Hematology/Chem/Cytology
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Inc PCV, Inc TP
Dehydration
Dec PCV, Dec TP
Whole blood loss, fluid therapy
Decrease PCV, Normal TP
Hemolysis, EPO/bone marrow suppression
Decrease PCV, Increase TP
Anemia of chronic disease/inflammation
3 pathophysiologic mechanisms of anemia
o Blood loss
o Hemolysis (anaplasmosis, mycoplasma hemolamae, clostridium hemolyticum, copper toxicity)
o Decreased production (Johne's, lymphoma, chronic BVDV, iron/Cu deficiencies, chronic renal failure
List and be able to identify morphologic changes in RBCs indicative of a regenerative response on a blood smear.
Reticulocytes, basophilic stippling, howell-jolly bodies, nRBC
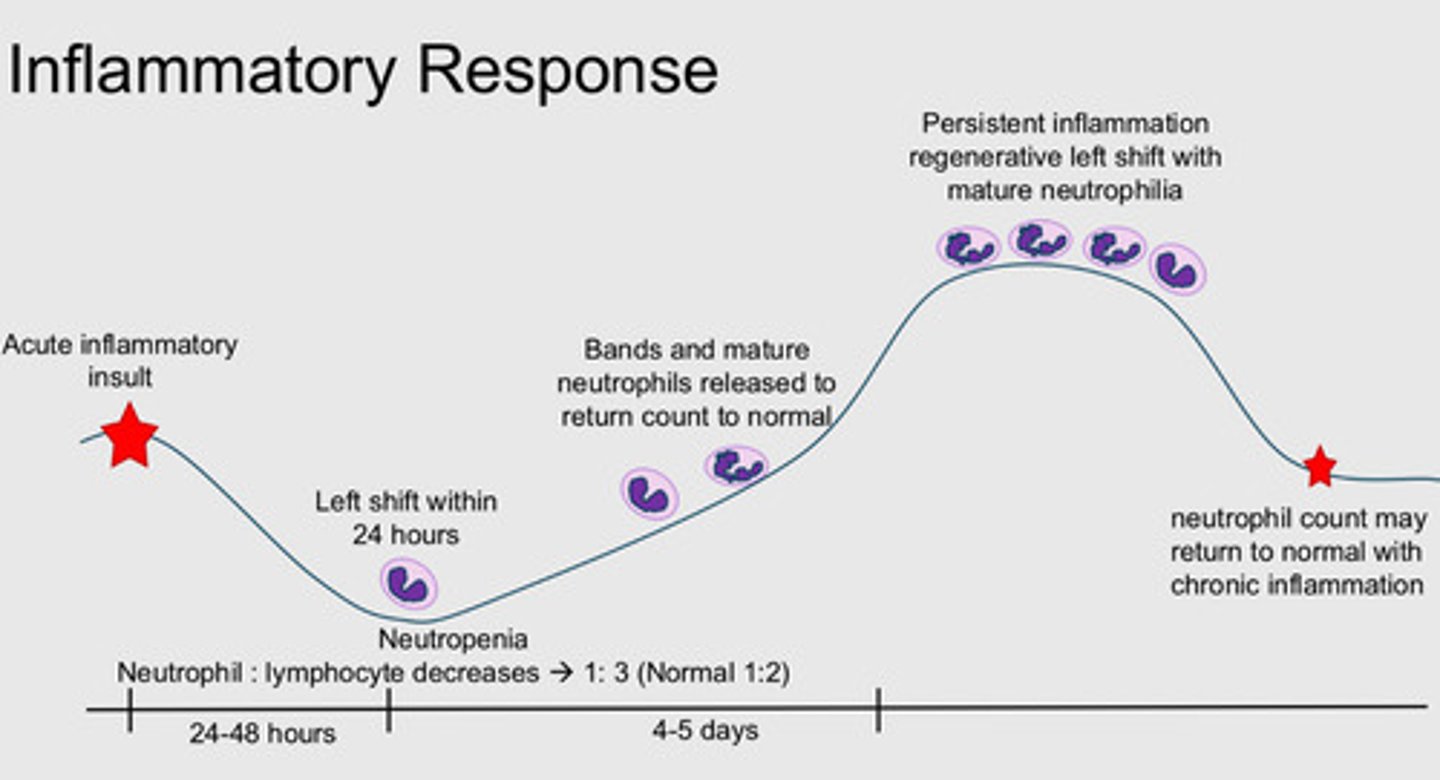
Explain how the neutrophil count changes following an inflammatory stimulus.
Explain glucose regulation in ruminants
carbohydrates must go through the rumen process (VFA —> proprionate —> glucose) = no postprandial hyperglycemia. Rarely see hypoglycemia, and if you do PSS should be high on differential list
Why are camelids highly susceptible to hyperglycemia?
Insulin resistant in peripheral tissues (down regulation of insulin receptors). There is also a risk with use of corticosteroids.
Why do we need to be careful when correcting hypoglycemia in camelids?
because it may result in dehydration, elevated Na+, and hyperosmolar syndrome
AG
AG (estimate of unmeasured anions such as ketones or lactate) = (Na+K)-(Cl+HCO3)
SID
SID (acid base status) = (Na+K) - Cl
What does it mean when SID is increased?
hypochloremic, hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis
What does it mean when AG is increased and SID is decreased?
Metabolic acidosis
Liver leakage enzymes
o SDH — volatile and unstable enzyme and expensive so is not used regularly in clin path anymore
o AST — hepatocellular enzyme, not very specific (muscle, blood draw issues)
o GLDH — specific for liver, good at showing leakage or disease with the tissue
Cholestatic enzymes
GGT — good for chronic inflammation, elevated in colostrum so calves will have a higher value
Albumin in ruminates
changes are not rapid, takes a long time to correct, usually will be low in chronic hepatic disease. Globulin will also be high in chronic inflammation (think abscess!)
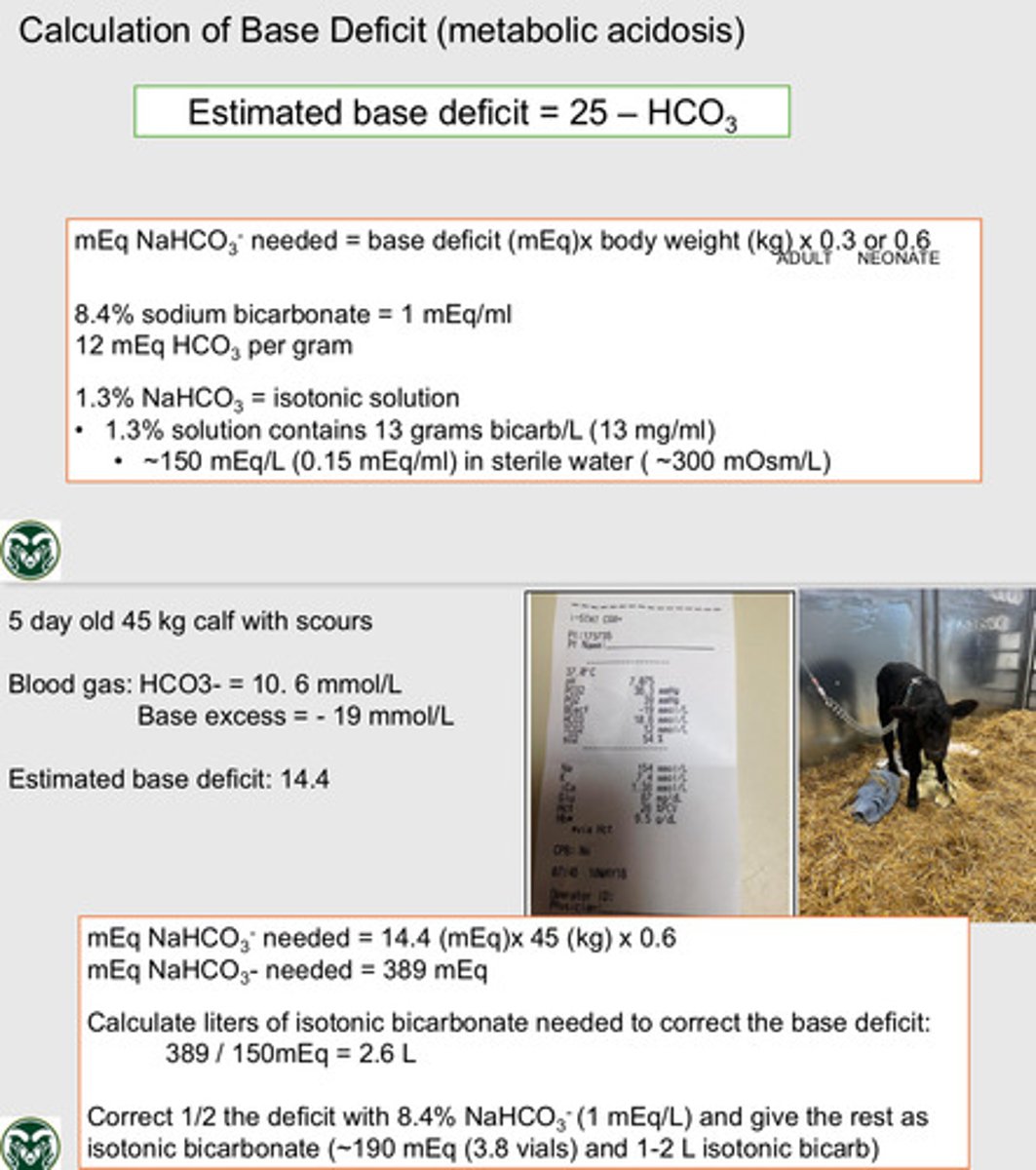
KNOW HOW TO CALC AND CORRECT BICARB DEFICIT
Clostridial spp
o GI bacterial overgrowth in ruminants is commonly associated with clostridial spp
o Gram positive rods (purple)
o C diff — enteritis
o C perf type A — abdomasocentesis in left lateral recumbency, sterility is crucial to prevent enteritis
Rumen fluid pH
o High pH = high forage diet
o Low pH = grain
Indications for abdominocentesis
o Rule in/out peritonitis, rule in lymphosarcoma, confirm intraabdominal blood loss, strangulating lesion, uroperitoneum, fever of unknown origin
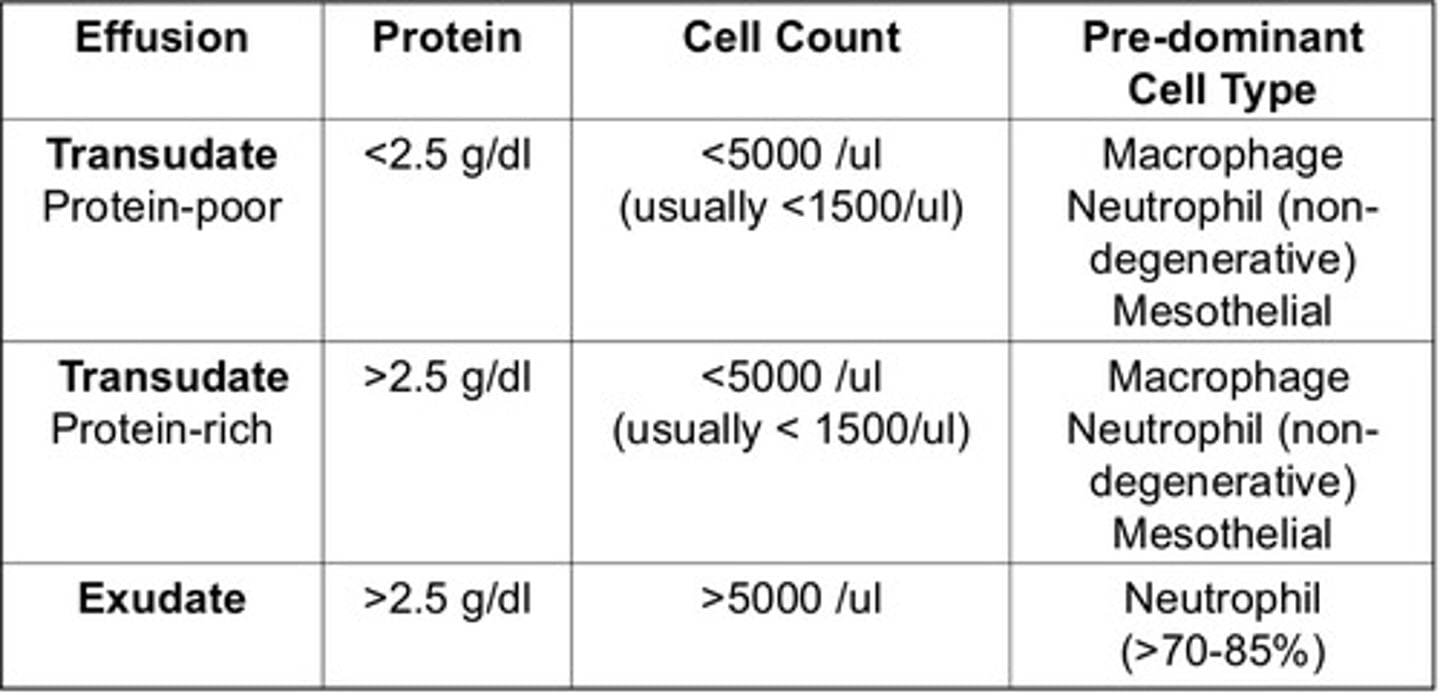
Know the abdominal effusion chart
Indication of visceral lymphoma on abdominocentesis
lymphocytes > 20% that are blast like, ddx chronic peritonitis
CSF collection sites
AO, LS intervertebral space (need to make sure your needle is angled cranially, different from other species)
CSF DDX
If you see eosinophils, worry about P tenius (in areas with high white tail deer populations)
Listeria = monocytes and lymphocytes
Lymphoma = lymphocytes, not very exfoliative like they are in the abdomen
Neutrophils = s dublin
Thoracocentesis DDX
pleuropneumonia, BRSV (ruptured bullae), trauma, neoplasia
Thoracocentesis technique
o AVOID CAUDAL ASPECT OF THE RIB (VAN runs here)
o Must use a one-way valve to prevent risk of iatrogenic pneumothorax