Final exam human resources management
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
148 Terms
Trend analysis
Forecast labor demand based on an organizational index such as sales
Management forecasts
Opinions (judgments) of supervisors, department managers, experts, or others knowledgeable about the organization’s future employment needs
Delphi technique
Attempts to decrease the
subjectivity of forecasts by soliciting and summarizing the judgments of a preselected group of individuals
Skill inventories
Files of personnel education, experience, interests, and skills that
allow managers to quickly match job openings with employee backgrounds
Replacement charts
Listings of current jobholders and people who are potential replacements if an opening occurs
Succession Planning
Process of identifying, developing, and tracking key individuals for executive positions
Human Capital Readiness
Evaluating the availability of critical
talent in a company and comparing it to
the organization's supply. Any difference between the number and quality of employees needed and employees available represents a gap that must be filled
Strategic planning process
The process of defining organizational strategy, or direction, and allocating resources toward its achievement
Employment Equity Act
It’s a Federal legislation that applies to 1) all federally regulated employers with 100 or more employees, or 2) any organization with more than 100
employees who do more than $1 million
dollar worth of business with the federal
government (i.e., Federal Contractors
Program
Who are the designated groups?
Women, indigenous people, people with disabilities and minorities
Slurs, jokes, written or verbal abuse, threats, and touching without consent, are all examples of ________
Sexual harassment
Joba Analysis
The process of collecting information about jobs by determining the duties, tasks, or activities of jobs
_______________ Identifies the human attributes (knowledge,
skills, abilities) required to perform the job
Job analysis
Job description
A statement of the tasks, duties, and responsibilities of a job to be performed
Job specification
A statement of the needed knowledge, skills, and abilities of the person who is to perform the job
Job design
An outgrowth of job analysis that improves jobs through technological and human considerations to enhance an organization efficiency and employee job satisfaction
Job enrichment
Enhancing a job by adding more meaningful
tasks and duties to make the work more
rewarding or satisfying
Job characteristics model
Job design theory that purports that three psychological states (experiencing meaningfulness of the work performed, responsibility for work outcomes, and knowledge of the results of the work performed) of a jobholder result in improved work performance, internal motivation, and lower absenteeism and turnover
What are the 5 core job dimensions of the job characteristics model?
Skill variety, task identity, task significance, autonomy and feedback
Informing applicants about all aspects of the job, including both its desirable and undesirable facets is the definition of_________
Realistic job previews
__________ is an equation used measures how well a candidate meet the job requirements
Quality-to-fill statistics
The number of days from when a job opening is approved to the date the candidate is selected is known for _______
Time-to-fill
Yield ratio
The percentage of applicants from a recruitment source that make it to the next stage in the selection process
Targeted recruitment
Recruitment strategies that meet diversity objectives through outreach to underused groups to maintain diverse representation in an applicant pool
What is the goal of selection?
To predict who will succeed and hire them!
When you accurate predict when a person would not have been able to succeed on the job you say that you had a ____________ hit
True negative
When you are able to accurately predict when a person is successful on the job you say that you had a _________ hit
True positive
When you make a mistake in predictions and the person would have succeeded on the job you say that you had a __________ hit
False negative
When you make a mistake in hiring somebody and the person fails on the job you said that you had a __________ hit
False positive
____________ are completed by candidates for employers to seek
basic information
Application form/blank
____________ are a method for quantitatively combining information
from application blank items by assigning weights that reflect each item’s value in predicting job success
Weighted Application Blanks (WAB)
________ are A pre-selection questionnaire that requires applicants
to provide detailed job related information concerning their personal background and life experiences
Biographical information Blank (BIBs)
The intent of the __________ is to introduce the applicant to the organization through a brief, written self-description
Résume
What are the phases of the Strategic model of Training?
Phase 1: needs assessment, phase 2: design, phase 3:implementation, phase 4: evaluation
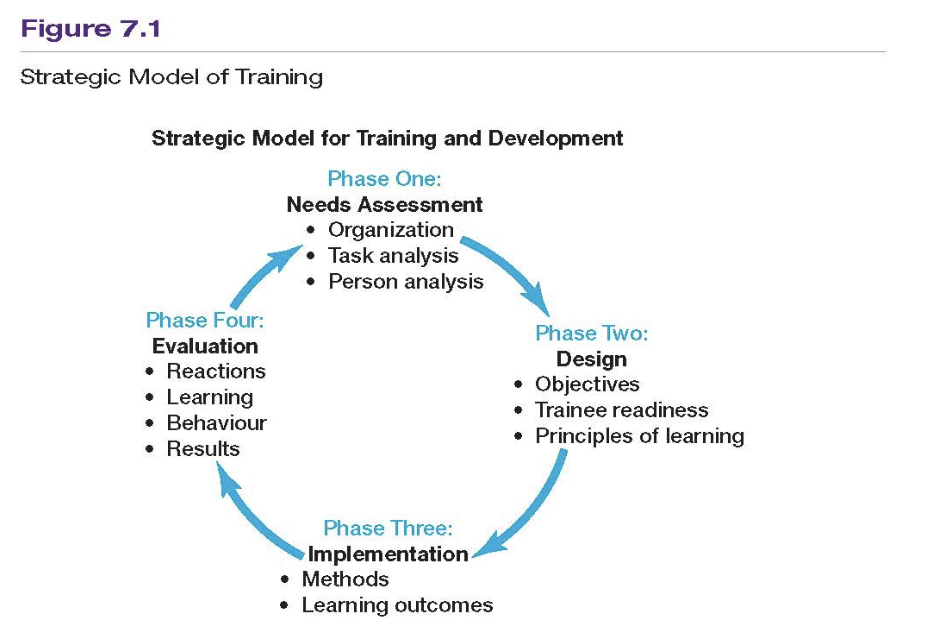
Phase 1 of needs assessment consists of 3 parts, what are the 3 parts?
Organization analysis, task analysis and person analysis
Name at least 5 characteristics of the principles of learning
Goals setting; meaningfulness of presentation, modeling, individual learning differences, active practice and repetition, experimental learning, whole-versus-part learning, masses, distributed and continuous learning, feedback and reinforcement
What are the two main purposes of performance appraisal ?
Developmental and administrative
Strategic relevance
Individual standards directly relate to strategic goals
Criterion deficiency
Standards capture all an individual’s contributions
Criterion contamination
Performance capability is not reduced by external factors
Reliability
Standards are quantifiable, measurable, and stable
The _______is when people generalize a positive trait across all aspects of performance
Halo effect
________________ is when all employees are rated average or close to average
Error of central tendency
___________ is when the appraiser tends to give employees either unusually high (leniency) or unusually low (strictness) ratings
Leniency or strictness error
__________ happens when the evaluation is based largely on the employee’s most recent behavior rather than throughout the evaluation period
Temporal (recency) error
When an employee's evaluation is biased either upward or downward because of comparison with another employee just previously evaluated is known as_________
Contrast error
When an appraiser inflates the evaluation of an employee because of a mutual personal connection is called __________
Similar-to-me error
The _______ is used by managers to rate employees according to a scale of characteristics
Graphic rating scales
__________ are based on comparison with (better than, equal to, or worse than) a standard
Mixed standard scales
when employees choose from statements designed
to distinguish between successful and unsuccessful performance you can say that they are engaging on ___________
Forced choice
When employees write long statement, they are engaging in ________
Essays
“The employee arrives at work on time; 1-Never, 2-sometimes, 3-Often, 4-Fairly often, 5-always” this is an example of _______
Behavioral checklist
The ________ is a scale that assesses the performance of new employees or trainees based on well-defined behavioral patterns
Behaviorally anchored rating scale (BARS)
Sales people - sales volume, production workers -number of units produced, executives- company profits, are all examples of ________
Productivity measures
The process that rates the performance of employees based on their achievement of goals set mutually by them and their manager is known as ________
Management by objectives (MBO)
What are the 4 categories that the Balance Scorecard focuses on?
Financial, customer, process and learning measures
Explain the 360- degree evaluation
Tools to help employees improve performance by using performance
information gathered from many sources: Superiors, Peers, Customers, Direct reports, and Employees. It’s all anonymous and most useful when used for development and not for administrative purposes
Feed-forward interview
Using an interview protocol that focuses on the positive aspects of
employee experiences, instead of focusing on “what is wrong” it helps to 1.Elicit a success story, 2.Uncover the underlying success factors, 3.Extrapolate the past into the future
When it is focused on the employee wages and salaries, incentives, bonuses, and commissions is known as ________
Direct compensation
_________ comprises the many benefits supplied by employers
Indirect compensation
Nonfinancial compensation
Includes employee recognition programs, rewarding jobs, organizational support, work environment, and flexible work hours
___________ captures all three components, plus other aspects of
organizational rewards, including career advancement/developmental
opportunities, recognition, work-life balance, and job security
Total rewards
_________ is the compensation of employees in a way that
enhances motivation and growth while at the same time aligning their efforts with the objectives, philosophies, and culture of the organization
Strategic compensation
Expectancy theory
The idea that Employees should exert greater work effort if they have reason to expect that it will result in a reward that is valued
Equity theory
Explains how people respond to situations in which they feel they
have received less [or more] than they deserve
Compensation strategy of an organization; the worth of the job; the employee’s relative worth; and the employer’s ability to pay is an example of _______________ affecting the pay mix
Internal factors
The conditions of the labour market; area wage rates, cost of living, collective bargaining, and legal requirements are all examples of __________ affecting the pay mix
External factors
Job evaluation
A systematic process of determining the relative worth of jobs to establish which jobs should be paid more than others within an
organization
Job ranking system
The simplest and oldest system of job evaluation by which jobs are
arrayed based on their relative worth
Job classification system
A system of job evaluation in which jobs are classified and
grouped according to a series of predetermined wage grades
Point system
A quantitative job evaluation procedure that determines the relative value of a job by the total points assigned to it
piece work, standard hour plan, bonuses, merit pay, lump-sum merit pay, incentive awards, sales incentives, incentives for professional employees and executive incentives are all examples of __________ plans
Individual
Team compensation, Scanlon plan, improshare are all examples of ________ plans
Group
Profit sharing, stock options, employee stock ownership plans (ESOPs) are all examples of _________ plans
Enterprise/organization
Flexible benefit plans
Benefits plans that enable individual
employees to choose the benefits that are best suited to their
needs
What are the 3 employee benefits required by the law ?
Canada and Quebec pension plan (CPP/QPP), Employment insurance (EI),Worker’s compensation insurance
Canada and Quebec pension plans (CPP/QPP)
Both plans require employers to match the contributions made by employees; Retirement pensions, disability benefits, and survivors’ benefits
Employment insurance (EI)
Payable to claimants who are
unemployed and are actively seeking employment; What about employees who resign from their jobs or who are
terminated for cause?
Workers’ compensation insurance
Insurance provided to workers to defray the loss of income and cost of treatment
resulting from work-related injuries or illness. The system is no fault
Healthcare benefits
Employers are under pressure to
include prescription drugs as well as dental, optical, and mental healthcare benefits
Payment for time not worked
Additional vacation time, personal use days, severance pay (payment depends on length of service), sick leave (most
employers offer short- and long-term disability plans)
Life insurance
Group life insurance is the
benefit most provided by an employer; it
provides financial security to the
dependents of the employee in case of the employee’s death
Pension plans
Used to supplement the
protection provided by government-sponsored programs
Contributory plan
Contributions are made jointly by employees and employers
Non-contributory plan
Contributions are made solely by the employer
Defined-benefit plan
The amount an employee is to receive on retirement is specifically set forth
Defined-contribution plan
Establishes the basis on which an employer will contribute to the pension fund
Vesting
A guarantee of accrued benefits to
participants at retirement age, regardless of their employment status at the time
Employee assistance programs
Services provided by employers to help workers cope with a wide variety of problems that interfere with the way they perform their jobs
occupational injury
Any cut, fracture, sprain, or amputation
resulting from a workplace accident or from an exposure involving
an accident in the work environment
Occupational illness
Any abnormal condition or disorder, other
than one resulting from an occupational injury, caused by exposure to environmental factors associated with employment (includes COVID-19)
Due diligence
Includes establishing a comprehensive
occupational health and safety management system; providing
competent supervision, training, and instruction; and taking every
reasonable precaution in the workplace for the health and safety of
workers
True or false: Workers have the right to refuse unsafe work without
fear of reprisal
True
Joint health and safety committee (JHSC)
The point of these joint committees is to establish a non- adversarial climate for creating safe and healthy workplaces
Workplace hazardous materials information systems include ________,______,_______
gas cylinders (for gases under pressure), corrosion (for corrosive damage to metals, as well as skins and eyes), skull and crossbones (can cause death or toxicity with short exposure to small amounts)
Eustress
Positive stress that accompanies
achievement and exhilaration
Distress
Harmful stress characterized by a
loss of feelings of security and adequacy
Burnout
The most severe stage of distress,
manifesting itself in depression, frustration, and loss of productivity
Common law of employment
The body of case law in which courts interpret employment contracts and the legal principles taken from those cases
employment equity legislation, pay equity
legislation, employment standards legislation) are all examples of _______
Statutory employment regulation