the easy stuff for dental anatomy unit 2omy
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
how many canines are in the permanent dentition
4
canines function
Support lip and facial muscles,
Cut/ sheer food,
& Protective (canine guidance)
the variations in canines
burficated root and shovel shaped canine
shovel shaped canine has
Very prominent marginal ridges

Bifurcated root has
Labial and lingual roots

4 most anterior teeth of each arch
incisors
incisors function
Cutting of food,
articulation of speech,
supporting the lip
2 types of incisors
central & lateral
varitations in incisors
shovel shaped & peg laterals
shovel shaped incisors
Maxillary incisors with prominent marginal ridges
Common in those of Asian descent as well as Native Americans
peg laterals
Maxillary lateral incisors with conical shape
‐ 1-2% of population
‐ Developed from 1 lobe instead of 4
‐ May be related to gene that results in missing maxillary laterals (1.91%)
‐ Can also have peg central incisors but this is very rare
Premolars in the permanent
● Function
○ Maintaining vertical dimension
○ Sheering food
○ Supporting the corner of the mouth
Most premolars develop from 4
lobes except
SOME mandibular second premolars - 5 lobes
More cervical on the distal except on
mandibular first premolar
Marginal ridges are horizontal except
mandibular first premolars
Triangular ridges join to form transverse ridges
but
○ Ridges do not line up on three cusp mandibular second premolars
Central groove separates the buccal and lingual cusp except on
mandibular first premolars
Mandibular premolars are
squarered or round
Maxillary premolars are
more oval or rectangular
TRAITS OF INCISORS
‐ 4 Developmental lobes
‐ Mesial
‐ Middle
‐ Distal
‐ Lingual
Wedge shaped crowns
‐ “S” shaped lingual contour
all incisors & canines
Maxillary incisors Roots are widest cervically
EXCEPT
maxillary central incisors
Almost always mesial marginal ridge groove
Maxillary First Premolar
Mandibular First Premolar occlusal’s have
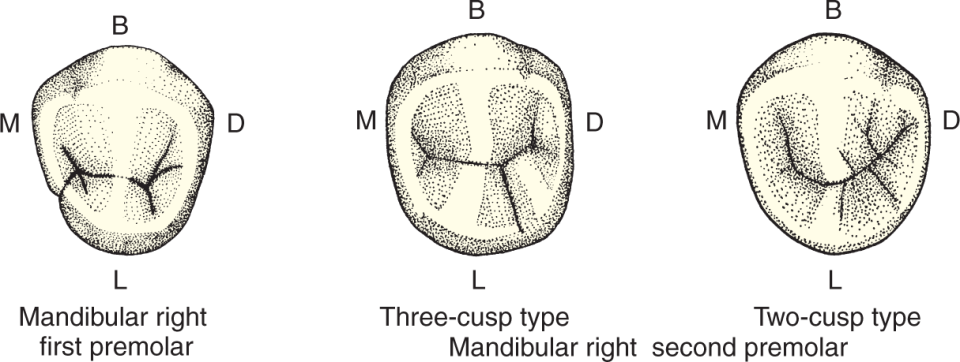
“H” or “U” groove pattern
Mandibular Second Premolar grove pattern
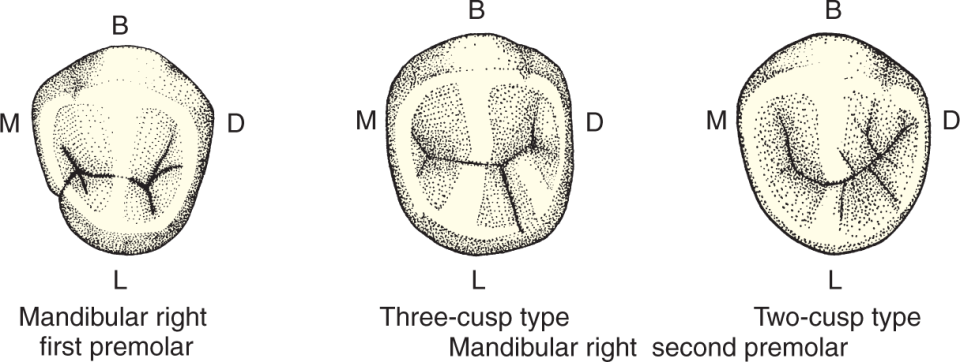
“Y” groove pattern on 3 cusp type
distolingaula twist
promitnet lingual side
macillary lateral incisors have
crown tip is POinty
lingual i side is not shallow
maxillary canines
less systrmical (look at the root)
has distolingual twist
madndibular lateral incisors
less pointed csup
shallow not promitetn lingual side
mandibular caninces
how to determine lefrt or tiht
look at it at the facail aspect
once you determine if its maxaillry or mandiubular, stand it up on how it would look in the mouth
look wear the root tilts (it wlasy tils to wards the distal)
2 roots
distal cusp is the shorter side
BOTH sides are close in height to make occulsal tbale
maxillary 1 st preolmats
distal cusp is the shorter side
BOTH sides are close in height to make occulsal tbale
maiallry 2nd premolars
does not have a cingulum but instead a csusps so dont confuse it for a canine !!
CUSPS ARE NO THIGH ENOUGH TO MAKE AN OCCULSAL TABLE
mandibular 1st premolar
root is curvy
HAS 3 CUSPS
manidular 2nd premolars
Narrower in the lingual half mesiodistally except
3 cusp mandibular second premolars
More rounded on distal incisal edge EXCEPT on
mandibular centrals
Heights of contour
○ Buccal- cervical third
○ Lingual - middle third
○ Mesial-Junction of middle and occlusal thirds*
○ Distal middle third* EXCEPT
mandibular first premolars
Shorter crowns than anterior teeth
Second premolar is shorter than first premolar
petaognal shape?
canines & Mandibular Second Premolar
have longer roots relative to their crown
Mandibular incisors
Rectangular crown shape
incisors