Chemistry Unit 10- Mixtures and Solutions
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Solute
Dissolved substance
Solvent
Dissolving substance, like H2O
H2O is polar, polar solutes dissolve better with polar solvents
Nonpolar substances dissolve in nonpolar solvents
Soluble
Solid solute that dissolves
Insoluble
Solid solute that doesn't dissolve
Miscible
2 liquids mixed
Immiscible
2 liquids don't mix
Like Dissolves Like
- Solutes and most ionic compounds because it's polar
- Nonpolar liquids mix with each other nonpolar liquids
- Other solvents needed for oils
- Polar and nonpolar do not mix
-Water- Strong IMFs
- Oil- No IMFs
Alcohol dissolves both polar and nonpolar liquids
Suspension/Heterogenous Mixtures
A heterogenous mixture in which particles can be seen and easily separated by settling or filtration
Colloids
Made of 2 or more phases
Medium size particles, don't settle out (1-1000nm)
ex: Jelly, jello, mayo, paint, milk, blood, smoke, fog, foam, whipped cream, pollen in air
Sits in air/liquid, moving. Heterogenous mixtures settle at bottom/on top of something
Homogenous Mixtures/Solutions
Particles conform to one phase, but it can be any phase
ex: Air (gas solution, mix of O2, CO2, N2)
Dalton's law of partial pressure
ex: Alloys: Solid solution of metals: Brass, stainless, sterling silver
Tincture
Solution that is alcohol based. Alcohol is solvent, not H2O
Emulsion
Mixture of oil and water that stays mixed because of an emulsifier
Mayo (eggs are the emulsifier), Lotions
Electrolytes
Ionic solutions that contain cations and anions that disassociate in water and conduct electricity
NaCl -> (Na+) + (Cl-)
C12H22O11 -> C12 H22 O11 non electrolyte, covalent
Solubility
How much solutes dissolve in 100mL of H2O at various temperatures
Categories of Solubility
Unsaturated
Saturated
Supersaturated
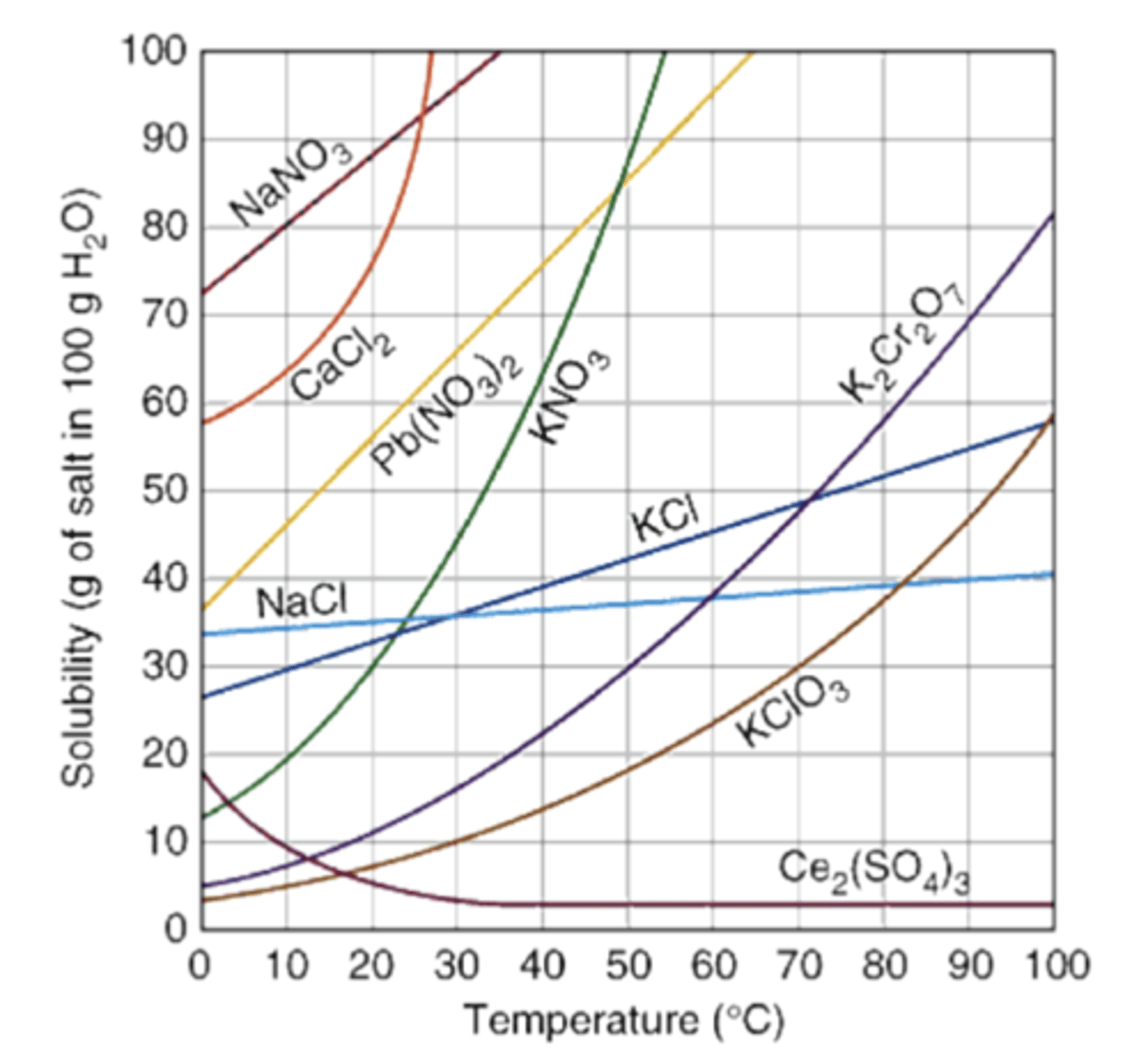
1. Unsaturated Solution
Less dissolved solute for a given temperature than a solvent could hold
More solute can be added to dissolve
ex: Cup of hot water with a small amount of NaCl dissolved in it, where more salt could be added and it would still dissolve
2. Saturated Solution
Completely full, maximum substance amount
Maximum amt. of solute in a given amount of solvent at a specific temperature
On solubility graph line
No more solute would dissolve
ex: Cup of hot water with NaCl, add more NaCl it becomes supersaturated.
3. Supersaturated Solution
Solution that contains more dissolved solute than the max (sat. solu) at the same temp due to cooling and drop in solubility
Very unstable
ex: Honey- Leave it for a bit but recrystallizes, rock candy, crystal formations
Points above saturated line formation
Colligative Properties of Solutions
Properties that make solutions different from pure water
Depends on the # of particles (concentration), not the indentity of the solute
Freezing Point Depression, boiling point elevation
Colligative Property 1. Freezing Point Depression
Solutions have a lower freezing point of water
Solute particles BLOCK the IMFs from forming a solid, so KE must be lower
Putting salt on roads in winter allows the road to stay wet a lower temperature and avoid turning into ice
Colligative Property 2. Boiling Point Elevation
Boiling point occurs when VP = ATM pressure
Decrease VP, increase BP
Increase VP, decrease BP
Adding solutes to H2O lowers VP (less evaporation, increase BP)
Takes more energy to increase evaporation (higher BP), increases VP to reach atm pressure
Solutions boil at a higher temp and freeze at a lower temperature than water
Wider range of temp in the liquid phase
Molarity
Most common unit of solution concentration
Molarity = (mols of solid)/(liters of solution)
Dilutions
Making a solution of lower concentration from a stock solution
(M1)(V1) = (M2)(V2)
M: Molarity
V: Volume