Midterm Crunch Time Study Guide
1/70
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Thyroid Gland
Lies in the anterior base of the neck and produces the hormones essential for proper regulation of metabolism such as thyroid hormone and calcitonin.
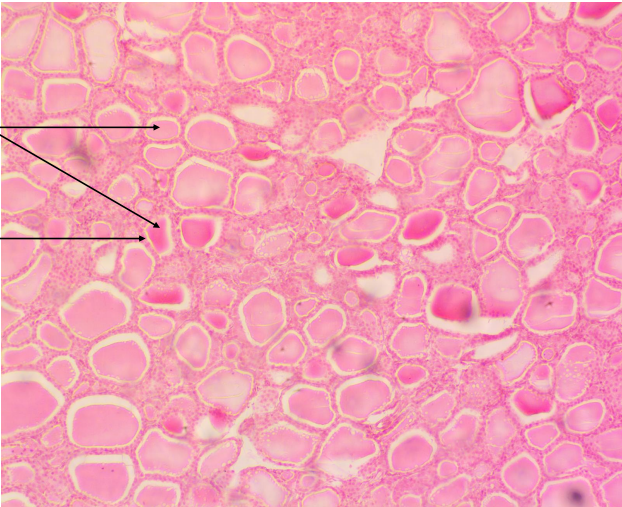
Thyroid - produces thyroid hormone and calcitonin.
Pituitary - Secretes Adrenocorticotropic hormone (Acth), Luteinizing hormone (LH), Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), Prolactin, and Growth hormone (GH)
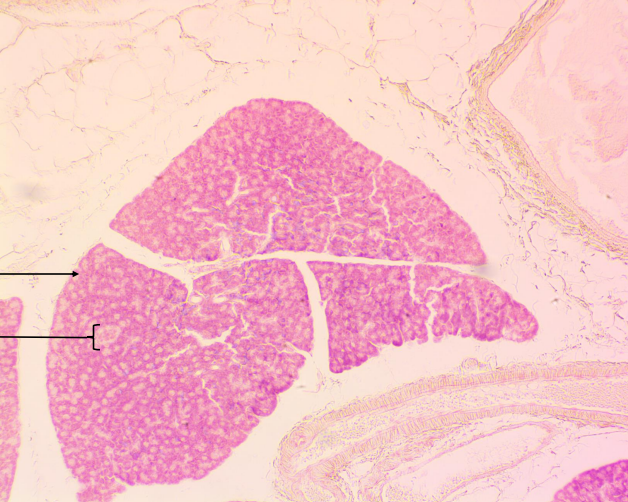
Pancreas - Secretes insulin and Glucagon
Testes - Secretes sperm and testosterone
Ovary - Secretes Estrogen and Progesterone
Pineal - Secretes melatonin
Parathyroid - Secretes parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Adrenal - Secrete cortisol and aldosterone.
Dwarfism
Endocrine Disorder that causes individual to grow shorter than average due to lack of Growth Hormone.
Hypoglycemia
Endocrine disorder where blood sugar levels are too low due to excessive presence of insulin in the body.
Role of Insulin
Manages blood sugar levels by allowing food (glucose) to be used as energy in the body.
Role of Glucagon
Regulates blood sugar levels from dropping to low by increasing the concentration of glucose and fatty acids in the blood.
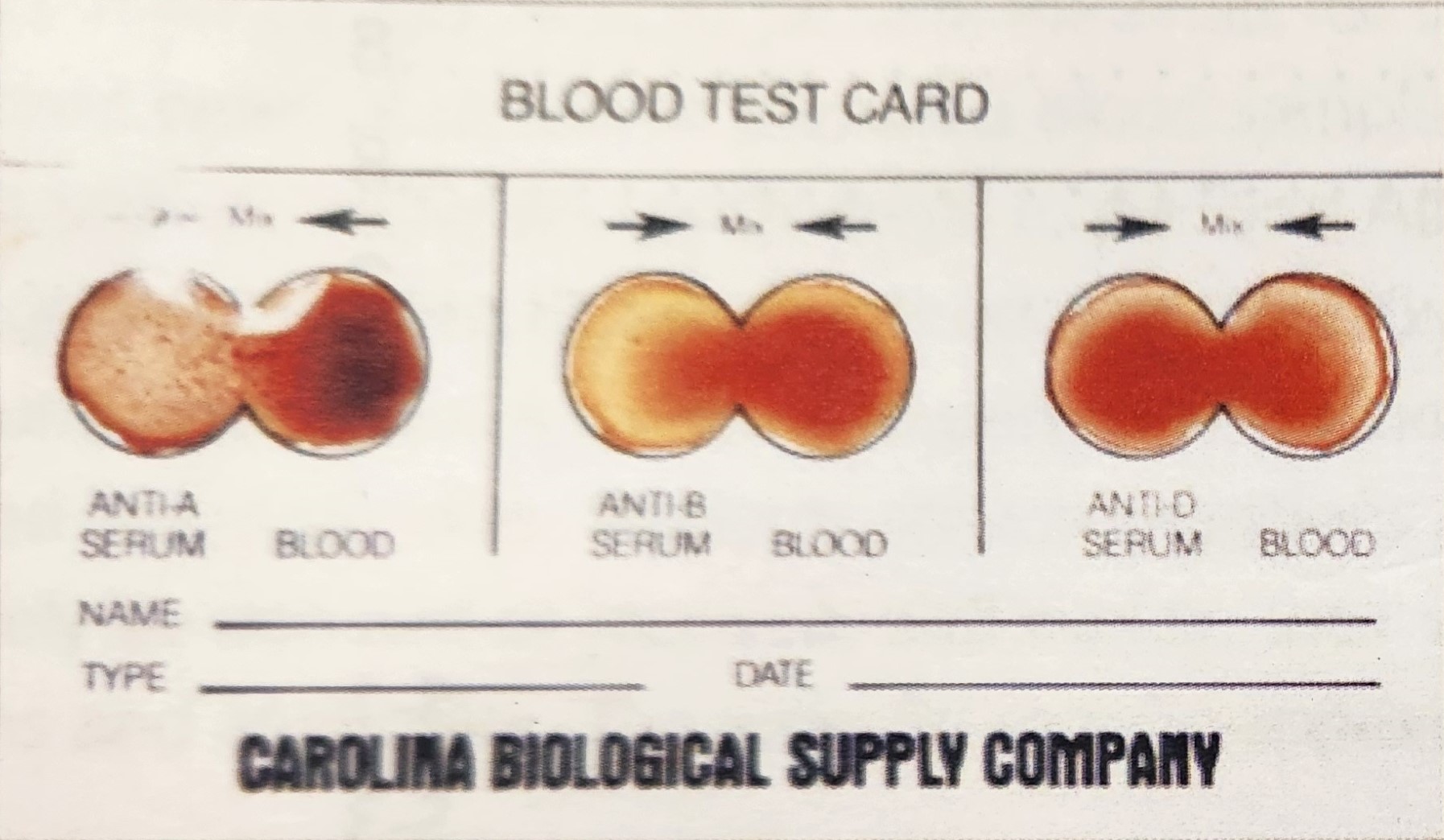
Blood Type A-
Antigens: A
Antibodies: B
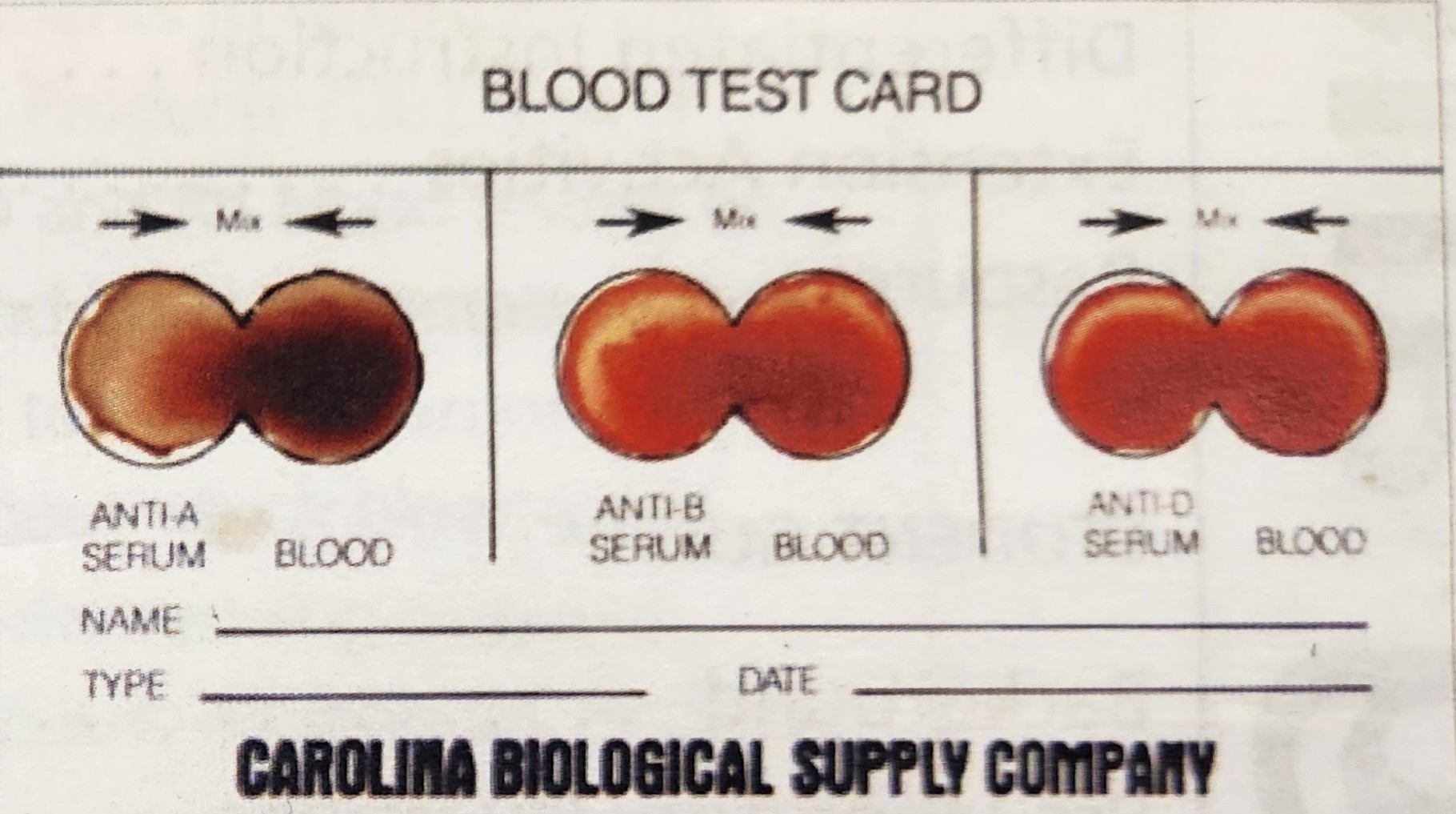
Blood Type B-
Antigens: B
Antibodies: A
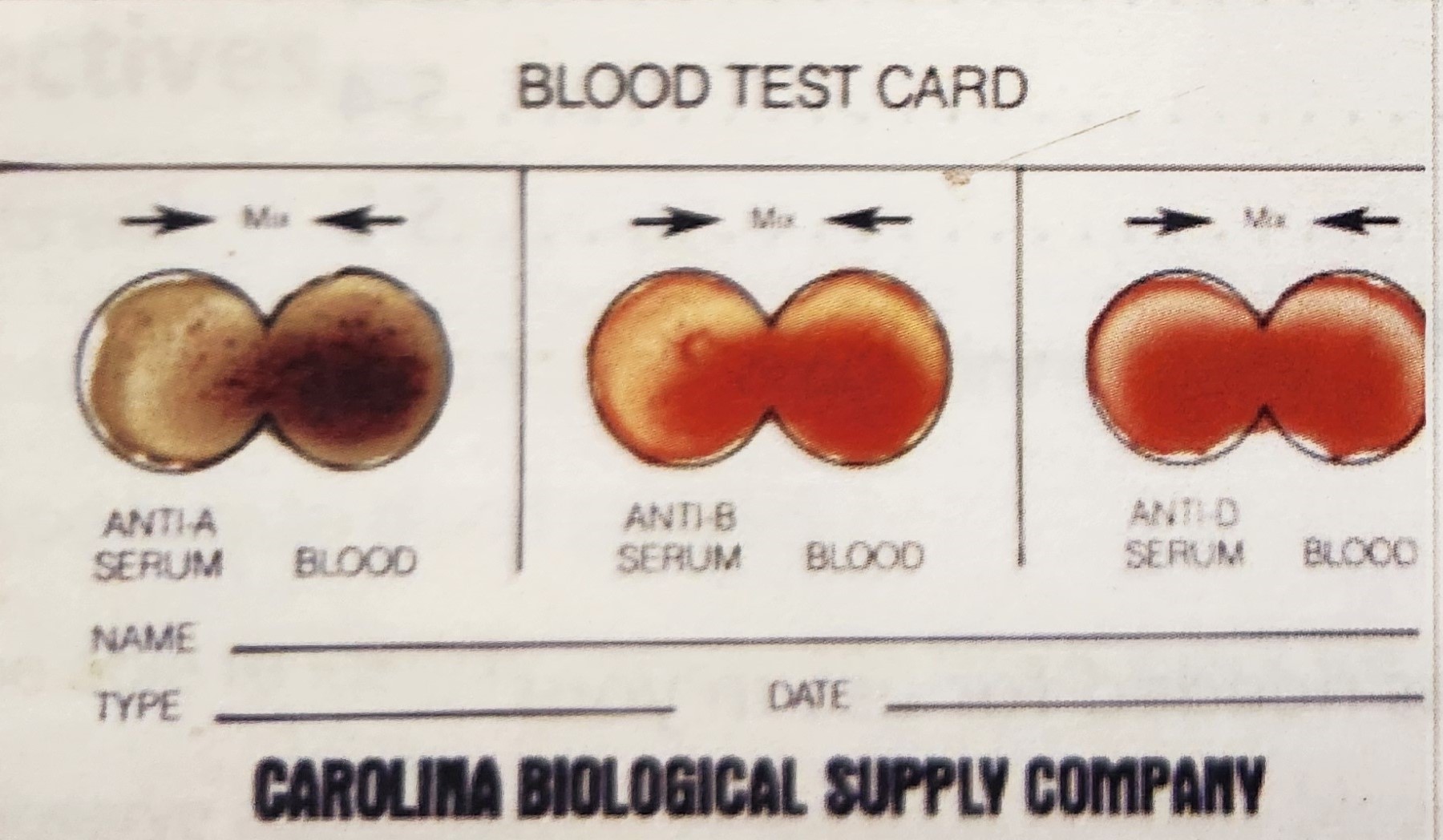
Blood Type AB+
Antigens: A, B, Rh
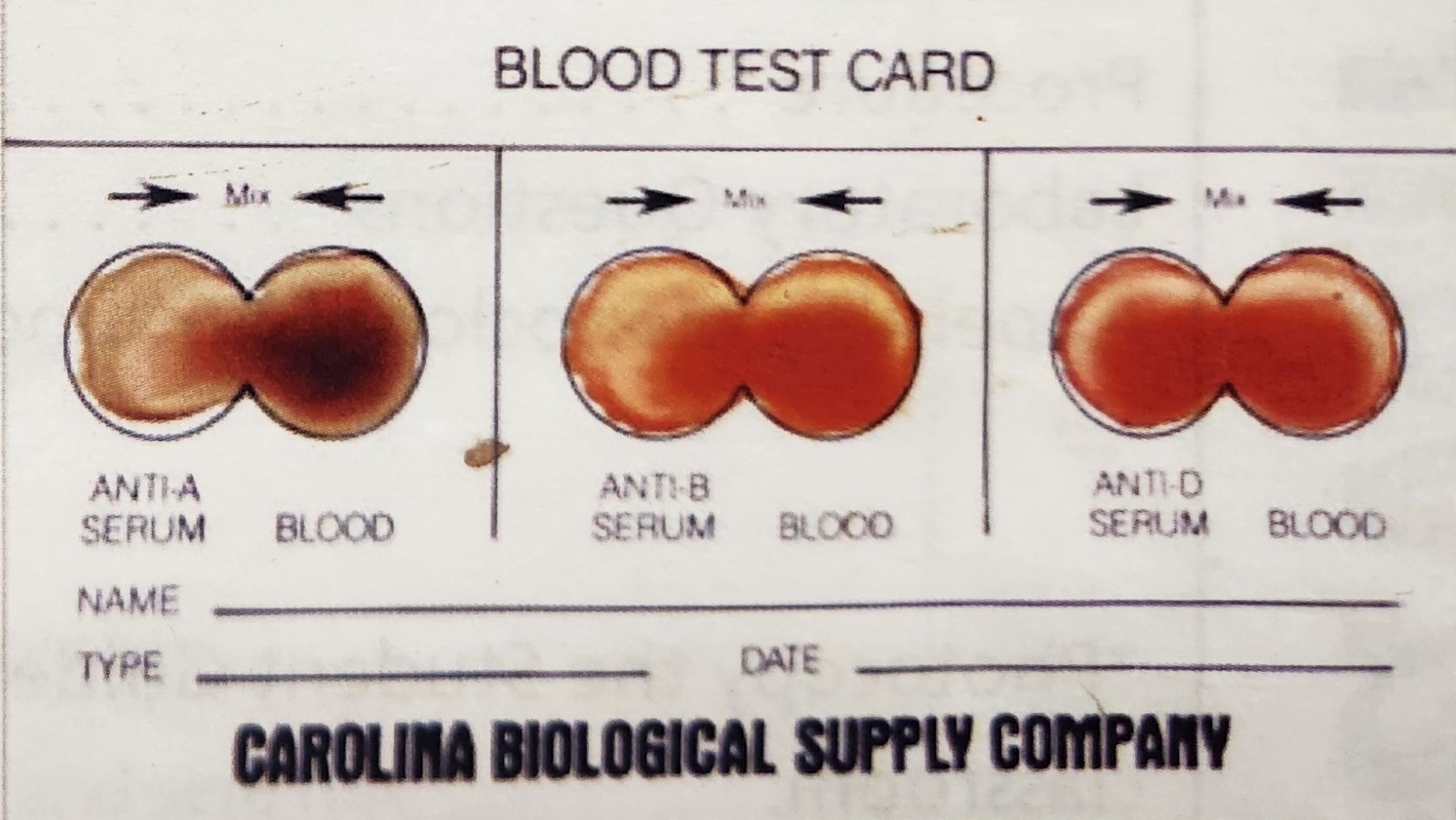
Blood Type O+
Antigens: Rh
Antibodies: A, B
Antigens
foreign substances that prompt an immune response
Correspond to the blood cell type. Ex. Blood A has A antigens.
Antibodies
Proteins that fight antigens
Present in the plasma of the cell, correspond to what the blood cell ISN’T. Ex. Blood A had B Antibodies
Universal Donor (Blood)
O- Blood
Universal Receiver (Blood)
AB+ Blood
Blood Composition Percentage
55% Plasma
45% Formed Elements
Makeup of Plasma
90% water
8% Proteins (albumin most common)
2% Electrolytes
Makeup of Formed Elements
Blood cells (Erythrocytes and Leukocytes)
Platelets

Capillary Tubes

Centrifuge
Stethoscope
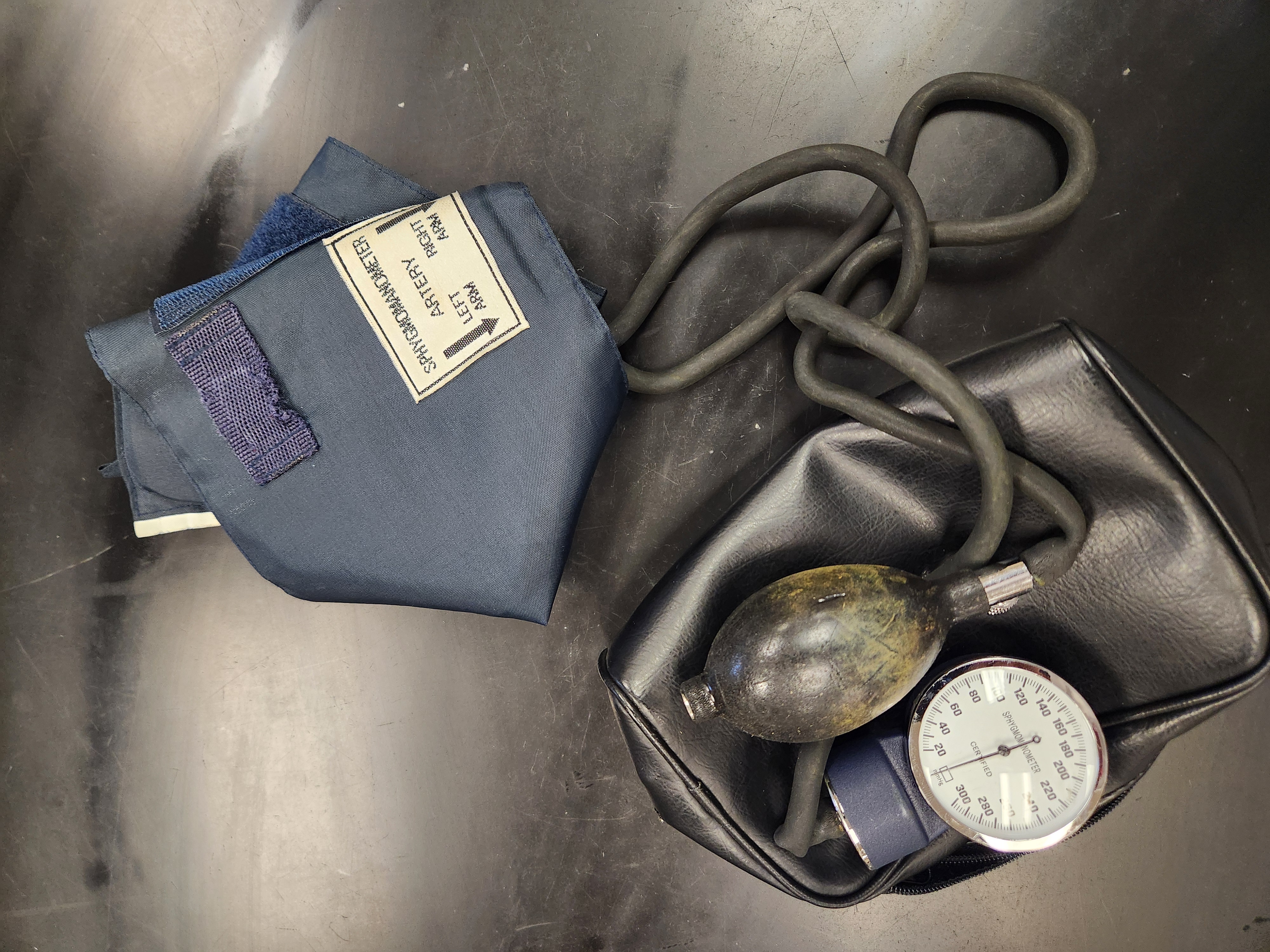

Sphygmomanometer
Eosinophil
Destroys parasites and modulates allergic inflammatory responses
Basophil
Releases histamine in certain immune reactions
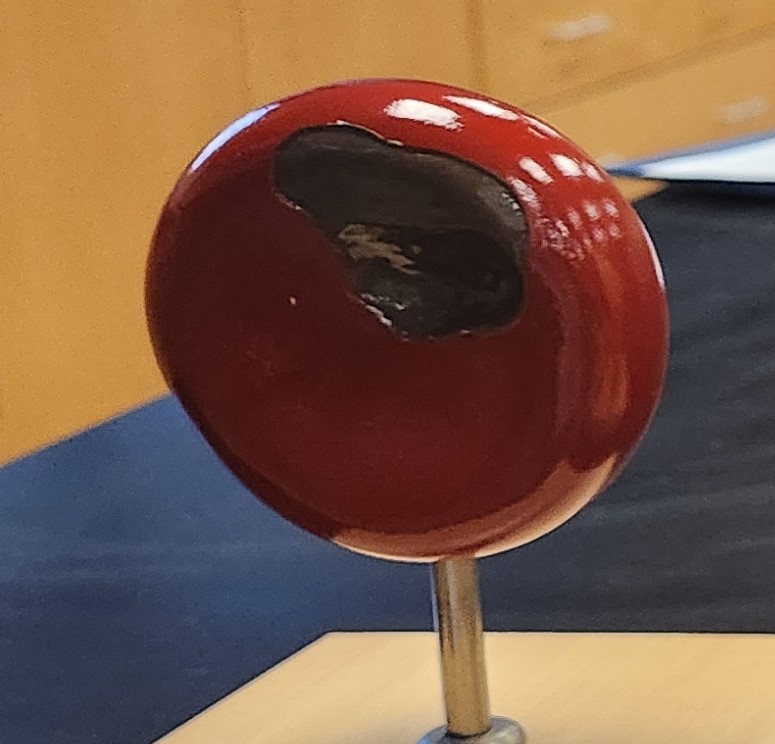

Erythrocyte
Transports O2 and CO2 bound to hemoglobin
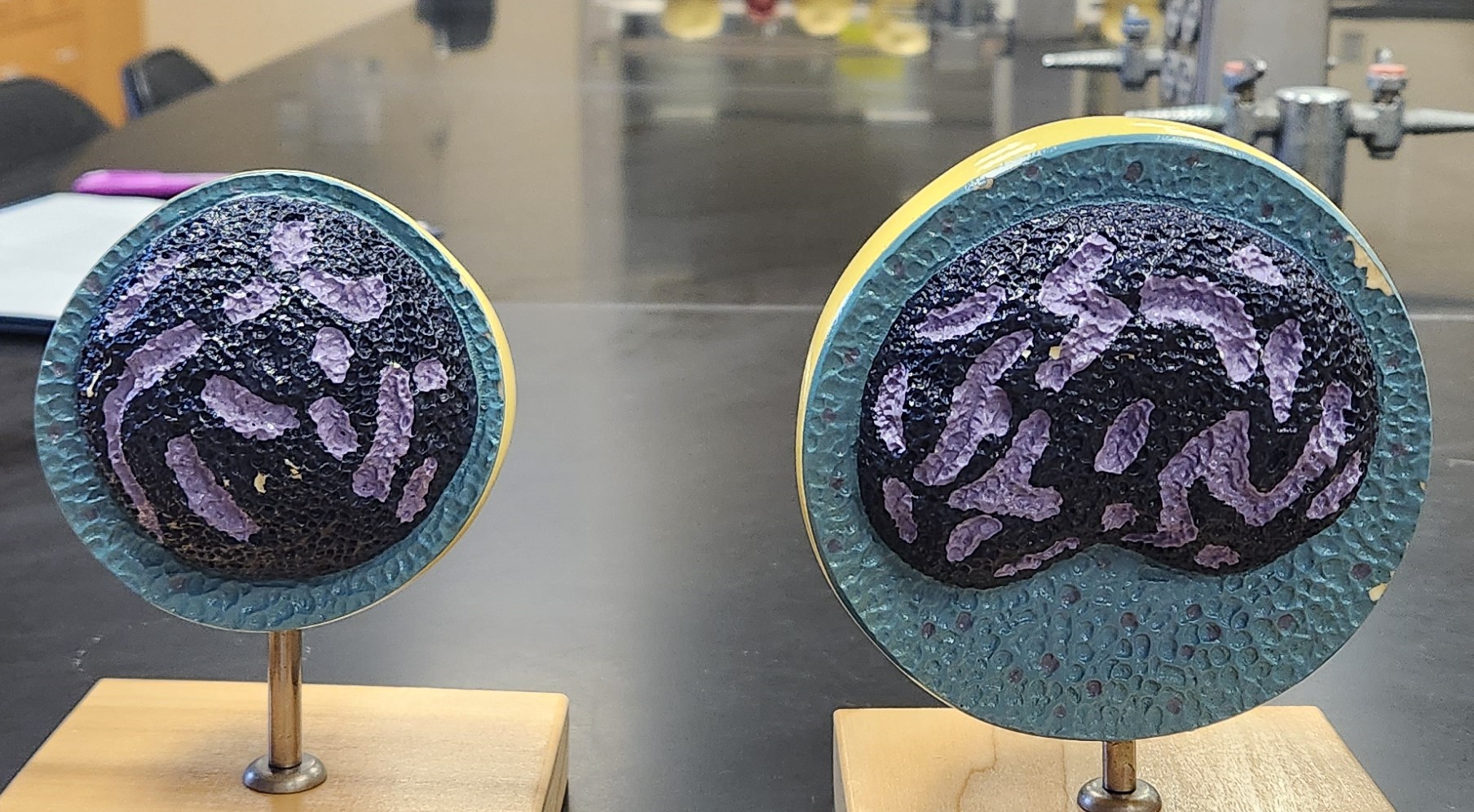

Lymphocyte
B cells: make antibodies/T cells: Kill infected cells and regulates leucocytes
Monocyte
Becomes tissue microphage, digest invading microorganisms and damaged senescent cells
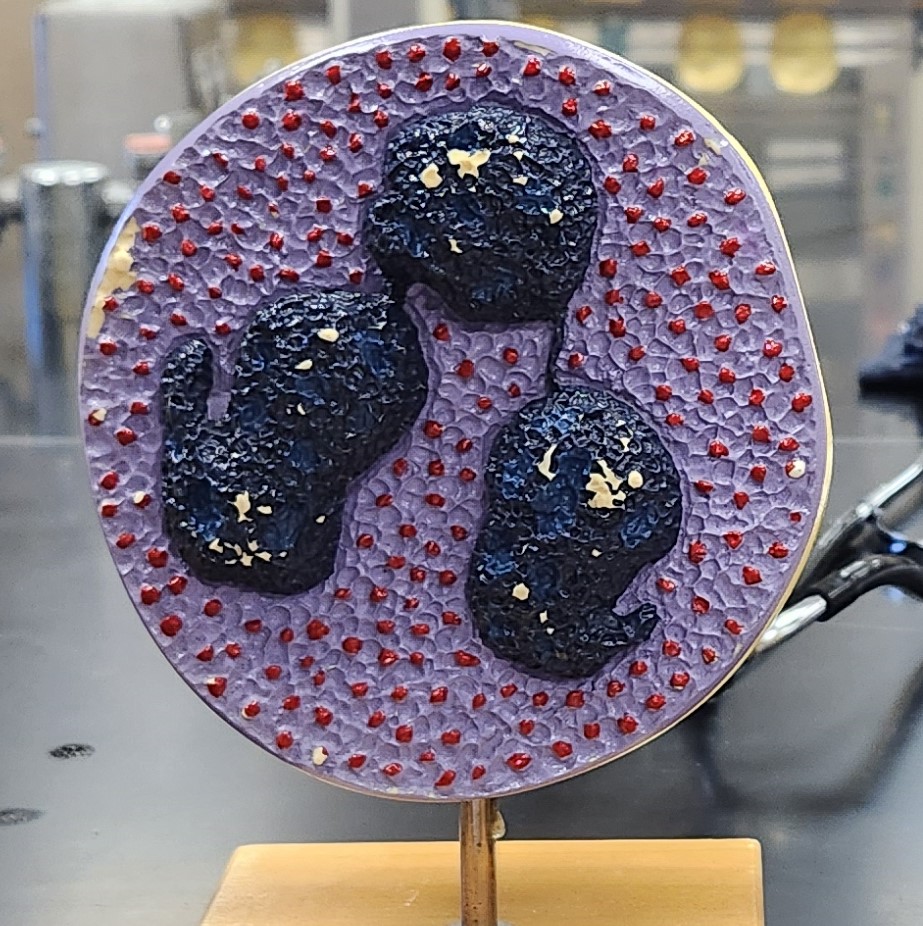

Neutrophil
Phagocytosis and destroy invading bacteria
Which side of the heart receives/pumps oxygen-rich blood?
Left
Which side of the heart receives/pumps oxygen-poor blood?
Right
Pulmonary Circulation/System
Facilitates blood between the heart and the lungs.
Systemic Circulation/System
Facilitates blood between the heart and the rest of the body.
Pulmonary Arteries
Carry oxygen-poor blood
Pulmonary Veins
Carry oxygen-rich blood
Systemic arteries
Carry oxygen-rich blood
Systemic veins
Carry oxygen-poor blood
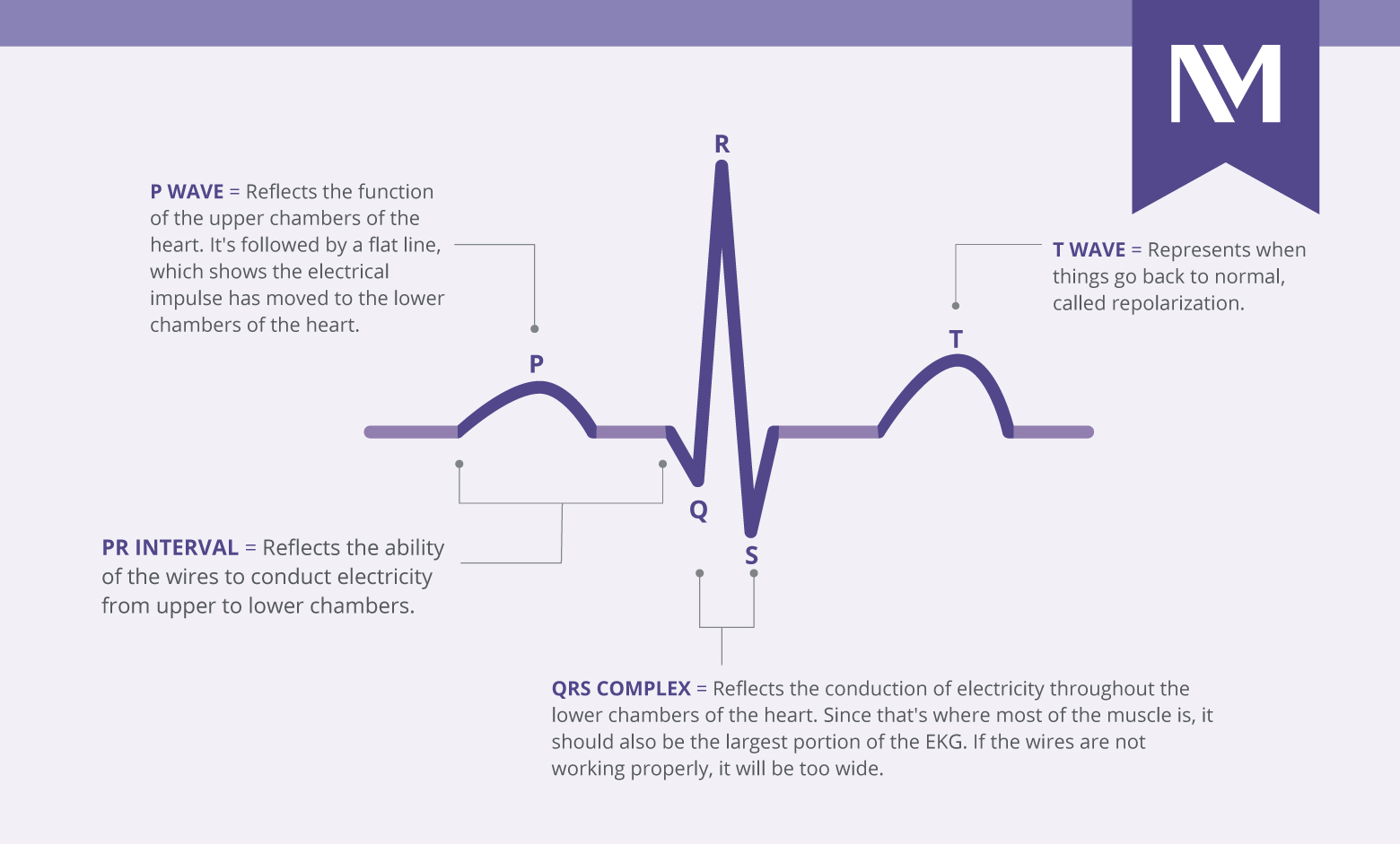
P Wave - Electrical impulse moves from upper chambers to lower chambers
PR Interval - Reflects ability to conduct electrical impulses from upper to lower chambers.
QRS Complex - Reflects conduction of electricity of the lower chambers.
T Wave - Repolarization
Arteries
Carry blood Away from the heat.
Veins
Carry blood towards the heat.
Tachycardia
Medical Term for Heart Rate over 100 beats per minute.
Bradycardia
Medical Term for Heart Rate slower than 60 beats per minute.
Fibrillation
a muscular twitching involving individual muscle fibers acting without coordination
Heart Sounds (Lub-dup)
First “lub-dub” - mitral and tricuspid valves closing
second “lub-dub” - aortic and pulmonary valves closing
Murmurs
Whooshing/Swishing sound caused by abnormal blood flow over heart valves
Hypotension
Abnormally low blood pressure
Hypertension
Abnormally high blood pressue
Systole
heart muscle contracts
Pushes blood OUT of the heart
Diastole
heart muscle relaxes
Heart chambers FILL with blood
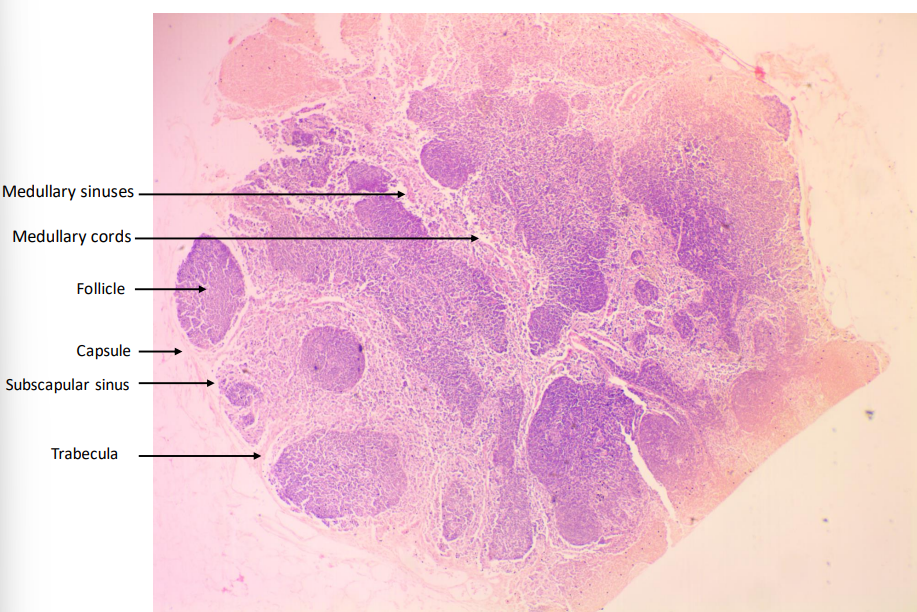
Lymph Node
Capsule
Medulla (Sinuses + Cords)
Trabeculae
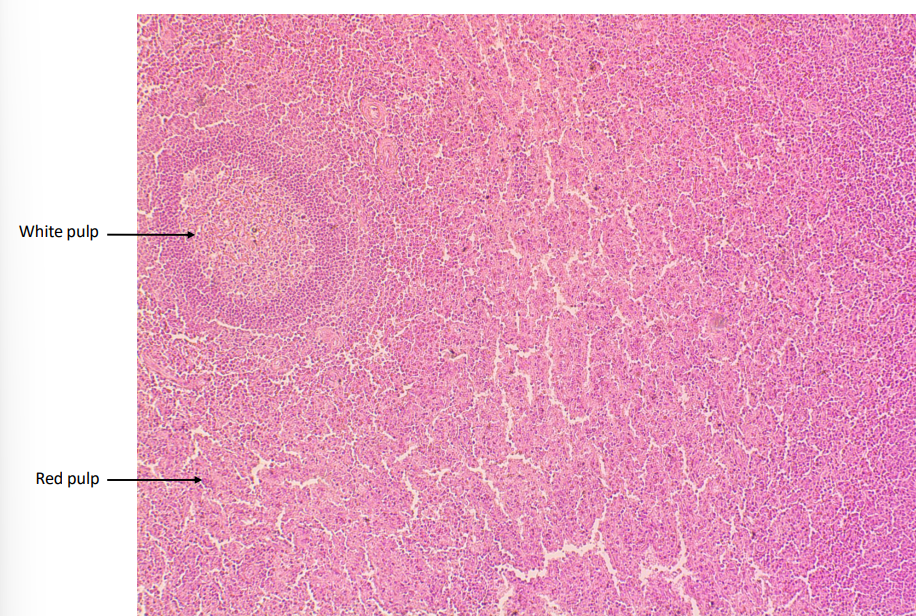
Spleen
White Pulp
Red Pulp
Autoimmunity
Immune system attacks the body’s own healthy cells and tissues
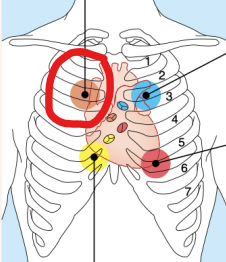
Aortic Valve
Sounds heard in 2nd Intercoastal space at right sternal margin
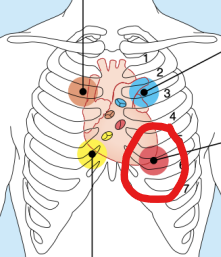
Mitral Valve
Sounds heard over heart apex, in 5th intercostal space, in line with middle of clavicle
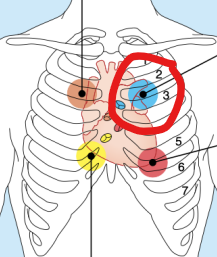
Pulmonary Valve
Sounds heard in 2nd Intercoastal Space at left sternal margin
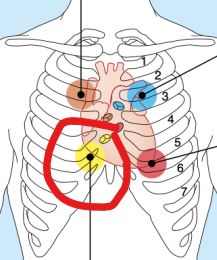
Tricuspid Valve
Sounds heard in right sternal margin of 5th intercostal space.
Variations: over sternum, over left sternal margin in 5th intercostal space.