Audiology Exam 2 (Midterm)
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
why is otoscopy used
detect collapsing canals, examining pinna for malformations, ensuring that canals are not occluded with cerumen
what is seen with otoscopy
tympanic membrane structures
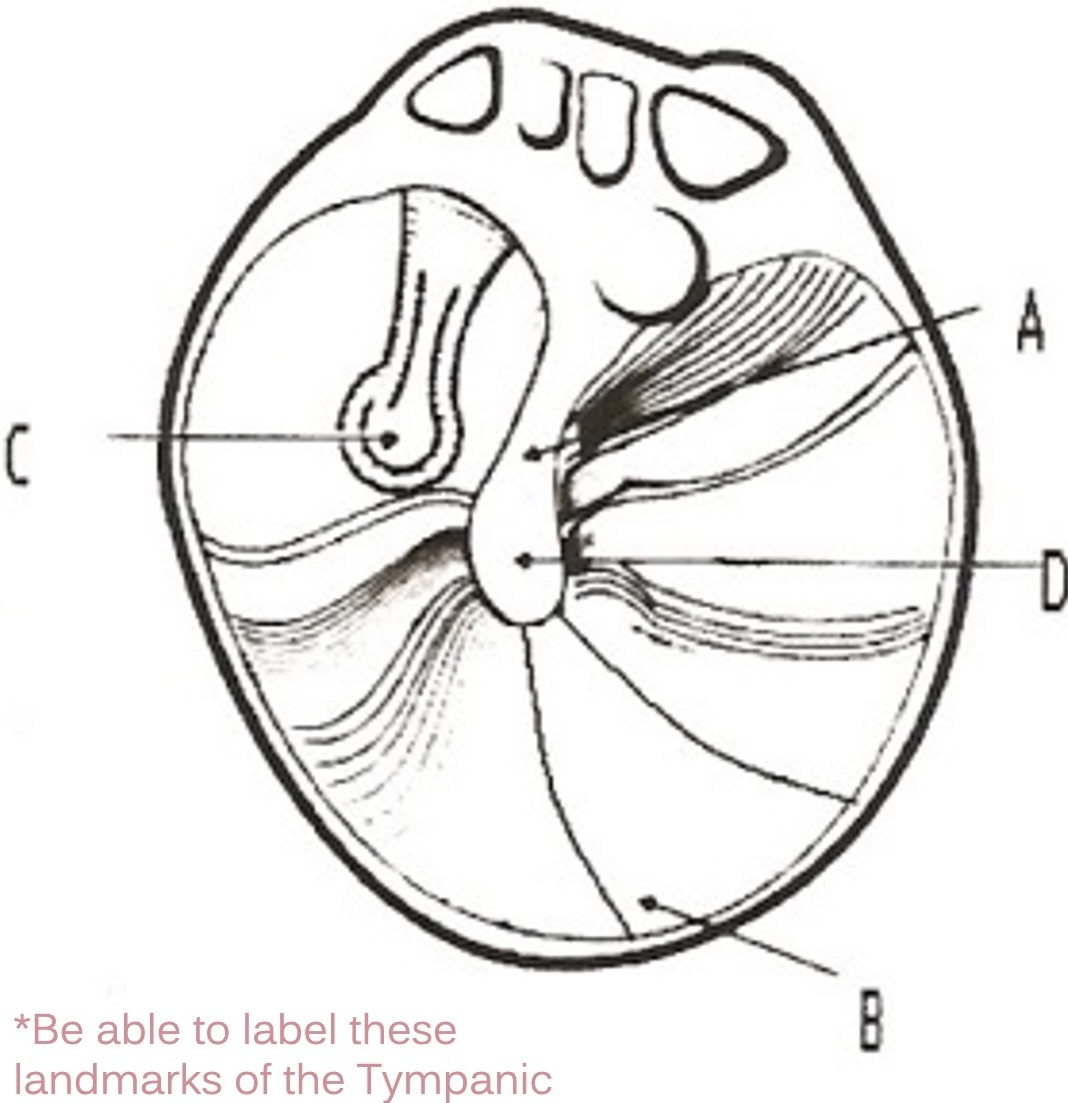
A
manubrium of malleus
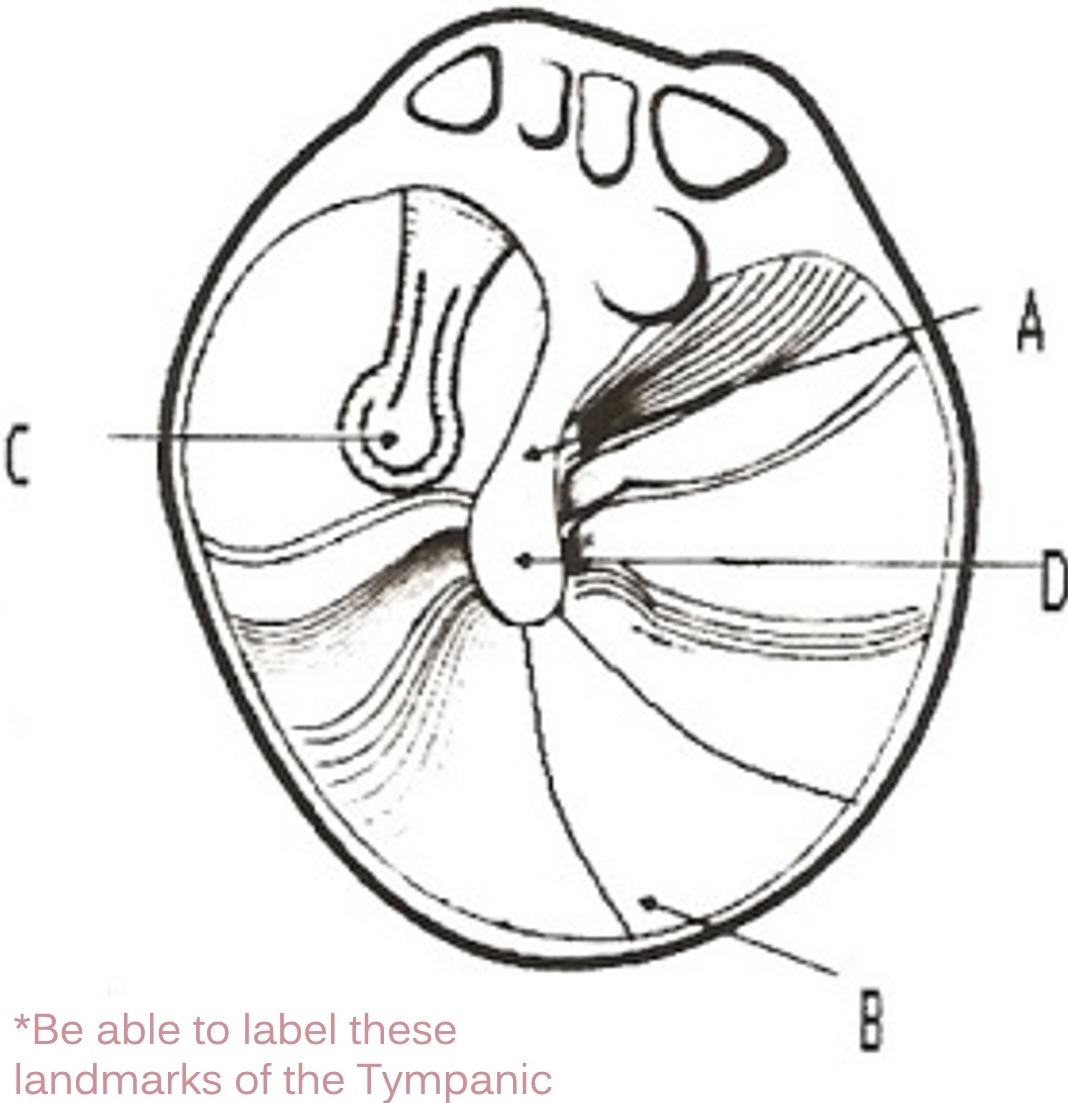
D
umbo of malleus
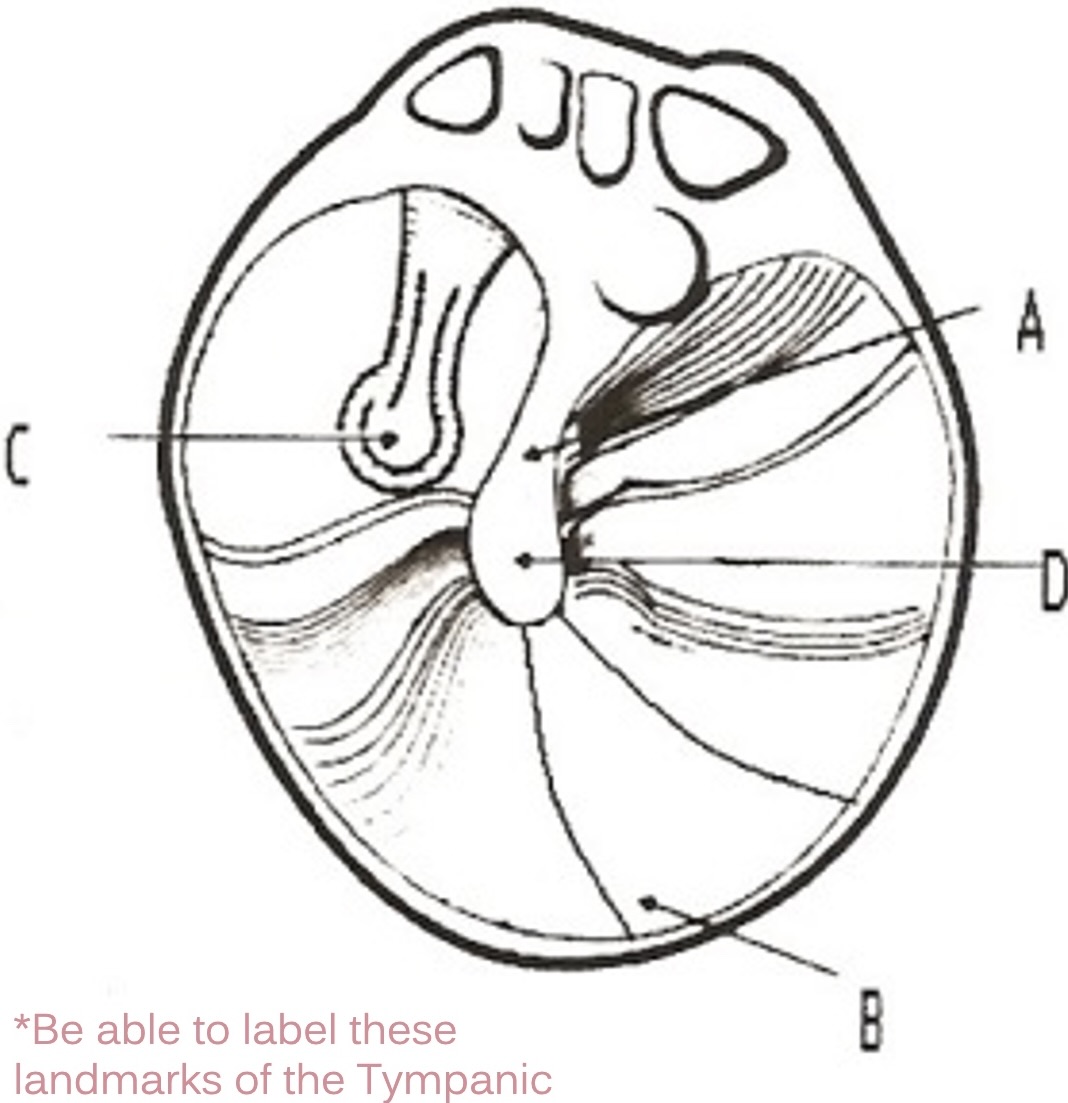
C
incus
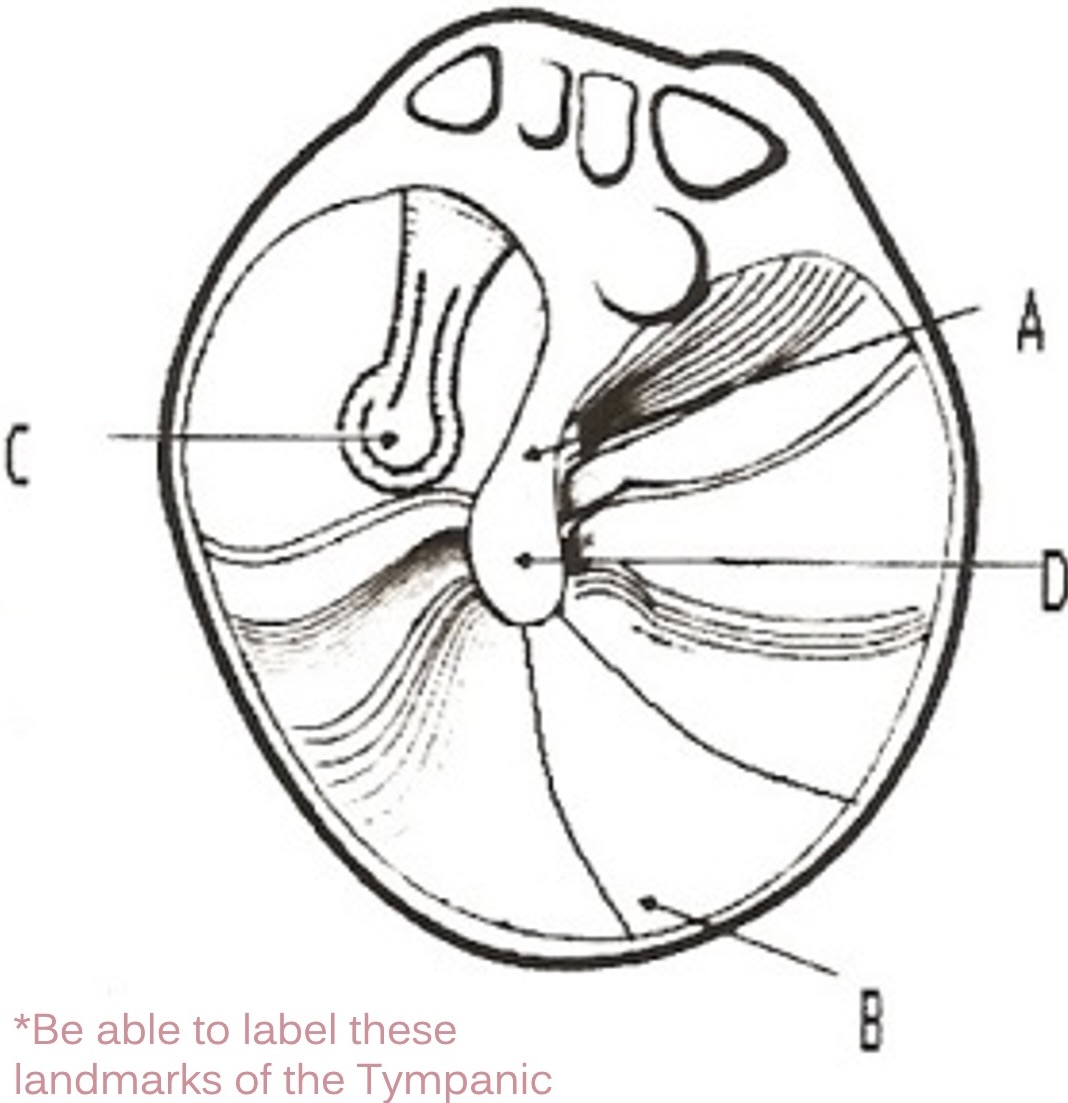
B
cone of light
what questions should you ask adults in a case history
open ended questions
types of testing for children
visual reinforcement audiometry & conditioned play audiometry
visual reinforcement audiometry
6 months- 2 years, use warble narrow band noise, use lights/toys/videos, placed at 45-90 degrees from the child's forward facing position
conditioned play audiometry
2 – 4 years, use different toys and stimuli, positive reinforcement and enthusiasm
purpose of audiometry
to find the hearing threshold
threshold
the lowest sound a person can reliably respond to 50% of the time
testing- pure tone AC
250-8000 Hz
testing- pure tone BC
250-4000 Hz
when do you test interoctaves
gap of 20 dB or more
testing- frequency presentation
1000 - 2000 - 4000 - 8000 - 1000 (retest) - 500 - 250
tuning fork types
weber & rinne
weber tuning fork
determines if affected ear has conductive or sensorineural hearing loss, stem placed on forehead
rinne tuning fork
tests air conduction vs bone conduction, stem placed on mastoid bone
3 parts of audiogram interpretation
degree, type, configuration
conductive hearing loss
BC normal, AC abnormal, gap between AC & BC > 10 dB
sensorineural hearing loss
BC abnormal, AC abnormal, gap between AC & BC ≤ 10 dB
mixed hearing loss
BC abnormal, AC abnormal, gap between AC & BC > 10 dB
headphones IA
40 dB
inserts IA
55 dB
what are inserts best used for
collapsing canals
IA bone conduction
0 dB
air conduction equation
TE AC-NTE BC= > IA
bone conduction equation
TE AC-TE BC= > 10
speech reception threshold
threshold test: lowest level a patient can accurately respond to stimulus, tested with spondee words (two syllable words with equal stress), 2/4 words or 50% of the time
pure tone average
average of thresholds of each ear individually (500, 1k, & 2k Hz)
word recognition score
supra threshold test, 40 dB SL to the SRT
stria vascularis
system of cells that maintains the positive charge of the endolymph
fundamental frequency
lowest frequency of a complex waveform
unit of measure is used to define intensity on the audiogram (hearing evaluation form used by audiologists)
dB HL
total effect of the middle ear allows for ___ dB of increased gain from the tympanic membrane to the oval window
33
acoustic reflex
bilateral response to loud stimuli and occurs above 80 dB SPL
phase locking
a theory which refers to which type of neural coding in the cochlea frequency coding
which part of the ear serves the function of transducing mechanical vibration into hydromechanical energy?
stapes
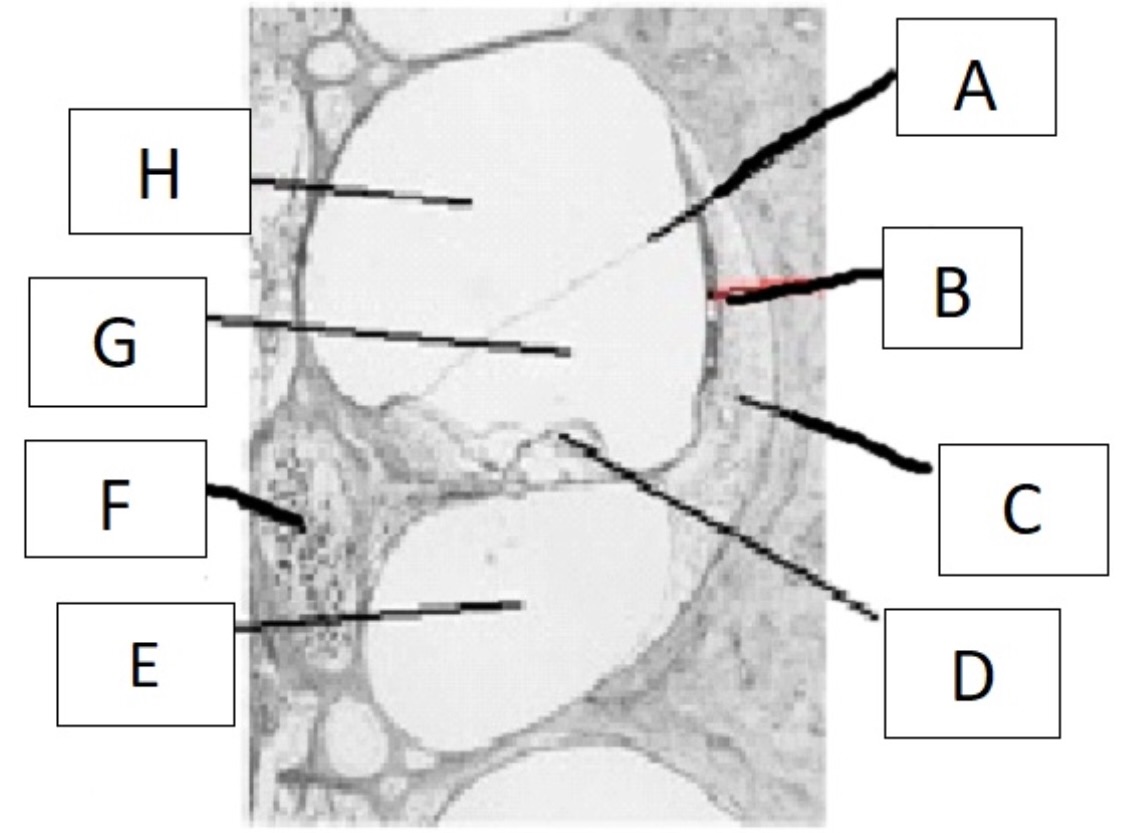
A
reissner’s membrane
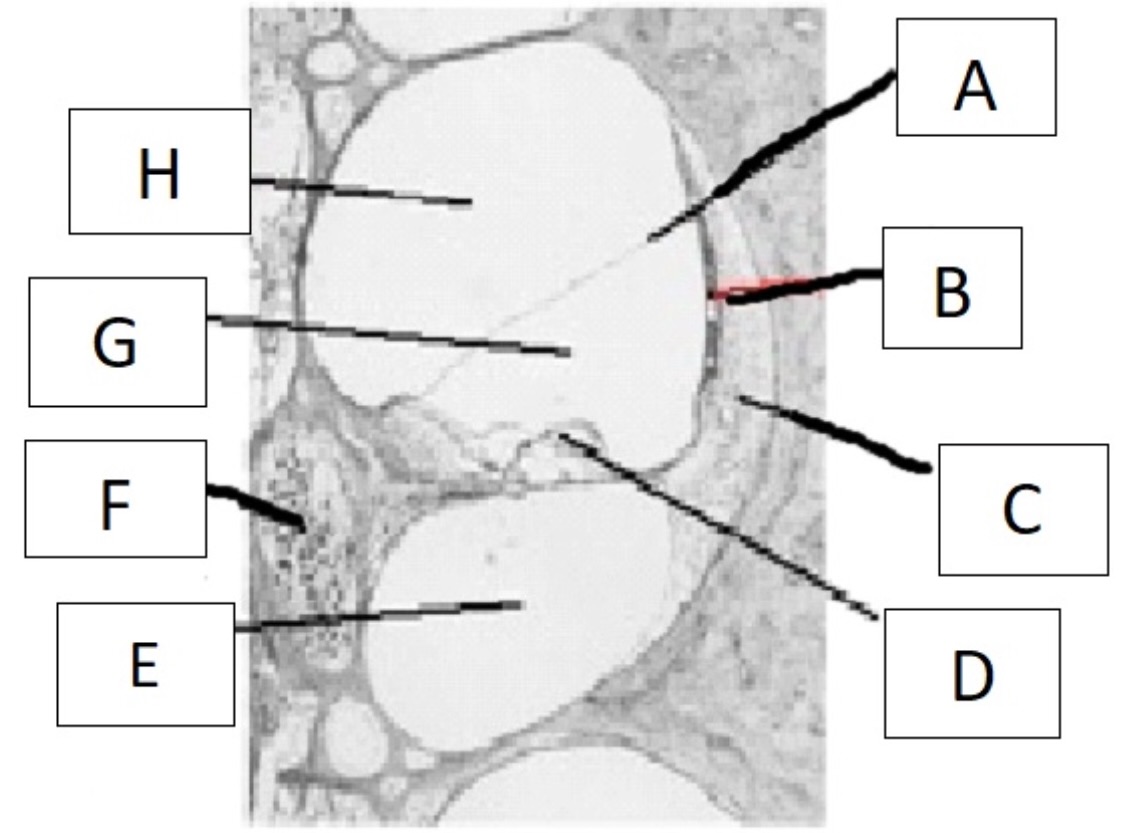
B
stria vascularis
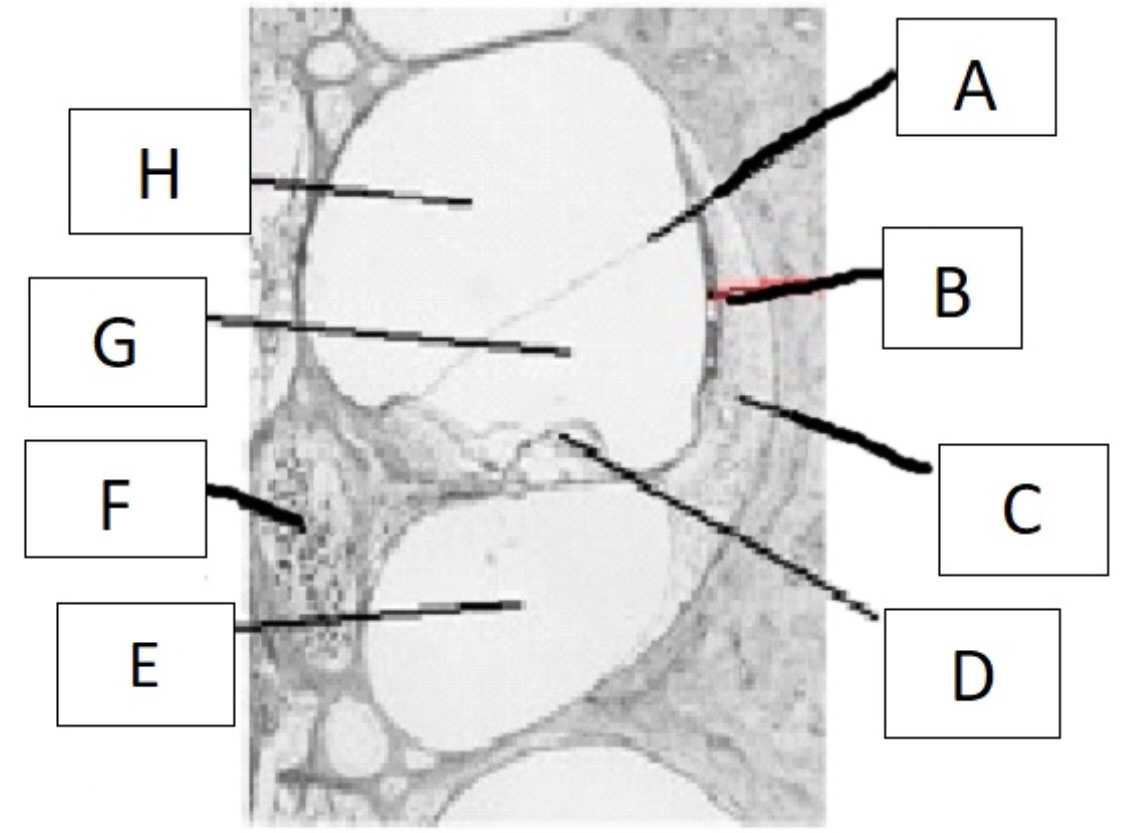
C
spiral ligament
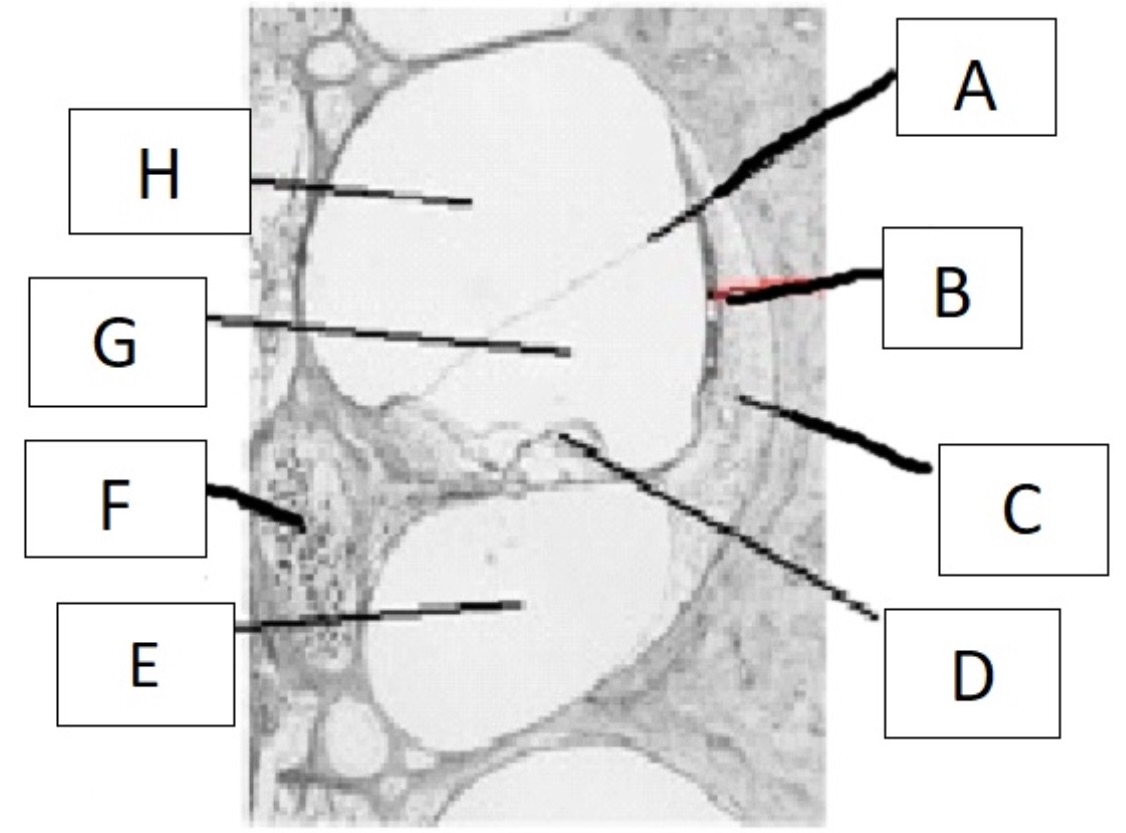
D
organ of corti
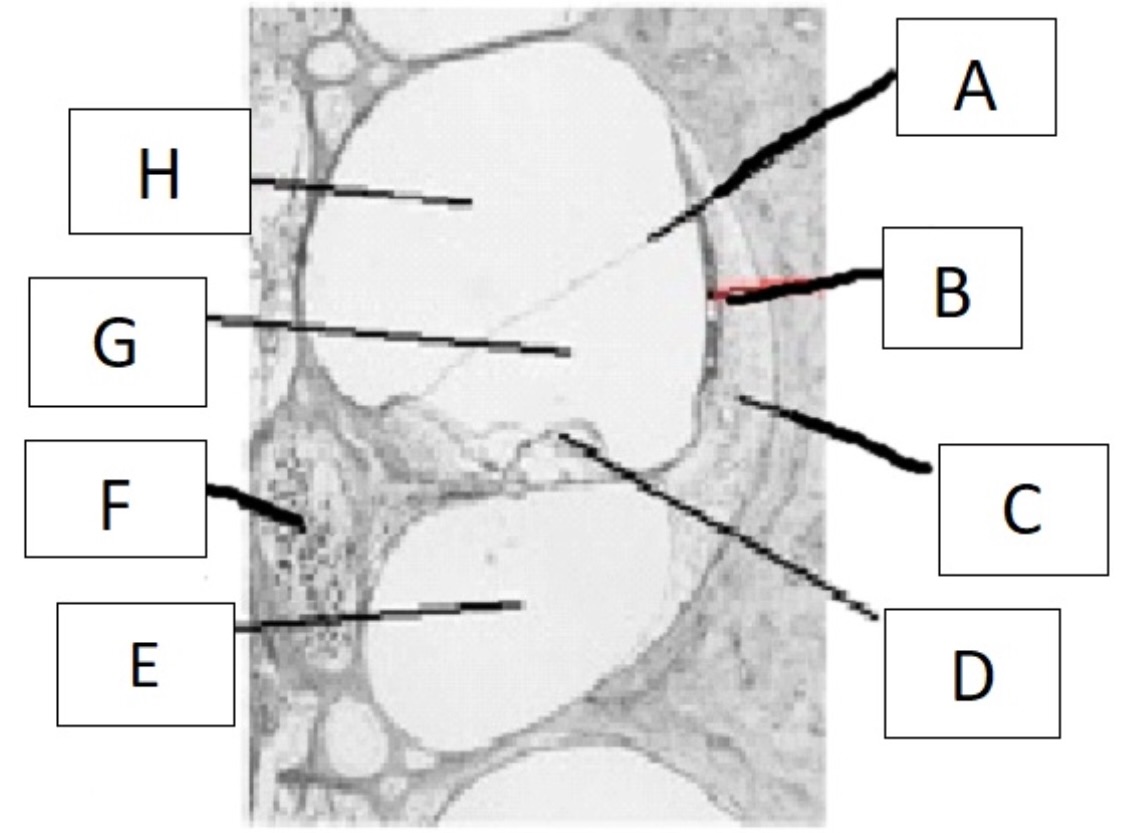
E
scala tympani
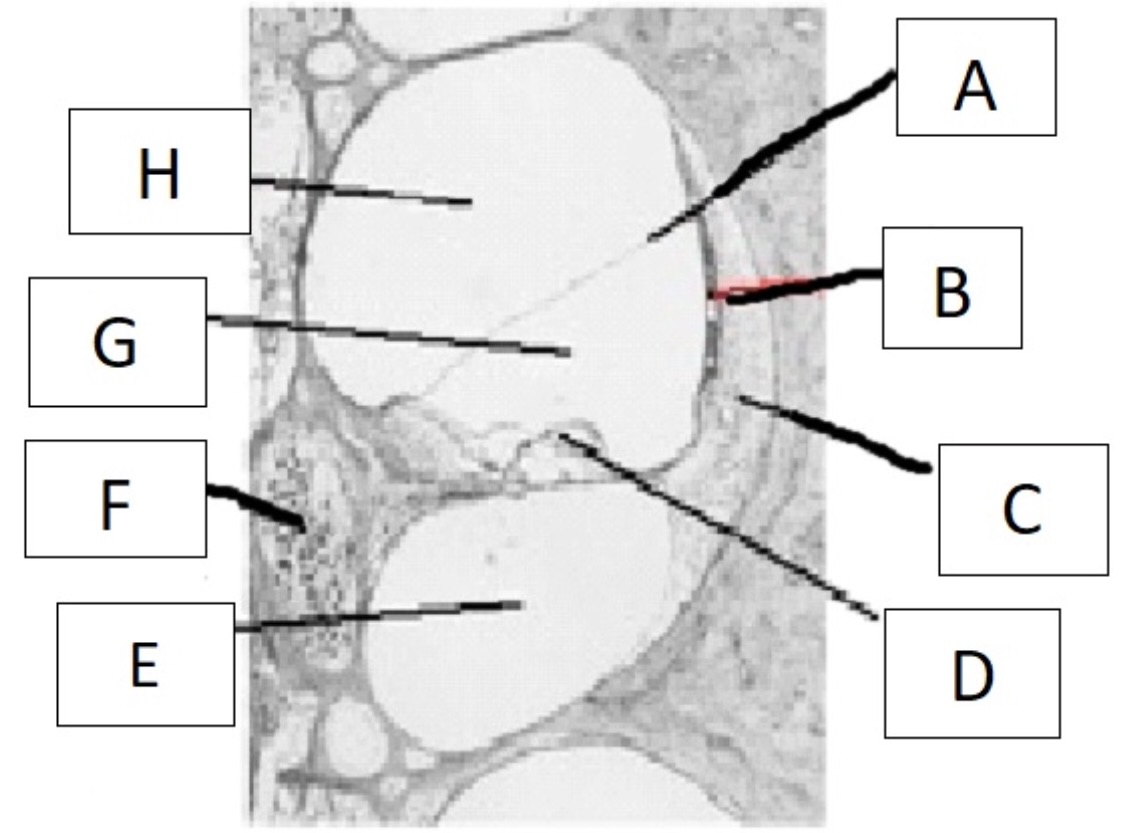
F
spiral ganglion
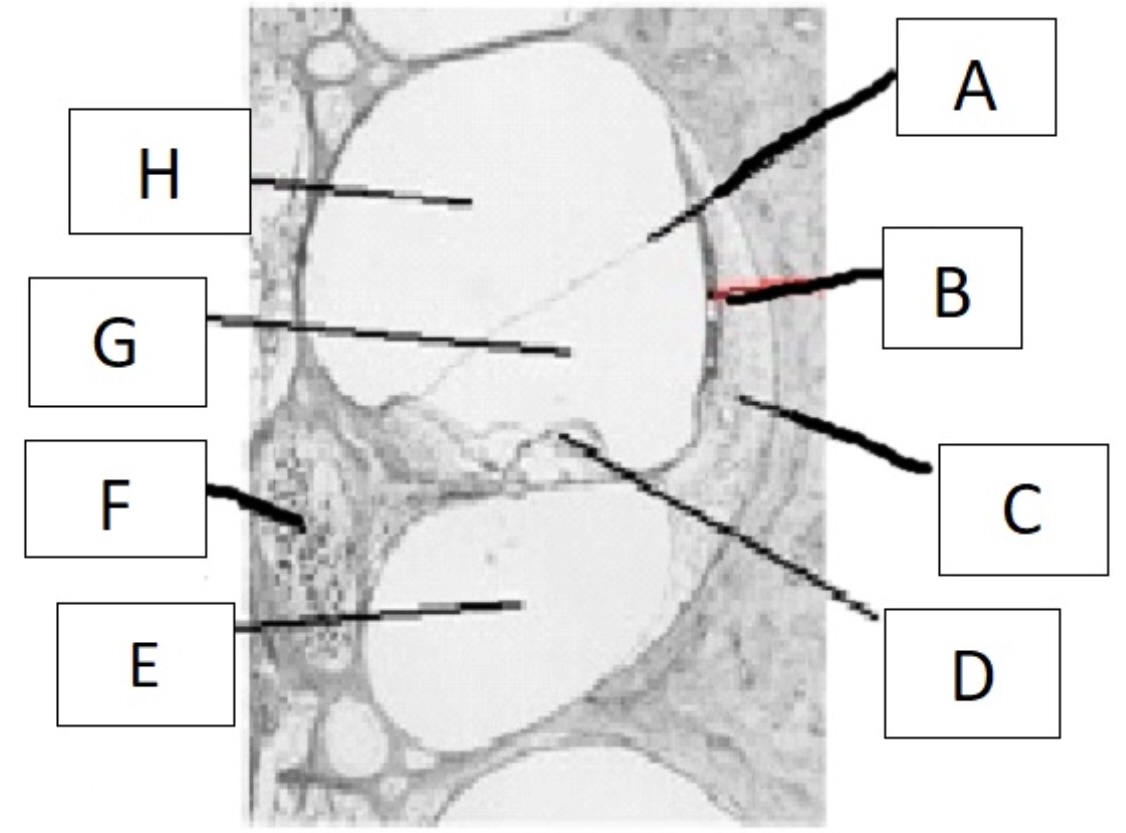
G
scala media
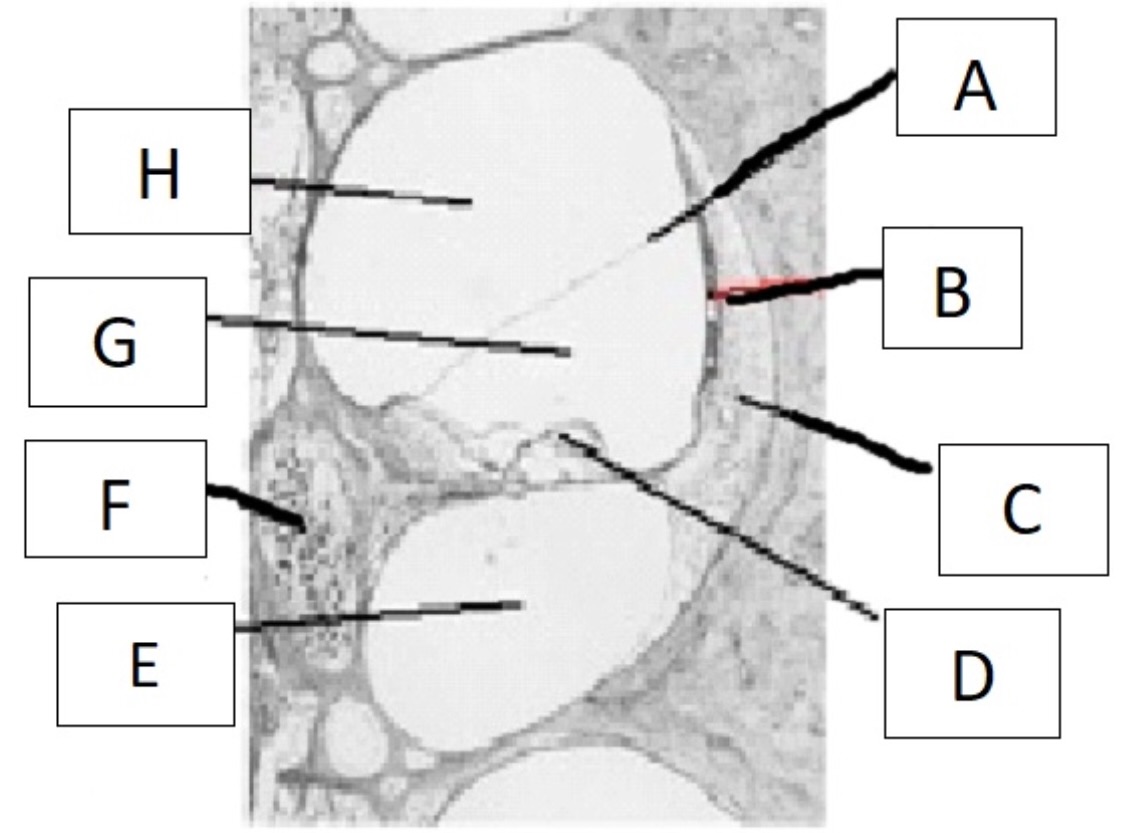
H
scala vestibuli
5 divisions of auditory system
outer, middle, inner, auditory nerve, central auditory nervous system
outer ear functions
funnels sound, protects ear, transfer function (15-20 dB), acoustic vibration
functions of middle ear
acoustic vibrations turn into mechanical vibrations, impedance matching (33 dB increase), acoustic reflex
eustachian tube normal state
closed
eustachian tube function
equalize pressure
inner ear functions
shearing of hair cells, depolarization, mechanical vibrations to hydromechanical, movement of basilar membrane (tonotopic organization)
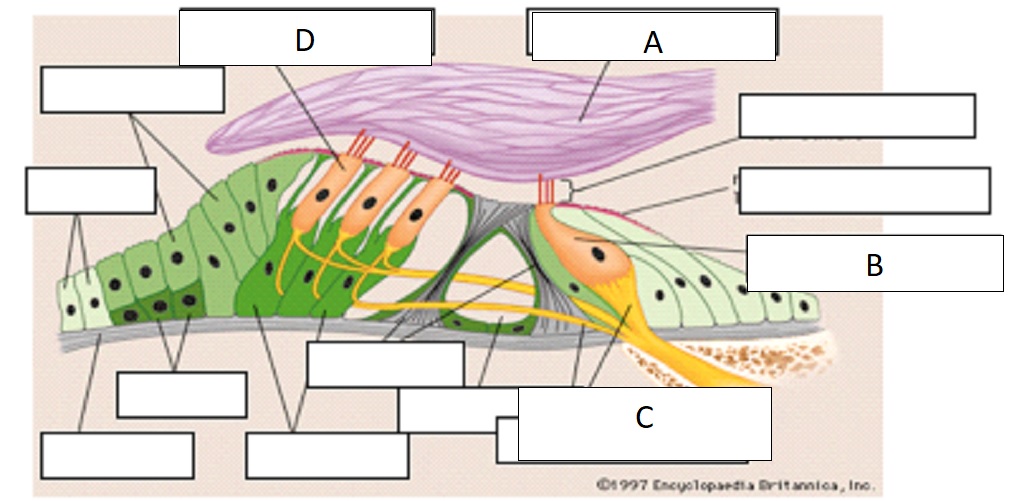
D
outer hair cell
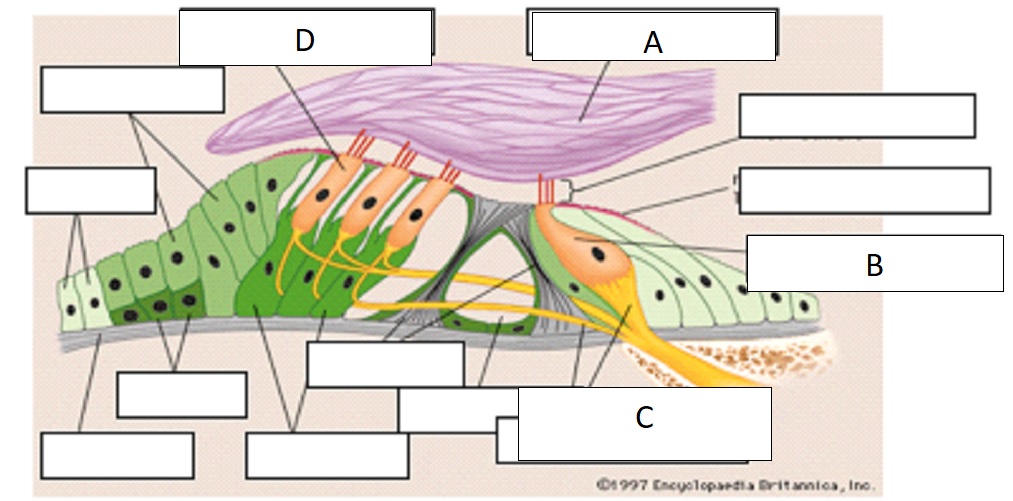
A
tectorial membrane
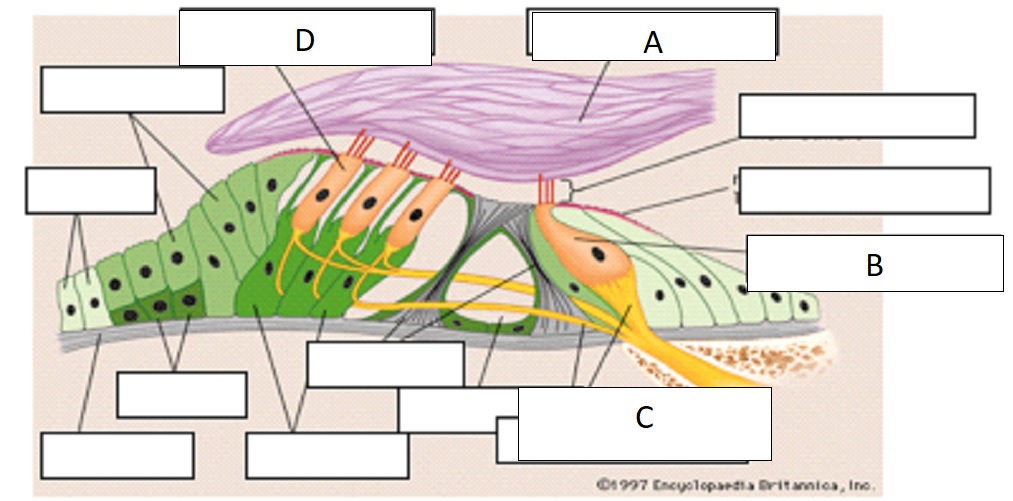
C
auditory nerve fibers
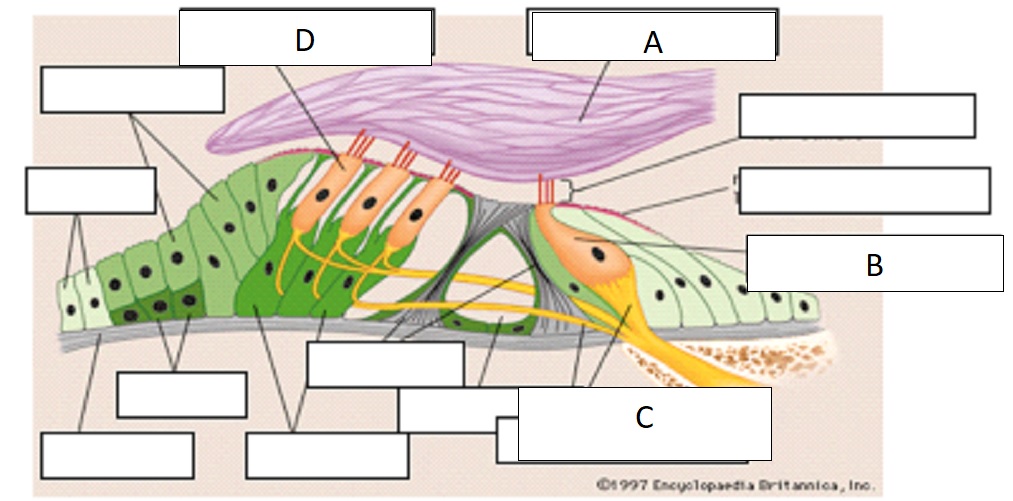
B
inner hair cell
inner hair cells
passive process of cochlea, 1 row, 3500 in single row
outer hair cells
active process of cochlea, 3 rows, w shaped, embedded in tectorial membrane
where is the cochlea houses
petrous portion of temporal bone
T or F- a lower frequency has a longer wavelength
true
frequency theory
pattern of discharge codes for frequency
place theory
frequency info coded where peak of traveling wave occurs
frequency coding
theories to describe how frequency is encoded within the cochlea