2.1 - Linear Motion - Theory
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Scalar Quantity
A quantity that has magnitude only. e.g. mass, time, speed, distance.
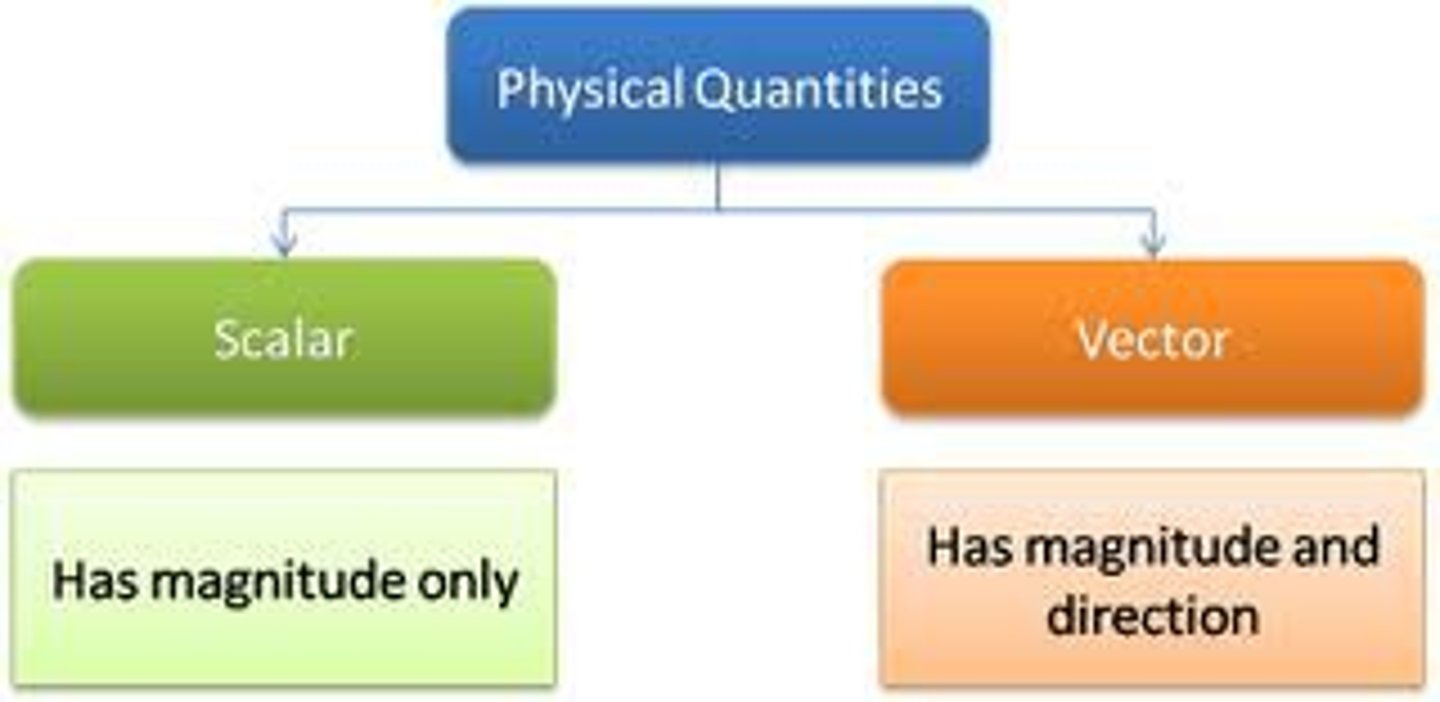
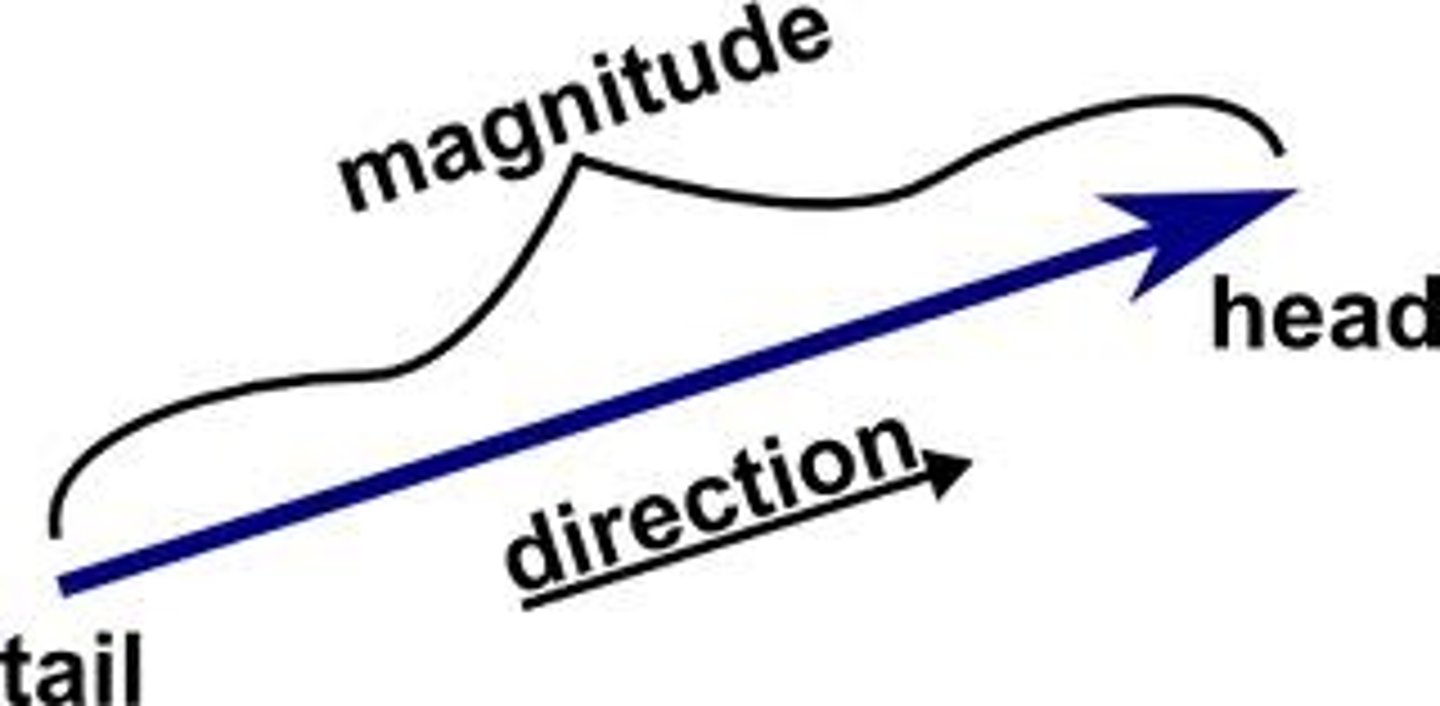
Vector Quantity
A quantity that has both magnitude and direction. e.g. force, weight, velocity, displacement.
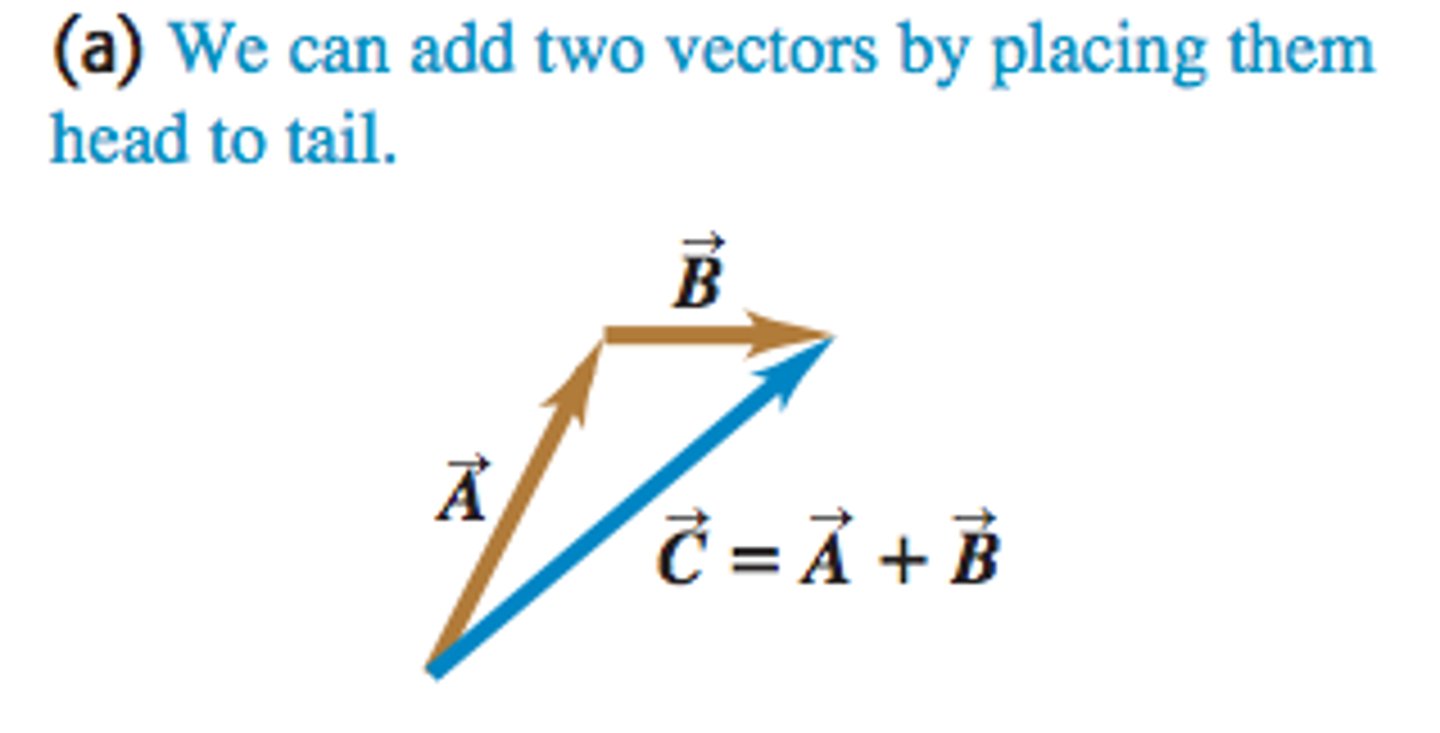
Triangle Law for Vector Addition
We can add two vectors by placing them head to tail.
(A→B) + (B→C) = A→C
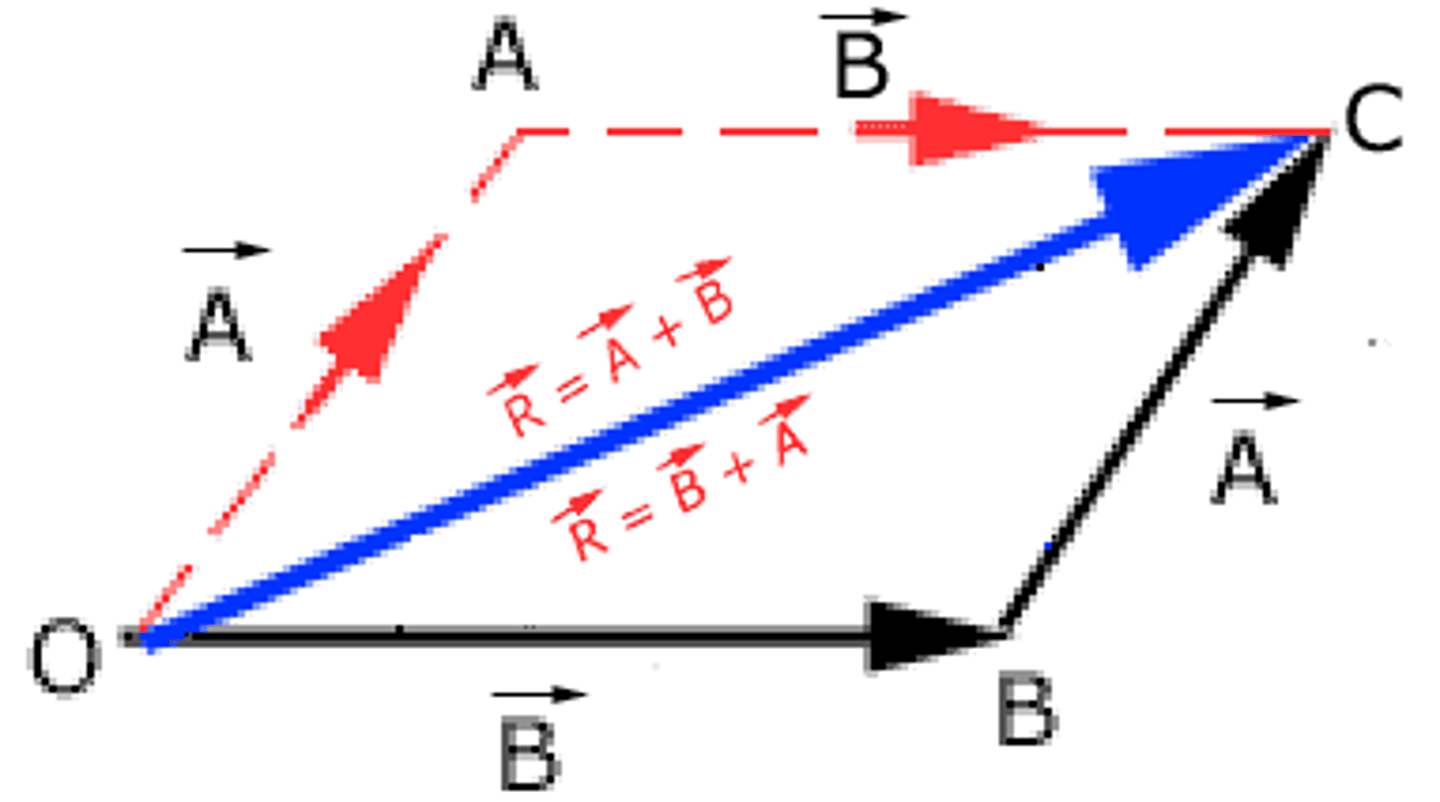
Parallelogram Law for Vector Addition
We can add two vectors by drawing a parallelogram (see image)
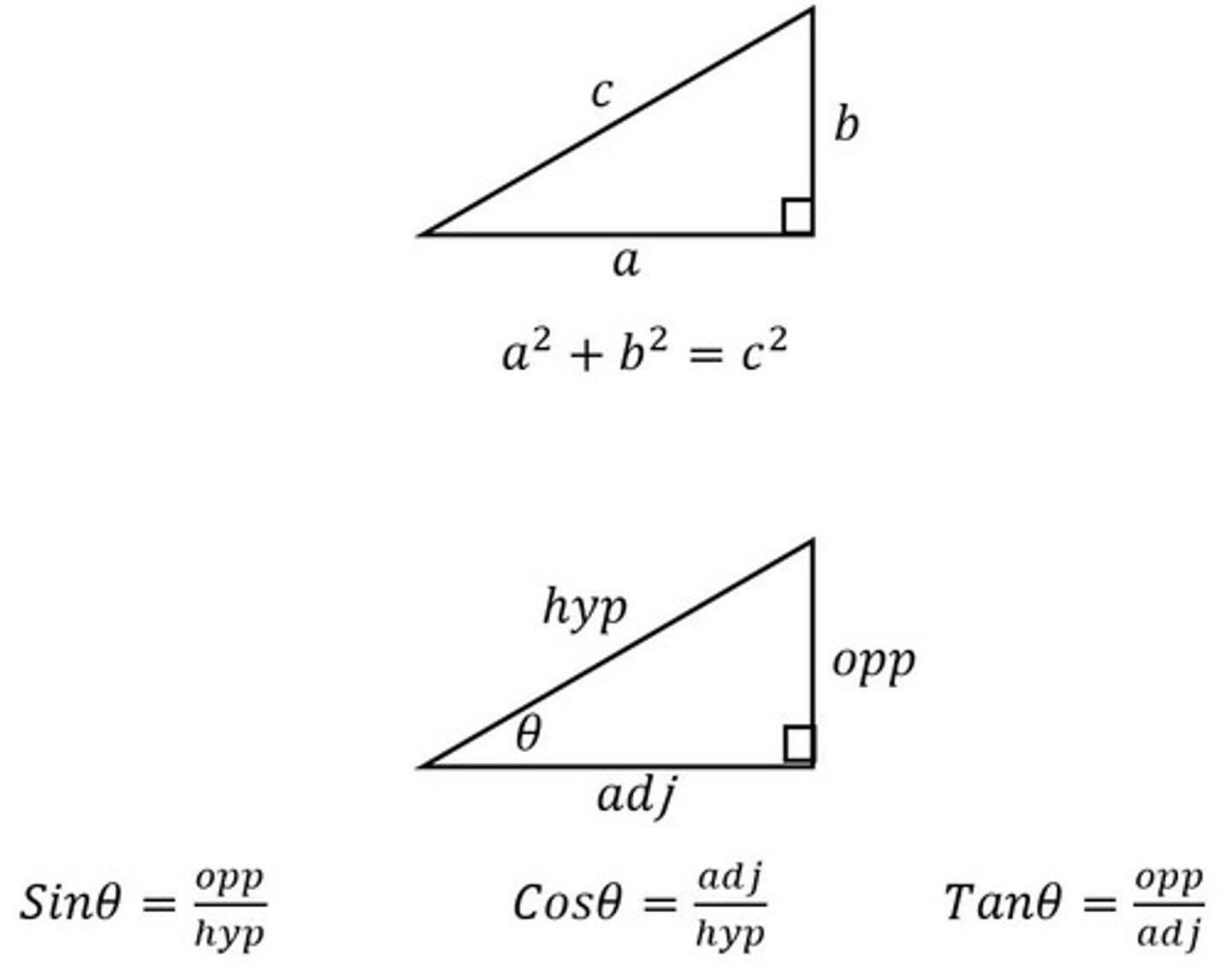
Equations needed to break a vector into its components parts
Pythagoras theorem
SOHCAHTOA
What does SI stand for?
International System of Units: a system of physical units (SI units) based on the metre, kilogram, second, ampere, kelvin, candela, and mole, together with a set of prefixes to indicate multiplication or division by a power of ten.

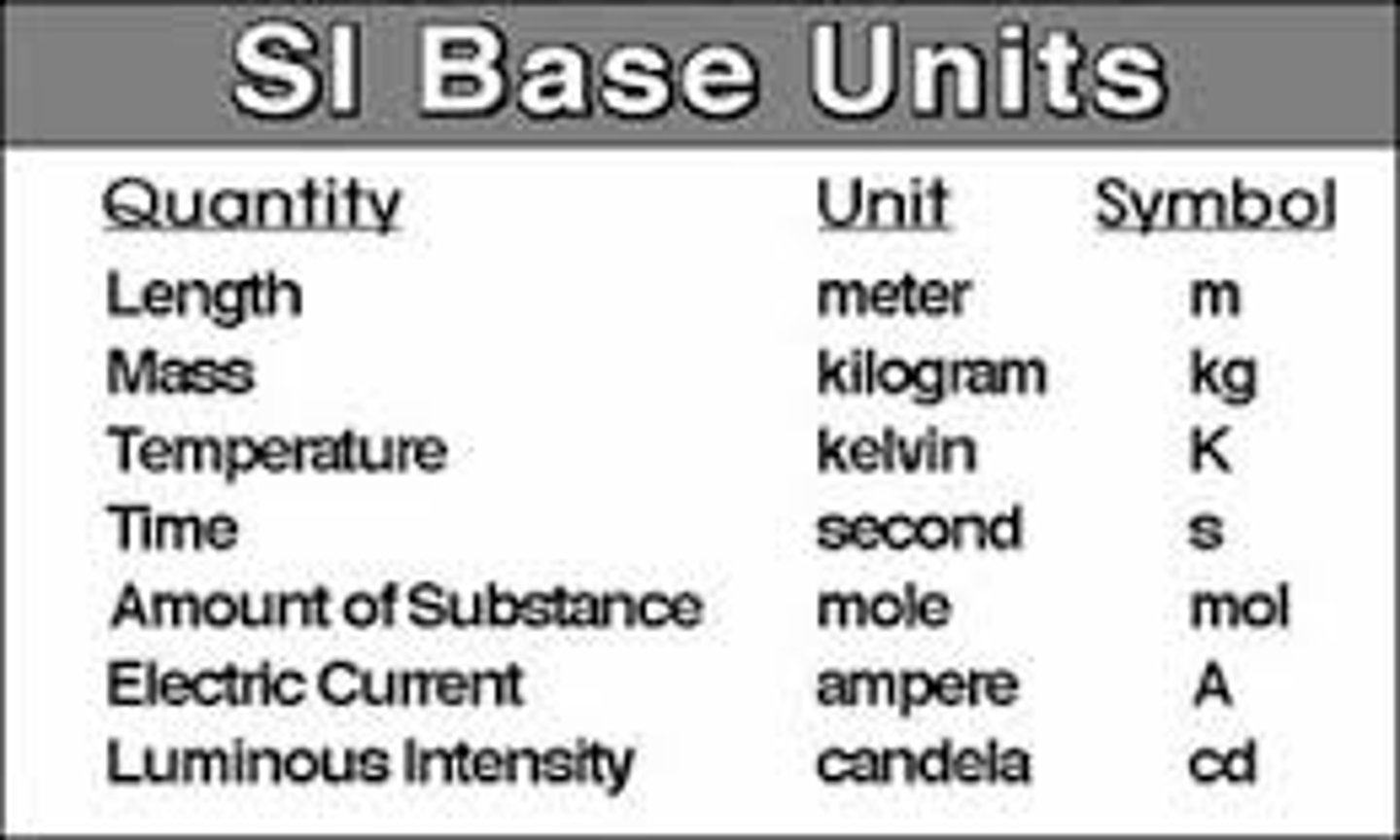
Name the seven SI units
Distance: Meters (m)
Time: Seconds (s)
Current: Ampere (A)
Temprature: Kelvin (ºC)
Particles of a Substance: Mole (mol)
Lumins intensity: Candela (cd)
Mass: Kilograms (Kg) Note Kilograms is the only SI unit with a prefix
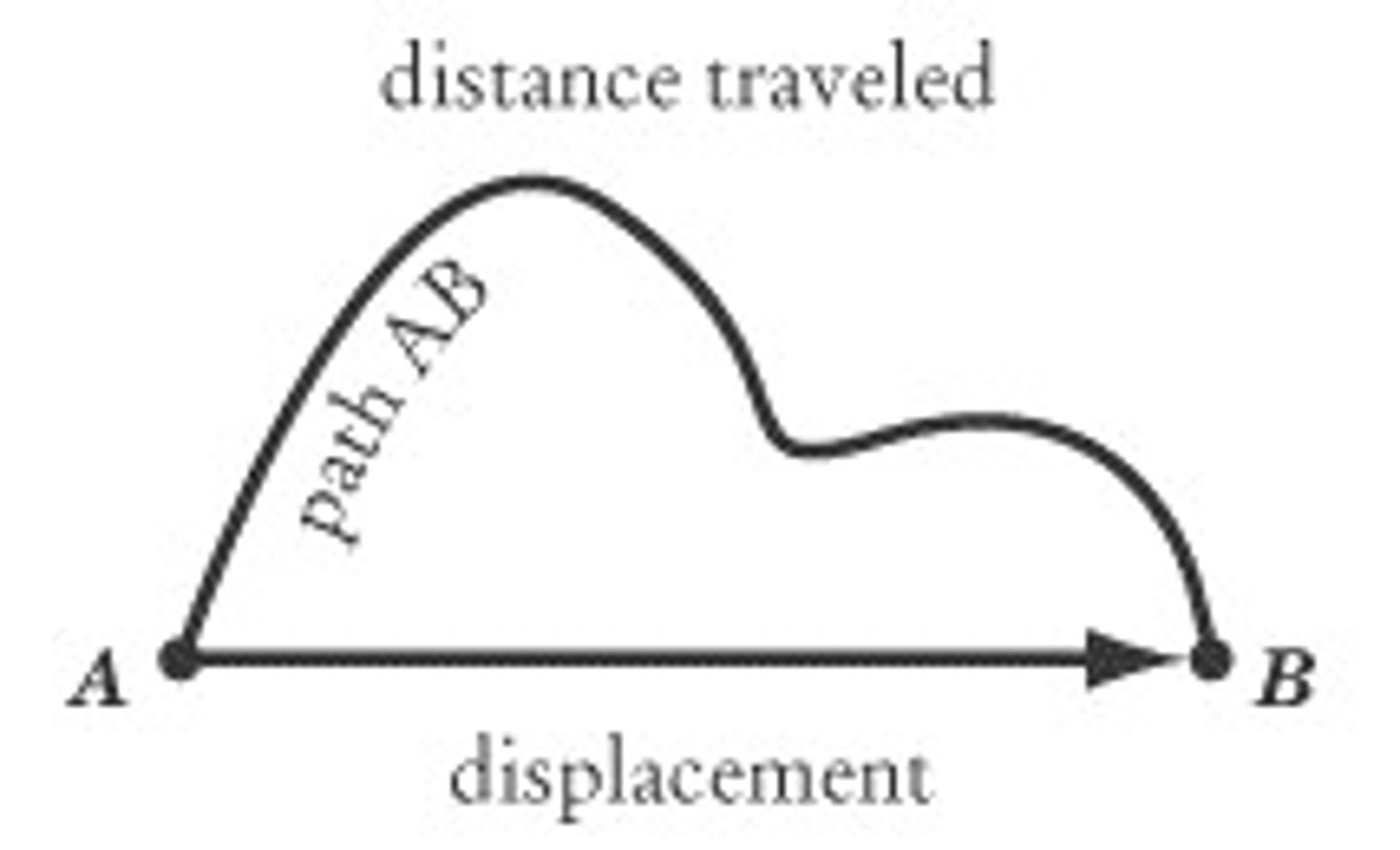
Distance
The total path taken between two points (m).
Scalar Quantity.
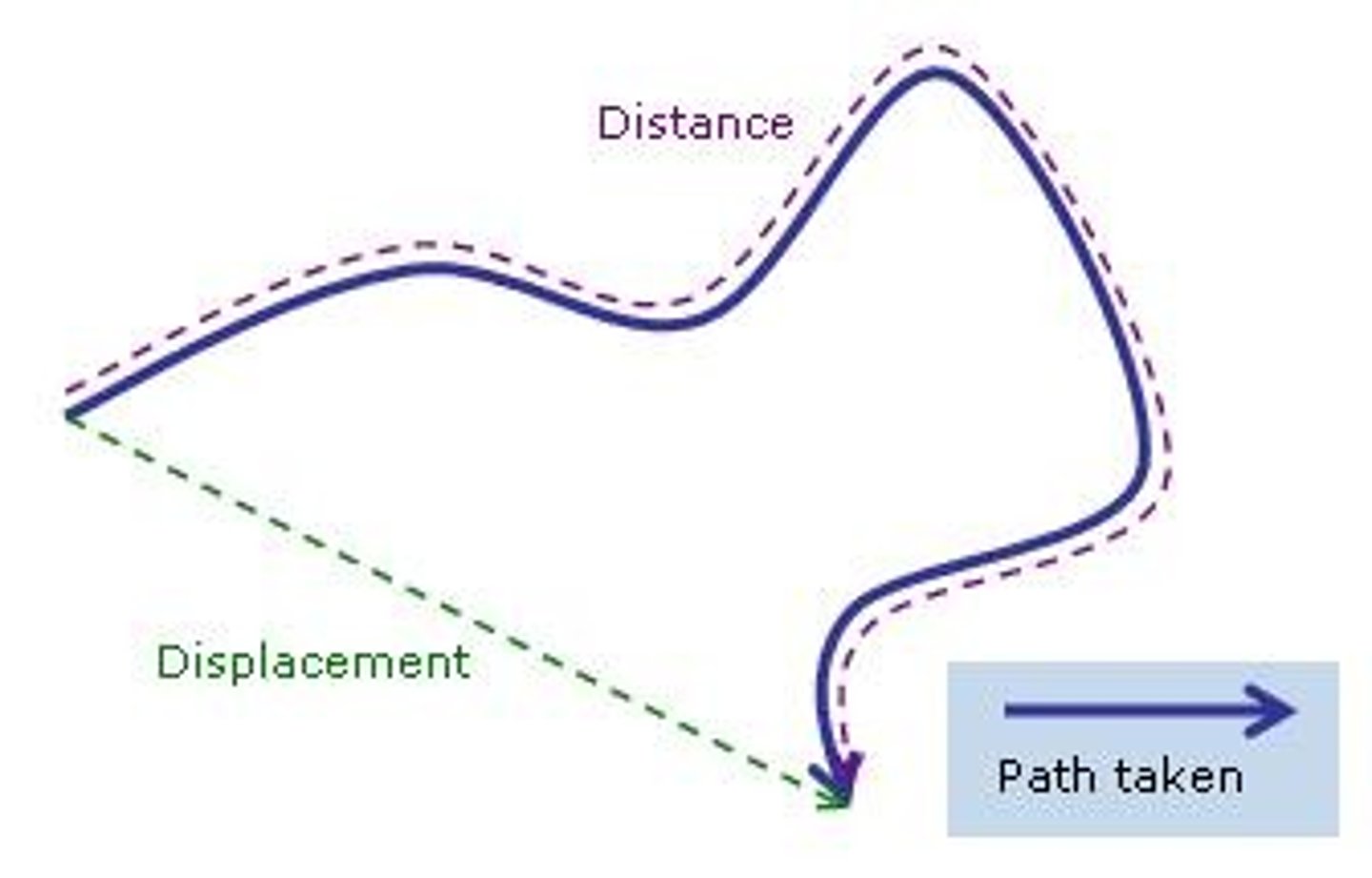
Displacement
The straight line distance between two points (m).
Vector Quantity.
Speed
The distance an object travels per unit of time (m/s)
Scalar Quantity.
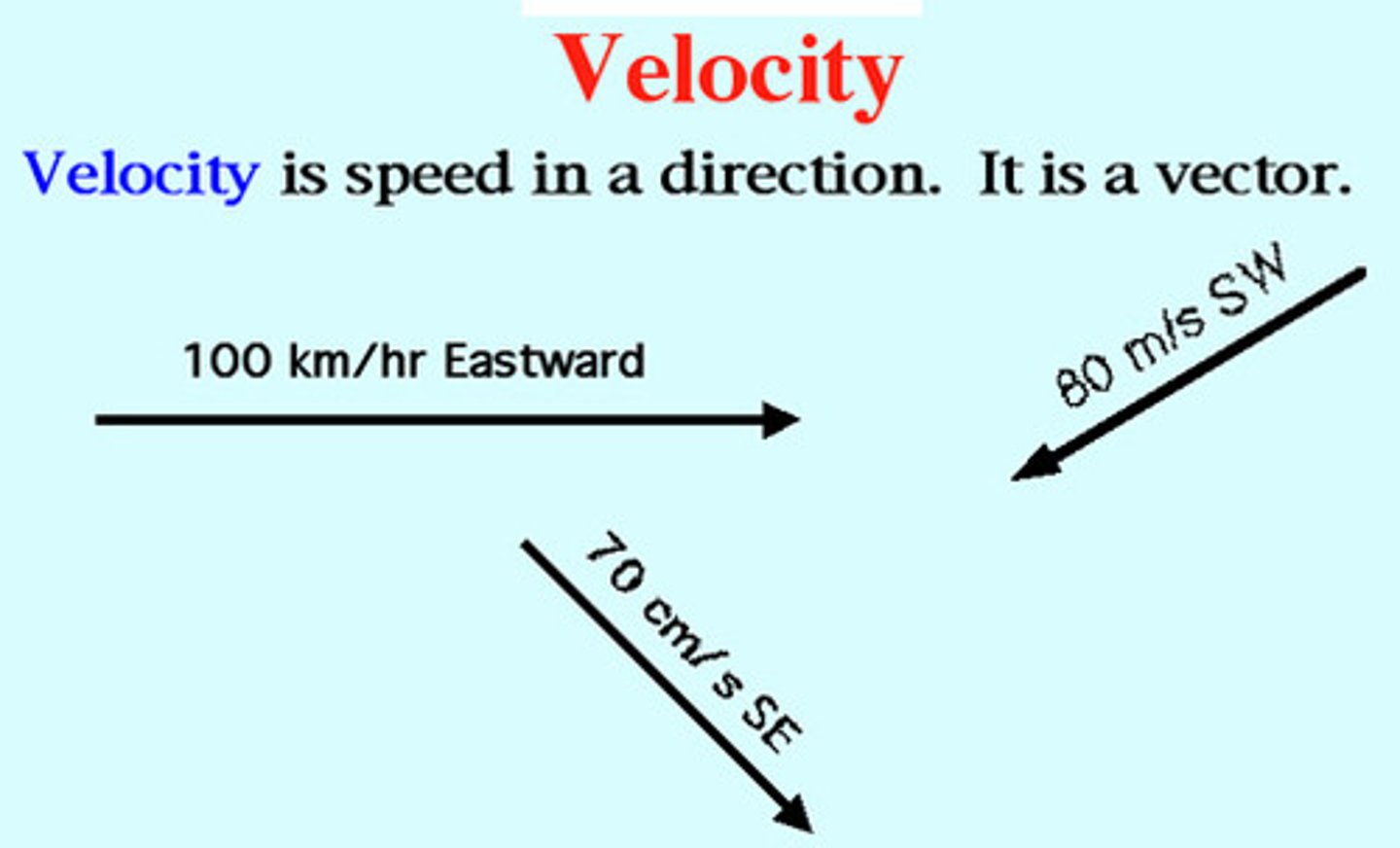
Velocity
Speed in a given direction (m/s)
Vector Quantity.
Acceleration
The rate of change of velocity (m/s^2)
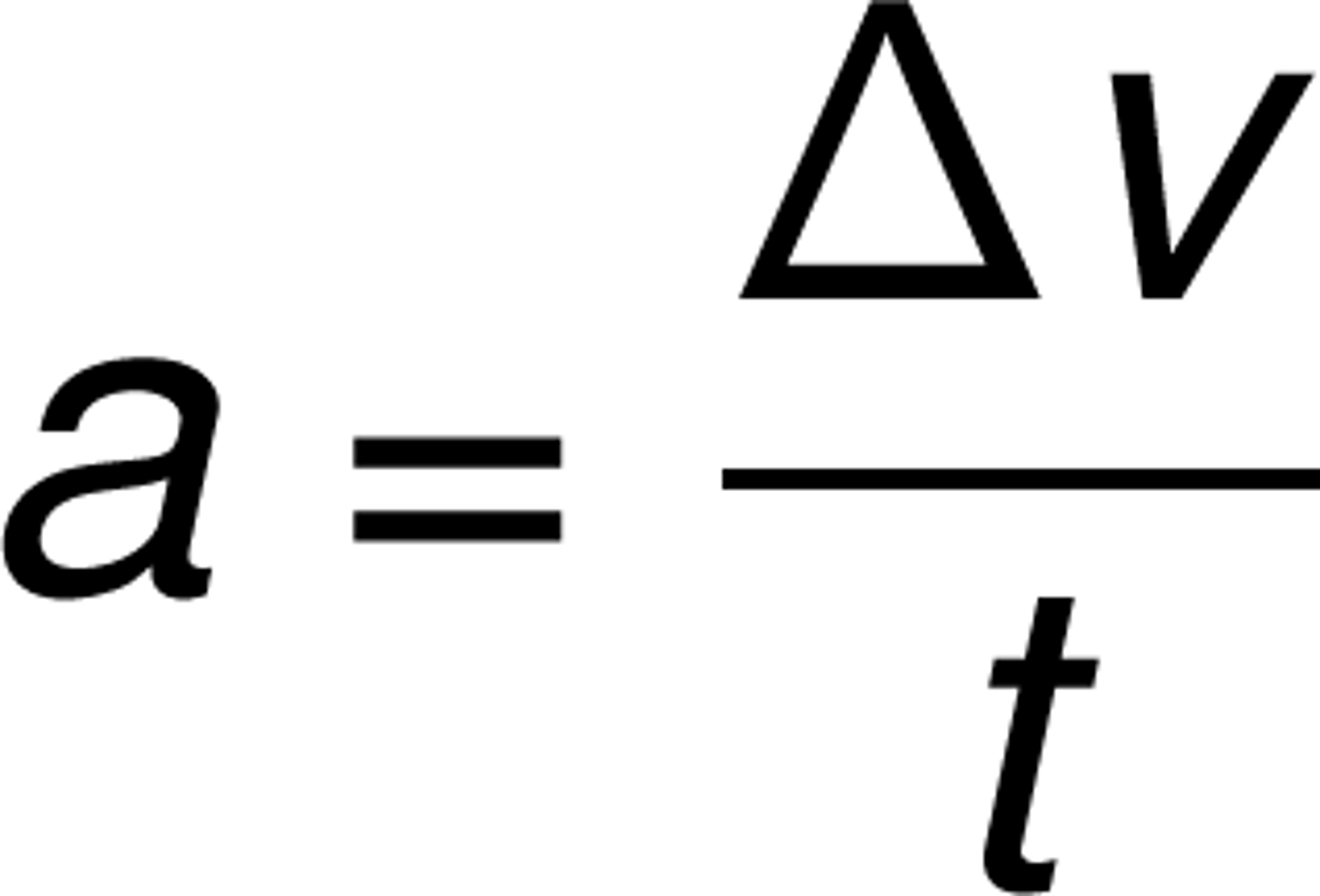
How could you demonstrate that objects fall with the same acceleration if their is no air resistance?
Using a vacuum pump. Remove air from the dropping tube. Drop a coin and a feather at the same time. They both should fall with the same acceleration.

Sketch a graph of displacement against time for a ball being thrown in the air and returning back to the thrower.
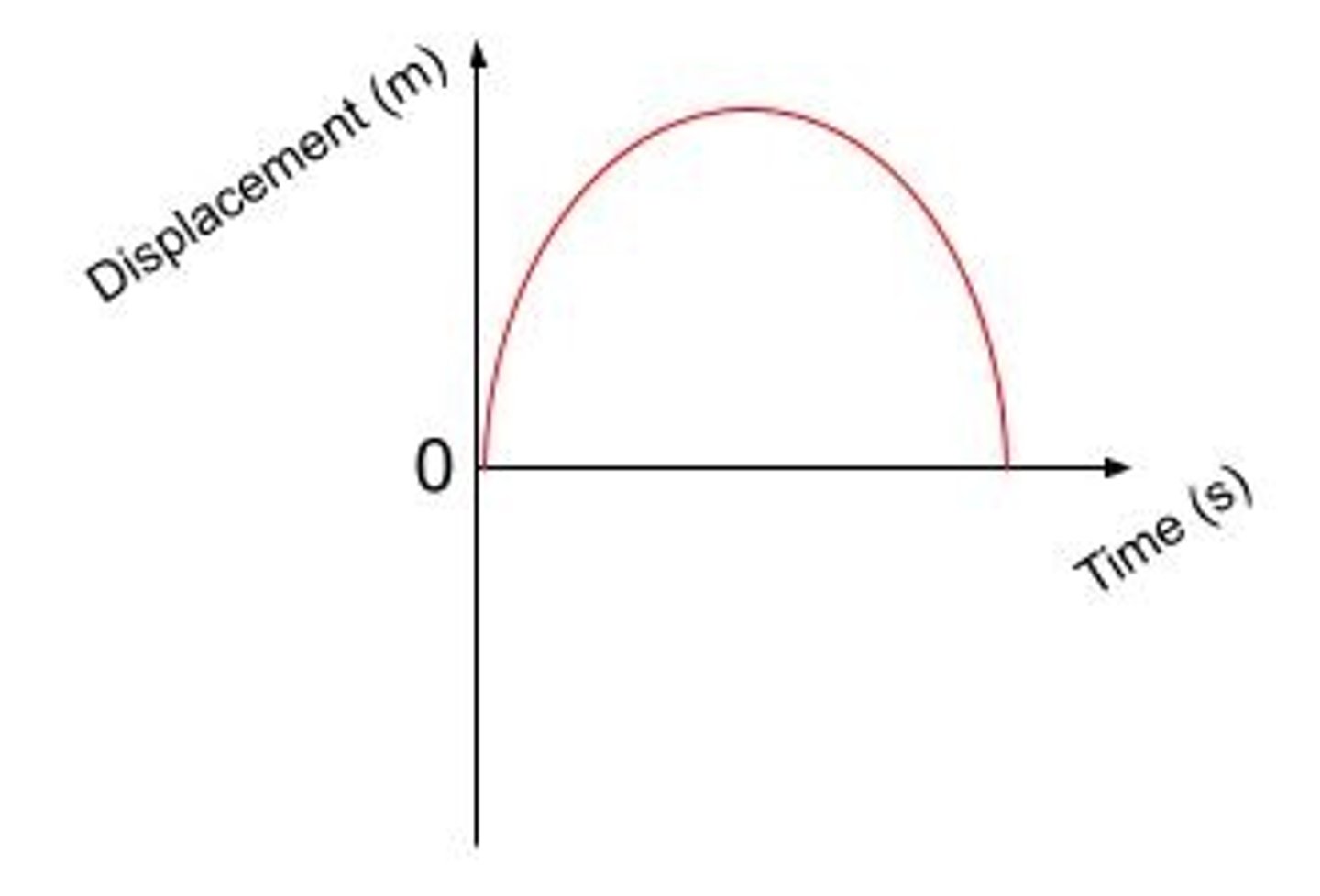
Sketch a graph of velocity against time for a ball being thrown into the air and returning back to the thrower.
Ball starts with velocity UPWARDS (hence positive value) and then goes to ZERO at the halfway point. Then has its maximum velocity DOWNWARDS (negative value) at the end.
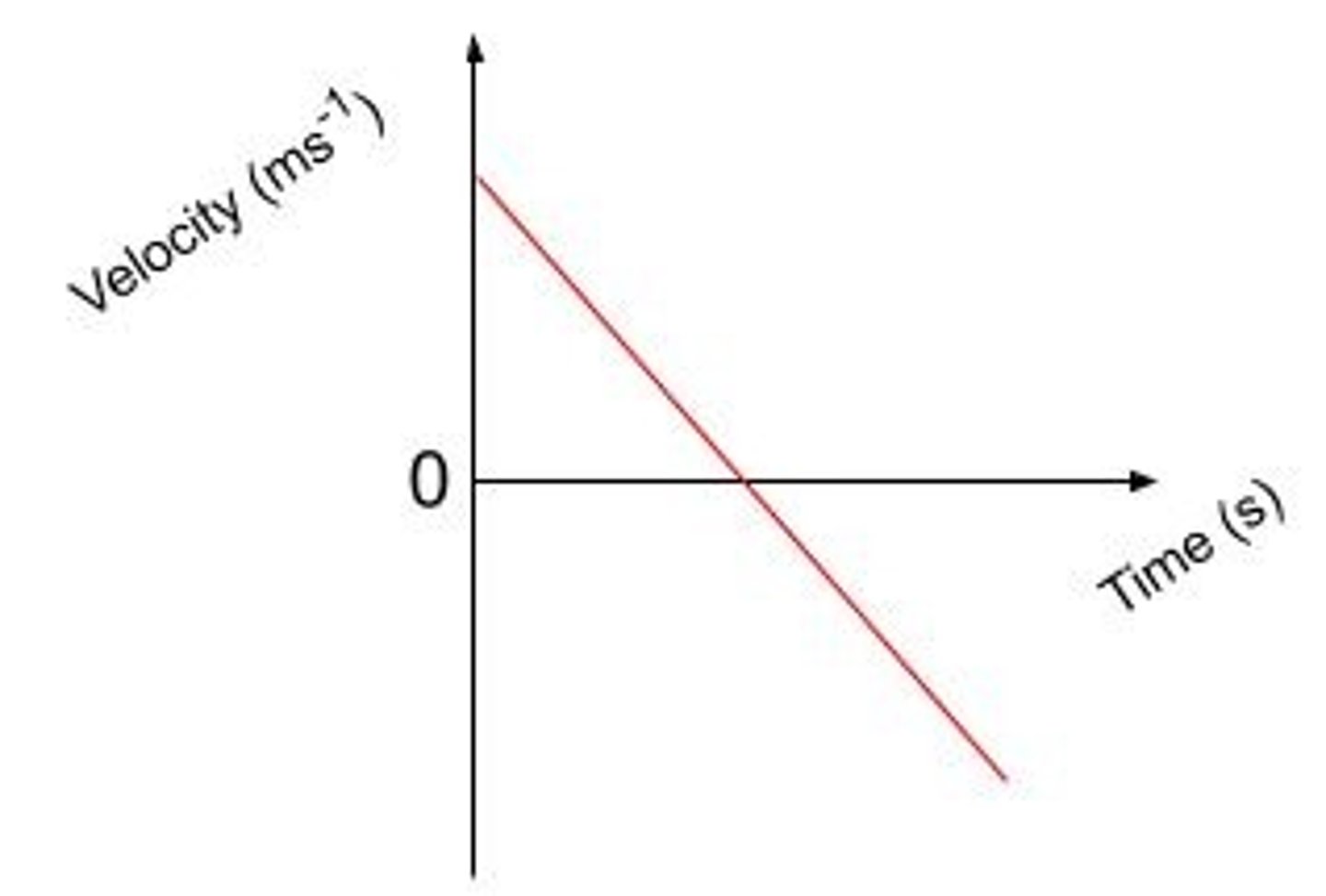
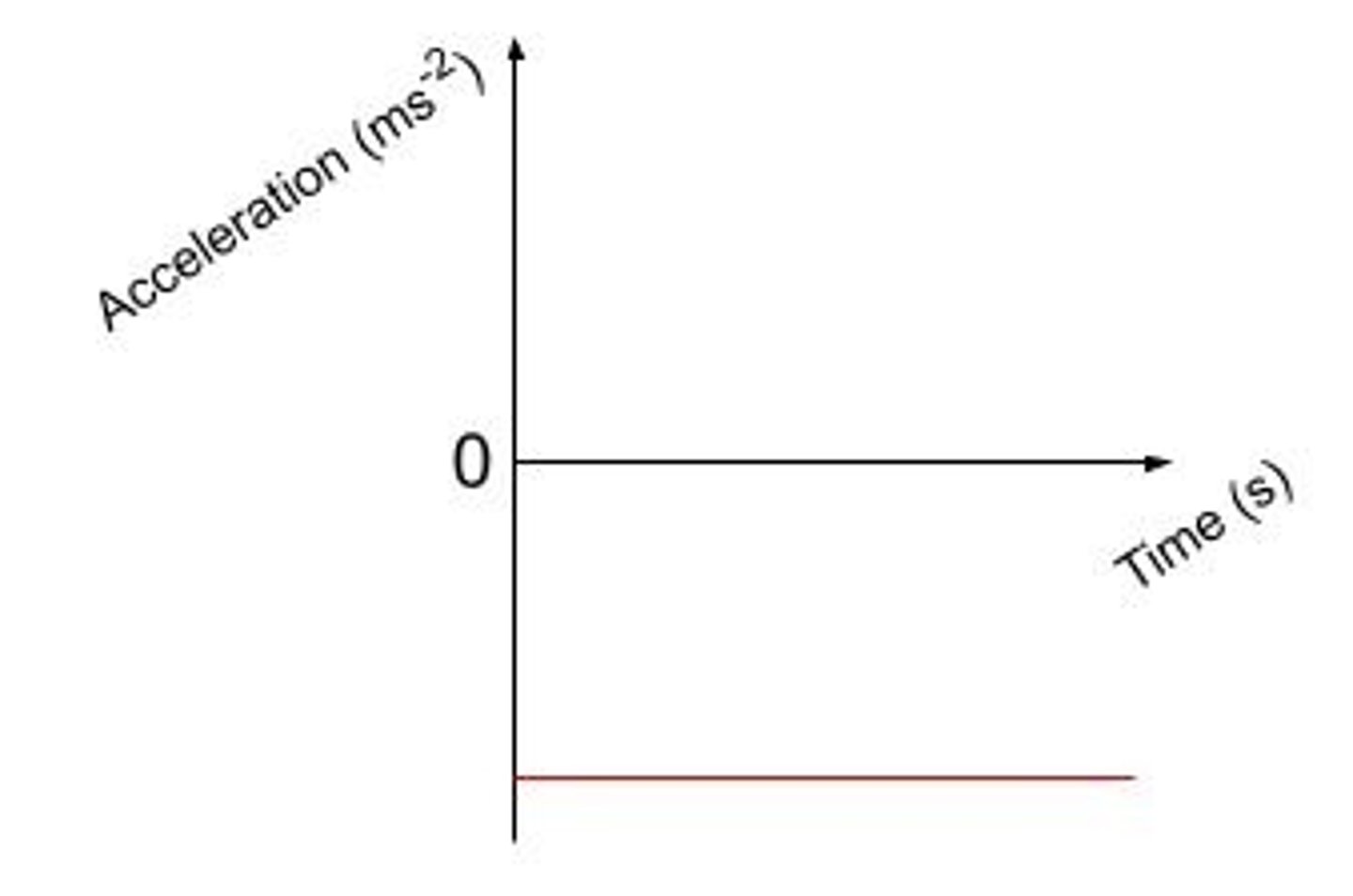
Sketch a graph of acceleration against time for a ball being thrown into the air and returning back to the thrower.
Always at -9.8 m/s^2 as the only force acting on the ball is gravitational.
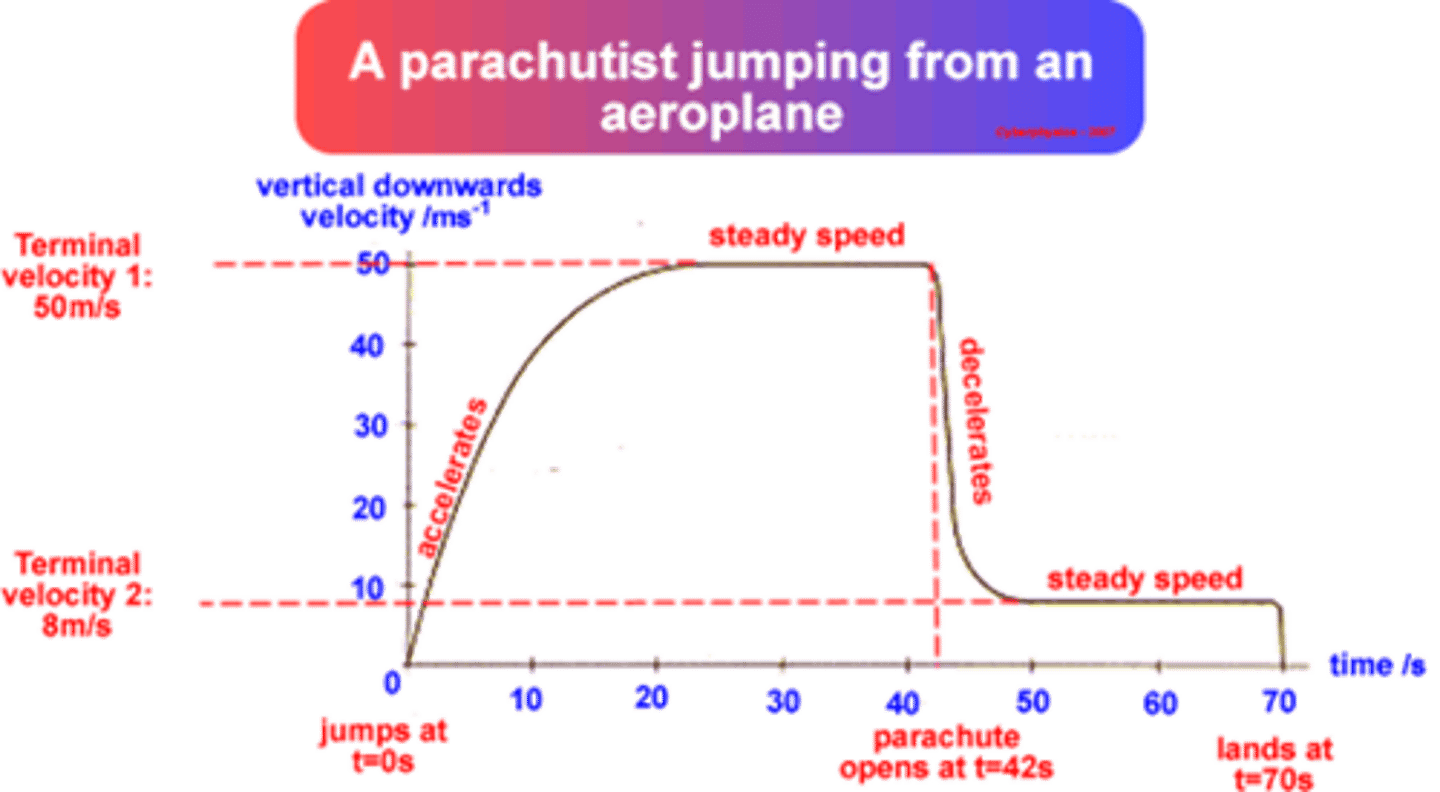
Sketch a velocity-time graph for a skydiver jumping from a plane, reaching terminal velocity, staying at that speed for some time, then pulling their parachute, reaching a second slower terminal velocity, the finally landing.
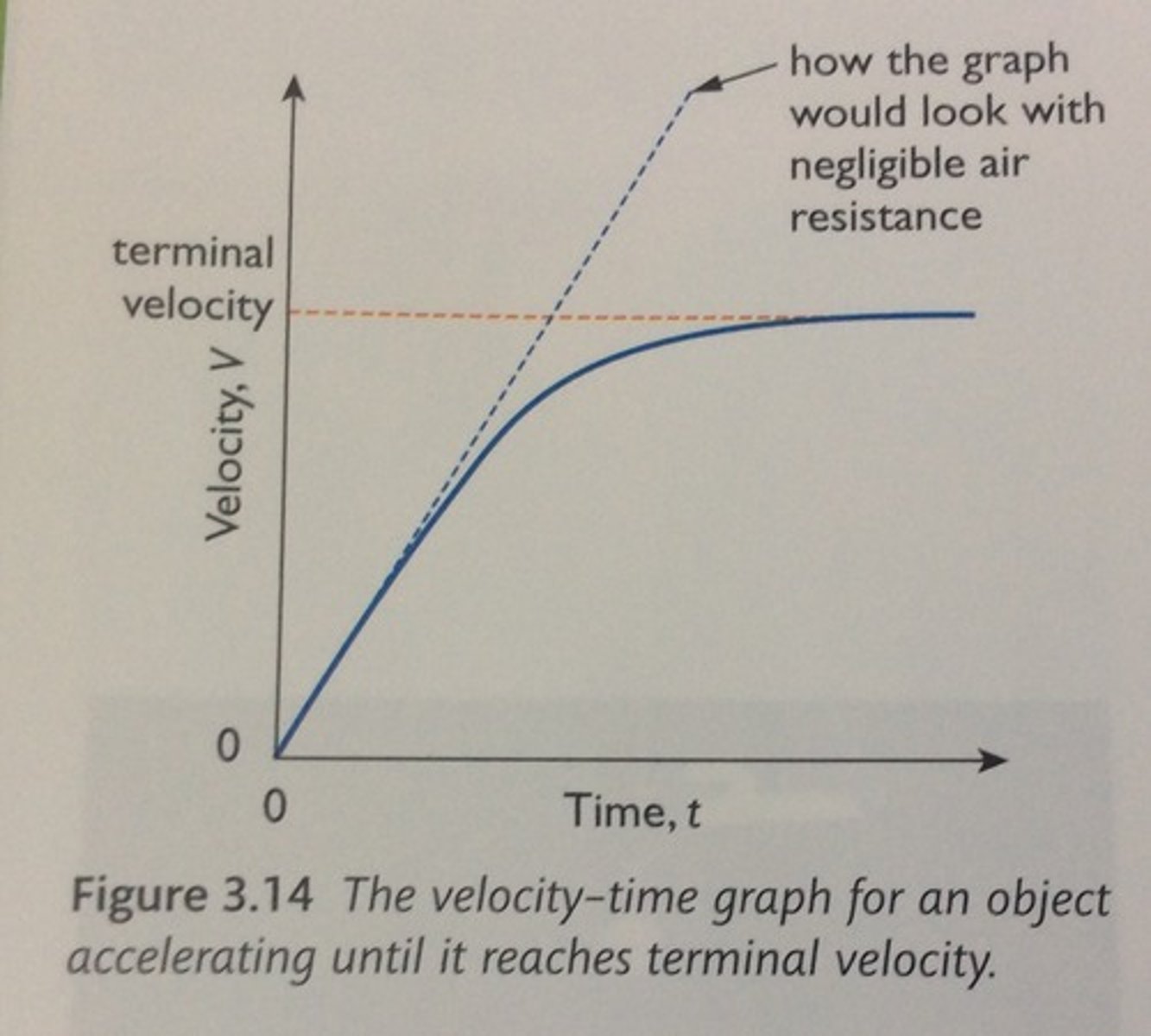
What is terminal velocity?
the constant speed that a freely falling object eventually reaches when the resistance of the medium through which it is falling prevents further acceleration.
How do you approach a projectile questions?
1. Resolve (break) the vector into its x and y components.
2. Solve using Pythagoras and Trigonometry.