AP Biology Unit 1 Chemistry of Life
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
126 Terms
What are the four classes of macromolecules?
- Carbohydrates
- Nucleic acids
- Lipids
- Proteins
Carbon can...
Form up to 4 single bonds, form rings or chains, and form strong covalent bonds
Organic molecules
Contain carbon (typically covalently bonded to hydrogen)
Functional groups
Clusters of atoms with characteristic structures and functions
Polar molecules are...
Hydrophilic (adhere to water)
Nonpolar molecules are...
Hydrophobic (repel with water)
Monomer
1 subunit of an organic molecule (general term)
Polymer
Many subunits of an organic molecule (general term)
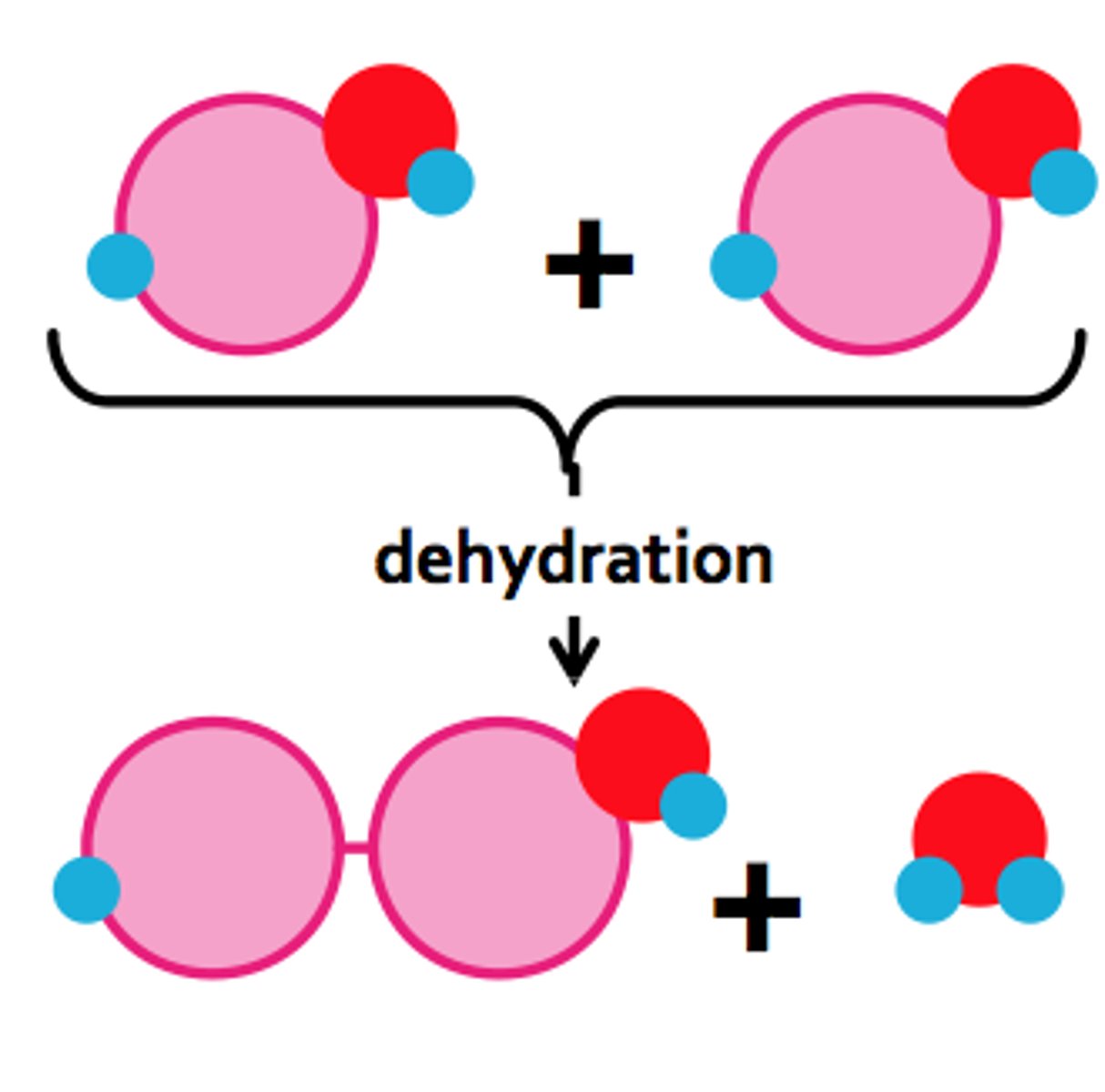
Dehydration synthesis / Condensation reaction
Forming polymers by removing water
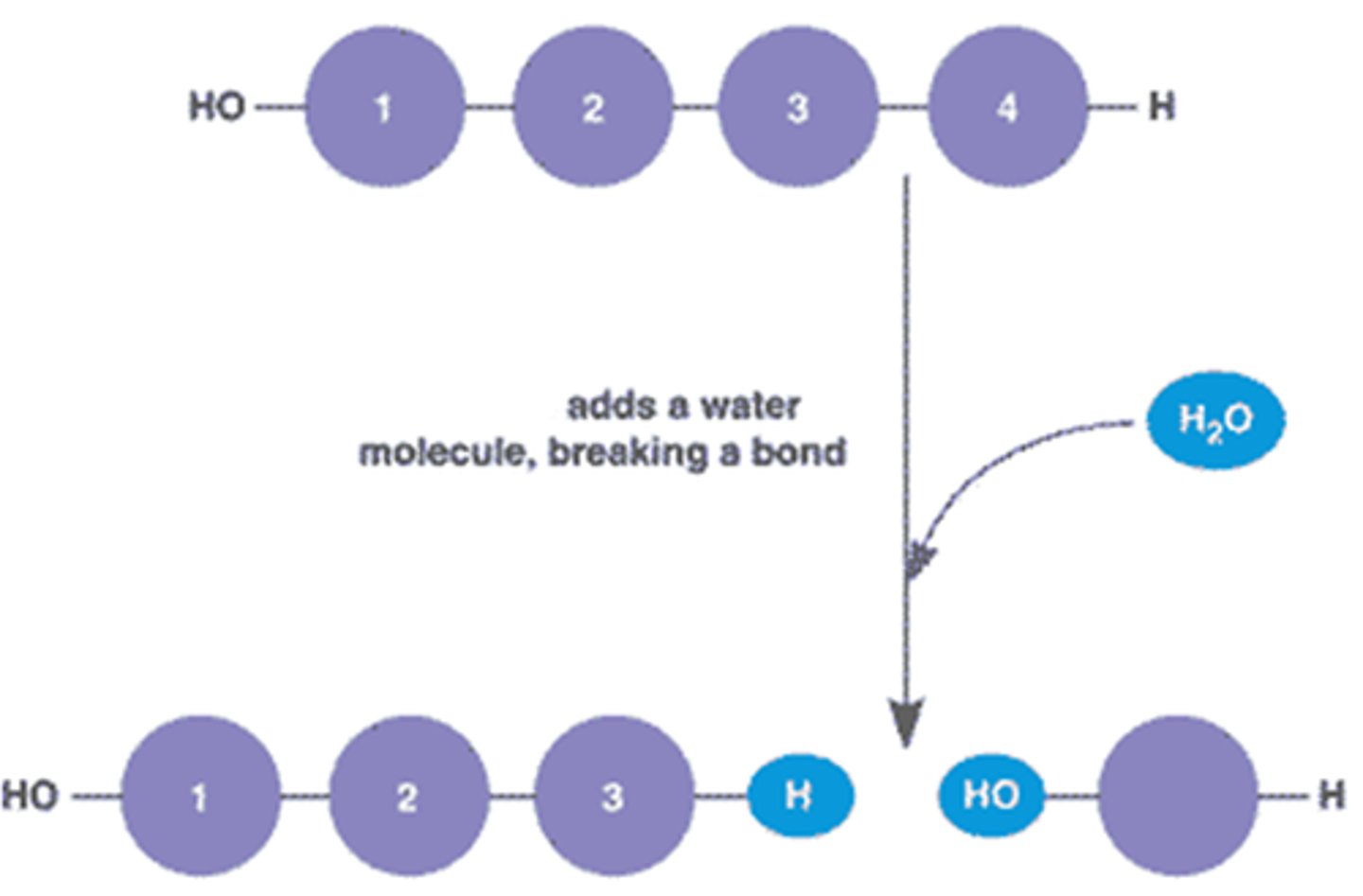
Hydrolysis
Breaking down polymers by adding water
Carbohydrates are composed of...
Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (CHO)
Basic/general formula for carbohydrates
CH2O
Where is energy stored in sugars?
C-C bonds
What is the suffix most sugars end in?
-ose
Monosaccharide
Simple 1 monomer sugars, either used as first energy source or to form polymers
Disaccharidase
Simple 2 monomer sugars
How are sugars classified?
By the number of carbons
Glycosidic linkage
Bond between two sugars
What is the main function of carbohydrates?
Energy (body's primary source of energy), as well as energy storage
What are the three hexose monosaccharides?
Glucose, fructose, and galactose
What is the formula for hexose monosaccharides?
C6H12O6
Glucose
Most common monosaccharide and monomer
Fructose
In corn syrup and fruits, makes things sweet
Galactose
Basic milk sugar
How are disaccharides formed?
Dehydration synthesis
Glucose + Fructose = ?
Sucrose (C12H22O11) + Water (H2O)
Glucose + Glucose = ?
Maltose (C12H22O11) + Water (H2O)
Glucose + Galactose = ?
Lactose (C12H22O11) + Water (H2O)
How is the energy release of simple sugars/monosaccharides and disaccharides?
Quick but little amount of energy
How do you test for sugars?
Add substance into test tube, add Benedict's solution, heat in boiling water bath for 3-4 mins; color change represents sugar (blue control, more green = less sugar, more red = more sugar)
Polysaccharide
Polymer of sugars
Building polysaccharides...
Stores energy (forms bonds)
Breaking down polysaccharides...
Releases energy (breaks bonds)
If sugars aren't used, they're stored as...
Polysaccharides
Glycogen
Stored energy in animals
Starch
Stored energy in plants
Cellulose is found in...
Plants' cell wall
Chitin is found in...
Arthropods' exoskeleton and the cell wall of fungi
How do you test for starches?
Drop of iodine on unknown substance; color change represents starch (darker black/purple = more starches)
What part of the structure of cellulose and starch makes them different? (Why is one digestible while the other isn't?)
Cellulose is made of beta-glucose monosaccharides and starch is made of alpha-glucose monosaccharides (these are different isomers of glucose, meaning they are built of the same atoms, but form different structures.) Cellulose is indigestible to humans because we lack the enzyme, cellulase, to break the beta-glycosidic bonds.
What is the most abundant organic compound on Earth?
Cellulose
How can herbivores digest cellulose?
Herbivores have evolved a mechanism to digest cellulose. For example, they tend to have longer digestive tracts and multiple stomach chambers to break down fibrous material. Herbivores also have bacteria that live in their digestive system, which helps them digest cellulose-rich food.
How is the energy release of complex sugars/polysaccharides?
Medium speed and more energy than simple sugars
Polymerization
The process of making polymers through dehydration synthesis
Examples of monosaccharides
Glucose, fructose, galactose, ribose, deoxyribose
Examples of disaccharides
Sucrose, maltose, lactose
Examples of polysaccharides
Cellulose, chitin, glycogen, starch
What are the two main groups of nucleic acids?
DNA and RNA
Nucleic acids are composed of...
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus (CHONP)
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid
RNA
Ribonucleic acid
ATP
Adenosine triphosphate
What is the sugar in DNA?
Deoxyribose
What is the sugar in RNA?
Ribose
What is the sugar in ATP?
Ribose
What is the name of the monomer of DNA, RNA, and ATP?
Nucleotide
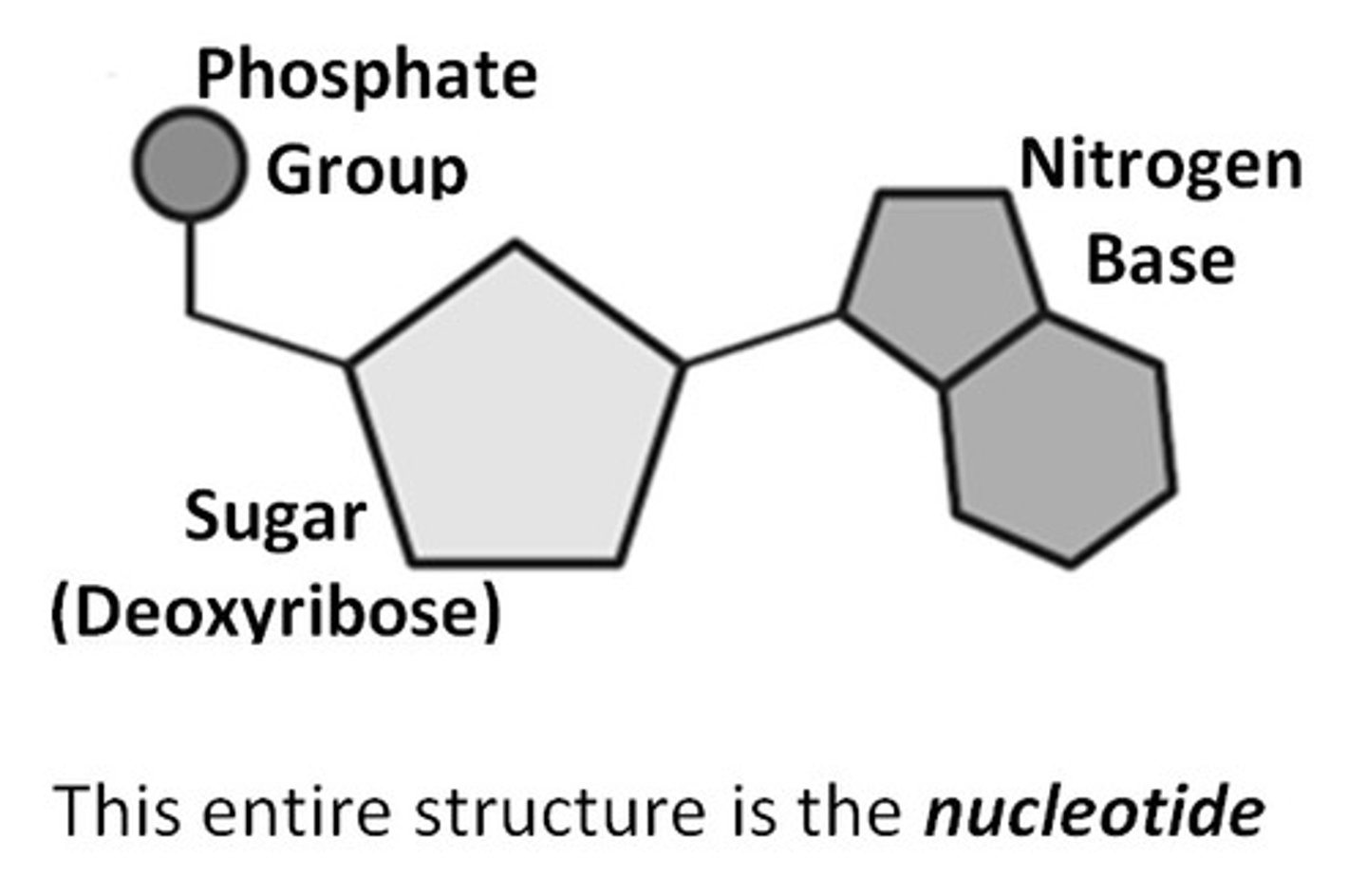
What are the three parts of a nucleotide?
Sugar (ribose/deoxyribose), nitrogen base, and phosphate group
What are the nitrogen bases in DNA?
Adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine
What are the nitrogen bases in RNA?
Adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil
What is the nitrogen base in ATP?
Adenine
Purine
2 rings: adenine and guanine
Pyrimidine
1 ring: cytosine, thymine, and uracil
Which nitrogen bases bond with each other?
Adenine and thymine, guanine and cytosine (because purine always bonds to a pyrimidine)
Qualities of RNA
- Single-stranded
- Ribose sugar
- A, U, G, and U nitrogen bases
- Located in nucleus and cytoplasm
- Helps genetic info turn into proteins
Qualities of DNA
- Double-stranded (helix)
- Deoxyribose sugar
- A, T, G, and C nitrogen bases
- Located only in nucleus
- Holds genetic info
Lipids are composed of...
Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen + sometimes phosphate (CHO + P)
All lipids are...
Hydrophobic
Do lipids form polymers?
No
What are the main "family groups" of lipids?
- Fats
- Phospholipids
- Steroids
- Waxes
What are fats made of?
Glycerol + fatty acid chains (hydrocarbon chains)
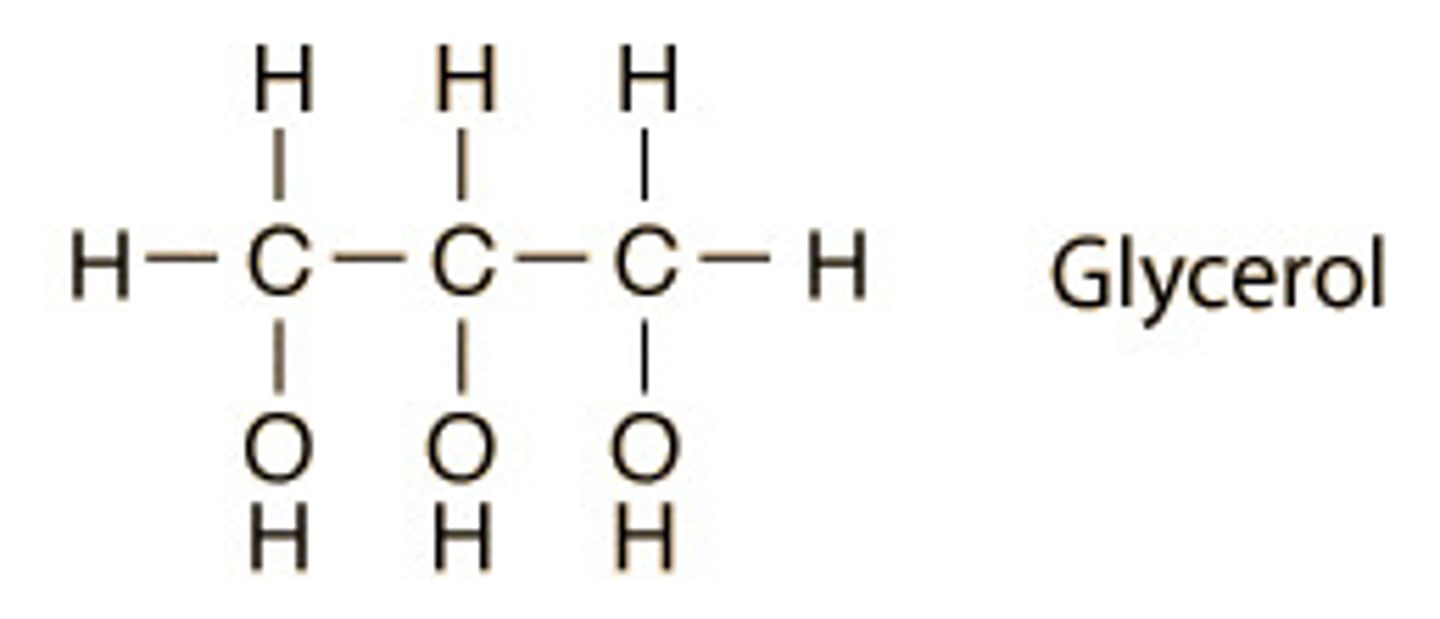
Glycerol
3C alcohol (C3H8O3)
Fatty acid
Long hydrocarbon "tail" with carboxyl group head
How many fatty acid chains are in a triglyceride?
3
What is the backbone of fatty acids made of?
Carbon
Properties of hydrocarbon chains
- Non-polar (no charge)
- Hydrophobic
What is the function of fats?
Energy storage (if you don't use sugars for energy, they are stored as fats), as well as to cushion and insulate body
How is the energy storage of fats?
- Concentrated (mostly in many H-C bonds)
- Twice as much energy as carbs
- Lots of energy, slow to break down
What is the order in which the body derives energy?
1. Simple sugars (eg. glucose)
2. Stored sugars (glycogen)
3. Stored fats
4. Proteins (last resort)
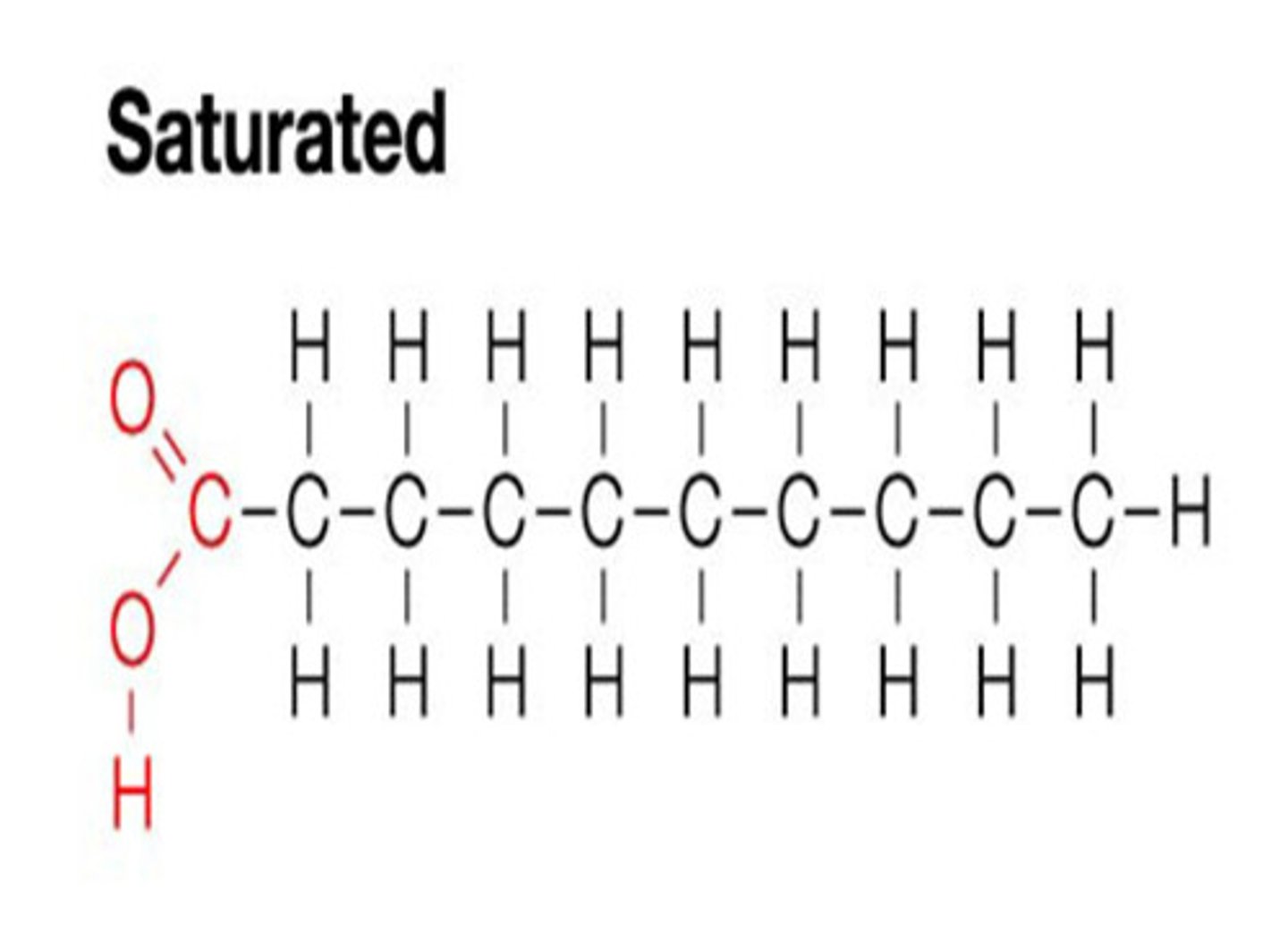
Saturated fats
- All C bonded to H
- Only single bonds
- Long, straight chains
- Solid at room temp
Unsaturated fats
- C=C double bonds in fatty acids, 1 or more
- Kinked chains
- Liquid at room temp
Why are saturated fats solid at room temperature?
The straight fatty acid chains stack on top of each other easily
Why are unsaturated fats liquid at room temperature?
The kinked fatty acid chains prevent packing together easily.
Examples of saturated fats
Most animal fats (eg. butter, tallow, lard)
Examples of unsaturated fats
Fish oils, vegetable oils
Why are the fatty acid chains in unsaturated fats kinked?
The double bonding of the carbon causes bending in the molecule, leading to the kinks.
Monounsaturated fats
One double bond in fatty acid chain, non-essential (body can produce),
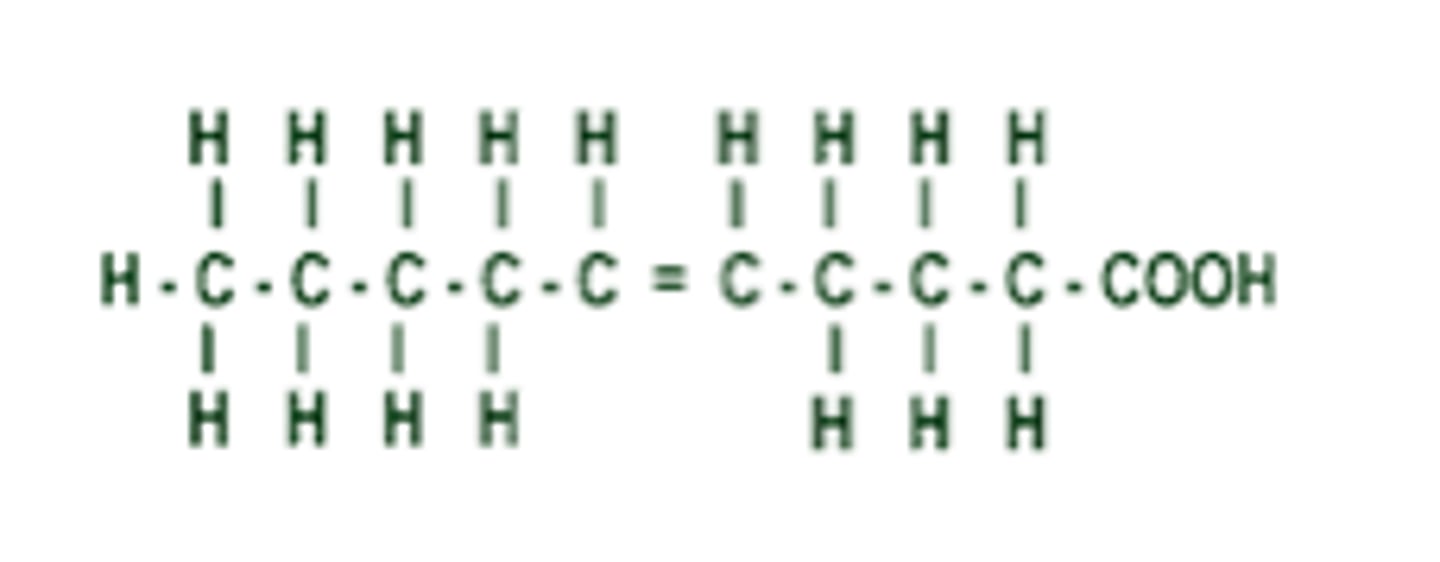
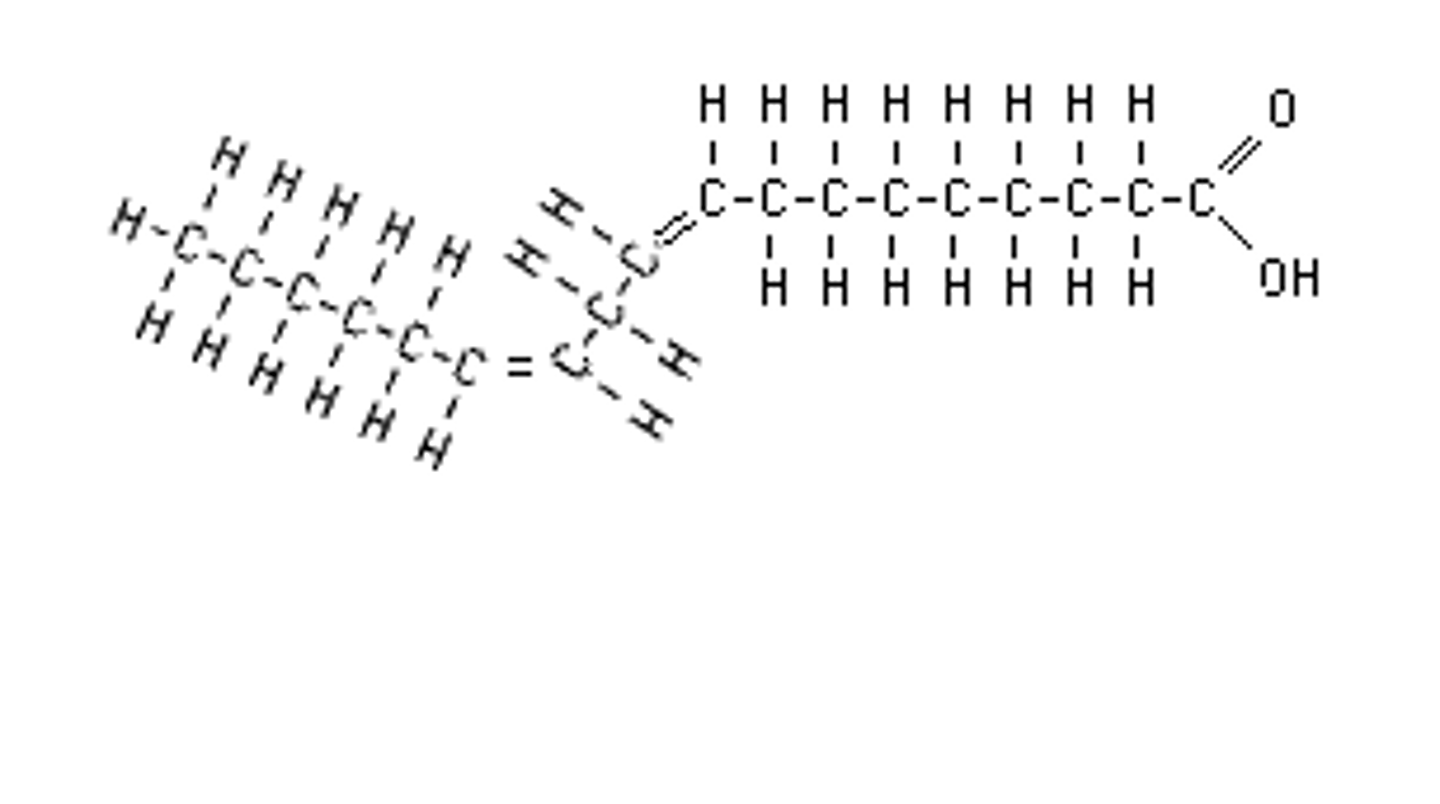
Polyunsaturated fats
Many double bonds in fatty acid chain, essential (body cannot produce)
Why are saturated fats considered less healthy than unsaturated fats?
Saturated fats have more hydrogen atoms than unsaturated fats (causes it to be more solid, thus having more artery-clogging potential)
What are phospholipids made of?
Glycerol + 2 fatty acid chains + phosphate group (PO4) instead of 3rd fatty acid chain
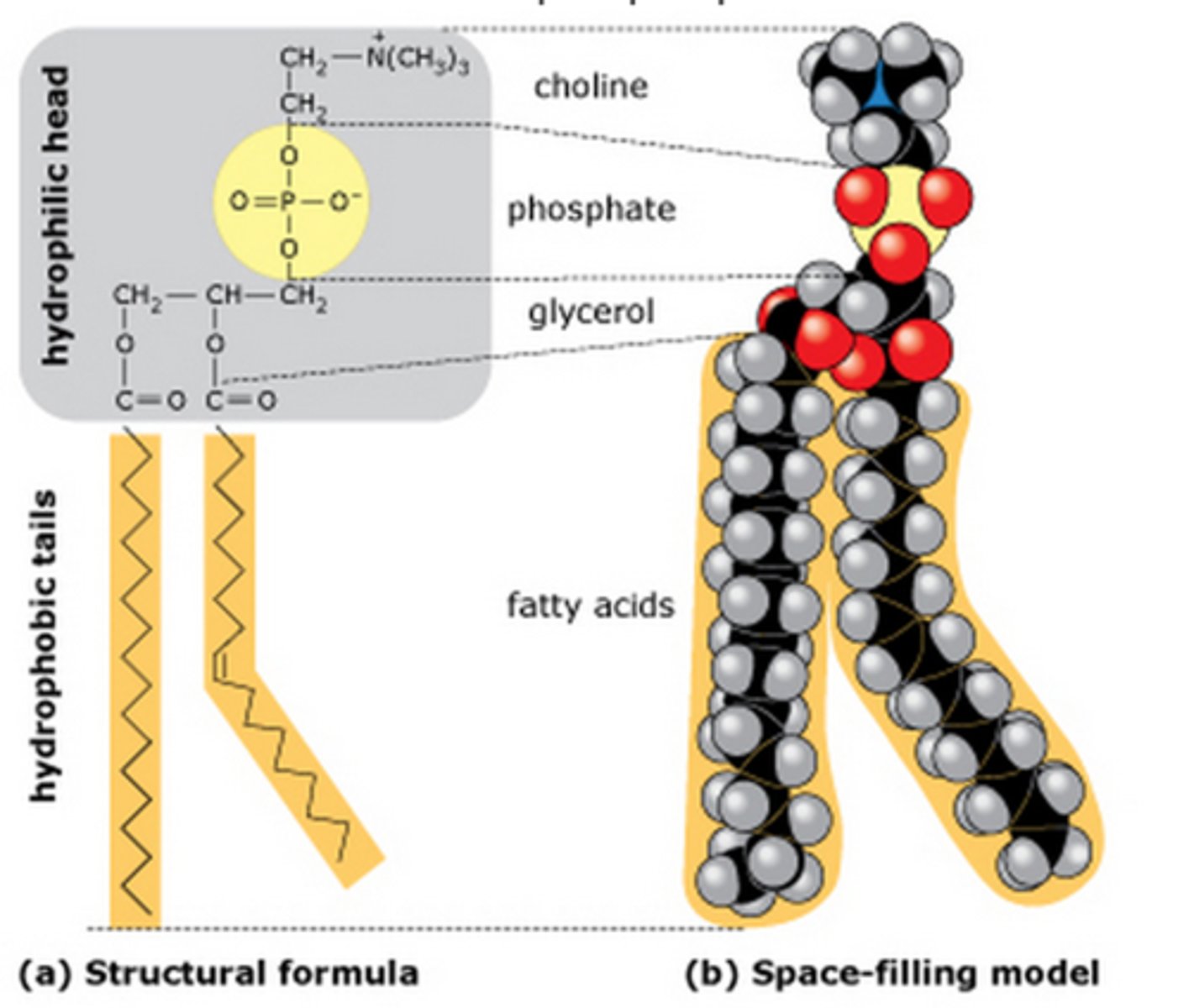
Why are phospholipids polar?
The phosphate group head has a charge, while the fatty acid tail does not have a charge, making the molecule (as a whole) polar
What is the function of phospholipids?
Form phospholipid bilayer (main component of cell membrane)
How are different steroids made?
By attaching different functional groups to rings
What is special about the structure of steroids?
There are 4 fused hydrocarbon rings (numbered consecutively from A to D)
Examples of steroids
Cholesterol, sex hormones (estrogen, testosterone)
What is the precursor of all steroids?
Cholesterol
HDL cholesterol
High-density lipoprotein, considered "good" cholesterol because it removes excess cholesterol to liver
LDL cholesterol
Low-density lipoprotein, considered "bad" cholesterol because it transports cholesterol from liver throughout body
What does cholesterol do for cells?
Component of cell membrane, providing structural support
Why is cholesterol considered bad?
High levels of cholesterol in blood may contribute to cardiovascular disease (builds up plaque in artery walls)
How are trans fats made?
Through a process called hydrogenation, where hydrogen atoms are added to the double bonds of fatty acid chains