GCSE AQA Geography Section B: The Living World
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
1
New cards
What is an ecosystem?
An ecosystem is all the biotic parts (e.g. plants and animals) and the abiotic parts (e.g. soil and climate) of an area
2
New cards
What are they key components of an ecosystem?
Producers, consumers and decomposers
3
New cards
What is a producer?
A producer (e.g. grass) uses sunlight energy to produce food
4
New cards
What is a consumer?
A consumer gets its energy by eating other organisms
5
New cards
What is a decomposer?
A decomposer is an organism that gets energy by decomposing dead material/e.g. bacteria/fungi
6
New cards
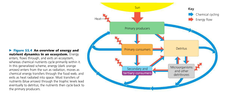
What is the nutrient cycle?
1. when dead materials decomposes nutrients are released into soil
2. nutrients taken up from soil by plants; plants may be eaten by consumers
3. when plants/consumer dies, nutrients returned to soil
2. nutrients taken up from soil by plants; plants may be eaten by consumers
3. when plants/consumer dies, nutrients returned to soil
7
New cards
What is a food chain?
A series of events in which one organism eats another and obtains energy.
{Blackberry -> Sparrow -> Sparrowhawk}
{Blackberry -> Sparrow -> Sparrowhawk}
8
New cards
What is a food web?
A system of interlocking and interdependent food chains.
9
New cards
Where is the Tundra found + characteristics?
- high latitudes [above 60° N] in Northern Europe/Canada + Alaska
- cold winters/brief summers
- little rainfall
- little vegetation [mosses/grasses]
- layer of permafrost
- cold winters/brief summers
- little rainfall
- little vegetation [mosses/grasses]
- layer of permafrost
![- high latitudes [above 60° N] in Northern Europe/Canada + Alaska
- cold winters/brief summers
- little rainfall
- little vegetation [mosses/grasses]
- layer of permafrost](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/6fb81ddfd6e543e78b7c6220f1672a2b.jpg)
10
New cards
Where is the Taiga found + characteristics?
- found between 50-60° N
- cold/dry winters
- mild/moist summers
- coniferous trees
- cold/dry winters
- mild/moist summers
- coniferous trees

11
New cards
Where are Grasslands [Savannah and Temperate] found + characteristics?
There are two types of grasslands.
Savannah grasslands found between tropics. There are distinct dry and wet seasons, rainfall is low. Vegetation includes grasses/scattered trees.
Temperate grasslands found at higher latitudes where there is more variations in temperature/less rainfall - there are no trees, just grasses.
Savannah grasslands found between tropics. There are distinct dry and wet seasons, rainfall is low. Vegetation includes grasses/scattered trees.
Temperate grasslands found at higher latitudes where there is more variations in temperature/less rainfall - there are no trees, just grasses.

12
New cards
Where are Temperate Deciduous Forests found + characteristics?
- found mid-latitudes
- four distinct seasons
- warm summers/mild winters
- rainfall all year around
- deciduous trees lose leaves in winter to cope with colder weather
- four distinct seasons
- warm summers/mild winters
- rainfall all year around
- deciduous trees lose leaves in winter to cope with colder weather
13
New cards
Where are Tropical Rainforests found + characteristics?
- found around equator, between the tropics
- hot/wet all year around
- lush forest + dense canopies of vegetation forming distinct layers
- hot/wet all year around
- lush forest + dense canopies of vegetation forming distinct layers

14
New cards
Where are Hot Deserts found + characteristics?
- found between 15°-35° North and South of equator
- little rainfall
- hot during day/cold at night
- shrubs/cacti are sparsely distributed in sandy soil
- little rainfall
- hot during day/cold at night
- shrubs/cacti are sparsely distributed in sandy soil
15
New cards
Where is the Polar found + characteristics?
- found around north and south poles
- cold, icy and dry
- dark for several months each year
- short growing season
- cold, icy and dry
- dark for several months each year
- short growing season

16
New cards
What are the physical characteristics of tropical rainforests?
Climate, Soil, Plants, Animals and People
17
New cards
Explain the characteristics of the climate in tropical rainforests
1. no definite seasons
2. It's hot (between 20-28°C)
3. high rainfall, 2000mm per year
2. It's hot (between 20-28°C)
3. high rainfall, 2000mm per year
18
New cards
What is the soil like in a tropical rainforest?
The soil isn't very fertile as heavy rain washes nutrients away; there are surface nutrients due to decayed leaf fall, but this layer is very thin as decay is fast in the warm, moist conditions
19
New cards
What types of animals are found in the tropical rainforest?
Gorillas, jaguars, anacondas, tree frogs, sloths and howler monkey + many species of insects and birds

20
New cards
What are plants like in the tropical rainforest?
1. evergreen/tall trees
2. dense vegetation cover - little light reaches the forest floor (2%)
3. epiphytes (plants that grow on other living plants and take nutrients and moisture from the air) e.g. orchids and ferns
2. dense vegetation cover - little light reaches the forest floor (2%)
3. epiphytes (plants that grow on other living plants and take nutrients and moisture from the air) e.g. orchids and ferns
21
New cards
How are people adapted to living in the rain forest?
Indigenous people are adapted to living in rain forests by making a living by hunting/fishing, gathering nuts and berries and growing vegetables in small garden plots
22
New cards
How do rainforests have very high biodiversity?
1. high biodiversity, 50% of world's plant, animal and insect species
2. stable/productive environments from the constant climate (hot + wet)
3. organisms evolved to depend on few species for survival
2. stable/productive environments from the constant climate (hot + wet)
3. organisms evolved to depend on few species for survival
23
New cards
What is likely to lead to reduced biodiversity in rainforests?
- deforestation
- uncontrolled development
- uncontrolled development
24
New cards
Give examples of how rainforests are interdependent ecosystems
1. warm/wet climate helps fungi/bacteria decompose dead plant material making surface soil high in nutrients, meaning plants grow easily
2. nutrient cycling
3. plants and animal species formed symbiotic relationships (dependent on the other for survival)
2. nutrient cycling
3. plants and animal species formed symbiotic relationships (dependent on the other for survival)
25
New cards
How are humans affecting the rain forest?
[deforestation]
1. trees intercept and take up lots of water
2. reduced tree covers increases risk of drought affecting wildlife
3. trees roots stabilise soil and provide nutrients when leaves drop
4. fewer trees mean soils has less protection for rainfall, nutrients will wash away and plants struggle to grow
1. trees intercept and take up lots of water
2. reduced tree covers increases risk of drought affecting wildlife
3. trees roots stabilise soil and provide nutrients when leaves drop
4. fewer trees mean soils has less protection for rainfall, nutrients will wash away and plants struggle to grow
26
New cards
How have plants adapted to the physical conditions in the tropical rainforest?
1. trees compete for sunlight by growing tall
2. thick, waxy leaves with pointed drop-tips channel rainwater to encourage runoff -> leaves' waxy coating coating helps repel the rain
3. lianas use tree trunks to reach sunlight
4. smooth and thin bark helps water to run off
5. large, stable buttress roots support the tall trees' trunks
6. plants drop their leaves throughout the year, so they can grow all year round
2. thick, waxy leaves with pointed drop-tips channel rainwater to encourage runoff -> leaves' waxy coating coating helps repel the rain
3. lianas use tree trunks to reach sunlight
4. smooth and thin bark helps water to run off
5. large, stable buttress roots support the tall trees' trunks
6. plants drop their leaves throughout the year, so they can grow all year round
27
New cards
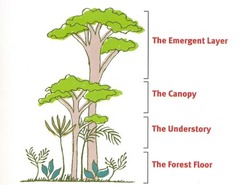
What are the four layer of the rainforest?
emergent trees
main canopy
undercanopy
shrub layers
main canopy
undercanopy
shrub layers
28
New cards
What is the emergent layer?
Trees thrusting above dense canopy having huge mushroom-shaped crowns
29
New cards
What is the canopy layer?
Trees form a tight, continuous canopy above ground; branches are covered with epiphytes and tied with lianas
30
New cards
What is the understory layer?
- layer receives 2-15% of sunlight
- spacious containing young trees and herbaceous plants tolerating low light
- spacious containing young trees and herbaceous plants tolerating low light
31
New cards
What is the forest floor layer?
- receives less than 2% of sunlight
- little grows here
- floor is a thin layer of fallen leaves, seeds, fruits and branches that decompose
- little grows here
- floor is a thin layer of fallen leaves, seeds, fruits and branches that decompose
32
New cards
How are animals adapted to finding food and escaping predators ?
1. strong limbs to move around habitat quickly and easily e.g. monkeys
2. birds have short pointed wings to manoeuvre between dense tangled trees
3. suction cups help animals climb
4. some animals can swim, e.g. jaguars
5. nocturnalism conserving energy in cooler territory e.g. sloths
6. camouflage to hide from predators
2. birds have short pointed wings to manoeuvre between dense tangled trees
3. suction cups help animals climb
4. some animals can swim, e.g. jaguars
5. nocturnalism conserving energy in cooler territory e.g. sloths
6. camouflage to hide from predators
33
New cards
How has the global rate of deforestation changing?
1. global rate of deforestation is high, from 2007-2017, average of 22m hectares of forest were lost each year
3. countries are working to reduce deforestation rates, e.g. from 2004-2012, rate of deforestation in Brazil decreased by about 80%
3. countries are working to reduce deforestation rates, e.g. from 2004-2012, rate of deforestation in Brazil decreased by about 80%
34
New cards
Why are tropical rainforests very valuable to people and the environment?
1. rubber, coffee, chocolate and medicines, are sourced from the rainforest
2. Sustainable development offers long-term economic benefits e.g. ecotourism
3. trees to continue absorbing CO2 and reduce global warming
4. regulate climate/water cycle - without them the risk of drought/flooding in areas can increase
2. Sustainable development offers long-term economic benefits e.g. ecotourism
3. trees to continue absorbing CO2 and reduce global warming
4. regulate climate/water cycle - without them the risk of drought/flooding in areas can increase
35
New cards
How can tropical rainforests be sustainably managed?
- Replanting
- Selective Logging
- Ecotourism
- Education
- Conservation
- Reducing Debt
- Selective Logging
- Ecotourism
- Education
- Conservation
- Reducing Debt
36
New cards
How can replanting help sustainably manage tropical rainforests?
- New trees are planted to replace ones that were cut down
- It's important the same type of trees are replanted
- Some countries have laws to replant trees when they are cleared by deforestation
- It's important the same type of trees are replanted
- Some countries have laws to replant trees when they are cleared by deforestation
37
New cards
How can selective logging help sustainably manage tropical rainforests?
- Some trees are felled (old ones), the rest remain -> overall forest structure is kept/the canopy remains/soil is not exposed allowing forest regeneration
- Least damaging form is 'helicopter logging' - dragging felled trees without the use of machinery
{e.g. Helicopter logging is used in Sarawak, Malaysia}
- Least damaging form is 'helicopter logging' - dragging felled trees without the use of machinery
{e.g. Helicopter logging is used in Sarawak, Malaysia}
38
New cards
How can ecotourism help sustainably manage tropical rainforests?
- Small number of visitors allowed into an area at a time + rules are imposed to minimise environmental impacts
- Provides a source of income for locals
{e.g. Costa Rica; 21% of country protected from development}
- Provides a source of income for locals
{e.g. Costa Rica; 21% of country protected from development}
39
New cards
How can education help sustainably manage tropical rainforests?
- People can buy products to encourage sustainable sources
- Locals might damage the forest to overcome poverty -> educating locals about deforestation impacts reduce damage
- Teaching locals alternative ways to make money that don't damage the environment means they won't be as dependent in unsustainable options to make a living
{e.g. The Rainforest Alliance is teaching communities in Guatemala about sustainable livelihoods}
- Locals might damage the forest to overcome poverty -> educating locals about deforestation impacts reduce damage
- Teaching locals alternative ways to make money that don't damage the environment means they won't be as dependent in unsustainable options to make a living
{e.g. The Rainforest Alliance is teaching communities in Guatemala about sustainable livelihoods}
40
New cards
How can reducing debt help sustainably manage tropical rainforests?
- debts can be cancelled by countries/organisations meaning LIC's do not have to log/mine the rain forest to repay the money so it can be reserved
- no guarantee money is spent on conversation so a conversation swap is better where a part of country's debt is paid in exchange for guaranteed money spent on conversation
{e.g. 2011, USA reduced Indonesia's debt by $29 million in exchange for conserving their rain forests}
- no guarantee money is spent on conversation so a conversation swap is better where a part of country's debt is paid in exchange for guaranteed money spent on conversation
{e.g. 2011, USA reduced Indonesia's debt by $29 million in exchange for conserving their rain forests}
41
New cards
How can conservation help sustainably manage tropical rainforests?
- national parks and nature reserves are set up in countries to reduce damaging activities but lack of funds makes it difficult to police the restrictions
- overseas governments/businesses can invest in funds for rain forest conservation
- money is used to enforce restrictions of damaging activities
{e.g. 2018, Norway paid $70 million into Brazil's Amazon Fund used for conservation}
- overseas governments/businesses can invest in funds for rain forest conservation
- money is used to enforce restrictions of damaging activities
{e.g. 2018, Norway paid $70 million into Brazil's Amazon Fund used for conservation}
42
New cards
What is the climate like in the desert?
- little rainfall, less than 250 mm p/y
- varied rainfall
- extreme temps because lack of cloud cover reaching 45°C in the day, dropping below 0°C at night
- varied rainfall
- extreme temps because lack of cloud cover reaching 45°C in the day, dropping below 0°C at night
43
New cards
What is the soil like in a desert?
- lack of leaf fall limits soil's fertility
- little rainfall so soil dries out
- soil is shallow + gravelly texture
- little rainfall so soil dries out
- soil is shallow + gravelly texture
44
New cards
What are the plants like in a desert?
- low rainfall, plant growth is sparse - plants that do grow, like thornbushes and cacti, don't need much water
45
New cards
What are animals like in the desert?
- animals adapted to harsh environment
- small, nocturnal mammals e.g. kangaroo rats
- Birds leaves desert during harshest conditions but roadrunners live there all year
- small, nocturnal mammals e.g. kangaroo rats
- Birds leaves desert during harshest conditions but roadrunners live there all year
46
New cards
What are people like in the desert?
- grow few crops near natural water sources, in desert fringes
- indigenous people are nomadic - keep travelling to find food/water for livestock
- indigenous people are nomadic - keep travelling to find food/water for livestock
47
New cards
Where are deserts located?
30 degrees N and S latitude + near interior of continents -> Arizona and Utah
48
New cards
How are deserts fragile and interdependent ecosystems?
- plants take up nutrients from soil providing nutrients/water to animals that eat them; animals spread seeds through dung helping plants reproduce
- hot + dry climate affects desert soil ; soils are salty due to high evaporation rates + low in nutrients from low decomposition of dead plant material by fungi/bacteria so plants struggle growing
- vegetation limits food availability, desert can only support low-density populations of animals/people
- hot + dry climate affects desert soil ; soils are salty due to high evaporation rates + low in nutrients from low decomposition of dead plant material by fungi/bacteria so plants struggle growing
- vegetation limits food availability, desert can only support low-density populations of animals/people
49
New cards
How are plants adapted to the physical conditions in hot deserts?
- roots are either deep or wide to absorb maximum water
- succulent plants have large, fleshy stems to store water and thick waxy skin to reduce transpiration
- small leaves/spines lowering s.a and reduces transpiration; spines contain toxins protecting plant from predators
- some plants only germinate after it rains growing quickly to make most of wet conditions
- succulent plants have large, fleshy stems to store water and thick waxy skin to reduce transpiration
- small leaves/spines lowering s.a and reduces transpiration; spines contain toxins protecting plant from predators
- some plants only germinate after it rains growing quickly to make most of wet conditions
50
New cards
How are animals adapted to the physical conditions in hot deserts?
- nocturnal to conserve energy and stay cool
- long limbs/ear giving larger s.a to lose heat from
- fat that breaks down into water e.g. camels' humps
- camels have triple eyelids/long eyelashes to block sand + ability to close nostrils to keep sand out, large + flat feet so they don't sink
- long limbs/ear giving larger s.a to lose heat from
- fat that breaks down into water e.g. camels' humps
- camels have triple eyelids/long eyelashes to block sand + ability to close nostrils to keep sand out, large + flat feet so they don't sink
51
New cards
How is biodiversity being threatened in deserts?
- areas with water have highest density of human populations; people threaten biodiversity by increasing desertification or over-using/contaminating water supplies
- development around desert margins means habitats are divided by roads threatening animals that migrate over large distances
- global warming makes deserts hotter/drier forcing species to move/become extinct
- development around desert margins means habitats are divided by roads threatening animals that migrate over large distances
- global warming makes deserts hotter/drier forcing species to move/become extinct
52
New cards
What is a biodiversity hotspot?
locations with high biodiversity threatened by mankind
53
New cards
What is desertification caused by?
- caused by vegetation dying/removed; exposed soil is easily removed by wind/water as there's no roots to hold in place -> nutrients in soil are lost, making it unproductive -> ground becomes sandy, dusty or bare rock.
54
New cards
What are the main causes of desertification?
- Climate Change { rainfall + temperatures }
- Human Activities { removal of fuel wood + overgrazing + over-cultivation + population growth}
- Human Activities { removal of fuel wood + overgrazing + over-cultivation + population growth}
55
New cards
How is climate change a cause of desertification?
rainfall: climate change expected to reduce rainfall in areas that are dry; less rain means less water available for plant growth so plants die
temperatures: global temperatures increasing so higher temperatures cause evaporation from land making the soil drier, so plants struggle growing
temperatures: global temperatures increasing so higher temperatures cause evaporation from land making the soil drier, so plants struggle growing
56
New cards
How are human activities causing desertification?
removal of fuel wood: removal of trees leaves soil exposed
overgrazing: too much cattle, plants eaten faster than they can re-grow; trampling by animals erodes soil
over-cultivation: crops continually planted in same area, all the nutrients in soil are used up so plants cannot be grown in those areas
population growth: more people, pressures land, more deforestation (e.g. for firewood), more overgrazing and more over-cultivation.
overgrazing: too much cattle, plants eaten faster than they can re-grow; trampling by animals erodes soil
over-cultivation: crops continually planted in same area, all the nutrients in soil are used up so plants cannot be grown in those areas
population growth: more people, pressures land, more deforestation (e.g. for firewood), more overgrazing and more over-cultivation.
57
New cards
How can a country reduce desertification?
- water management
- tree planting
- soil management
- appropriate technology
- tree planting
- soil management
- appropriate technology
58
New cards
How can water management reduce the risk of desertification?
crops that need little water reduces water use -> drip irrigation on crops instead of surface irrigation means soil isn't eroded by water being added all at once
59
New cards
How can tree planting reduce the risk of desertification?
- trees act as windbreaks, reducing wind erosion
- trees stabilise sand preventing desert from encroaching on farm land
- growing trees amongst crops protects them and soil by providing shade, reducing temperatures and evaporation rates
- trees stabilise sand preventing desert from encroaching on farm land
- growing trees amongst crops protects them and soil by providing shade, reducing temperatures and evaporation rates
60
New cards
How can soil management reduce the risk of desertification?
- leaving areas of land to rest in between grazing/planting recovers nutrients
- rotating crops that take different nutrients from soil prevents same nutrients being continually removed
- compost used to add extra nutrients to soil
- rotating crops that take different nutrients from soil prevents same nutrients being continually removed
- compost used to add extra nutrients to soil
61
New cards
How can appropriate technology reduce the risk of desertification?
- sand fences (barriers trapping windblown sand) or terraces constructed stabilising soil + reducing erosion
- rate of deforestation reduced by using solar cookers, uses the sun's energy to heat food -> cheap + easy to make not requiring fuel wood
- rate of deforestation reduced by using solar cookers, uses the sun's energy to heat food -> cheap + easy to make not requiring fuel wood