(BIO 2300) Unit 2 - Concept C: Structure of Brain
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Structural functional unit of the nervous system
Define a neuron
Send neural impulse
revive neural impulse
integrate neural impulse
Describe the function of nervous tissue
CNS= brains and spinal cord
PNS= everything else (cranial, spinal and peripheral nerves)
Name the components of each structural subdivisions of the nervous system
A nerve is a collection of axons a tract is a collection of nerves sharing a common function.
Describe the difference between a nerve and a tract
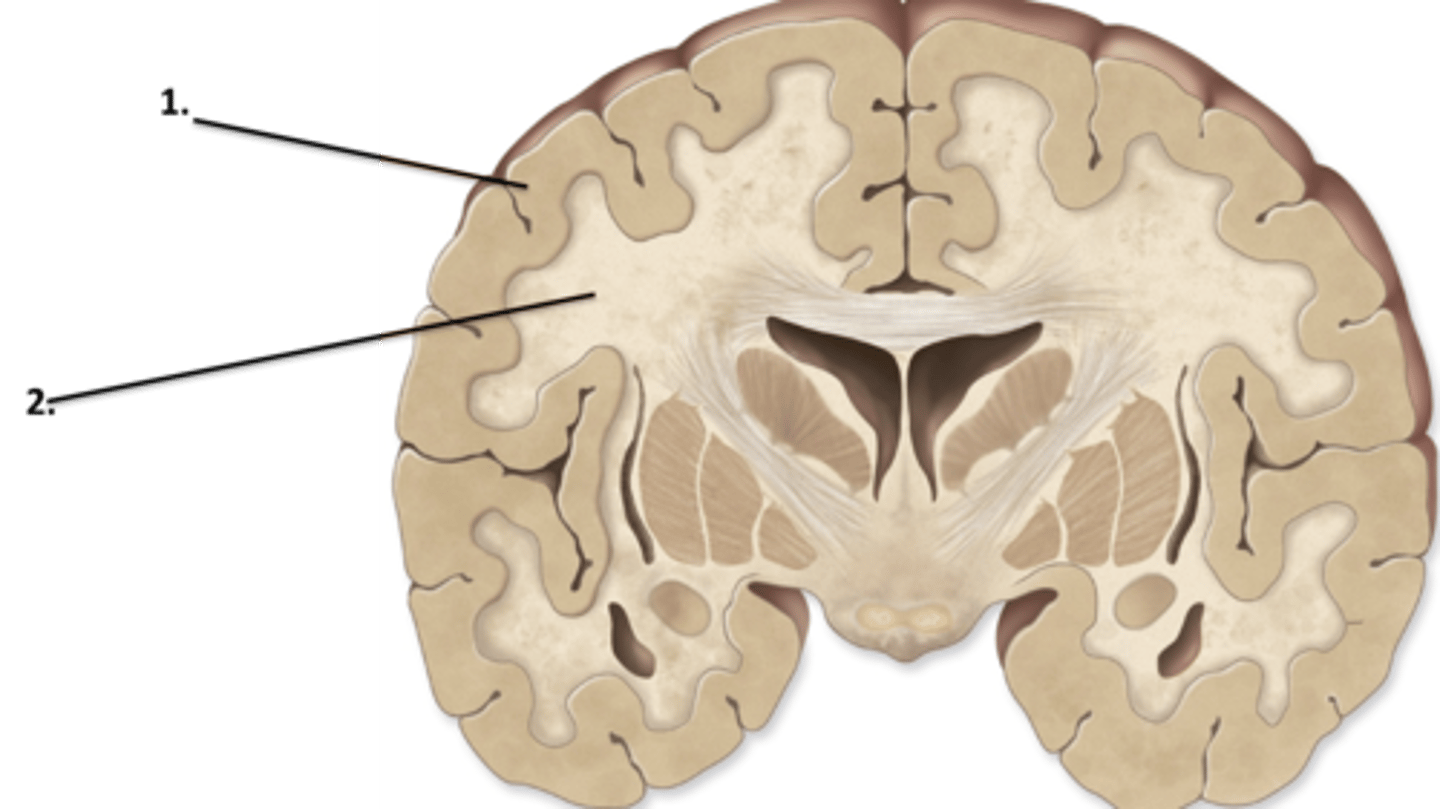
gray matter is the location of cell bodies on the superficial layer of the brain. white matter is the myelinated axon deep layer in the brain.
Describe the difference between gray matter and white matter
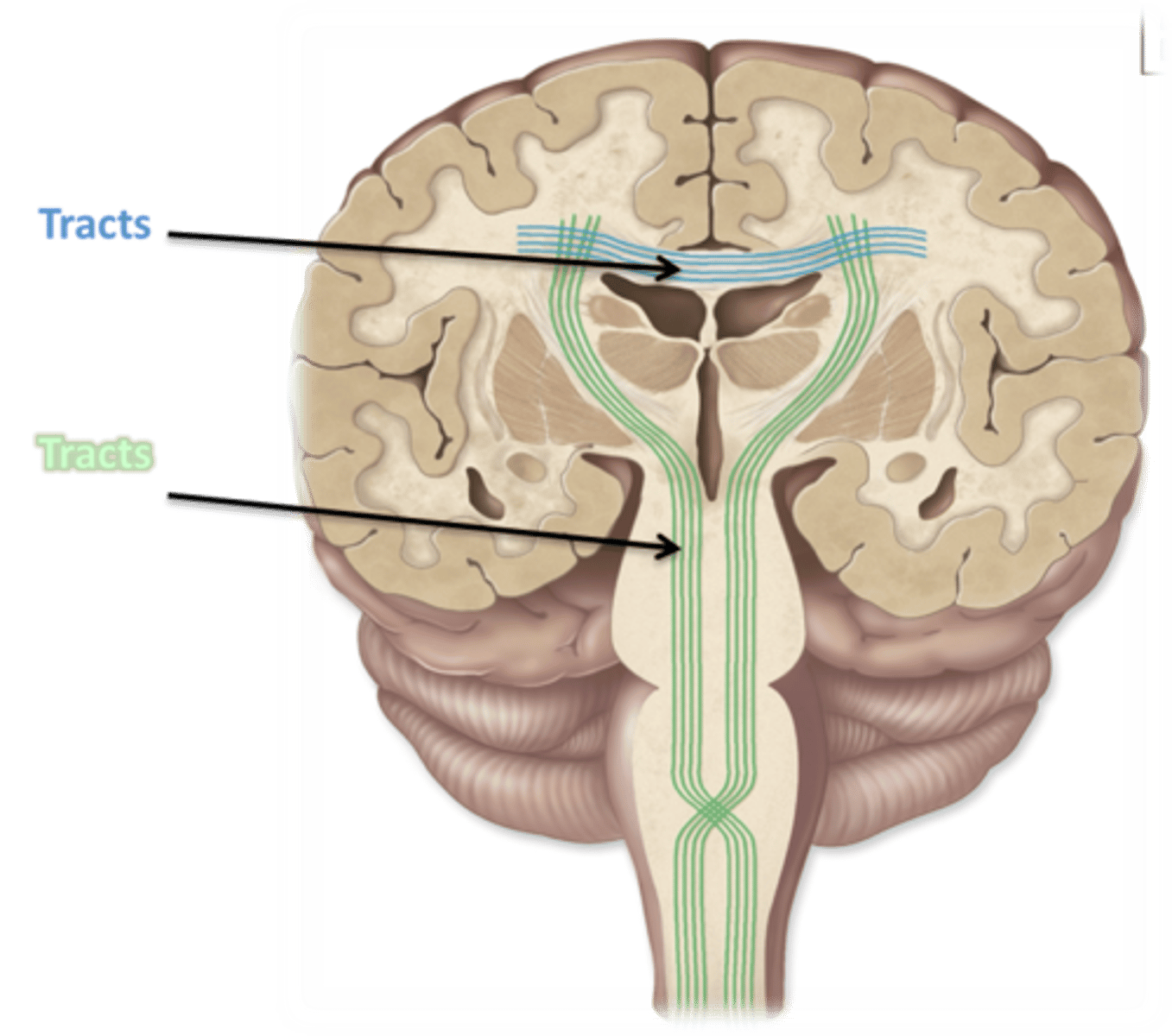
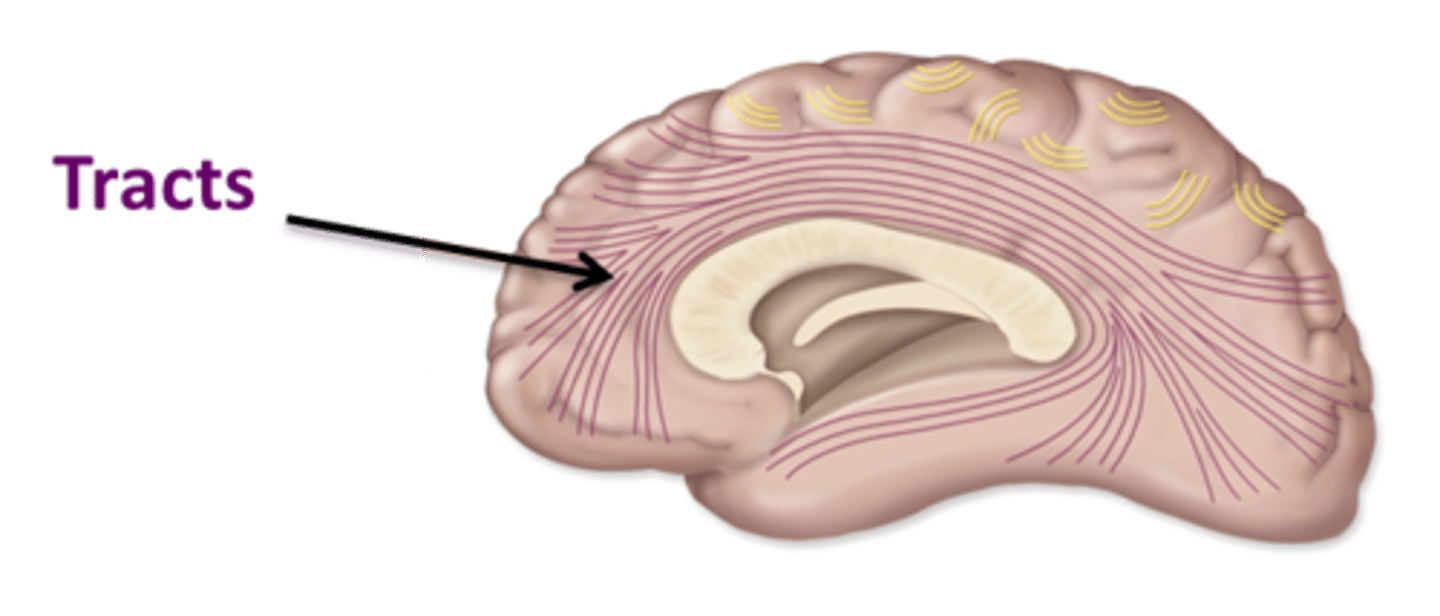
Association tracts= connect same hemisphere
Commissural tracts= Connect opposite hemispheres via corpus callosum
Projection tracts= projects to lower region of brain/spinal cord. ascending are sensory input and descending are motor output.
Describe the white matter tracts within the CNS
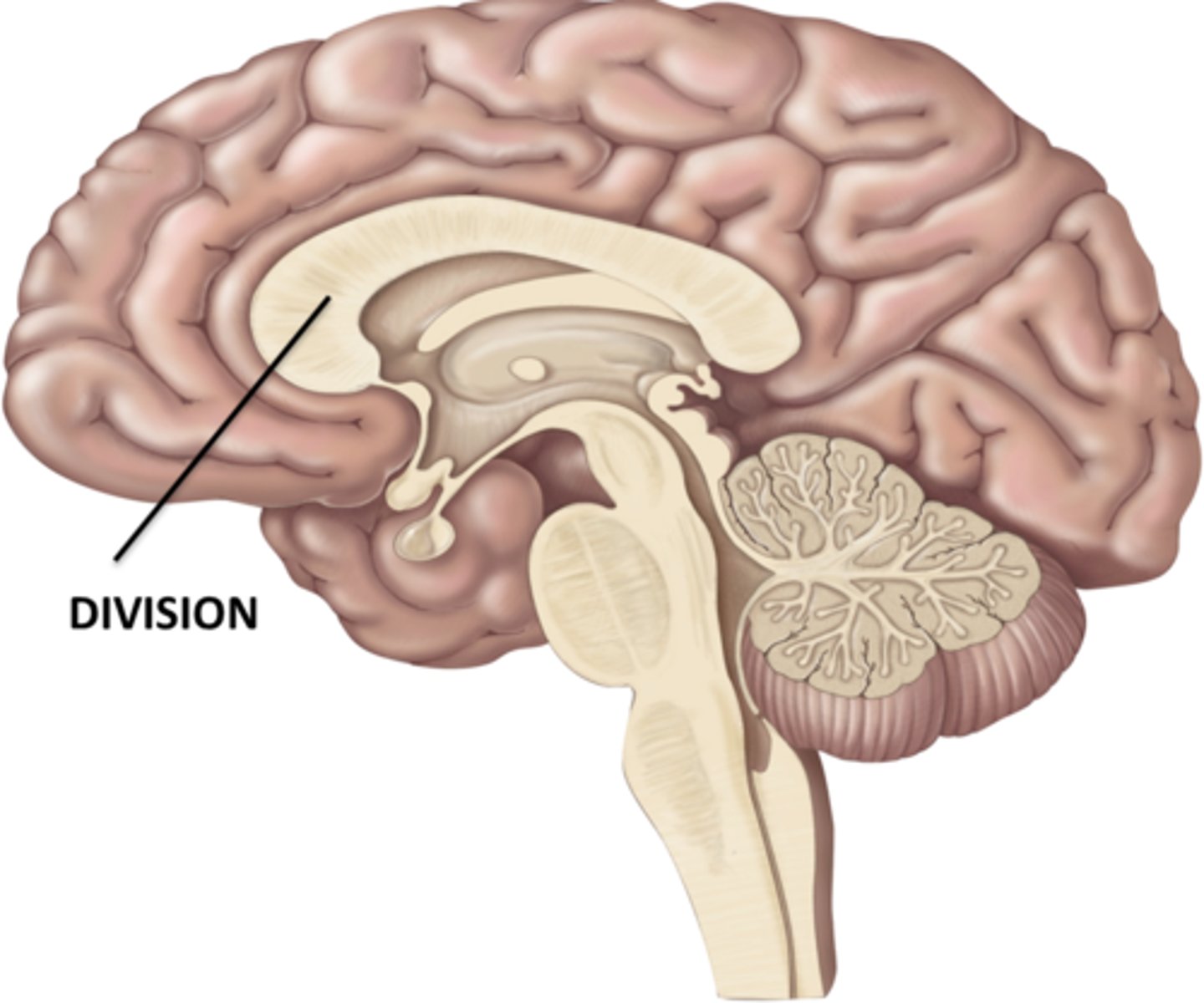
Corpus callosum
Name the commissural tract that connects left and right cerebral hemisphere.
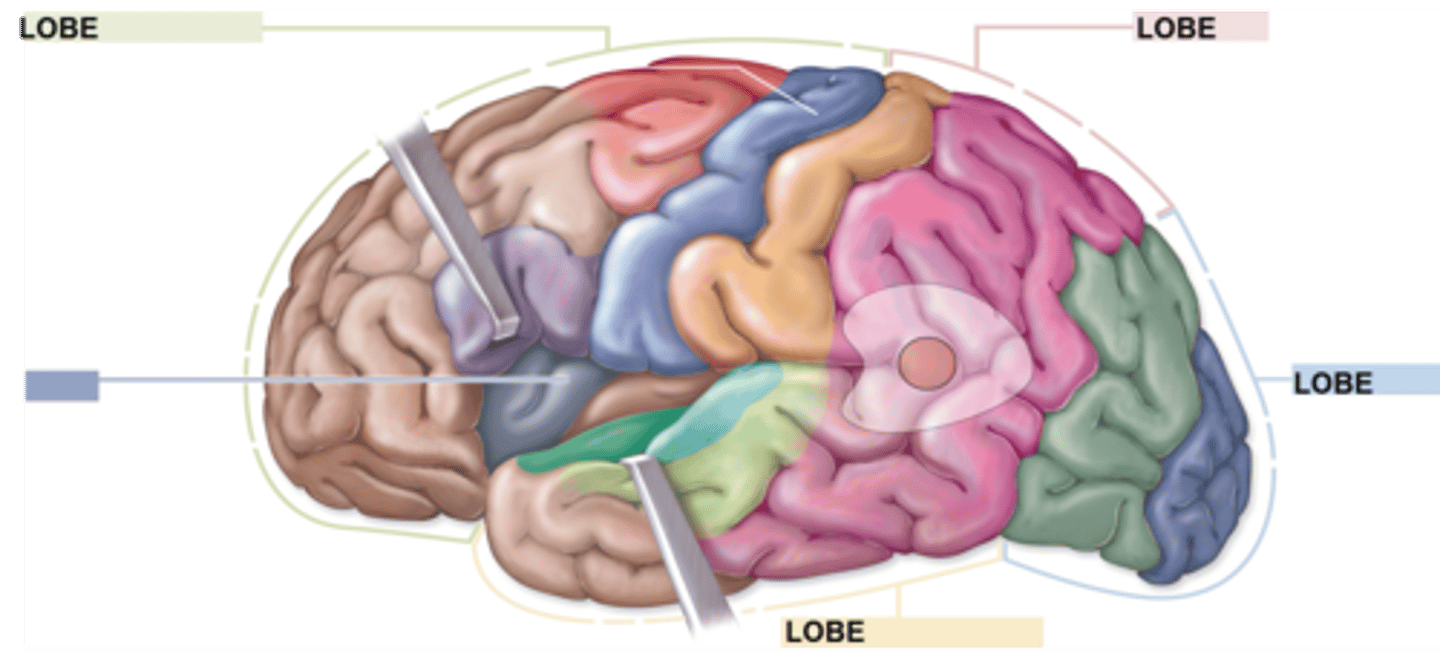
Frontal lobe
1) Personality
2) Primary motor cortex ( indicates/starts movement)
3) Memory
Parietal lobe
1) Primary sensory cortex
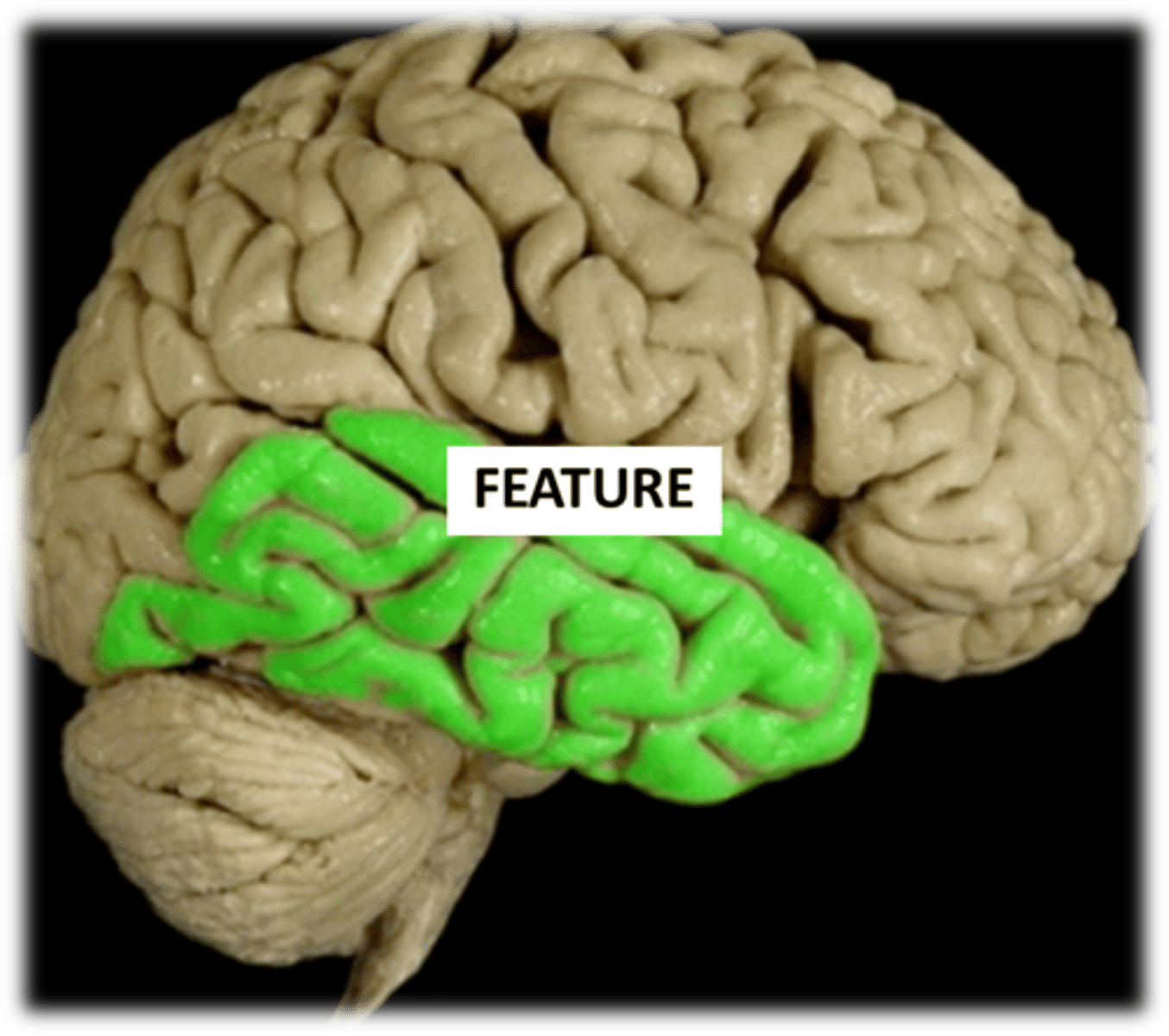
Temporal lobe
1) Primary auditory cortex
Occipital lobe
1) Primary visual cortex
Name and describe each of the functional lobes of the cerebrum
neurons with similar structure coming together to perform a function
Define Cortex
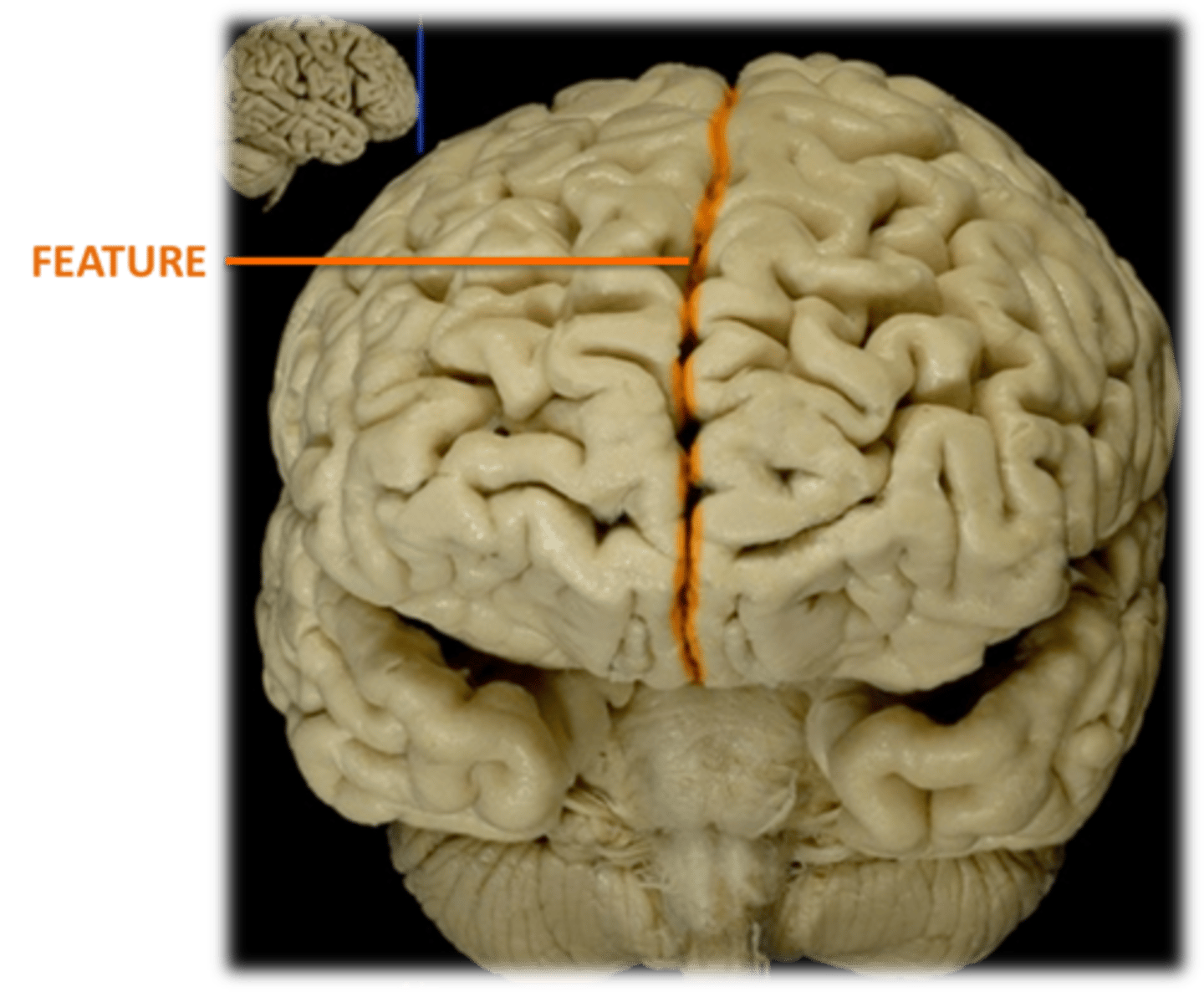
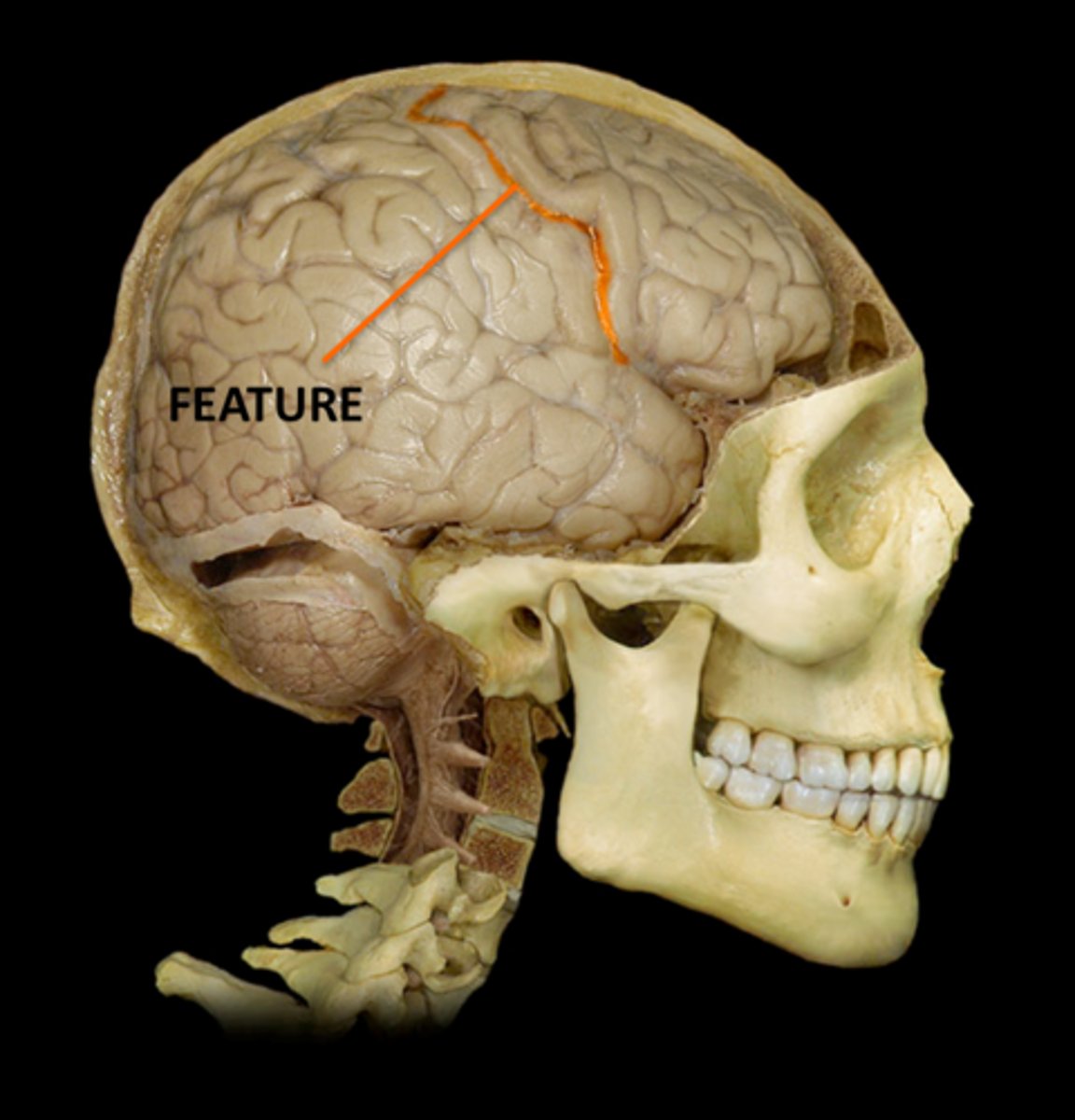
Fissure- deep groove (cleft)
1) Longitudinal- between left and right hemispheres
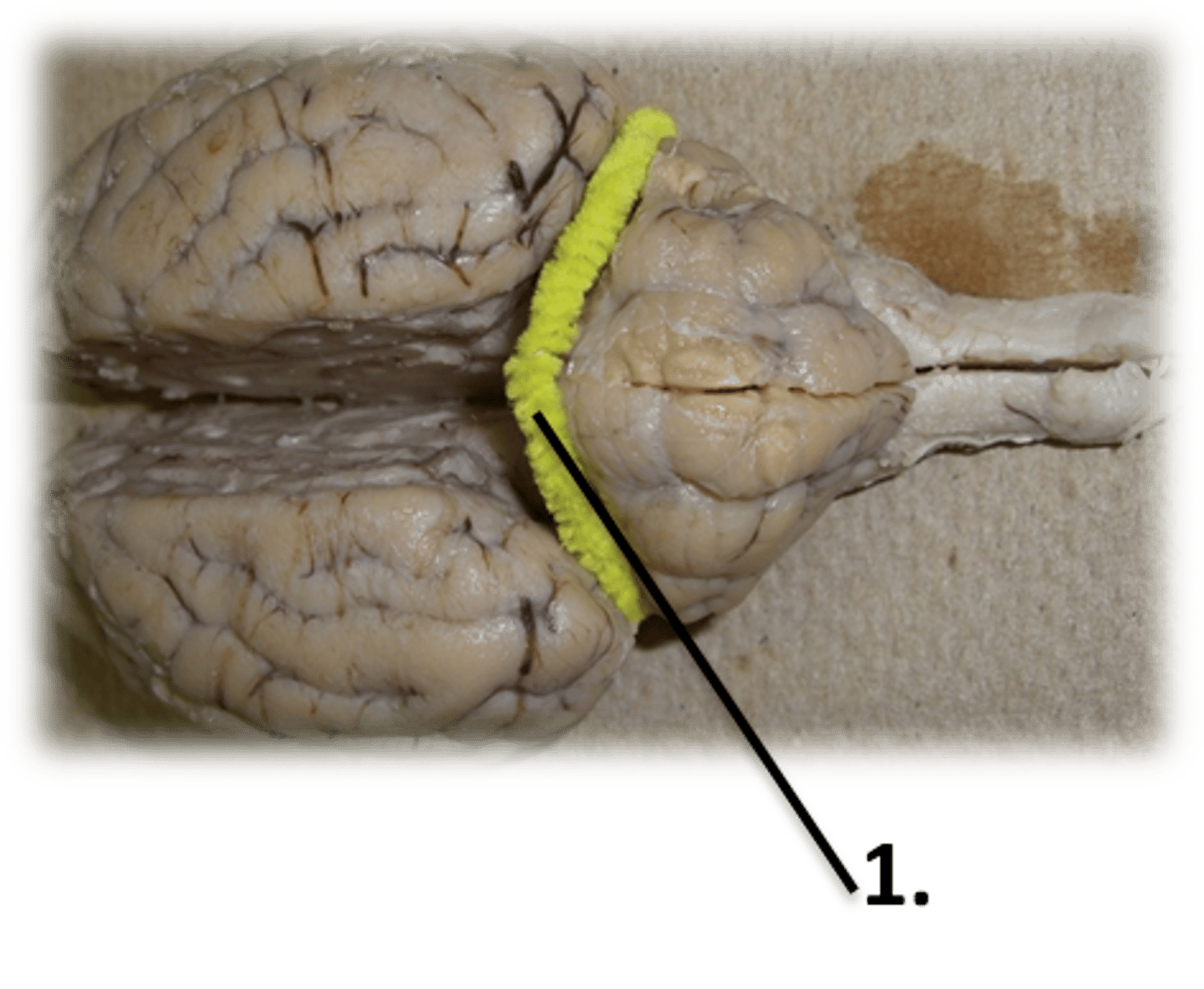
2) Transverse- between cerebrum and cerebellum
Define fissure and describe the two examples
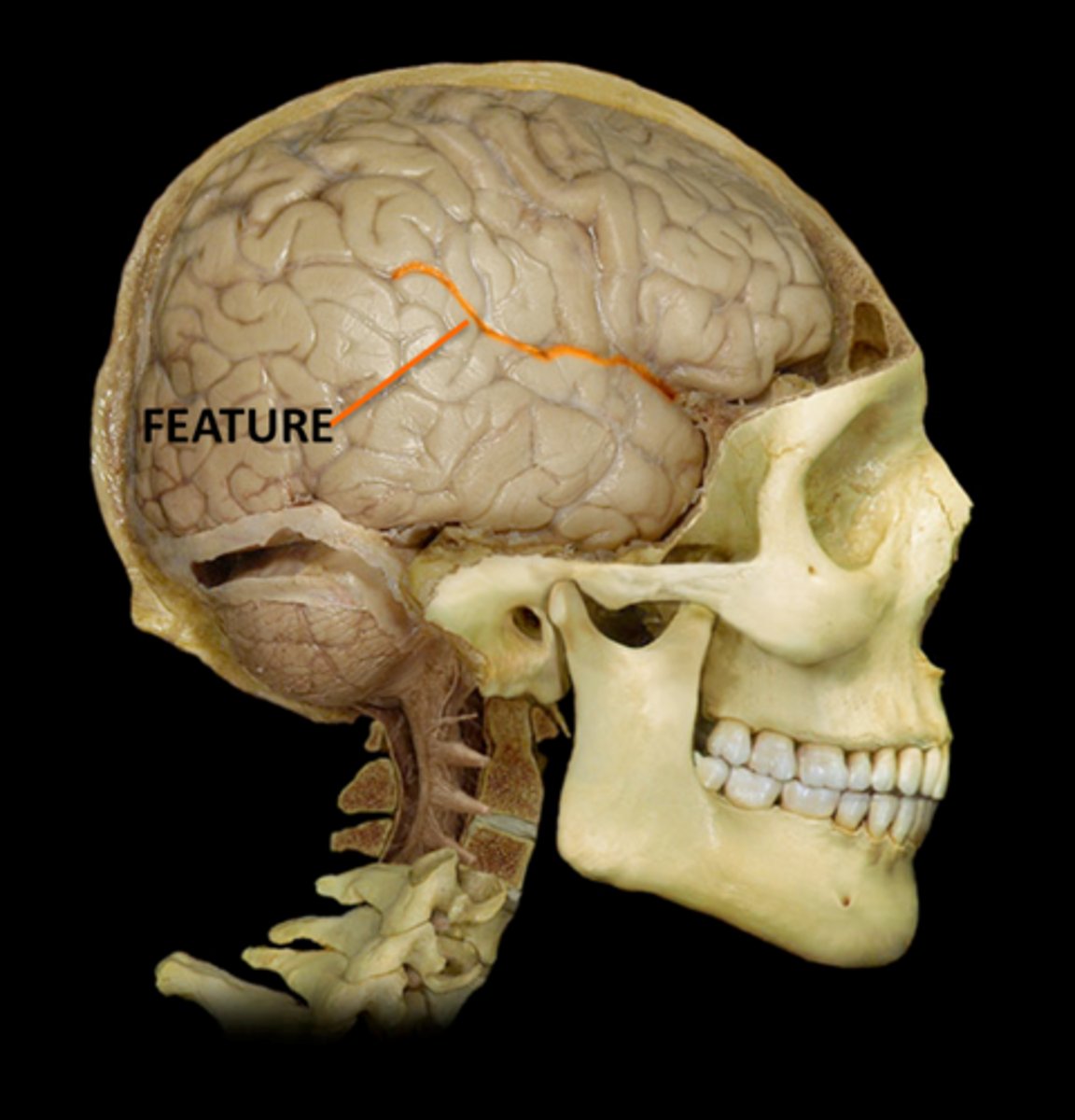
Gyrus- ridge "grow up"
1) precentral- primary motor cortex, frontal lobe, starts movement
2) Postcentral- primary sensory cortex, parietal lobe
Define gyrus and describe the two examples
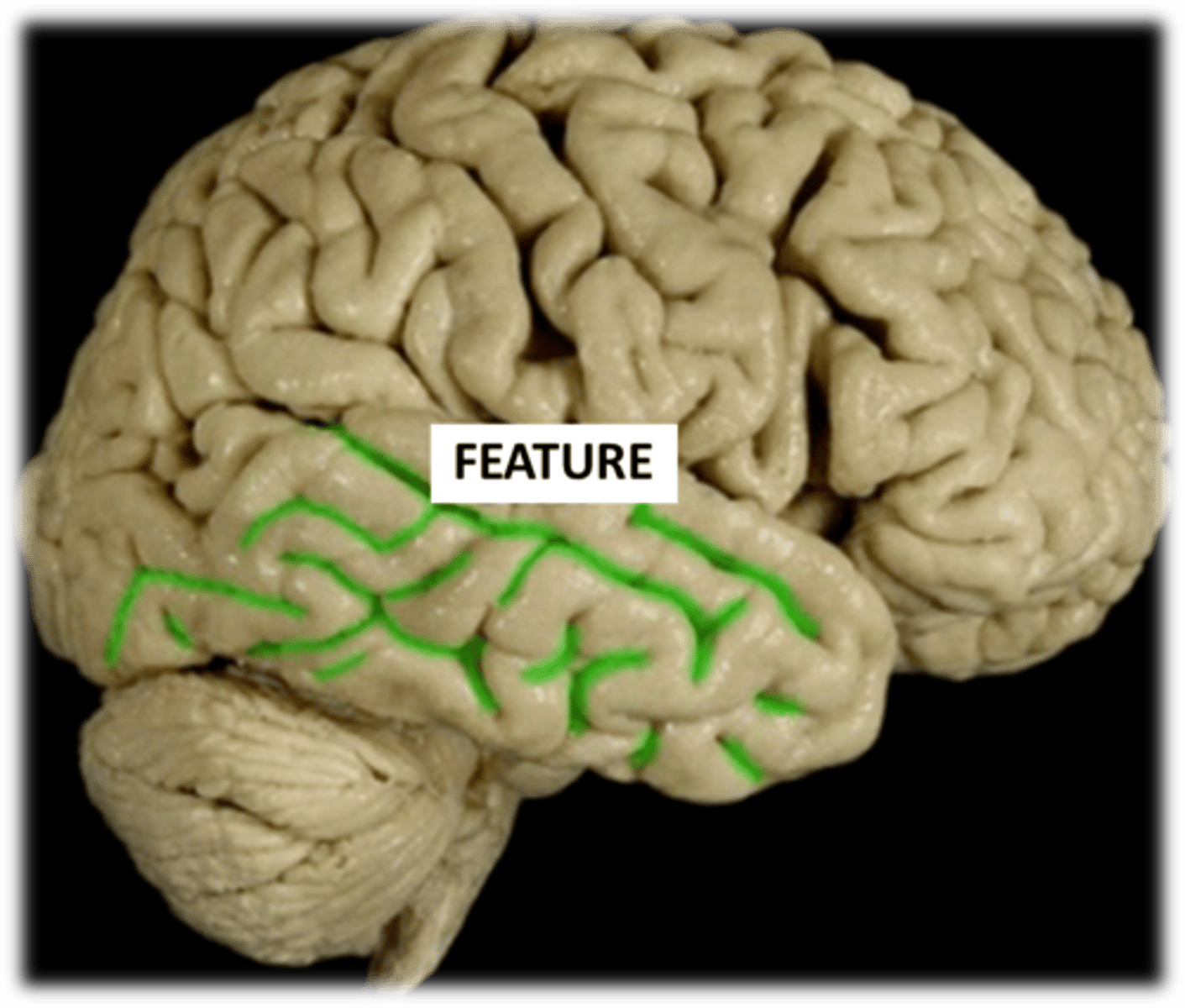
sulcus- shallow groove 'sink down'
1) Central- located between precentral and postcentral gyrus
2) Lateral- separates the temporal lobe from frontal and parietal lobes
Define sulcus and describe the two examples
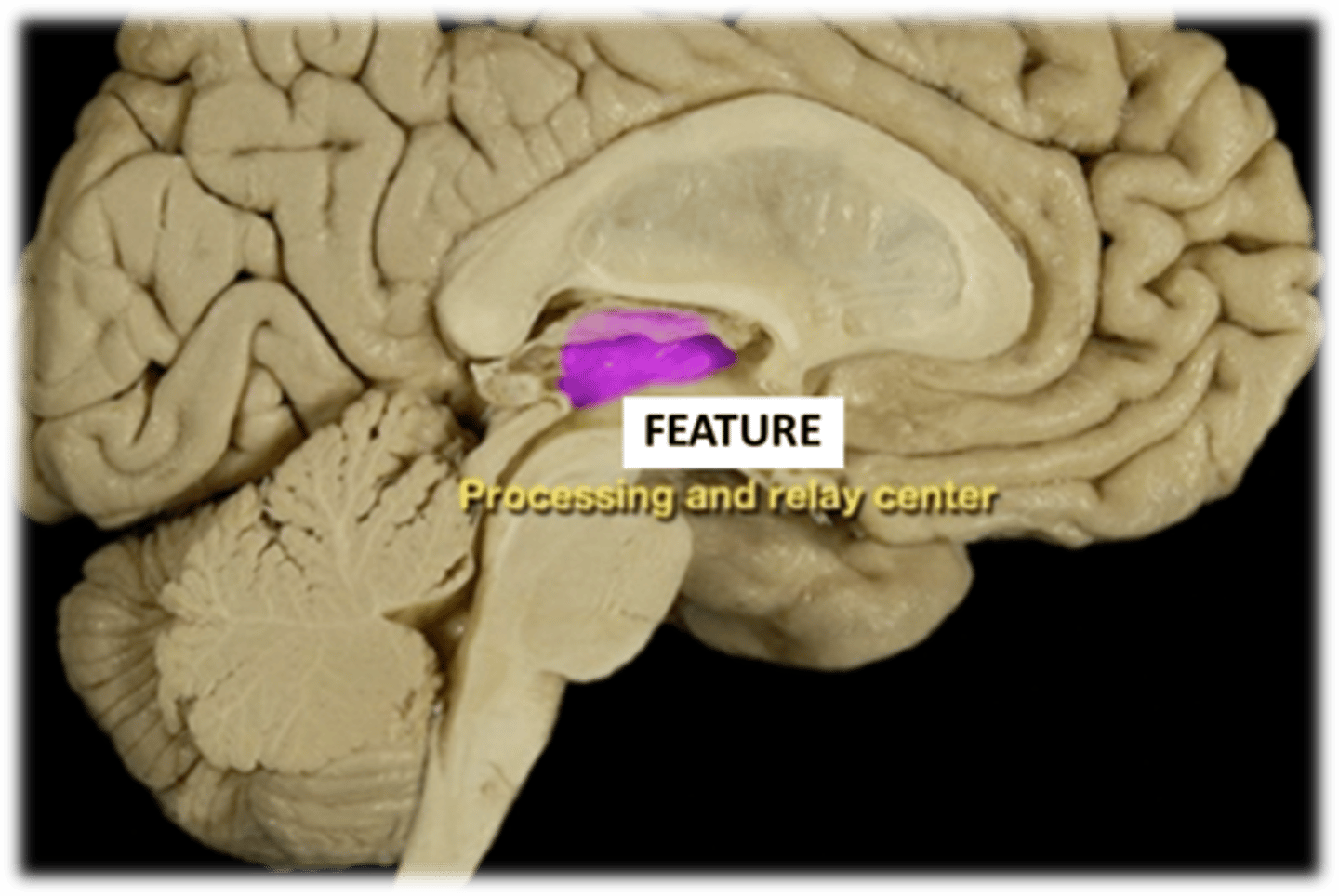
"processing/relay center" receives, groups and relay the sensory info to the cerebrum, except for smell.
Describe the role of the thalamus in the diencephalon
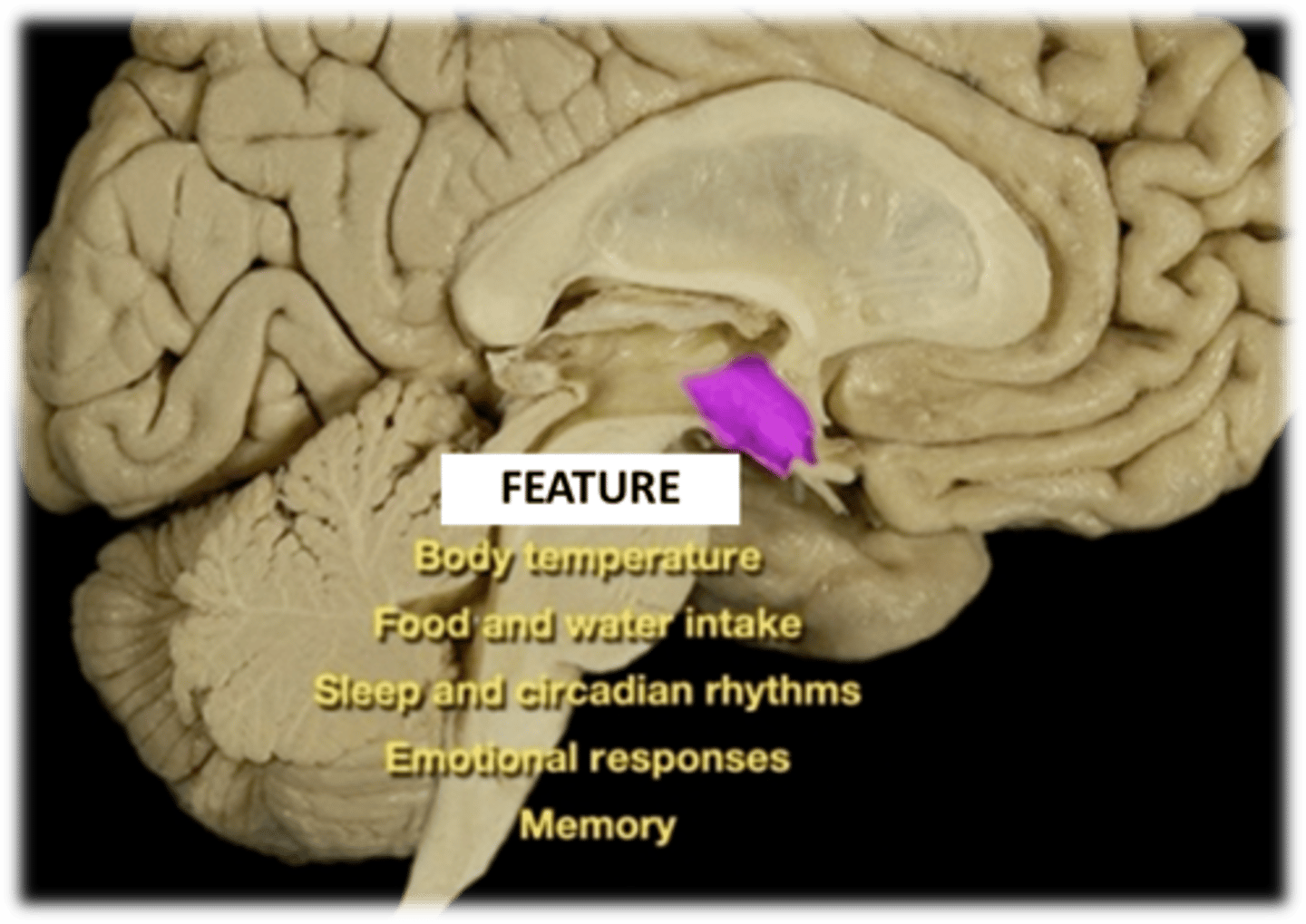
is the command center for the endocrine system
1) body temp
2) food/water intake
3) sleep/circadian rhythms
4) emotional responses
5) memory
Describe the role of the hypothalamus in the diencephalon
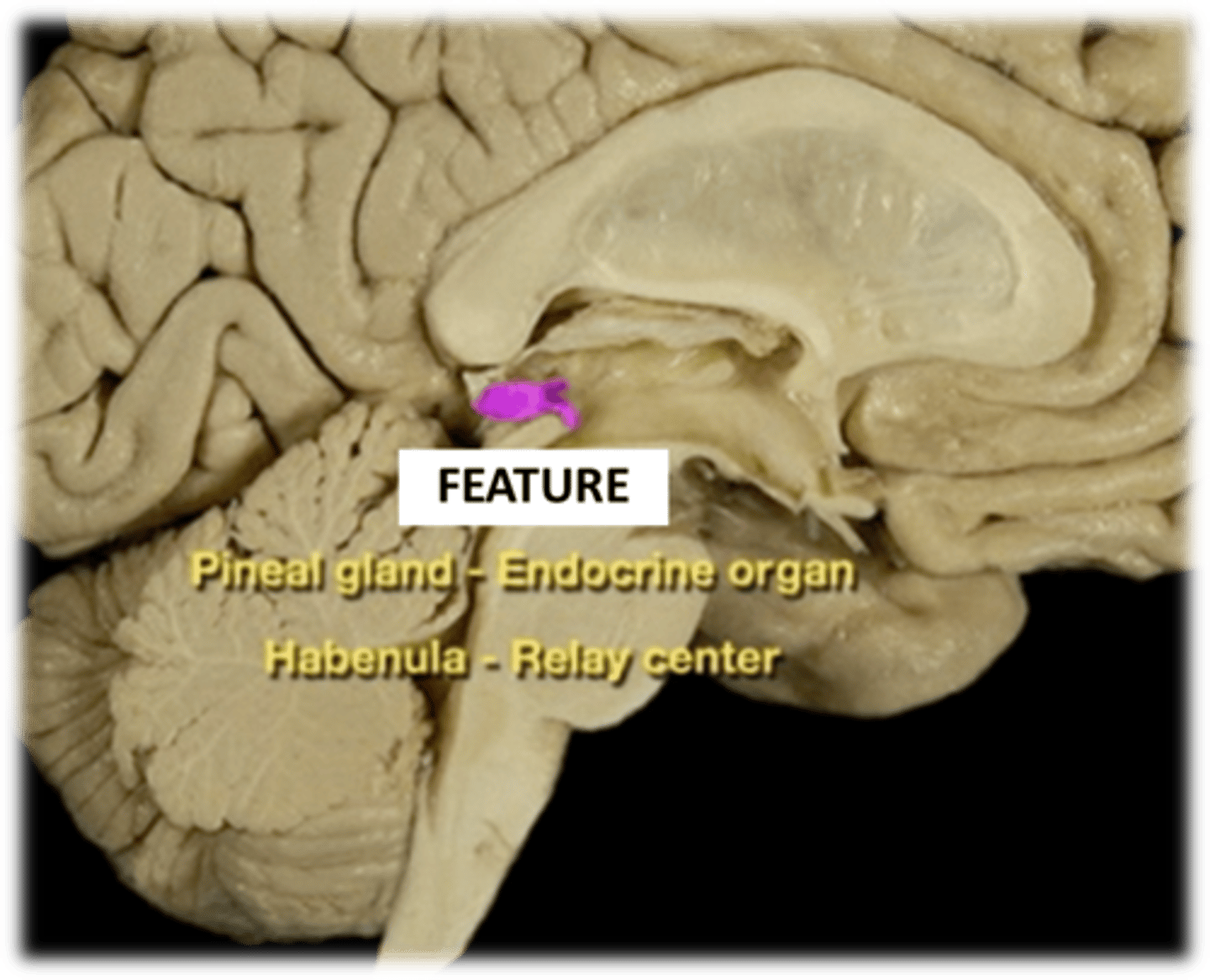
pineal gland produces Melatonin (regulates sleep/wake cycle)
Describe the role of the epithalamus in the diencephalon
Pineal gland (endocrine origin) + Habenula (relay center)
What are the components of the epithalamus
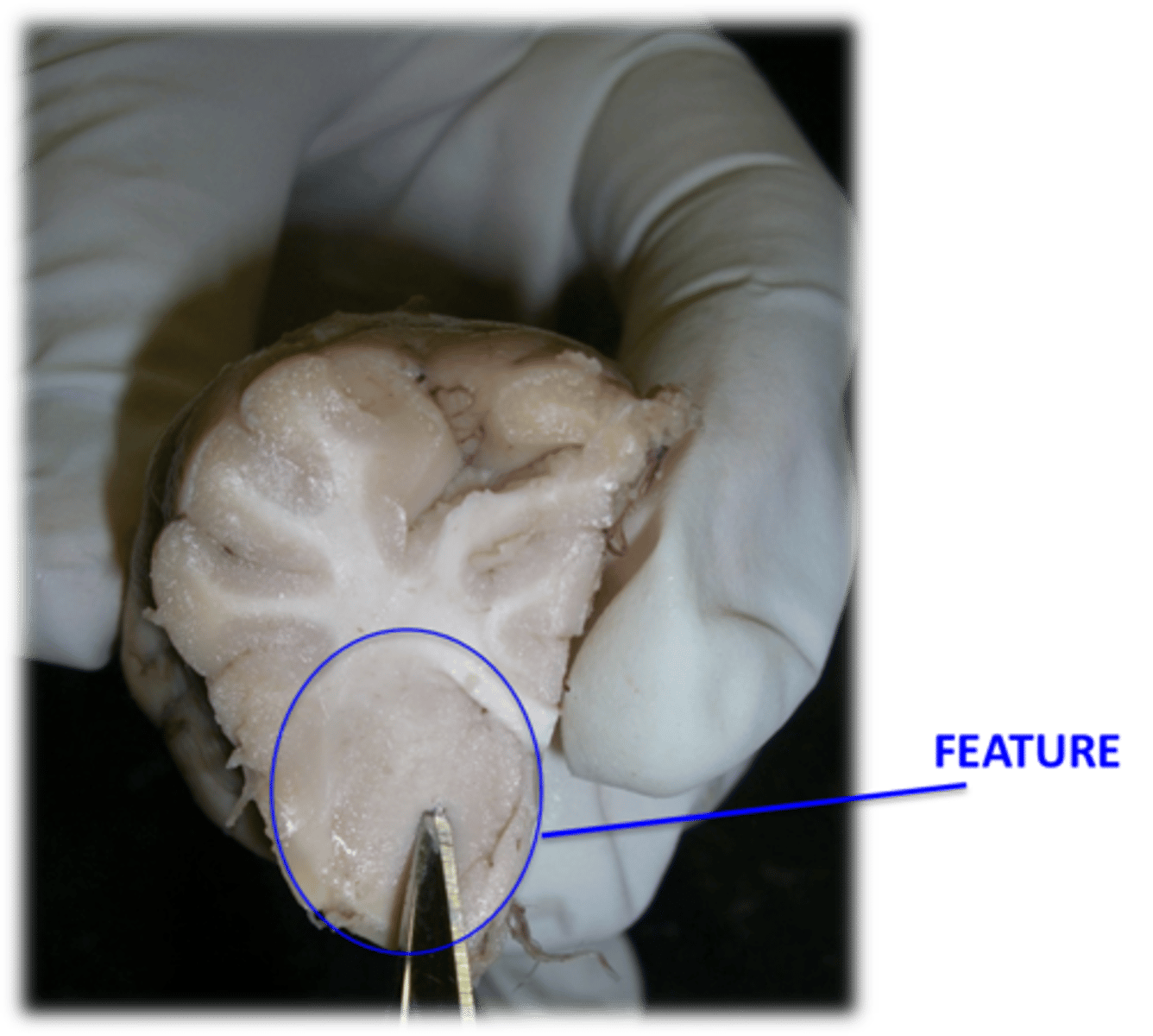
"Action selection "Paired,irregular masses of gray matter buried deep within the central white matter in the cerebral hemispheres
Define basal nuclei
does not initiate movement but helps maintain movement
1) Body posture
2) Balance
3) fine coordination
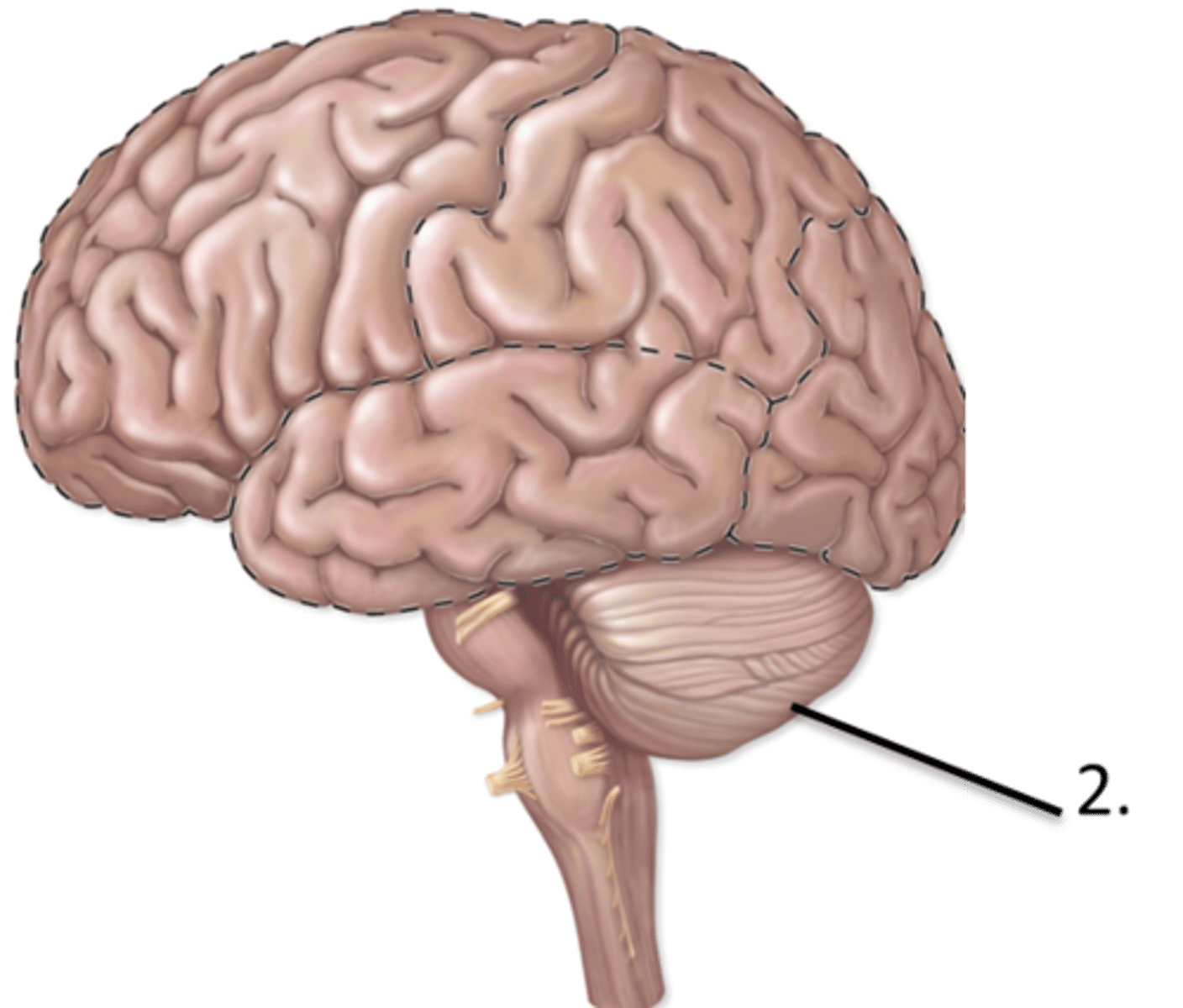
Describe the function of the cerebellum
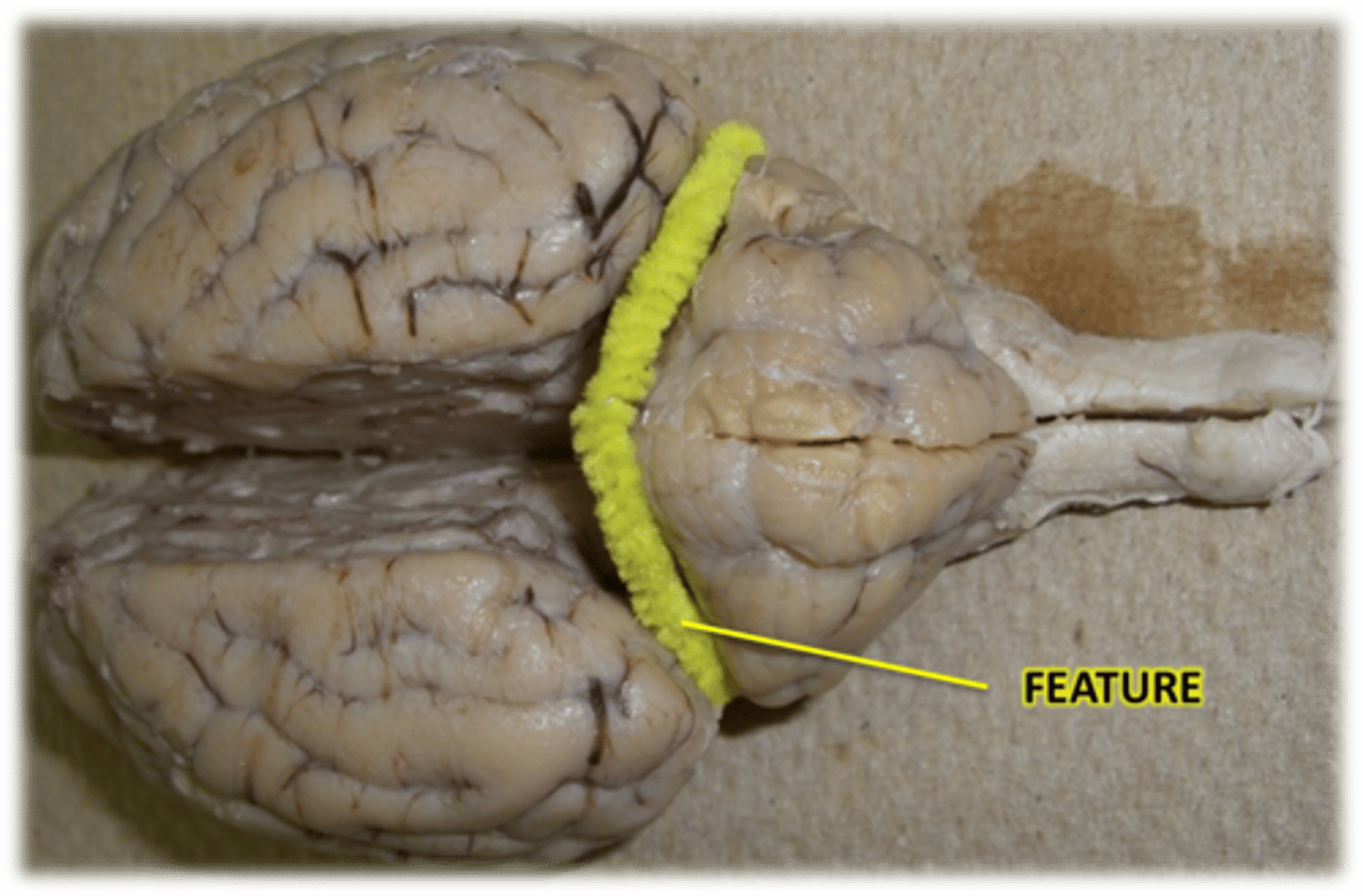
Grey matter of cerebellum = superficial cortex grey matter
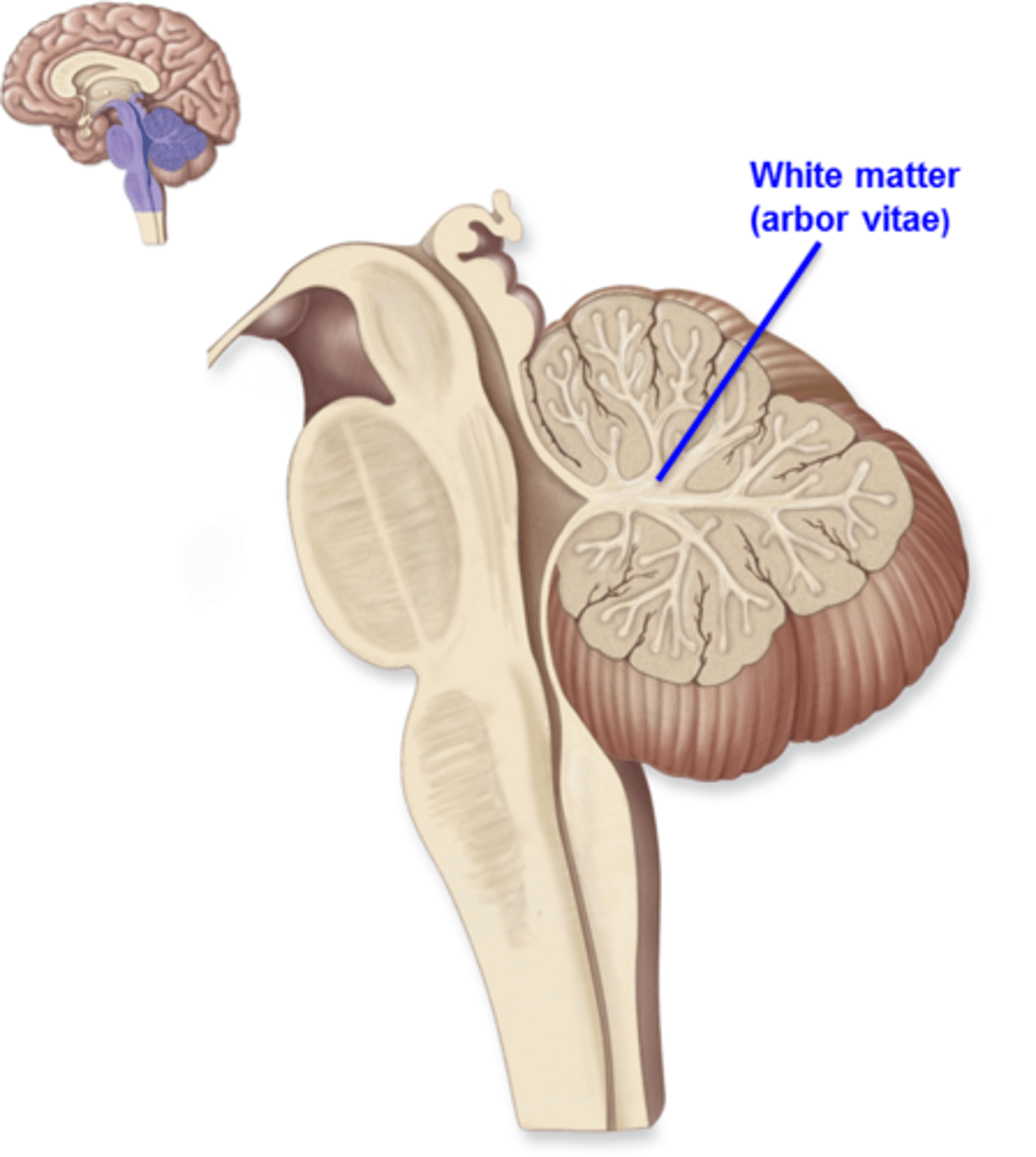
White matter of cerebellum = "Arbor Vitae" (braining tree)
Cerebellum hemispheres= left and right "wings"
Describe the feature of the cerebellum
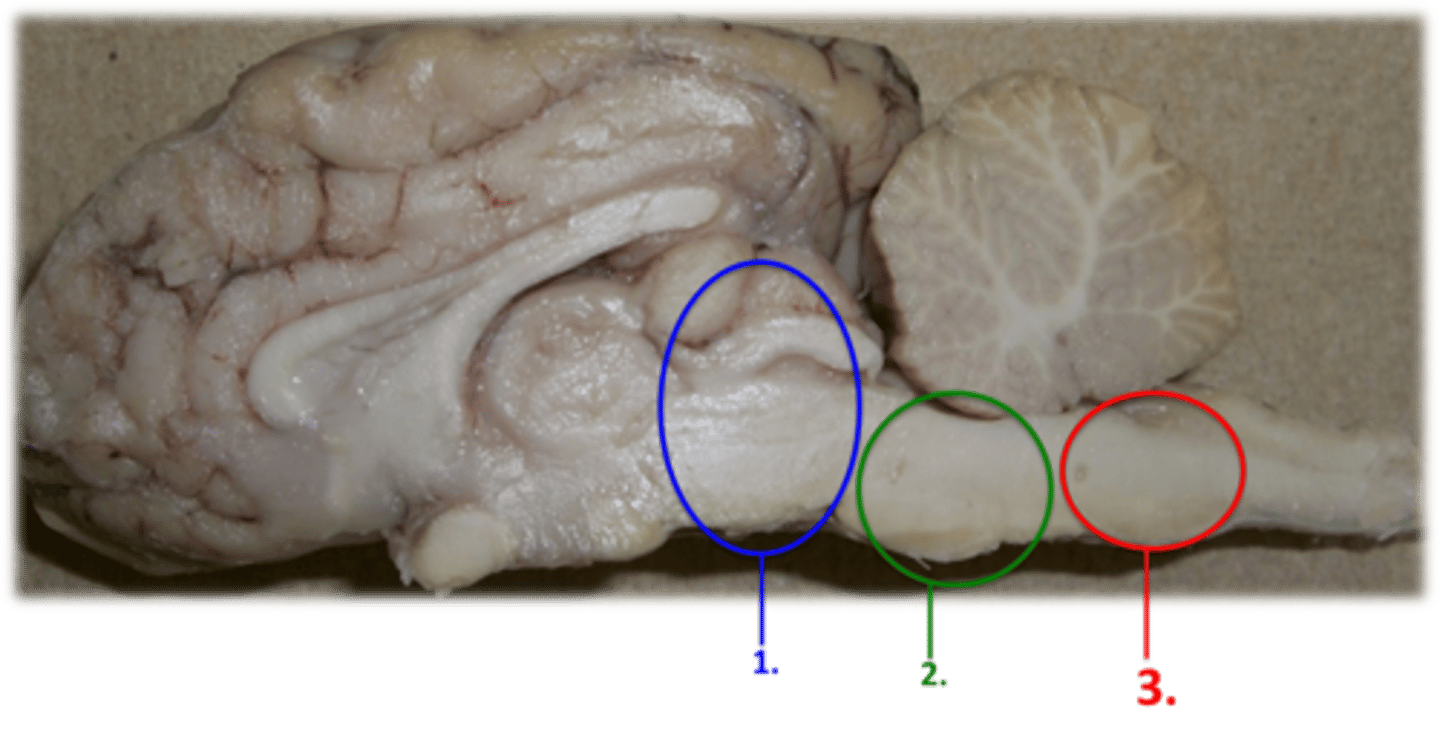
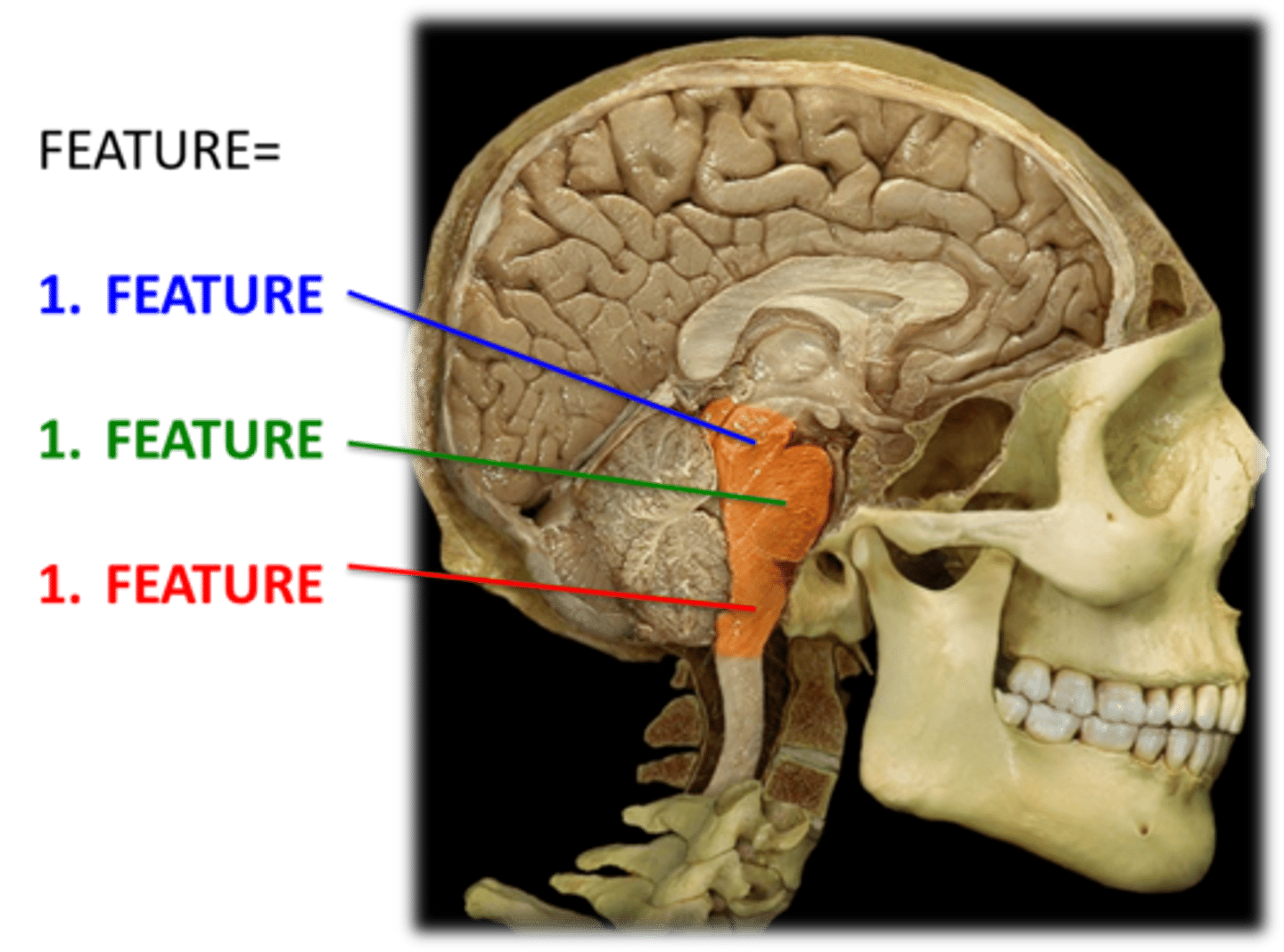
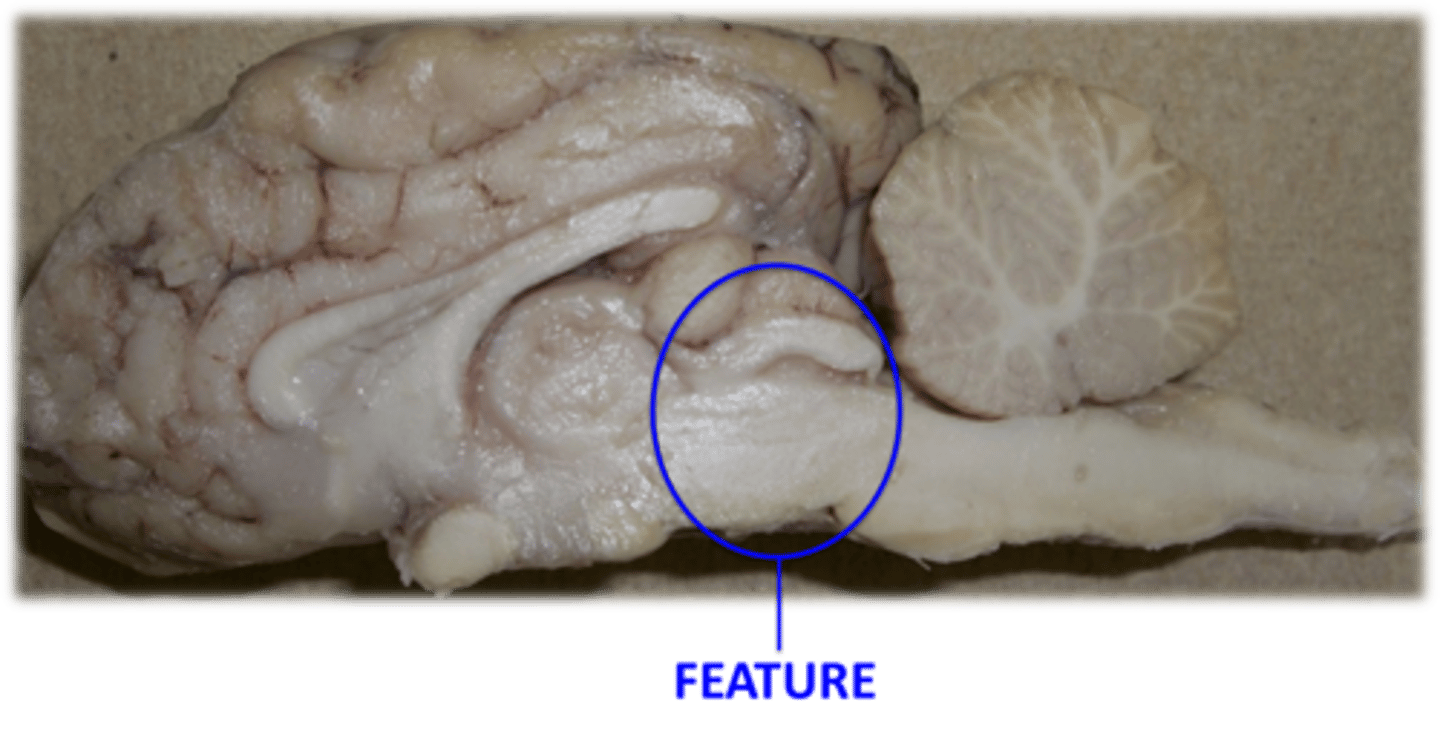
Midbrain: Superior portion of brain stem
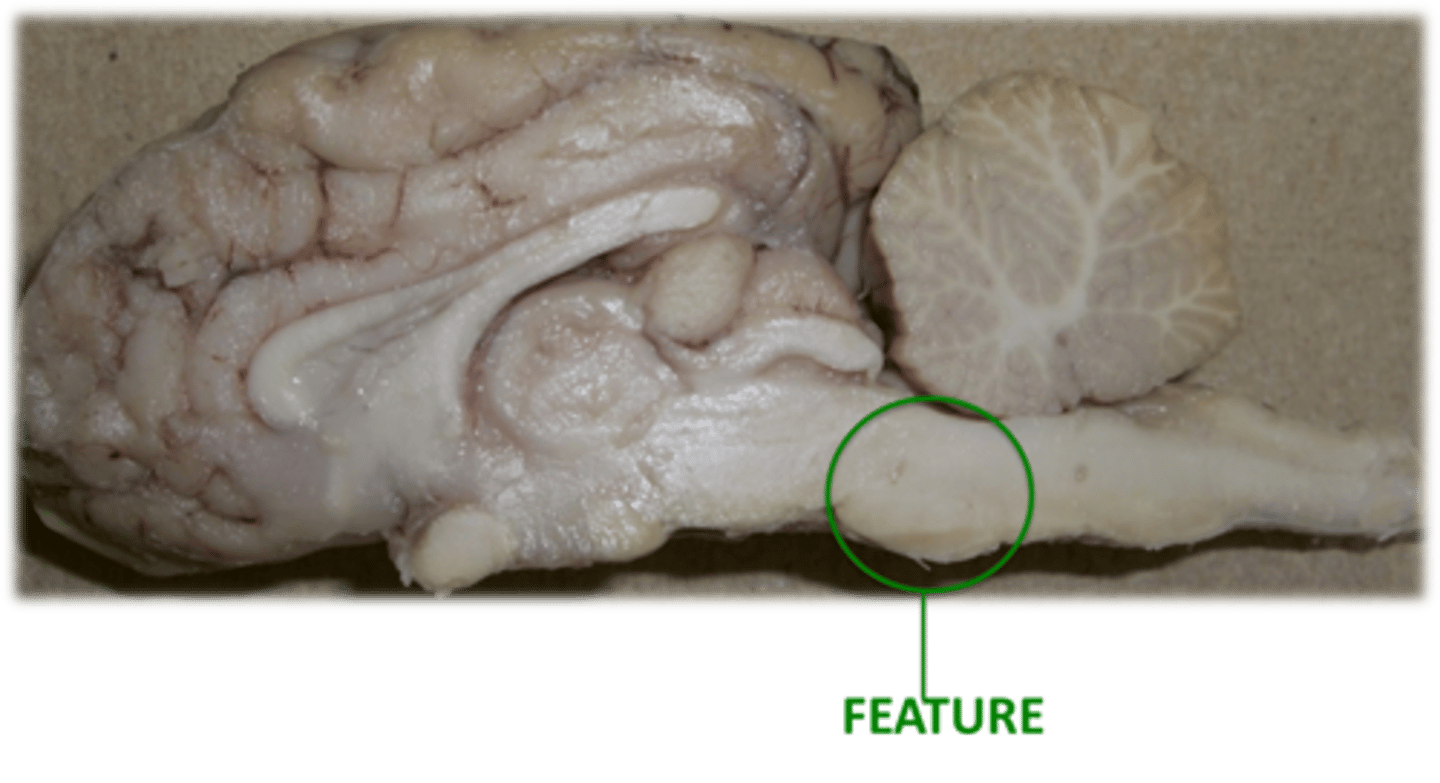
Pons: Directly inferior to midbrain
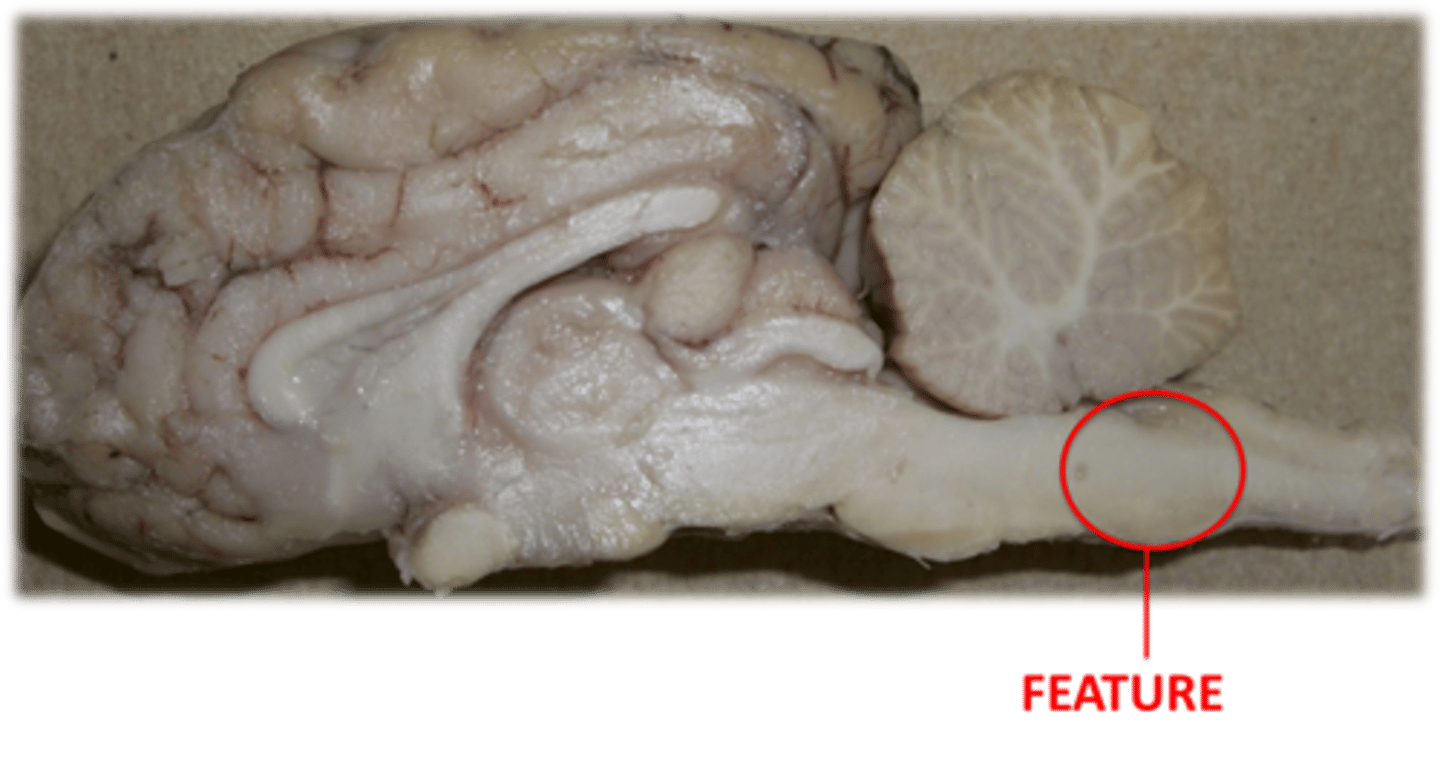
Medulla: Directly inferior to pones
Describe the division of the brain stem
1) relay station for visual and auditory info (via superior and inferior colliculi)
Describe the function of the Midbrain
1) In Latin means "Bridge"
2) Serves as a communication and coordination center for the spinal cord and various portions in the brain
Describe the function of the Pons
1) continuation of medulla is the spinal cord
2) controls autonomic (involuntary functions) i.e breathing and heart rate
Describe the function of the Medulla
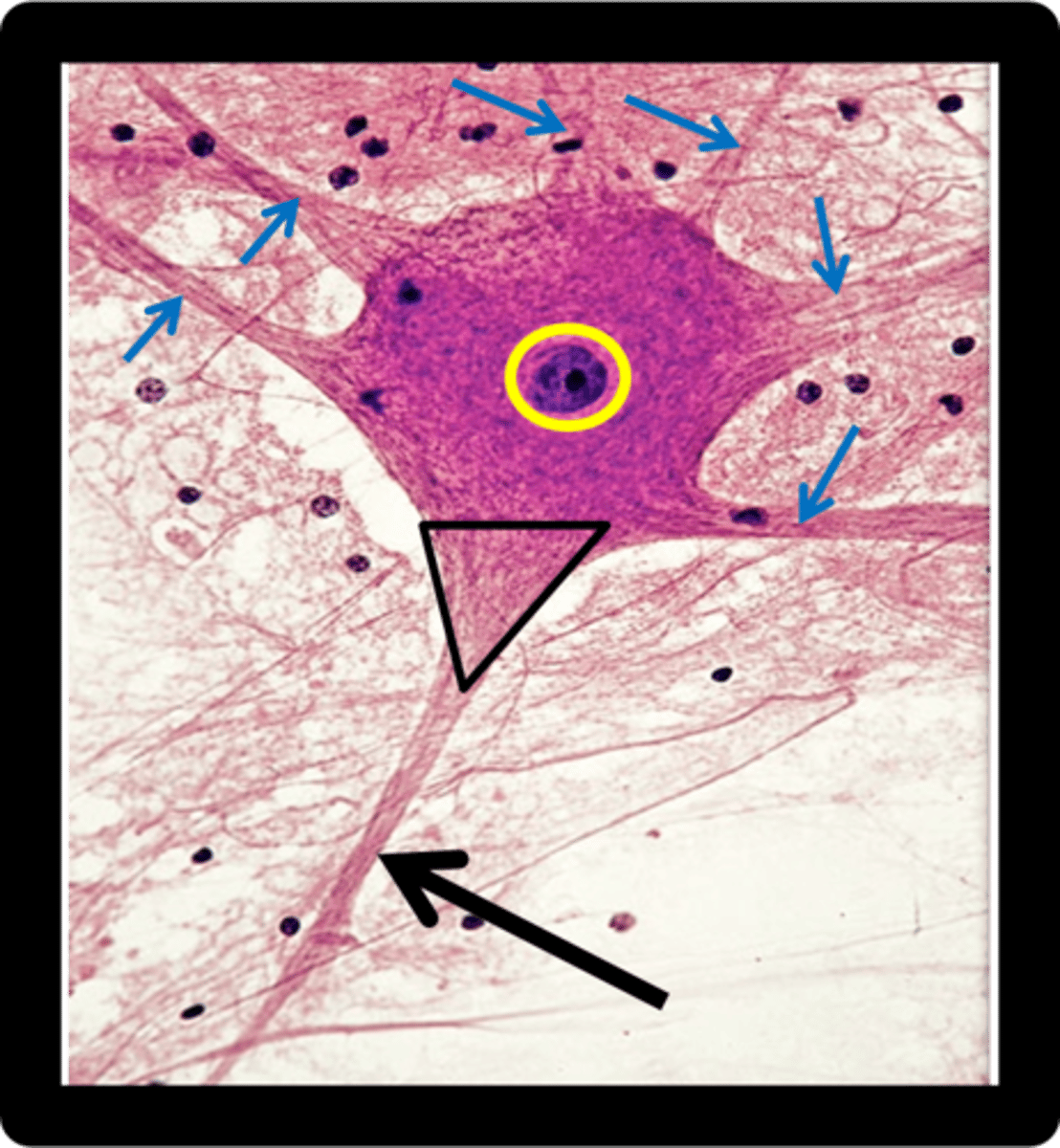
Yellow Circle = Nucleus
Black Triangle = Axon Hillock
Black Arrow = Axon
Blue Arrows = Dendrite
Nucleus/Nuclei
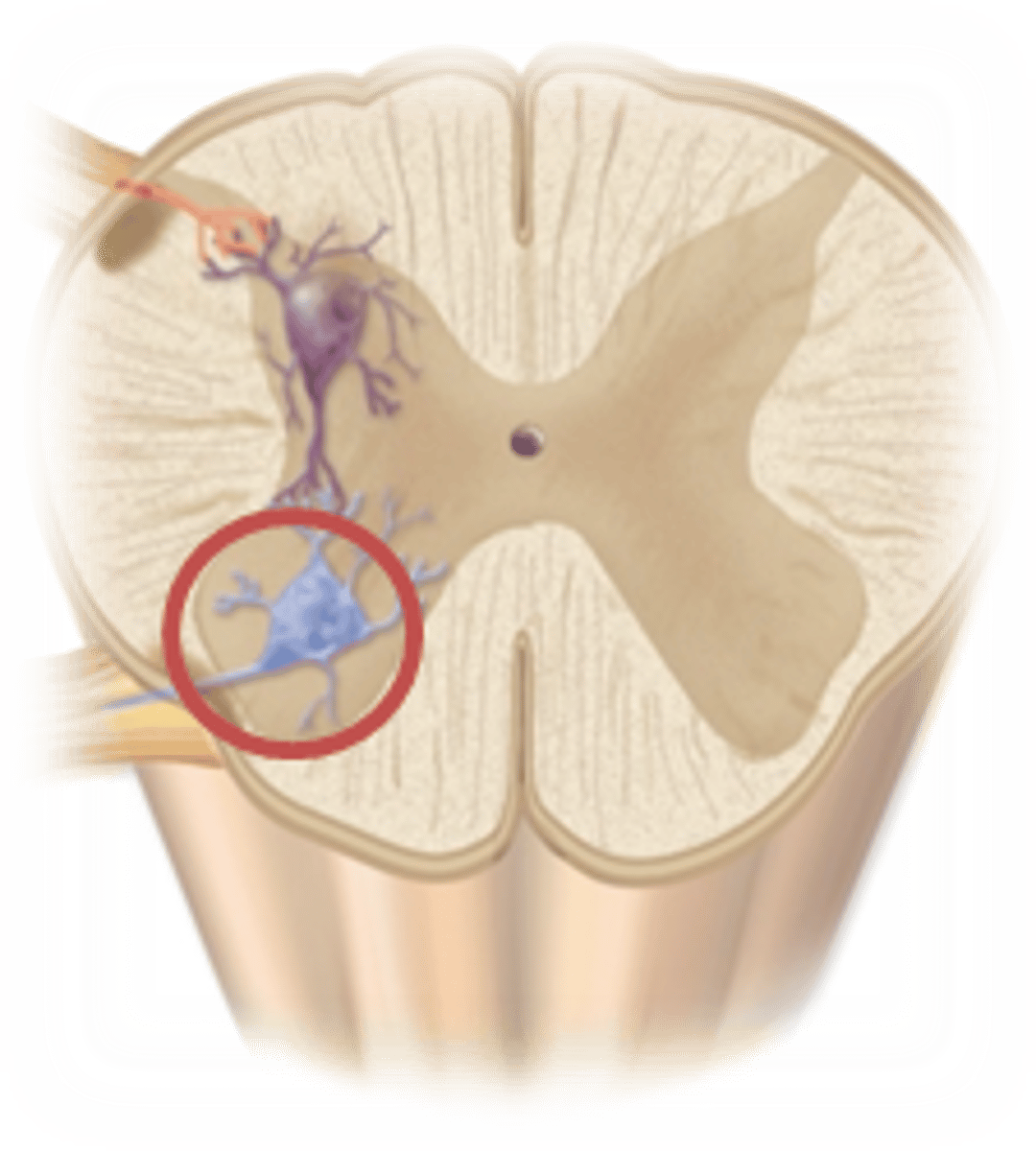
Ganglion/Gangli
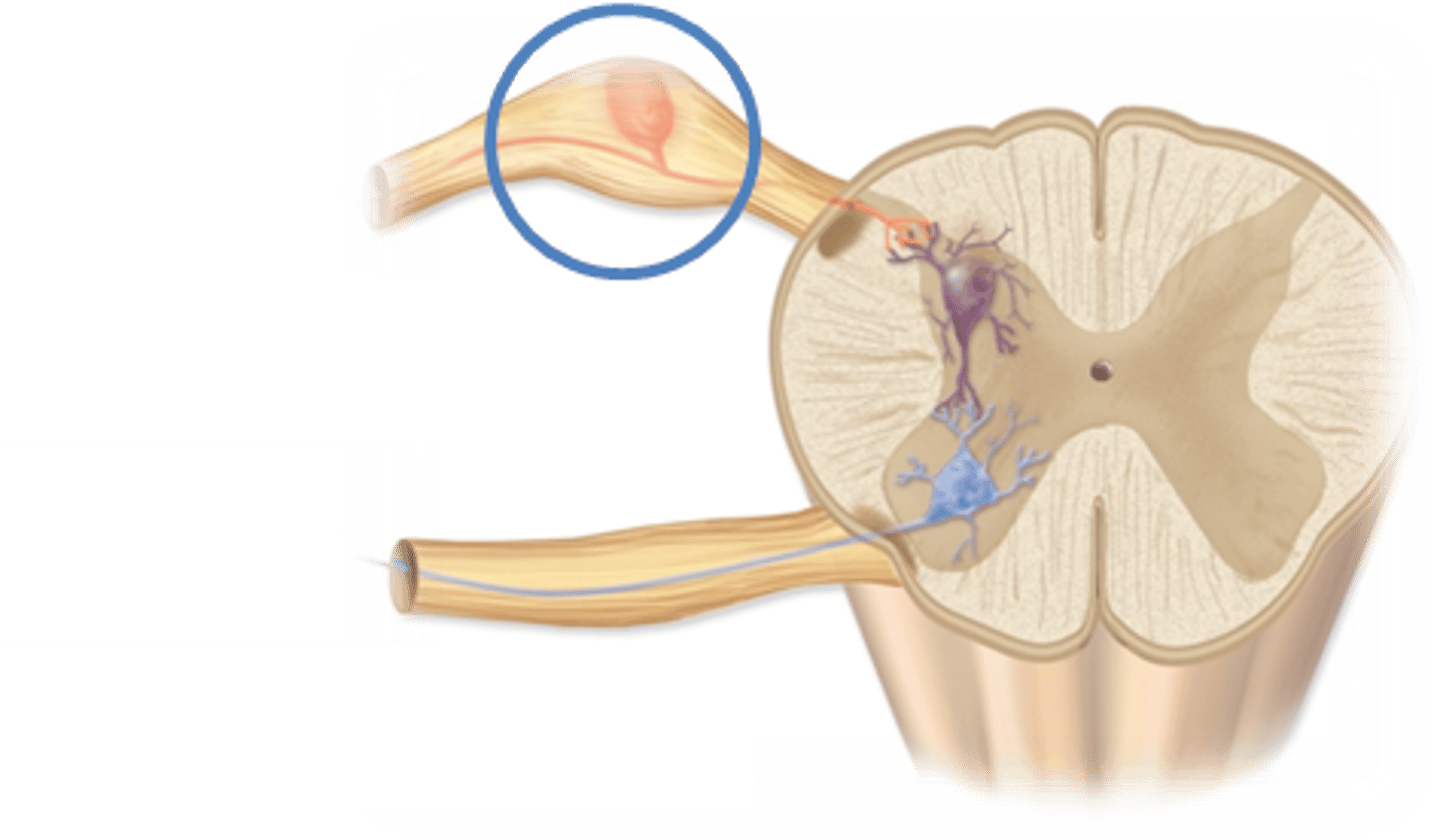
Gray Matter
White Matter
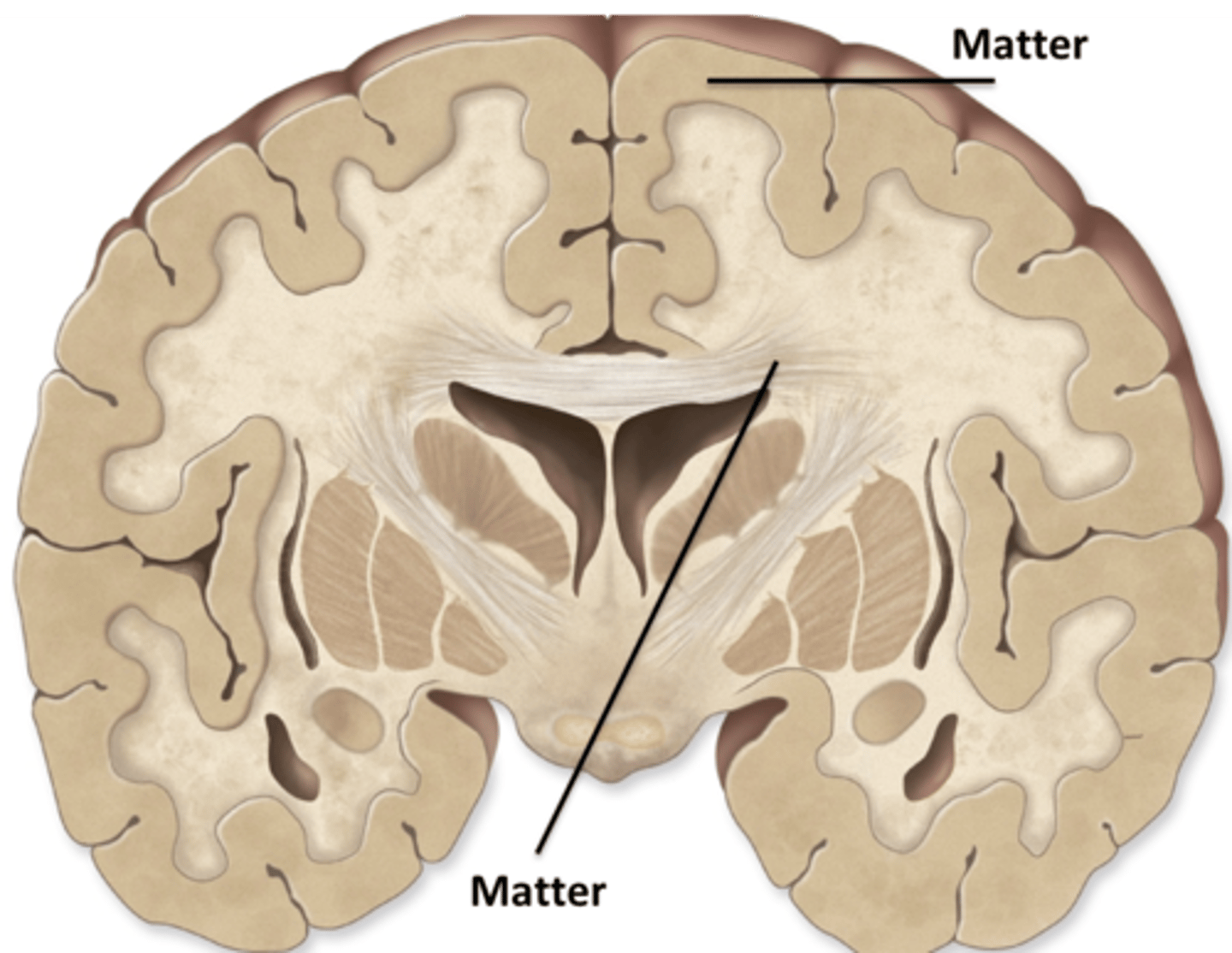
Gray Matter
White Matter
Commissural Tracts
Projection Tracts
Association tracts
Brainstem
Cerebrum
Cerebellum
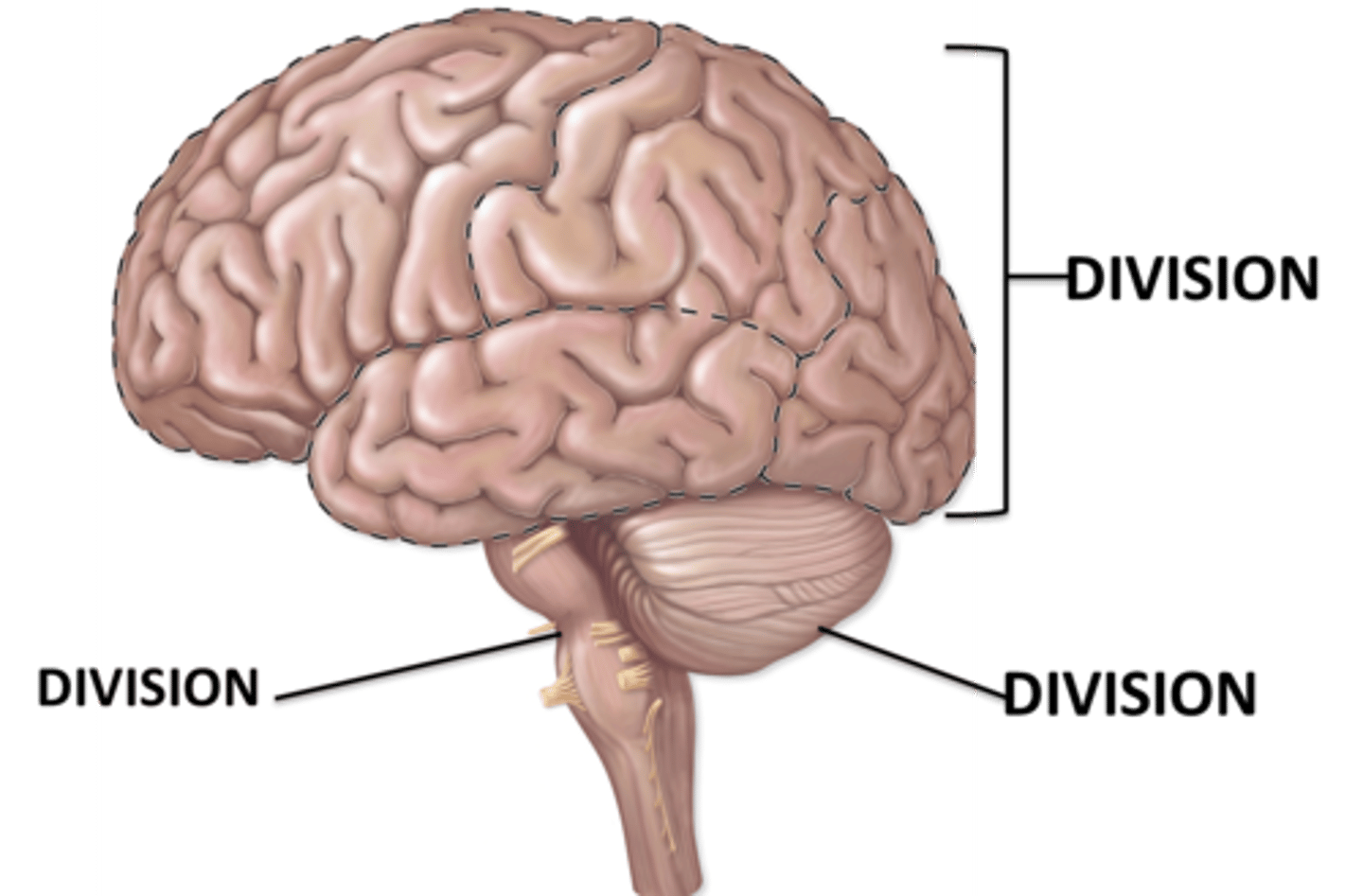
Brainstem
Midbrain
Pons
Medulla
Cerebrum
Cerebellum
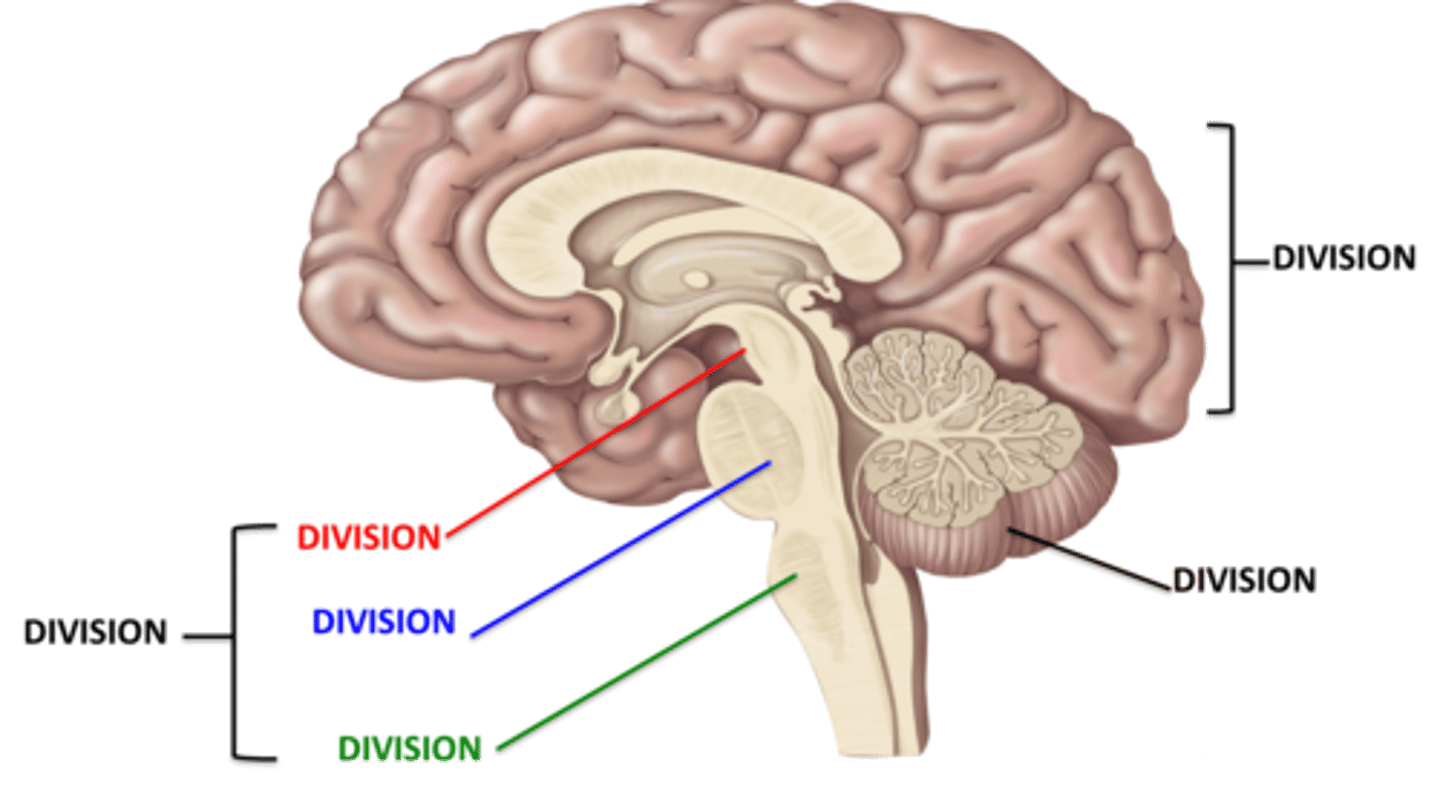
Brainstem
Midbrain
Pons
Medulla
Cerebrum
Cerebellum
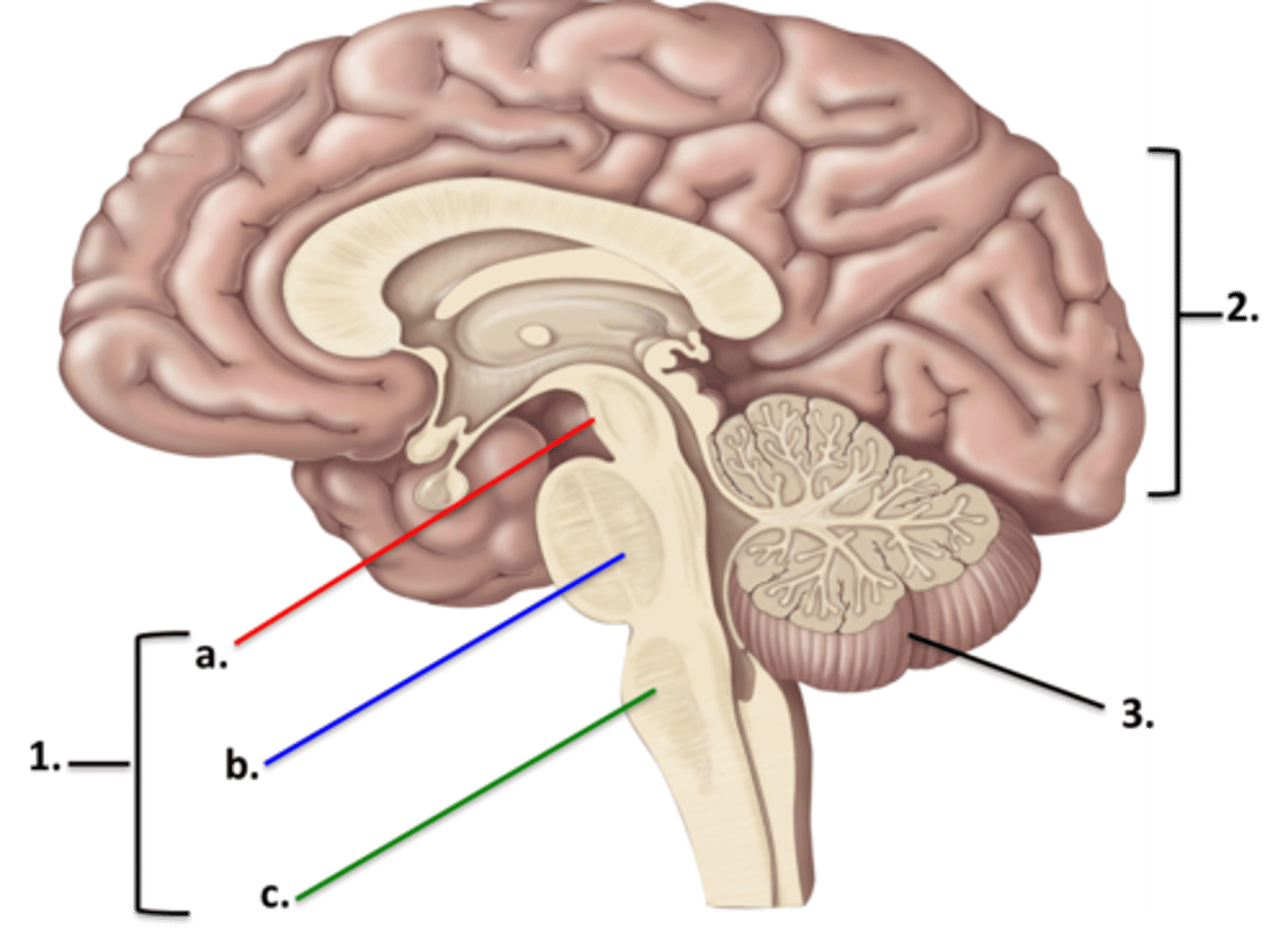
L. Hemisphere
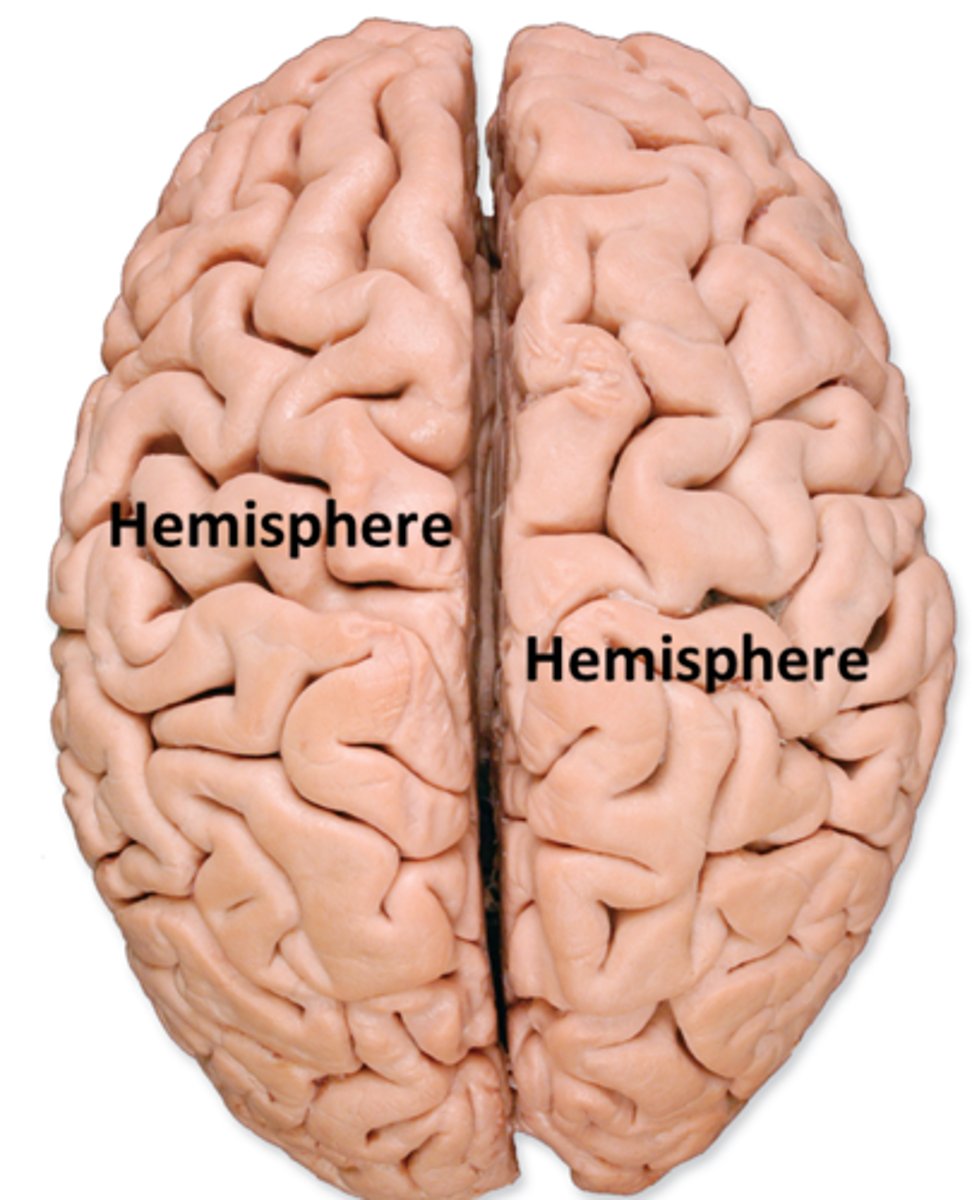
R. Hemisphere
Corpus Callosum
Frontal lobe (retracted)
Parietal lobe
Occipital lobe
Temporal lobe (retracted)
Longitudinal Fissure
Transverse Fissure
Sulci
Central Sulcus
Lateral Sulcus
Gyri
Precentral Gyrus
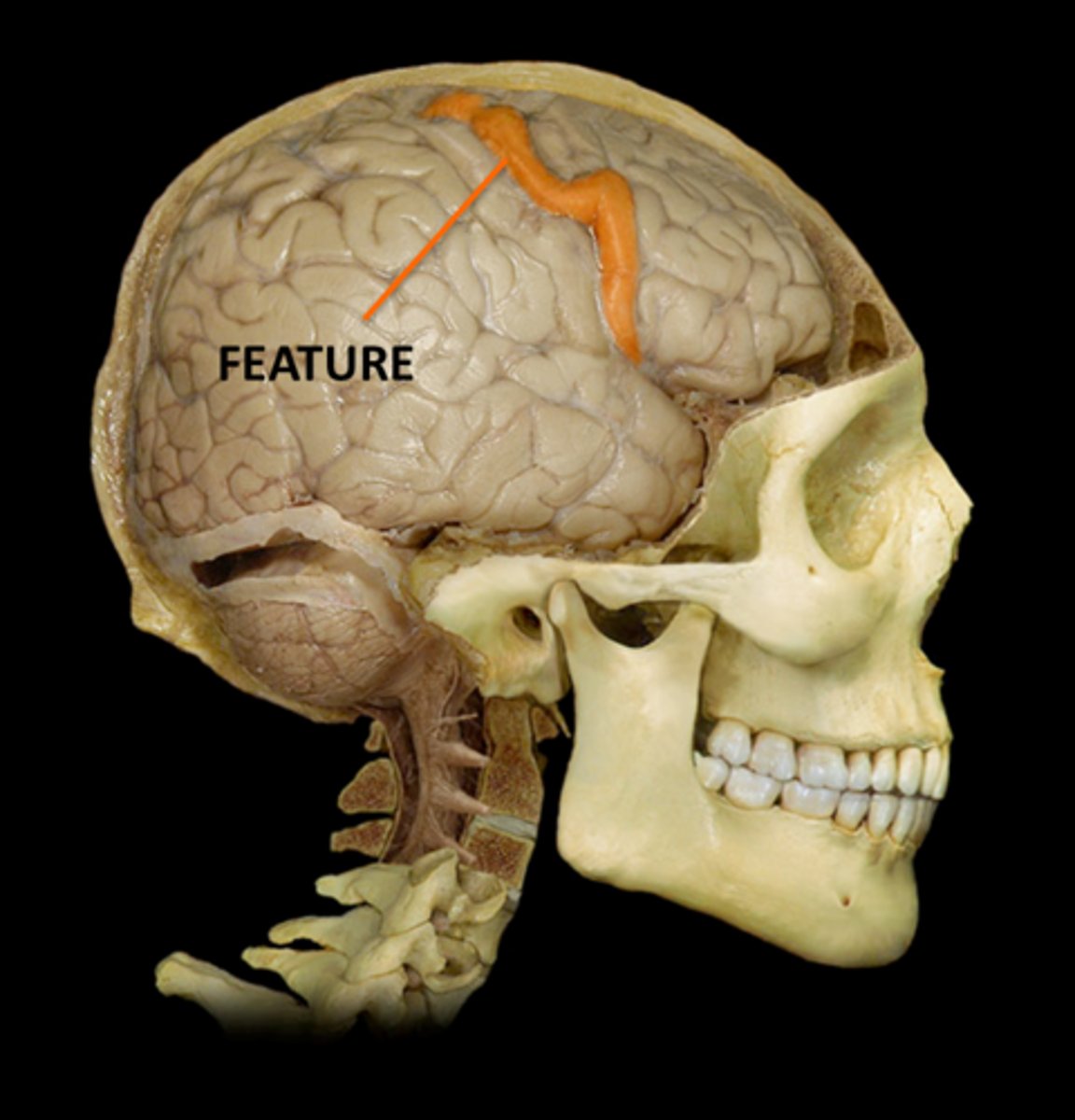
Postcentral Gyrus
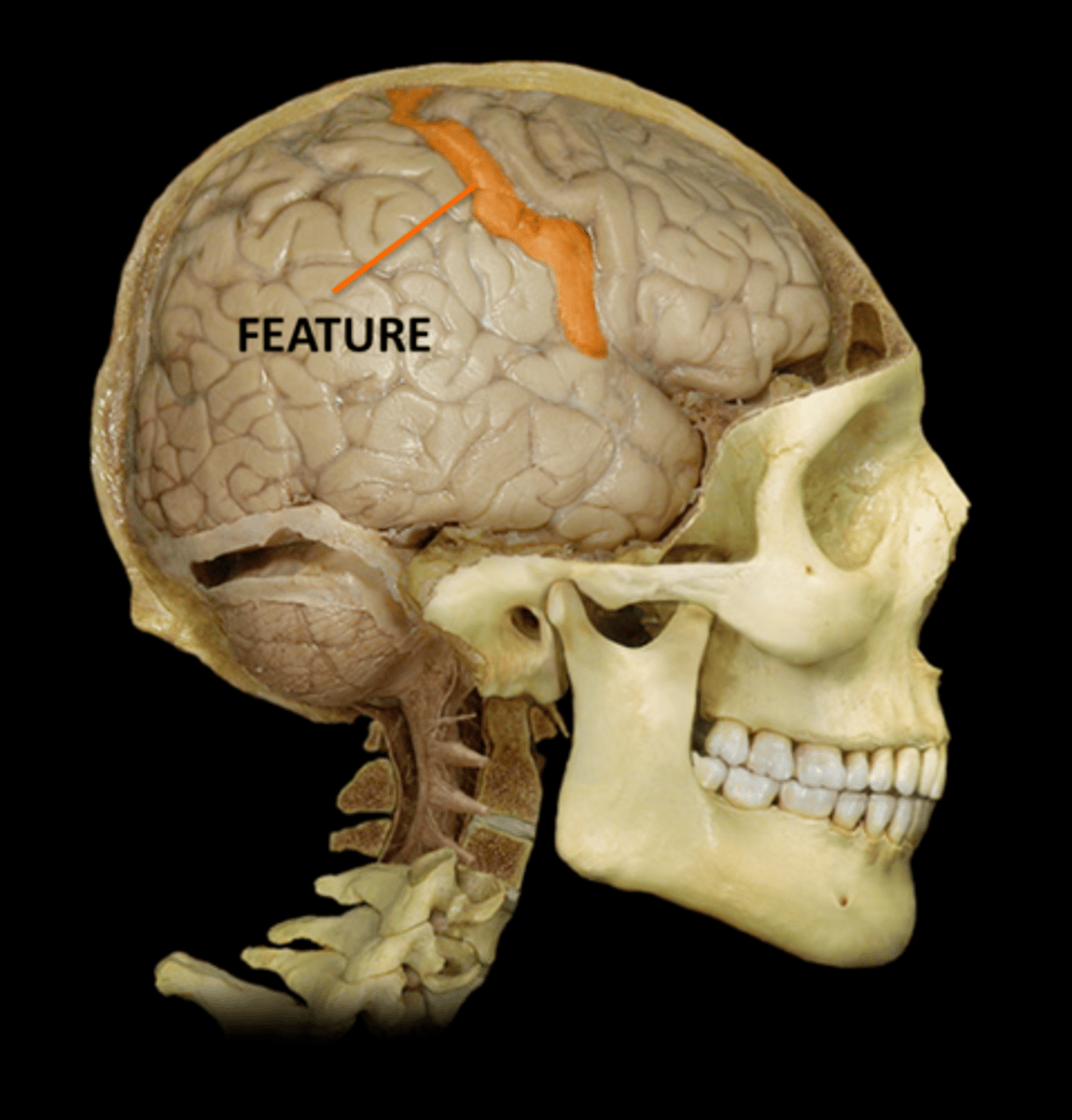
Transverse Fissure
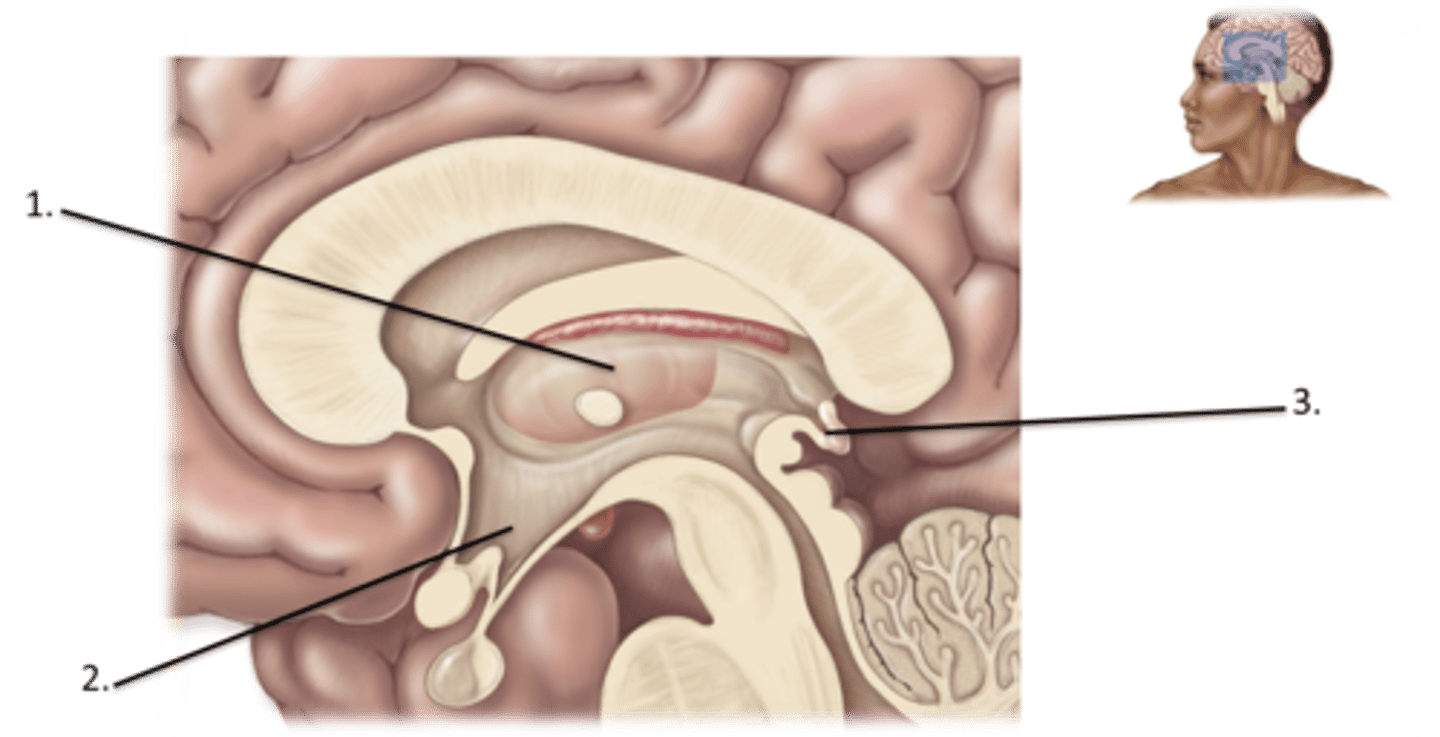
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Epithalamus
Hypothalamus
Thalamus
Epithalamus
Basal Nuclei
Arbor vitae
Cerebellum
Arbor Vitae
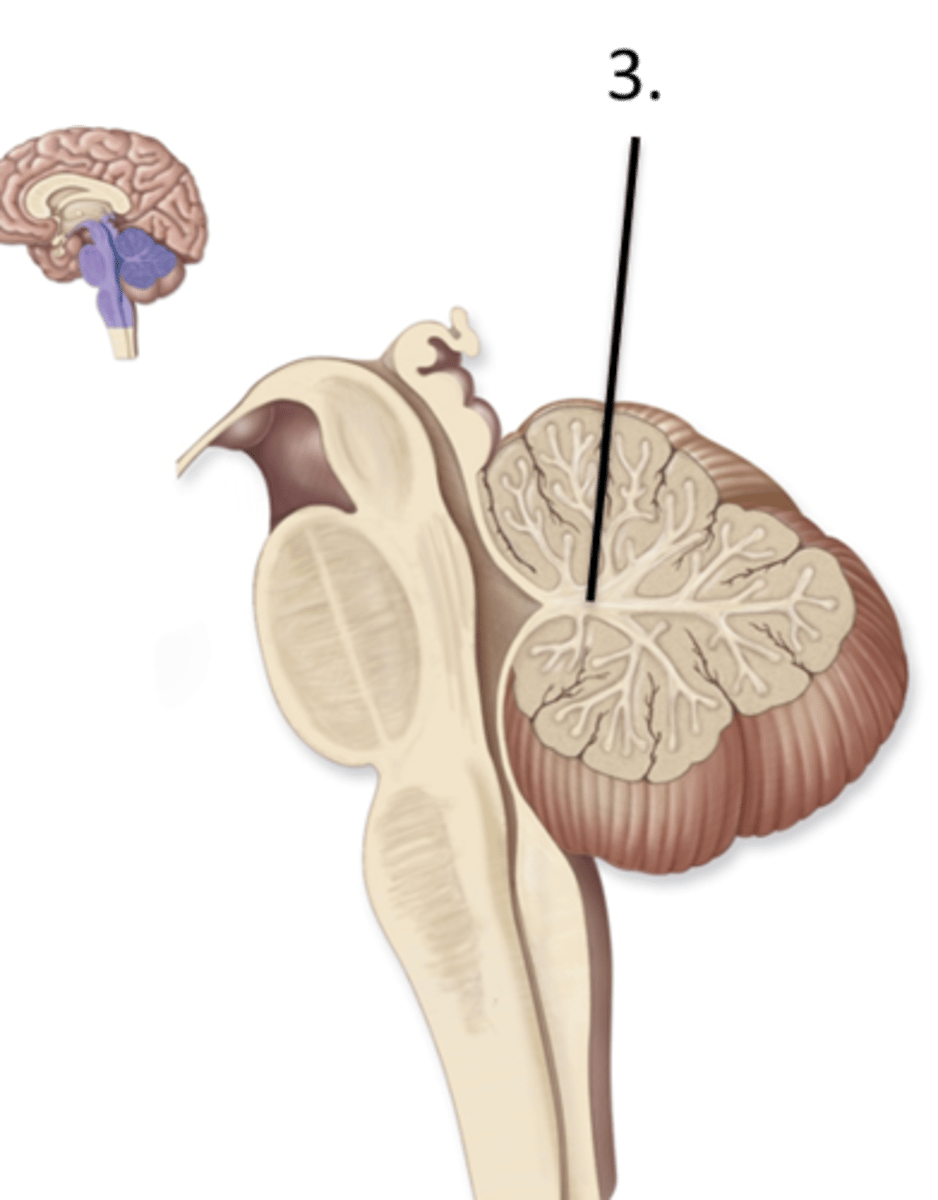
Basal Nuclei
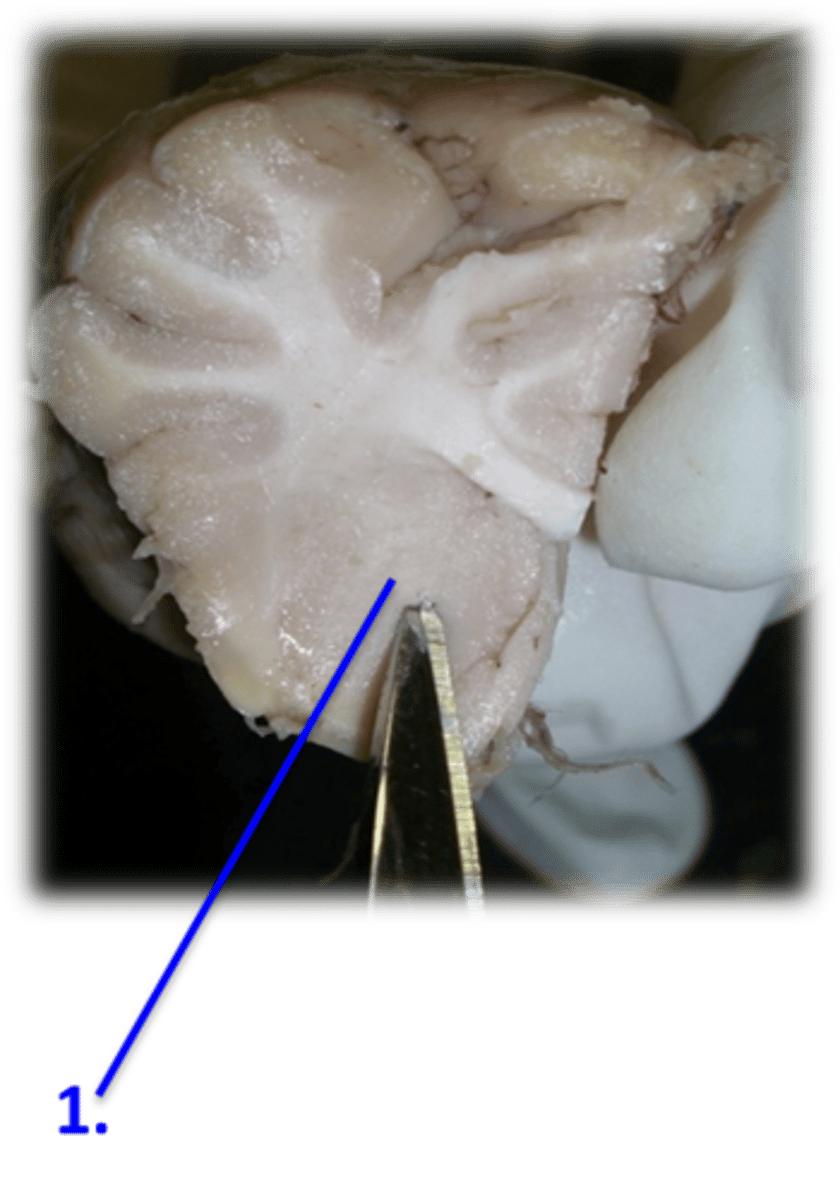
Midbrain
Pons
Medulla
Midbrain
Pons
Medulla
Midbrain
Pons
Medulla