Organic Chemistry - Unit 1 Exam
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
When was the field of organic chemistry originally developed?
as scientists began to study living things at the molecular level
Why was the word “organic” chosen?
this field was studying the chemistry of life
Name the 4 most important elements in organic chemistry in order of relevance to the field.
carbon
hydrogen
oxygen
nitrogen
What is the first step of the process of science?
making observations (of naturally occurring phenomena or through experiments)
What is the second step of the process of science?
organizing the data collected through these observations by finding patterns
What is the third step of the process of science? (2 parts)
using the patterns to make predictions about how similar things would behave in other situations
developing scientific theories to explain why these patterns are occurring
What is the fourth step of the process of science?
What is the goal of this step?
setting up experiments, observing results and seeing how well the new data fits i with the predictions and theories
the goal is to test and refine the predictions and theories
What is the fifth and final step of the process of science?
new and useful inventions (technology) can be created once good scientific theories have been developed and accurate predictions have been made
Name the 2 analytical methods that can be used to visualize the surfaces of some molecules.
atomic force microscopy (AFM)
scanning tunnel microscopy (STM)
Describe how atomic force microscopy (AFM) works.
a probe with a very fine tip is dragged across the molecule’s surface, moving down where the surface is lower and moving up where the surface is higher; up & down movements must be amplified to produce a useful readout because they are so small; a laser is reflected off the probe and the movements change the angle of reflection; the resulting movement of the laser spot is used to determine probe’s height
Describe how scanning tunneling microscopy (STM).
a probe with a very fine tip is moved across a surface, remaining at a constant height so that the distance between the surface and the probe varies depending on the height of the surface at that point; an electric voltage is connected from the probe to the edge of the surface; electrons must tunnel from the probe to the surface in order to complete a circuit which becomes easier as distance increases; the flow of the electrical current through the circuit can be used to measure the height of the surface
What is the most important technique for looking at the structures of organic molecules?
x-ray crystallography
What is the purpose of x-ray crystallography?
precisely determine the 3-dimensional position of individual atoms within a molecule
What are the simplest family of organic molecules?
alkane hydrocarbons
Describe the structure of alkane hydrocarbons.
consist of carbon and hydrogen atoms connected by only single bonds
What is meant by alkane hydrocarbons being saturated?
each carbon atom forms the maximum number of bonds possible
How many bonds do hydrogen atoms form?
1
How many bonds do carbon atoms form?
4
Differentiate between the meaning of each word in alkane hydrocarbon.
alkane - saturated (carbons form max number of bonds, 4)
hydrocarbon - compound formed just from carbon and hydrogen atoms
What is the simplest of the alkane hydrocarbons?
methane
Describe the structure of methane.
one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms
Describe the structure of propane.
three carbon atoms bonded to eight hydrogen atoms
When hydrocarbons are burned, they react with oxygen to produce…
carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O)
What can combustion help determine?
the molecular formula of a hydrocarbon
How do we use combustion to study the molecular formula of a hydrocarbon?
by measuring the ratio of carbon dioxide versus water that is produced when it is burned
What are two shortcomings of Lewis structures?
they become tedious & difficult to read once molecules become larger & more complex
they say nothing about molecular geometry
What do wedges & dashes represent?
wedges: something coming in front of the page towards you
dashes: something going behind you from the page away from you
Since carbon is so common in organic molecules, what happens to them in regard to skeletal structures?
the “C” is omitted from all carbon atoms and instead it is assumed that every unlabeled intersection represents a carbon atom
What else do organic chemists omit from skeletal structures?
hydrogen atoms and the bonds that they form
Why are molecular structures in constant motion?
at regular temperature, all the single bonds in a molecule are rotating very rapidly
Which alkane hydrocarbons are gas at room temperature & which are liquid at room temperature?
gas: methane, ethane, propane & butane
liquid: pentane, hexane, heptane, octane, nonane & decane
What do the cores of simple organic molecules tell you?
how many carbon atoms the molecule contains
What do the suffixes of simple organic molecules tell you?
which family the molecule belongs to
What do the prefixes of simple organic molecules tell you? Describe two examples.
structure
cyclo - ring
iso - isomeric structure (branched v.s. linear)
Describe the relationship between alkane size & boiling point.
as alkanes get larger, their boiling points get higher
What is the purpose of distillation?
separation of mixtures of alkanes based on their different boiling points
Describe how distillation works.
electric mantle heats gradually heats up a mixture of liquids; as the compound w/ the lowest boiling point begins to boil, its vapors move up the distilling column, providing vertical space for compounds of higher boiling points to re-condense and drip back into the heating mixture; the pure vapors of the low-boiling compound make it back into the downward sloping condensing column which is cooled by water flowing around the outside of the column, so the vapors condense and drip back into the collection flask as a pure liquid; the collection flask can be changed, the temperature can be increased and the next compound can distill and be collected
What alkane hydrocarbons are waxy solids?
alkanes that have at least 20 carbon atoms
What are these molecules used for?
insect communication signals
How many bonds do oxygen atoms form?
2
Describe the structure of alcohols.
oxygen atom bonded to one carbon atom & one hydrogen atom
Describe the structure of ethers.
oxygen atom bonded to two carbon atoms
Why do chemists find it useful to subdivide molecules into families like these?
they often have similar properties to each other
What are these small groups of atoms or families called? Why?
functional groups because they add particular type of functionality to a molecule
What is the purpose of infrared (IR) spectroscopy?
analyzation of the functional groups in a molecule
How does infrared (IR) spectroscopy work?
the instrument shines a beam of infrared light through a sample of the molecule; some wavelengths of the light get absorbed by the molecule, while others do not
What is the significance of a sharp IR signal at 3000-28000 cm-1?
presence of C-H bonds, so all hydrocarbons have this absorbance
What is the significance of a broader IR signal from 3500-3000 cm-1?
presence of O-H bonds, indicating an alcohol molecule
What does the core of systematic names of alcohols & ethers tell you?
the number of carbon atoms
What does the suffix of systematic names of alcohols tell you? Specify.
which family the molecule belongs to
anol → alcohol
What does the number prefix tell you?
the carbon atom that the functional group is on
Describe how common names work for alcohols.
yl is added to the core to represent the hydrocarbon portion of the molecule and alcohol is the word that represents the OH portion of the molecule; this method does not use numbers to indicate between isomers, but instead nicknames
List two examples of nicknames used in the common naming system.
n-propyl (linear)
isopropyl (branched)
What system is primarily used for ethers?
common naming system
Describe how ethers are named using the common nickname system.
each side of the ether is named individually
What is the purpose of mass spectrometry?
to measure the mass of individual molecules
Describe how mass spectrometry works.
a sample of molecules is injected into the instrument, then the ionizer transforms some of the molecules into charged ions, typically +1 cations, then the instrument accelerated those ions into a linear stream which is sent through a magnetic field which puts a force on the ions; the positive field repels the ions and the negative field attracts the ions which causes the stream to curve; the amount it curves depends on the mass of the ion, because acceleration equals force divided by mass; heavier ions will curve less and lighter ones will curve more; the instrument uses an amount of magnetic field that only allows molecules with a specific mass to get through a small opening to the detector
How do you determine the molecular weight of the compound from MS data?
the signal with the largest mass number matches the molecular weight of the compound
What causes fragmentation in mass spectrometry?
the ionization technique is harsh and breaks the molecules down into smaller pieces before they are analyzed
What is the purpose of gas chromatography (GC)?
to separate molecules based on their boiling points and molecular sizes
How is gas chromatography different from distillation?
gas chromatography is performed on a very small amount of mixture to analyze just the mixture rather than being used to isolate large quantities of pure compounds from mixtures
Describe how gas chromatography works.
a couple of microliters of dilute solution of the mixture is injected into the instrument by a robotic injector needle; the instrument heats the mixture to a hot temperature to vaporize the whole mixture; the vapors then flow through a very long and skinny tube which coils; lighter compounds diffuse through the tube more quickly whereas heavier ones diffuse more slowly;
What are the two ways to detect material as it exits the GC tube?
burn it in a flame ionization detector
connect the output stream from the GC directly into an EI mass spectrometry instrument to analyze the mass
What is an amine?
molecules that incorporate nitrogen atoms into hydrocarbon structures
How many bonds does nitrogen form?
3
How are amines named?
the common name/nickname system
What is the significance of a sharper IR signal of 3000-28000 cm-1?
presence of N-H bonds, indicating an amine group
What are tertiary amines?
amines where the nitrogen bonds to three carbons instead of any hydrogens, so they do not have a sharp 3500-3000 cm-1 IR signal
During combustion, what does each atom form?
C, H, O and N
CO2, H2O, NO and O2
Why can’t the produced oxygen gas be detected?
the burning is happening in an excess of oxygen gas
What are alkyl halides?
hydrocarbons that include halogen atoms
Why don’t fully halogenated molecules produce IR absorbance 3000-2800 cm-1?
the hydrogen atoms bonded to carbon are replaced by halogen atoms so there are no C-H bonds to produce this signal
Why don’t mass spectrometry data for compounds containing bromine or chlorine atoms not exactly match their molecular weights?
molecular weights are calculated based on average weights of all different isotopes in a sample; for hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen & oxygen, this does not matter much because at least 99% of their atoms are the main isotope; Cl and Br on the other hand can each be one of two main isotopes
Describe the distribution of Cl and Br isotopes.
half of Br atoms are 79Br while the other half are 81Br; ¾ of Cl atoms are 35Cl while the other ¼ are 37Cl, making their avg MW 80 and 35.5 respectively
Describe the observed pattern of these isotope distributions.
molecules containing a Br atom have a pair of equal height signals that are one higher and one lower than the average mass; molecules containing a Cl atom also gave a pair of signals but the lower mass one is 3x as tall as the higher mass one
Describe the naming of alkyl halides.
halogen groups do not control suffix, but instead are considered substituents on core, incorporated into the prefix portion of name
Describe the periodic trend in regard to bonding patterns.
bonds decrease from left to right
C-4, N-3, O-2, H-1
What are the particular numbers of electrons that make atoms very stable?
2, 10, 18, 36, etc
What is classical bonding theory?
sharing electrons (creating covalent bonds) or giving/taking electrons (creating charged ions) to reach a stable number of valence electrons
What do curly arrows represent?
movement of electrons
What type of electrons are not involved in bonding? Why?
core electrons because they are already stable
What is a full octet?
8 valence electrons
Where are lone pairs going to be in skeletal structures? Why?
heteroatoms (not carbon); it is implied that carbons are already completely bonded to hydrogens which are not explicitly shown
What is the earliest point on the three of life we can reconstruct using data.
LUCA
List the 5 properties of life.
homeostasis
structural organization
metabolism
growth and reproduction
response to environmental conditions
Define homeostasis.
ability to adjust internal environments to maintain stable equilibrium
Define structural organization.
ability to maintain distinct parts and the connections between them
Define metabolism.
control of chemical reactions
List the 10 major transitions.
origin of self replicating molecules capable of heredity
transition of RNA to DNA and proteins
first cells
first eukaryotic cells
evolution of sexual reproduction
first multicellular organisms
complexity in multicellular organisms
individuality and gametes
sociality
eusociality
why can’t natural selection act on this population?
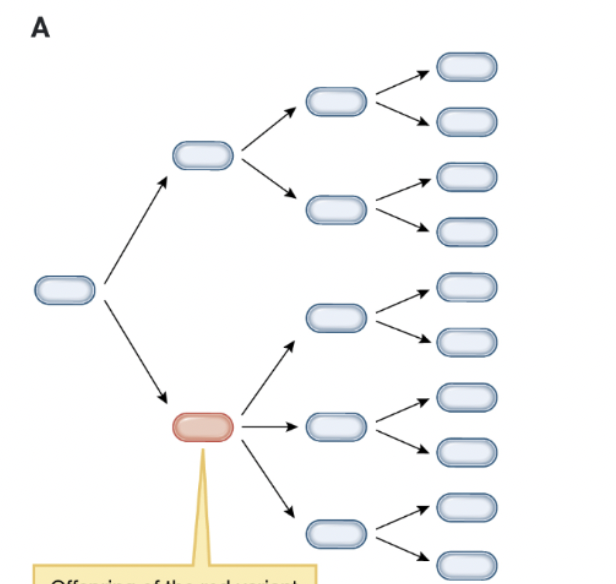
offspring of the red variant are blue, because variation is not heritable yet
why can natural selection act on this population?
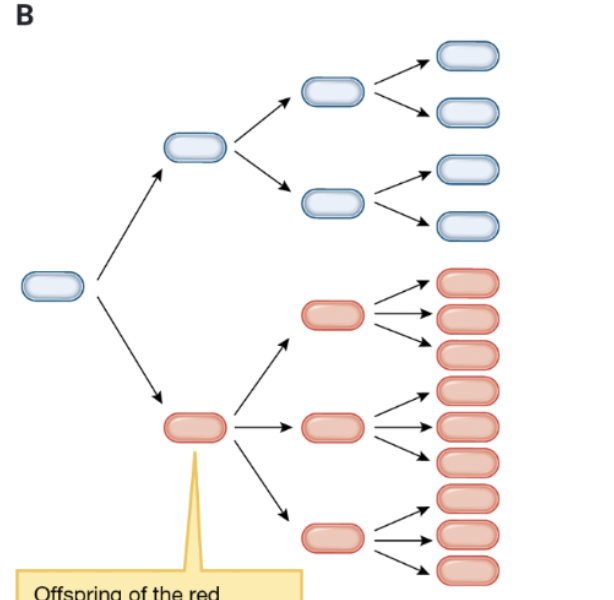
offspring of the red variant are red, meaning variation is now heritable
diagram the relationship between these three
what are ribozymes capable of doing? when was this discovered?
DNA → RNA → proteins
1980 scientists discovered that enzymes made from RNA (ribozymes) were capable of breaking and reforming chemical bonds between nucleic acids
Name two examples of the fossil record of early cells.
3.26 BYA fossil from South Africa believed to be bacteria
2 BYA fossil from Michigan believed to be eukaryotic algae
How did eukaryotic cells gain their complexity? What supports this hypothesis?
in 1970, Lynn Marguis proposed the endosymbiosis hypothesis, claiming that both mitochondria and chloroplasts evolved through symbiotic relationships with bacteria, giving rise to eukaryotic cells
mitochondria and chloroplasts having their own genome supports this
Describe the relationship between genome size and organism’s complexity.
genome size is not correlated with complexity of the organism
What is the C-value?
the amount of DNA found in a cell
Why does genome size not correlate with organismal complexity (C-value paradox)?
because much of the genome consists of noncoding or nonfunctional DNA, so total genome size doesn’t reflect the amount of coding DNA.
Describe the staying together model or unicellular bottleneck for multicellular life.
daughter cells stay together after cell replication because increased genetic similarity leads to decreased genetic conflict (more cooperation); this explains multicellularity in most plants and animals
Describe the coming together model for multicellular life (3).
independent cells came together early on; nonclonal propagules (unrelated founding cells); fitness benefits of group over individual
Define “individual” according to Rich Michod.
integrated and indivisible wholes