Benzene and aromatic compounds
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Kekule’s model of benzene:
6 carbon atoms in hexagonal ring, alternating single and double C-C bonds
What does Kekule’s model therefore suggest:
It should react like an unsaturated alkene
What is the acc structure of benzene?
Each carbon in ring forms 3 σ bonds using sp2 orbitals
remaining p obriballs overlap laterally with p orbitals of neighbouring carbons forming a pie system
side-ways overlap of p orbitals means electrons r delpcalised and move to freely spread over entire ring vausing pie system made of two ring shaped clouds of electron density (below + above)
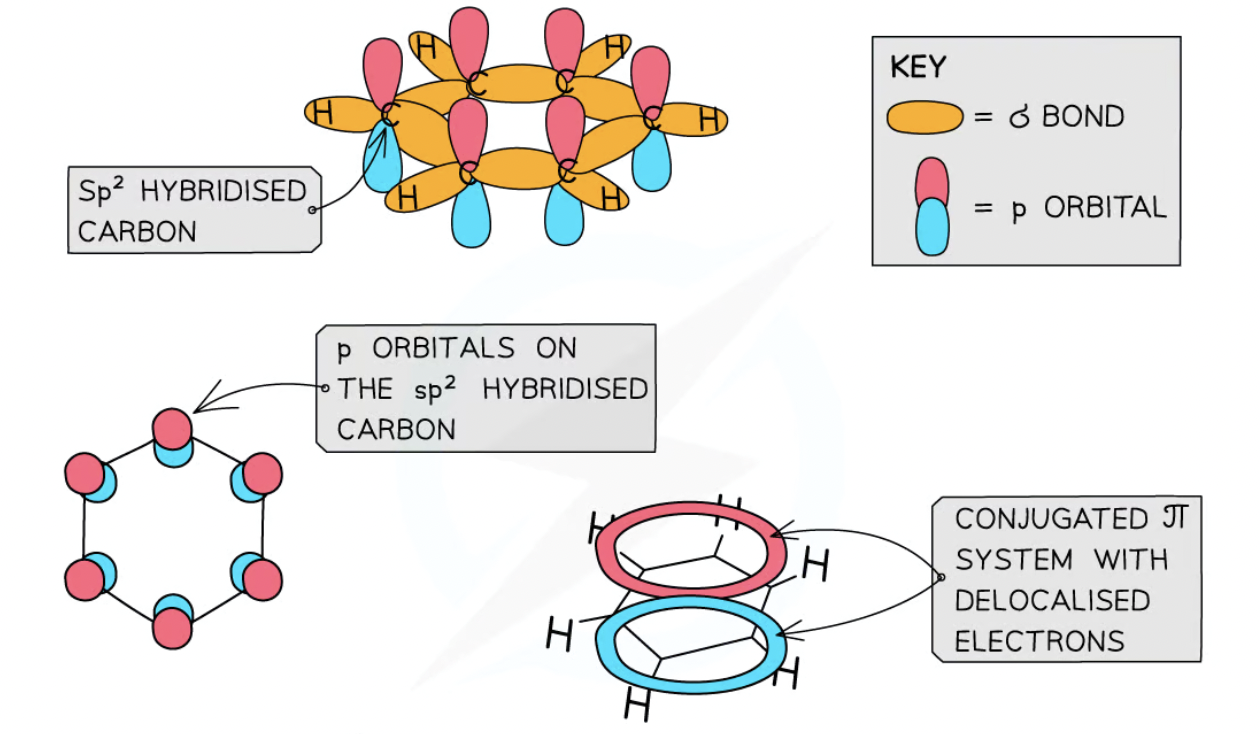
What is the name and bond angle of benzene and other aromatic compounds?
regular and planar
120
what do the delocalised electrons therefore mean for C-C bonds?
bonds identical and have both single and double bond character
What is evidence for the delocalised ring structure of benzene?
same length
What other evidence is there to disprove kekule’s model?
enthalpy changes of hydrogenation
Enthalpy for cyclohexene vs. benzene?
Cylohexene- each molecule has one C=C double bond. Enthalpy is -120 kJ mol-1
Benzene- Kekules model has 3 double C=C bonds therefore its ecpected that the enthalpy change would be X3 the enthalpy change for the one C=C bond in cylohexane e.g. -360 kJ mol-1
But it is acc far less eco -280 kJ mol-1
Aromatic meaning
molecules with 1 or more benzene rings
How does benzene’s resistance to halogenation reject Kekule’s structure and why?
alkenes undergo bromination easily
in benzene there are no localised areas of high electron density, preventing it from being able to polarise bromine molecule
What are reactions of benzene and electrophile called?
electrophile substitution
General steps of electrophilic substitution mechanism for benzene:
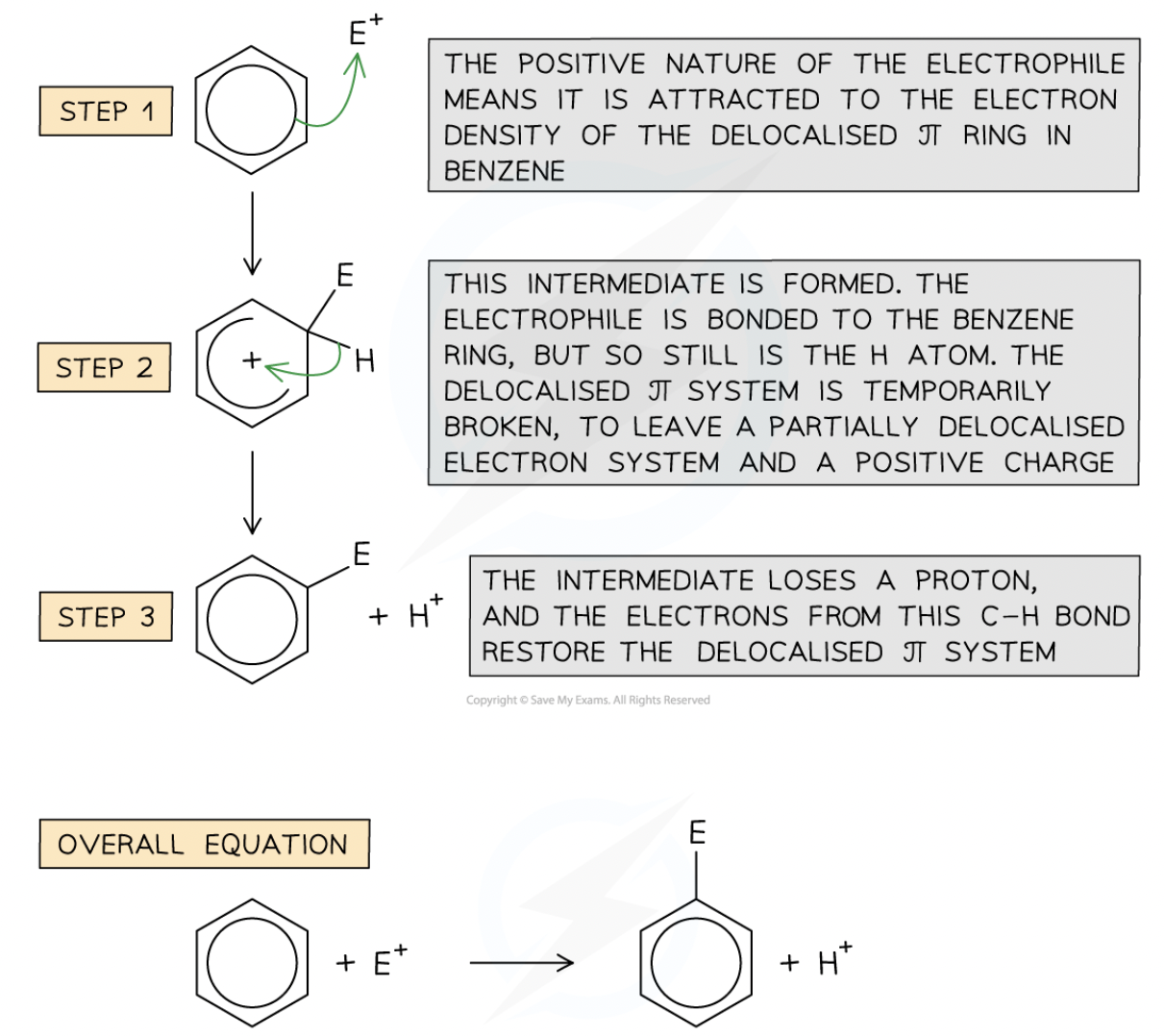
Overall reaction of Benzene Nitration

Nitration of benzene mechanism:
once electrophile is formed NO2+, HNO3 and H2SO4 is refluzed with arene (aromatic compound) at 25-60
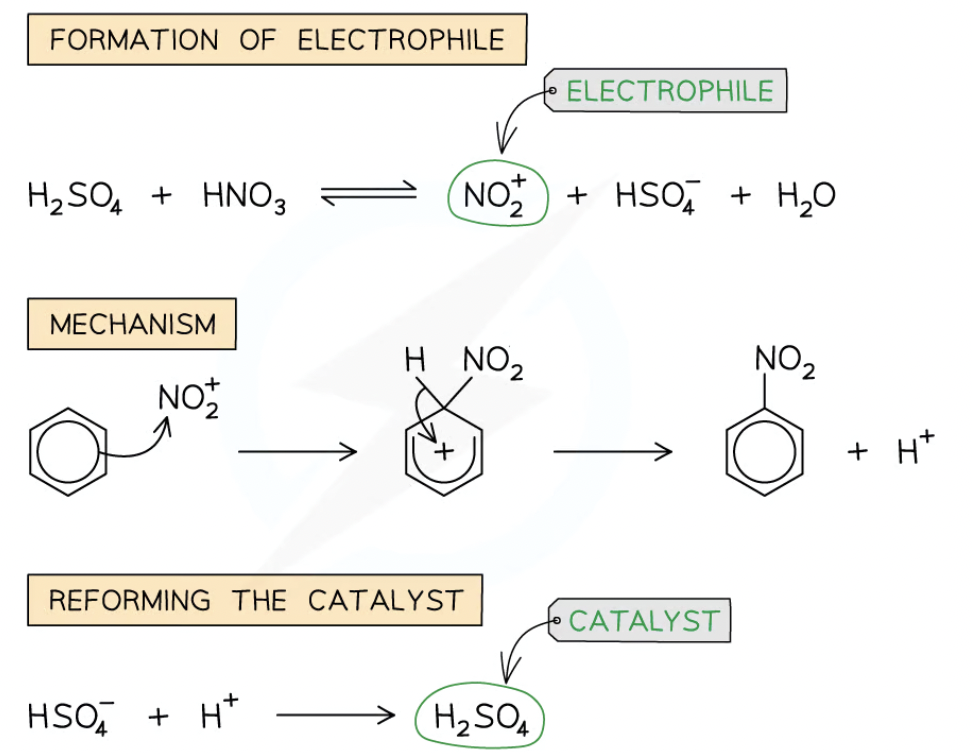
What do aromatic compounds need to react halogens and why?
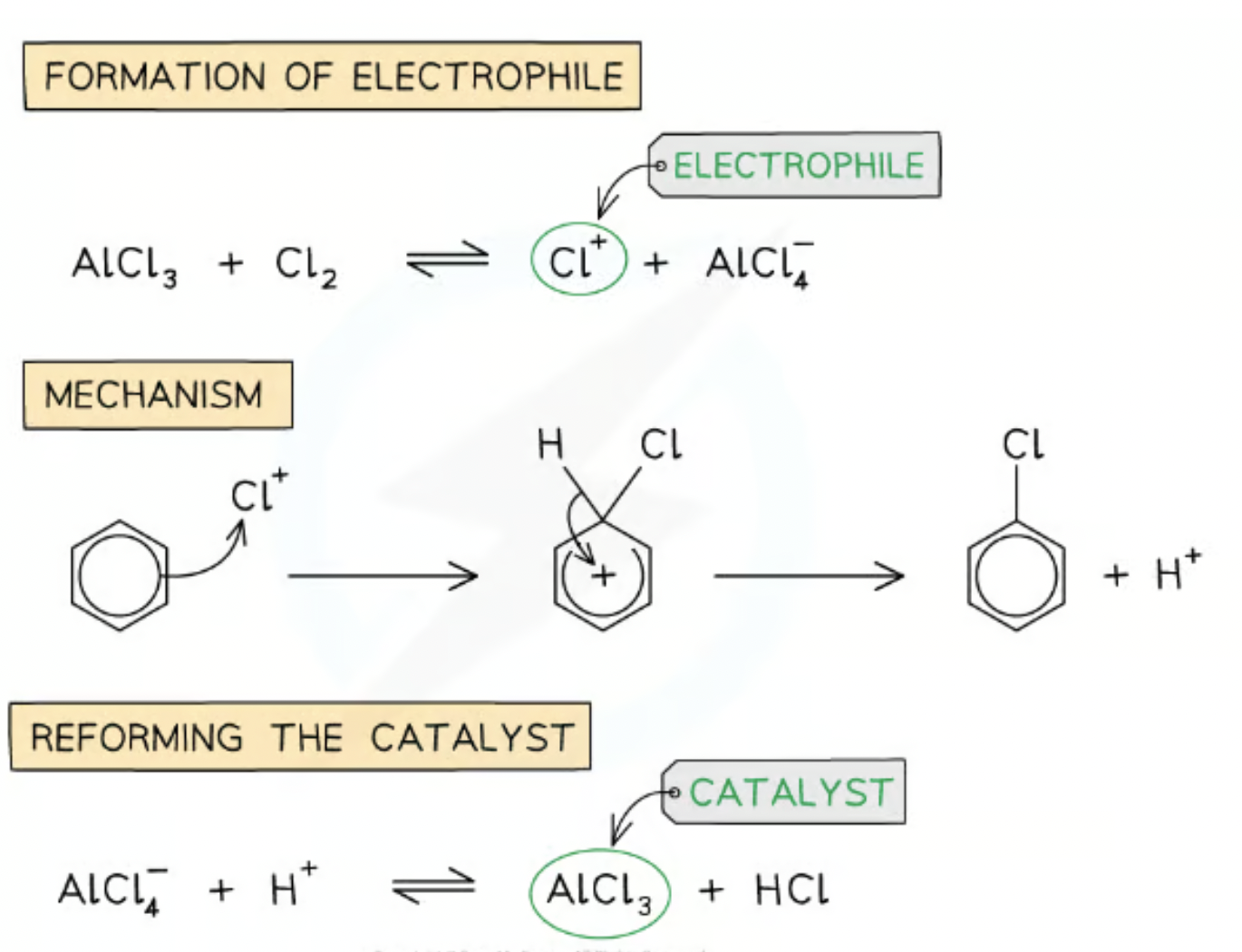
Metal halide carrier
e.g. Irom(III) bromide
Aluminium chloride
Acts as catalyst and creates electrophile e.g. Cl+
Equation of metal halide breaking down
AlCl3 + Cl2 → AlCl4- + Cl+
FeBr3 + Br2 → FeBr4- + Br+
Overall equation of halogenation
C6H6 + X2 → C6H5X + HX
chlorination of benzene
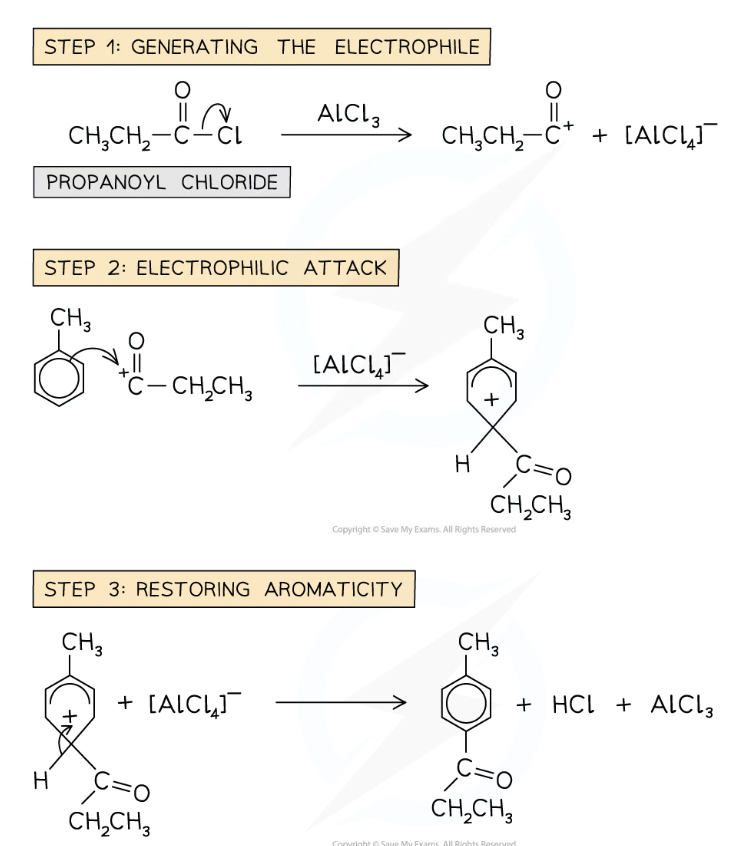
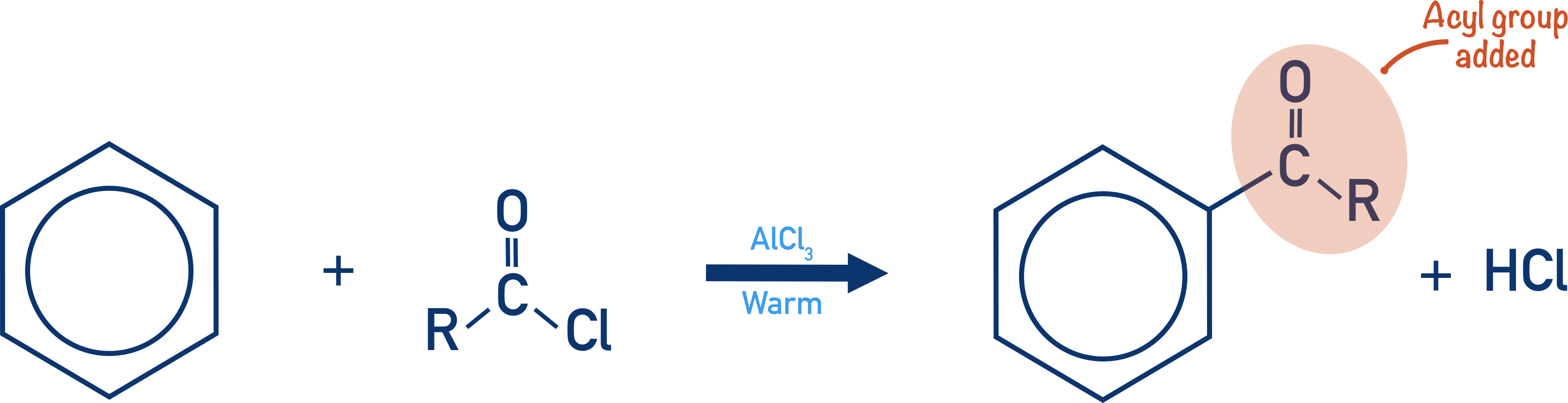
Friedel-Crafts Acylation
Acyl group (alkyl group containing C=O group) is sub into benzene ring
Metal catalyst needed to generate alkyl electrophile
Benzene ring is reacted with acyl chloride in presence of AlCl3 cat
Complex reacts with benzene ring
Phenol is a ___
very weak acid
typical pH __
5-6
How phenols break down?
Hydrogen ion can break from -OH group and transfer to a base
C6H5OH + H2O ⇌ C6H5O- + H3O+
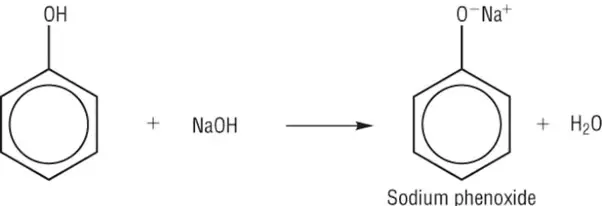
Phenol reaction with NaOH
Phenols dissolve in alkaline solutions and undergo acid-base reactions with bases to form a soluble salt and water

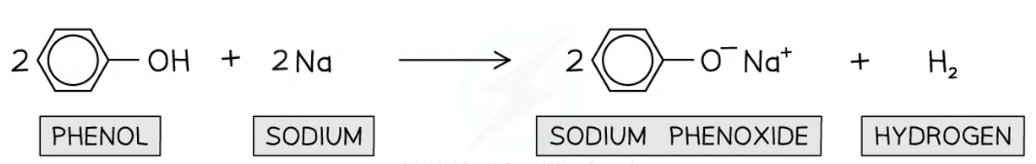
How phenols react with metals??
E.g. sodium
Forming soluble salt and hydrogen gas
How does benzene compare to phenol
Phenols react readily with electrophiles compared to benzene
cuz one lone pair on oxygen in OH overlaps with π bonding system
increasing electron density ∴ more susceptible to electrophilic attack
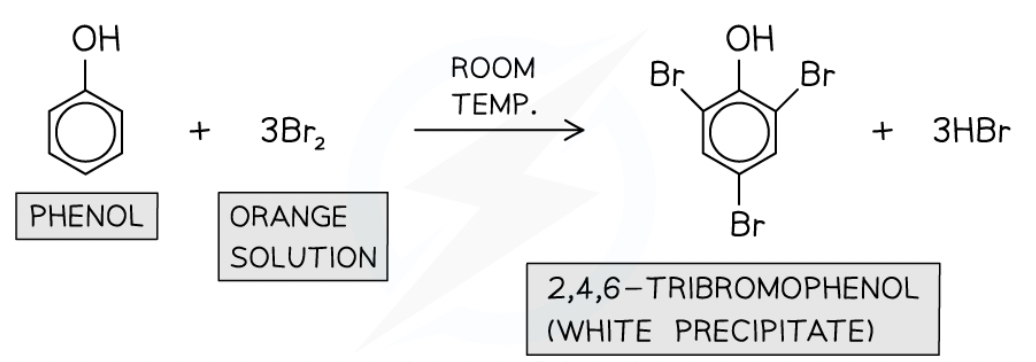
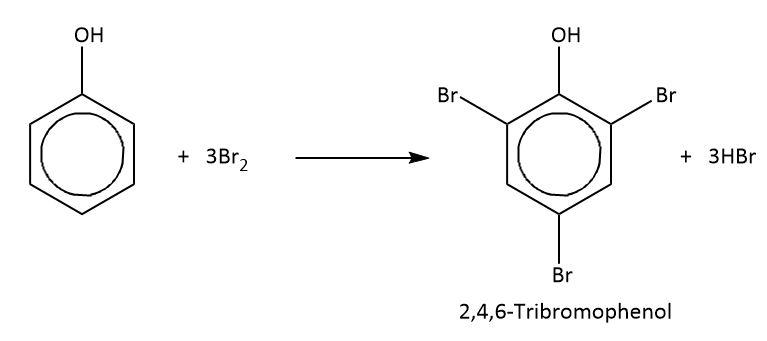
Bromination of phenol
At room temp with bromine water
decolourises orange —> white ppt
forms 2,4,6-tribromophenol
Electrophilic substitution.
Nitration of phenols
What are arenes?
aromatic hydrocarbons that contain 1 or more benzene rings
What was used to identify the length of benzenes bonds?
X-ray Crystallography
Double bonds are __ than single bonds
shorter
This ∴ means Kekules structure would be ______
asymmetrical
X-ray showed the structure of benzene was ____
perfect hexagon, all internal bond angle were 120° and all bonds were of equal length
delocalised model of benzene:
Each carbon forms bonds with 2 other carbon atoms and a hydrogen atom
Remaining electron ound in p-orbitak at right angles to plane of bonded carbon + hydrogen atoms
overlap of p-orbitals above and below ring creating pi bonds spread over 6 carbons
6 electrons in p-orbitals are delocalised
benzene is ___ (structure)
planar
the delocalised electrons make benzene ___
extra stable
∴ addition reactions would need to ____
disrupt the delocalised electron system, leading to lower stability so ∴ is resistent to electrophilic addition
benzene names
presence of other groups is denoted with use of prefix
exceptions to bezene naming
COOH-
CHO-
NH2-
COOH- benzoic acid
CHO- benzaldehyde
NH2- phenylamine
Benzene undergoes hydrogenation when ____ forming ___
heated under + Ni
cyclohexane
Nitration of benzene
Forms nitrobenzene
With nitric acid —> slow form
Rate increase- sulphuric acid as cat and 50°
Nitrobenzene uses:
Dyes
Pesticides
Pharmaceuticals e.g. paracetamol
If reaction of nitration of benzene is carried out above 50° what happens?
further nitration of benzene forming 1,3-dinitrobenzene
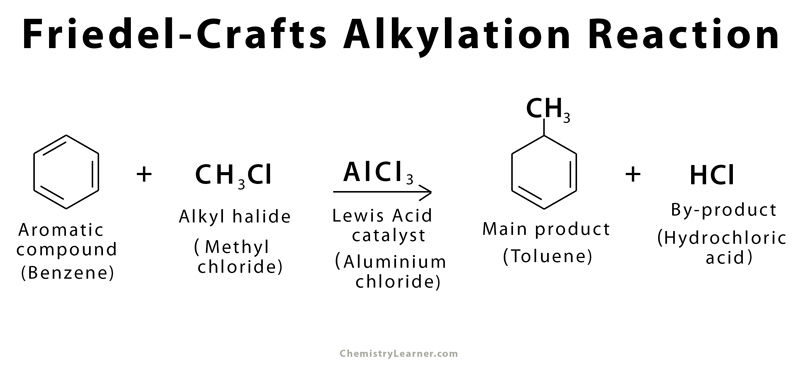
Alkylation:
benzene is reacted with haloalkane in presence of halogen carrier e.g. AlCl3. Sub of hydrogen atom from benzene ring with alkyl group
acylation:
when benzene reacts with acyl chloride CH3COCH2Cl in presence of AlCl3
benzenes are ____ soluble than alc in water
less
phenol is ___ acidic than alc
and ____ acidic than carboxylic acids
more
less
How phenol reacts with sodium hydroxide:
neutralisation
What can be used to distinguish between phenols and carboxylic acids?
reaction with metal carbonates
Phenol not acidic enough to react
the ___ in phenols means it has different chemical reactions to benzene
hydroxyl group
what causes increased electron density in ring in phenol?
lone pair on oxygen of hydroxyl group donated to pie system
what does the increased electron density therefore mean and for reactivity of phenol compared to benzene?
can attract electrophiles more strongly than benzene
more reactive and easily undergo electrophilic sub
what forms when phenol reacts with bromine water + conditions?
form white ppt decloloursing bromine water
room temp
the increased electron density can polarise the bromine molecule meaning no halogen carrier is needed
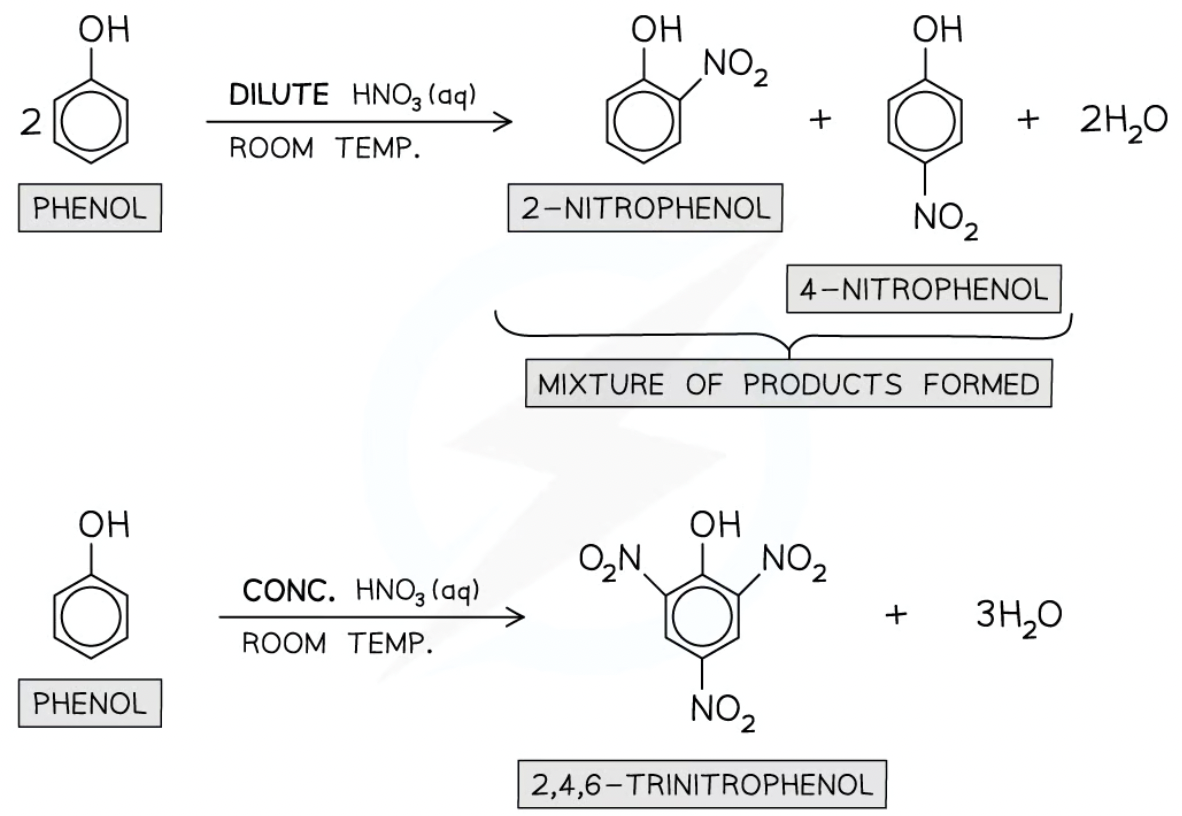
what else does phenol readily react with a room temp?
dilute nitric acid
what forms when phenol reacts with dilute nitric acid?
2-nitrophenol and 4-nitrophenol and water
activating groups definition?
attached to aromatic ring that cause compound to be more susceptible to electrophilic sub
groups that cause it to be less susceptible are called ____
deactivating
NH2 ___
activates to 2/4 position so reacts more readily with bromine
forms t
2,4,6-tribromo
NO2 ___
deactivates to 3 position so is less susceptible
forms 3-bromonitrobenzene
-OH is
2-4 directing and activating
2,4- directing are activating except ___
halogens
Similarities between Kekulé model and the delocalised model of benzene?
Overlap of p-orbitals
π bond/system/ring above and below
Differences between Kekulé model and the delocalised model of benzene?
Kekule has: alternating π bonds OR 3 π bonds / localised (π electrons) / overlap in one direction / 2 electrons in π bond
Delocalised has: π ring (system) / all p orbitals overlap OR (π electrons) spread around ring / overlap in both directions / 6 electrons in π bond
Why is benzoic acid unreactive?
–COOH group on benzoic acid is an electron withdrawing group
arenes vs aromatic
"arene" specifically refers to only the hydrocarbon version of an aromatic compound
"aromatic" can encompass broader structures including rings with heteroatoms like nitrogen or oxygen, which are not considered "arenes.