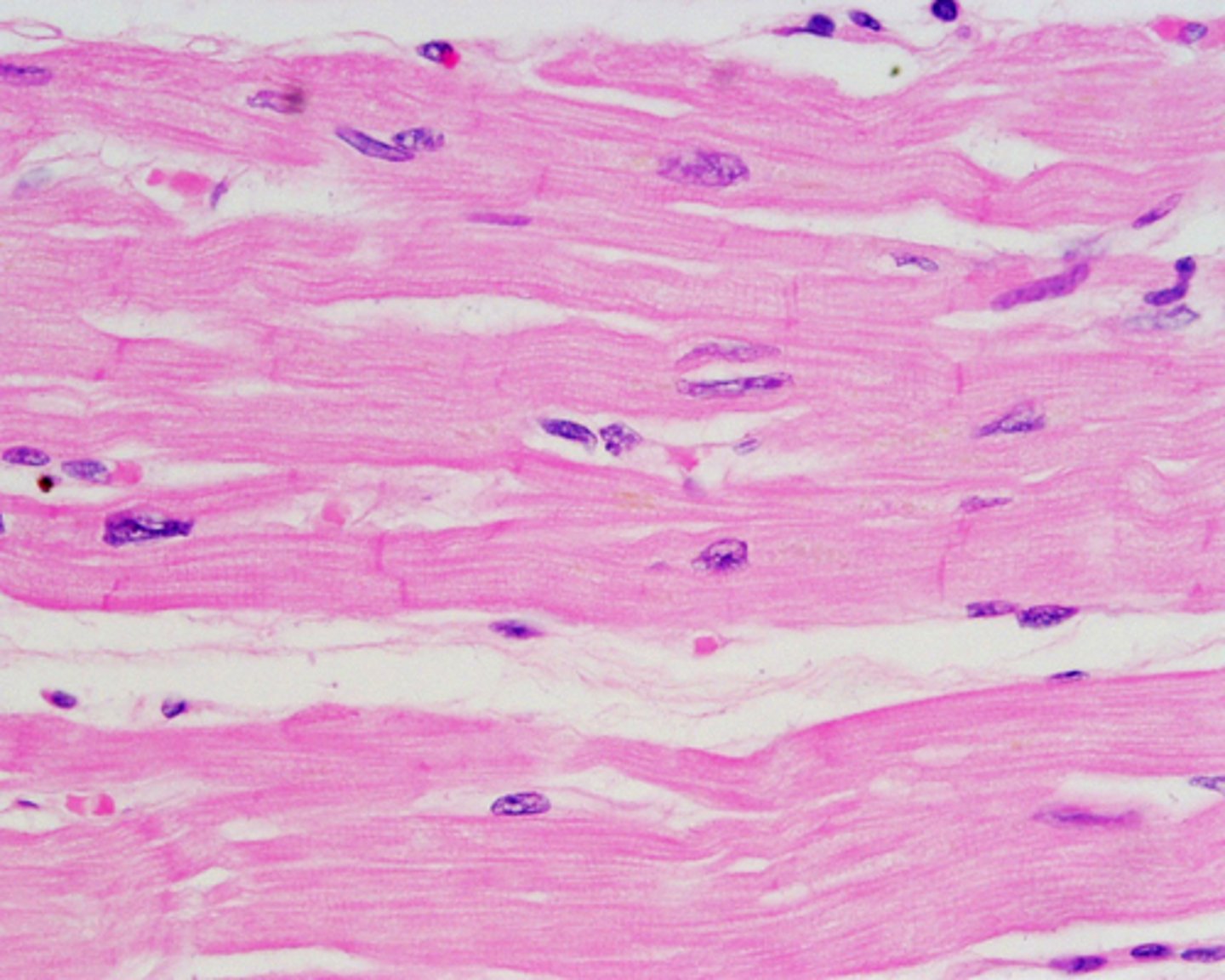
skeletal muscle
Voluntary muscle attached to bones. (type 1 & type 2)
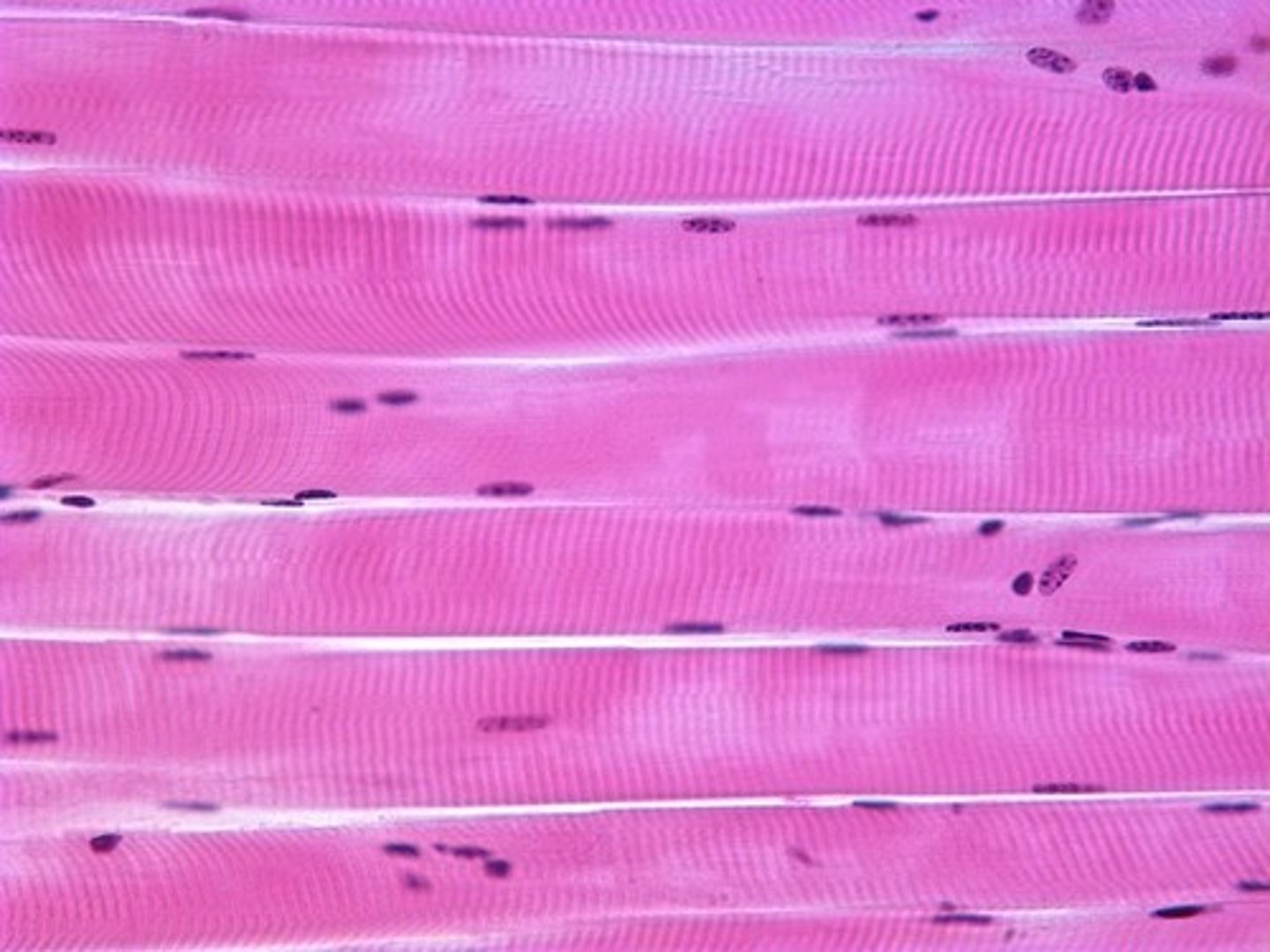
Type 1 (Slow-twitch)
muscle fibers are slow to fatigue and are prevalent in postural muscles (posterior-chain, back muscles, etc.)
Type 2 (fast-twitch)
muscle fibers are capable of generating a high amount of force in a short amount of time
Nervous tissue
Nerves conduct afferent and efferent impulses via action potentials: dendrites (1), nerve body (2), axon (3)
- most therapeutic modalities have some affect on nerve function (NA-K pump) and slow rate of painful nerve transmission
Connective tissue
The most abundant type of tissue in the body that is produced by fibroblasts, formed by cell matrix and collagen(fascia, tendons, ligaments, etc.)
Primary injury
associated with the tissue destruction directly resulting from the traumatic force
Secondary injury
cell death caused by a blockage of oxygen supply to the injured area (ischemia) or caused by enzymatic damage and mitochondrial failure.
- Treatment efforts used after trauma attempt to limit the amount of secondary injury
Phases of the healing process
1. acute inflammatory response (0-3 days)
2. proliferation phase (1-10 days)
3. maturation phase (3-30 days)
Acute Inflammatory Response
Inflammation is a necessary part of the healing process (we just manage it)
- Migration of phagocytes and fibroblasts to the area and formation of granulation tissue isolate and localize the trauma
- Histamine released from the traumatized cells increases capillary permeability, resulting in swelling as the proteins follow water out into the tissues
Stages of inflammation after injury
acute (0-14 days)
subacute (14-31 days)
chronic (>31 days)
Proliferation Phase
The number and size of fibroblasts increases, causing ground substance and collagen to collect in the traumatized area in preparation to rebuild the damaged tissues
- revascularization
- wound contraction
- wound remodeling
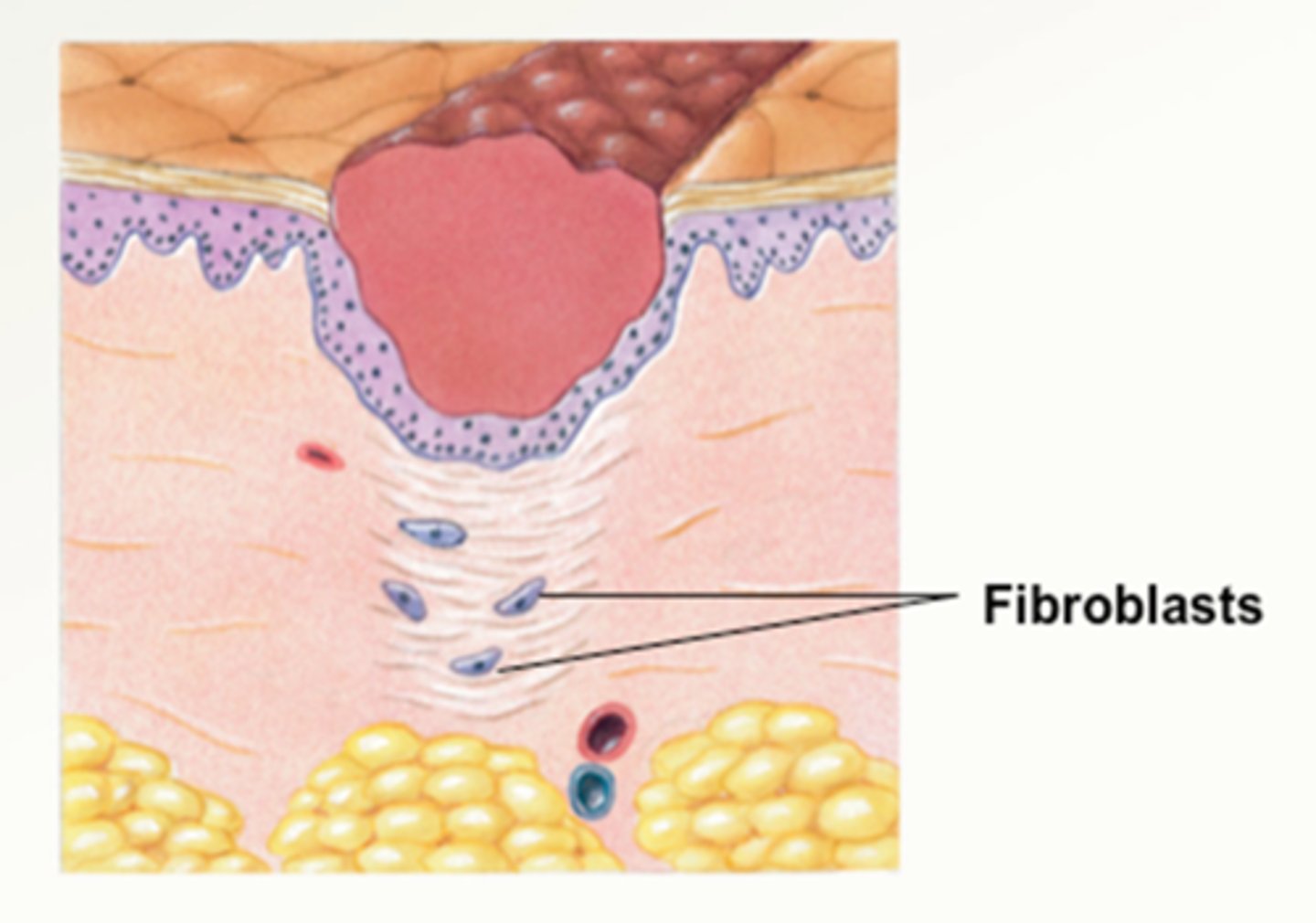
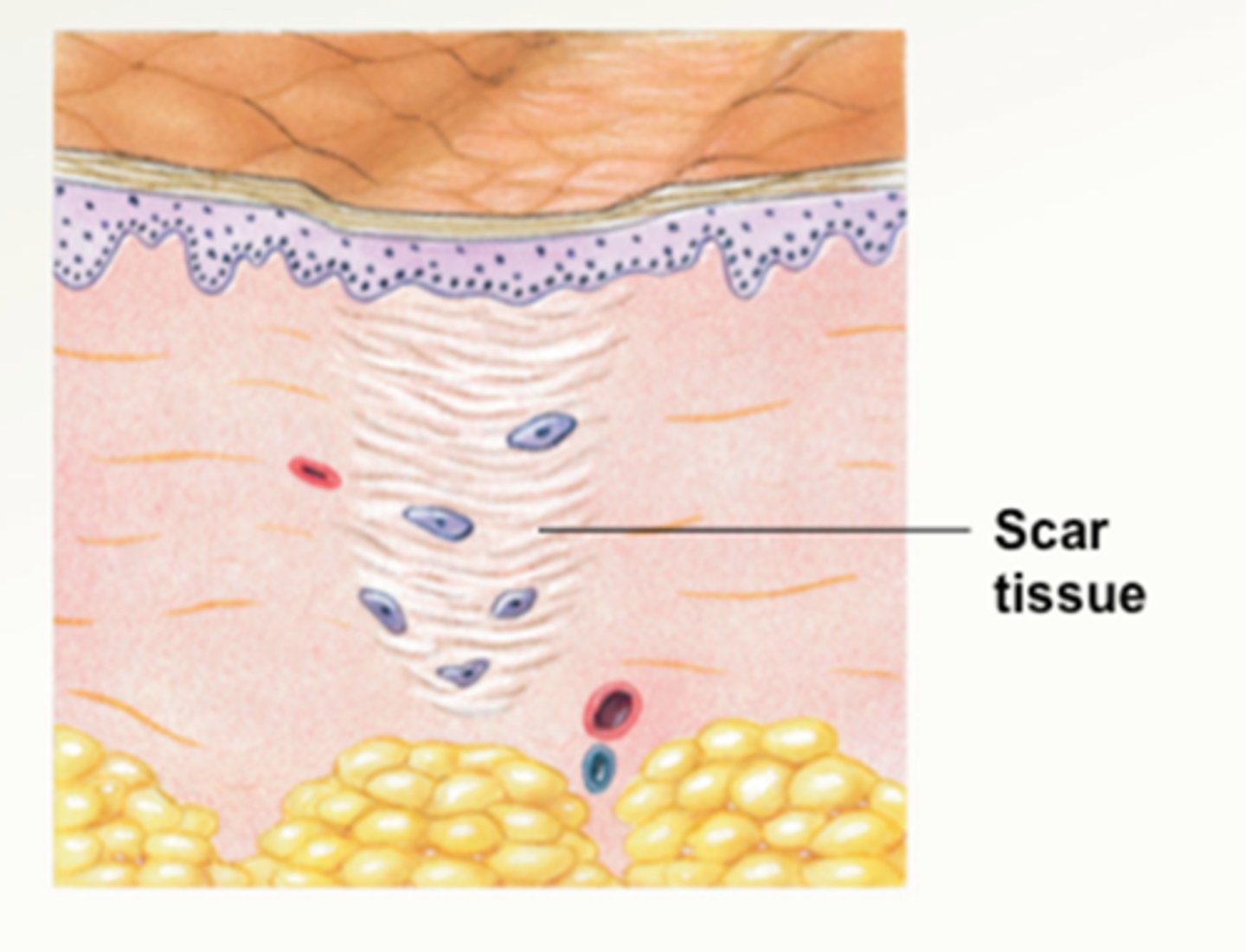
Maturation phase
- number of fibroblasts, myofibroblasts, and macrophages is reduced to the preinjury level
- number of capillaries, the overall vascularity of the area, and water content are reduced
- proportion of type 1 collagen continues to increase, replacing the existing type 3 collagen and other parts of the collagen lattice
Cardinal signs of inflammation
redness, swelling, heat, pain, loss of function
Swelling
increase in the volume of a body part as the result of fluid build-up
Edema
build-up of excessive fluids and protein in the interstitial space resulting from the imbalance between pressures inside and outside the cell membrane of an obstruction of the lymphatic return and venous return mechanisms
- Ice application reduces edema formation
- removed by increasing venous and lymphatic return
Starling's Law
Describes the movement of fluids across the capillary membrane that results in the formation or removal of swelling
Muscle spasm
involuntary contraction of muscle fibers
- direct trauma, decreased O2, neurological dysfunction
Muscle atrophy and weakness
- Disuse atrophy and denervation
atrophy
- Edema and inflammation
stimulate Golgi tendon organs,
increasing the rate of atrophy