South College AVL Lab Med: BMP, CMP, Electrolytes - Lecture 5
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
BMP
basic metabolic panel
Glucose (normal 65-99)
For BMP, what are we assessing when it comes to endocrine function?
BUN (blood urea nitrogen), creatinine, BUN:Cr ratio, eGFR calculation
For BMP, what helps us assess kidney function?
Calcium, sodium, potassium, chloride
For BMP, what helps us assess electrolyte levels?
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
For BMP, what helps us assess blood gas/pH of blood?
age, gender, location, race
What can impact the results of a BMP/make the results abnormal?
CMP
complete metabolic panel
BMP + LIVER FUNCTION PANEL
What does a CMP tell us?
routine lab testing, serum
What are some uses of a CMP? What is preferred for this type of testing?
FASTING (no caloric intake for 8 hours)
What criteria is needed for a normal range of glucose to be valid (70-100 mg/dL)?
assess blood glucose levels, diabetes evaluation
What are some uses for obtaining glucose?
males: <50 and >450 mg/dL
females: <40 and >450 mg/dL
What are the critical glucose values for males? females?
hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia
low blood glucose levels? high blood glucose levels?
stress (trauma, infection, myocardial infraction (MI), strenuous exercise, shock)
What can increase serum glucose levels?
TREAT THE PATIENT, NOT the values
When it comes to glucose levels, normal/abnormal, what is important to remember in terms of treatment?
56 YO M - symptomatic
Who should we attend to more urgently:
- 56 YO M who is having extreme hunger, headaches, and tremors - glucose 45
- 37 YO F who has sedentary job, fasting at time of test, no symptoms reported - glucose 45
40 YO diabetic M - high glucose for fasting
Who should we attend to more urgently:
- 40 YO very active, non-diabetic F who just finished eating spaghetti dinner with garlic bread an hour ago - glucose 150
- 40 YO diabetic M who just awoke in AM and is still fasting - glucose 150
normal waste product of skeletal muscle metabolic processes - muscle contractions (released at a CONSTANT rate)
where does creatinine (Cr) come from?
kidney function
What do we use creatinine levels to assess?
YES (also not reabsorbed by tubules, secreted in minimal amounts)
Under normal circumstances, is creatinine freely filtered across the glomerulus?
INCREASED serum creatinine levels
What would happen to creatinine levels if kidney filtration was decreased?
muscle mass
What is a commonly known interfering factor that can impact creatinine levels?
ARTIFICIALLY LOW levels of creatinine - overestimating GFR and renal function
What kind of interference would we expect to see if an individual had LOW muscle mass (ex: elderly, amputee)?
HIGHER levels of creatinine - underestimating GFR and renal function
What kind of interference would we expect to see if an individual had HIGH muscle mass (ex: body builder)?
age
What is something that can impact the normal range of creatinine (normal: 0.6 - 1.2 mg/dL)?
HIGH dietary meat consumption
What can temporarily/transiently elevate serum creatinine levels?
Increased SCr by >/= 0.3 (mg/dL) within 48 hours OR 50% increase SCr in 7 days
OR
Decrease urine output <0.5 (ml/kg/hr) for >6 hours
How can creatinine levels/urine output help us assess if someone has an Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)?
YES, but with special equation that accounts for age, +/- ethnicity, and gender
Can creatinine help us estimate GFR function?
Formed in liver, product of protein metabolism and digestion
Where does BUN (blood, urea, nitrogen) come from?
mainly kidney function (BUN is excreted by kidneys), can be used to measure liver function as well
What do we use BUN to assess?
Dietary protein intake, muscle mass, and advanced pregnancy
What can impact the normal range of BUN (10-20 mg/dL)?
Bun:Cr ratio
What is the main lab value used to assess kidney and liver function?
Increases w/ age, decreases w/ muscle mass
What are some factors that can impact the normal Bun:Cr ratio?
low protein intake, advanced liver disease, rhabdomyolosis, kidney damage, hypothyroidism
What are some reasons for having a low Bun:Cr ratio?
dehydration, GI bleed, CHF, kidney disease, hyperthyroidism
What are some reasons for having a high Bun:Cr ratio?
eGFR
estimated glomerular filtration rate
Assess kidney function
serum Cr, sex, and age (CKD-EPI equation is fine for clinical use, even though it doesn't include race)
What is the main purpose for obtaining eGFR (normal: >60 mL/min/1.73 m^2)? What is needed to calculate this value?
elevated glucose (suggest diabetic), elevated Cr (not critical elevation, but still elevated), decreased GFR (in line with kidney disease)
What do we notice on this chart?
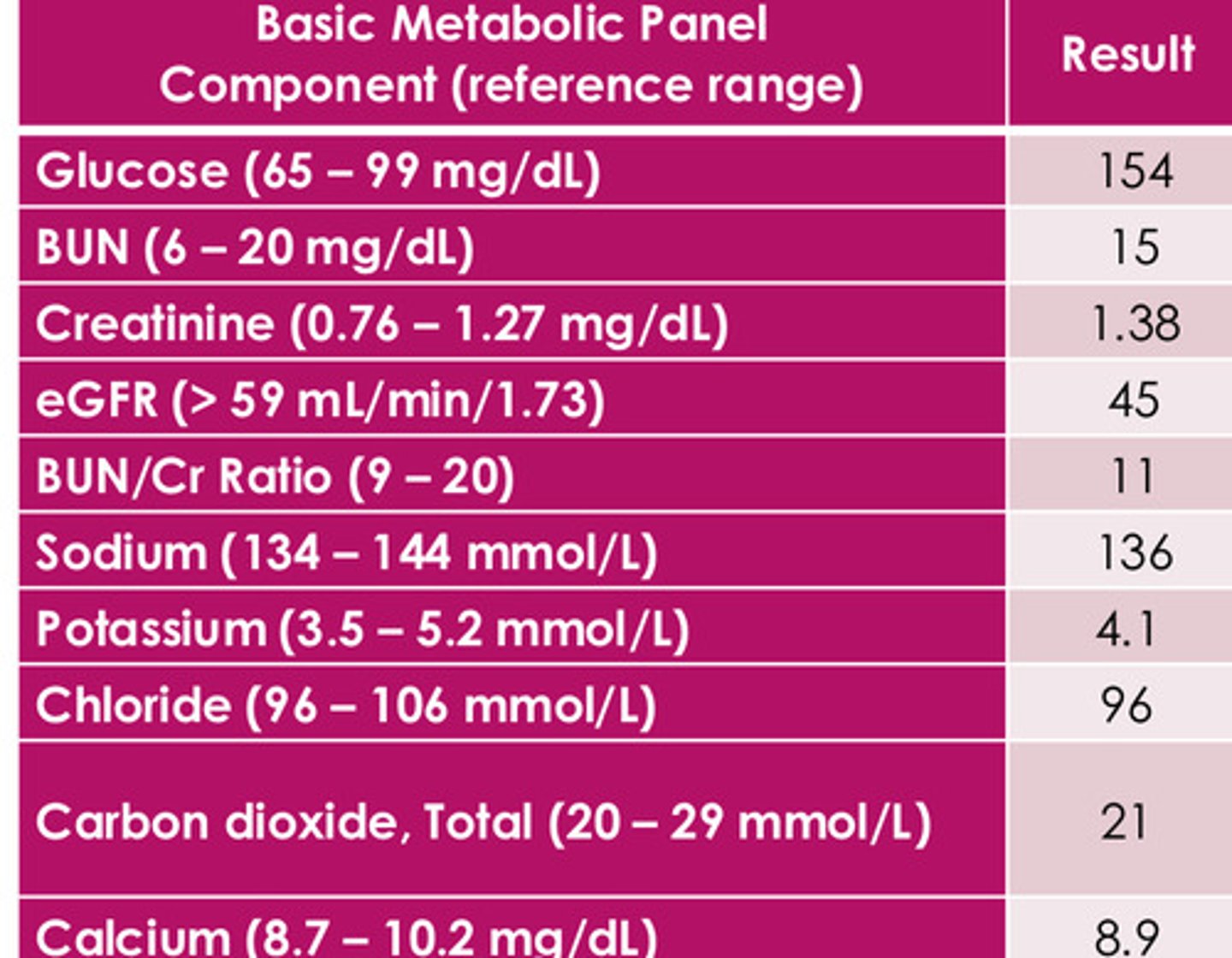
acute/chronic?
Does PT have diabetes, HTN, heart failure, acute illness, dehydration, autoimmune disease, etc.?
What is PTs baseline kidney function?
(PT has diabetes and stage 3 kidney disease)
What are some important questions to be asking based on the results of this chart?
Low glucose, elevated Cr, decreased GFR, elevated K (hyperkalemia - really worrisome - affects action potentials - concerned for cardiac issues)
What do we notice on this chart?
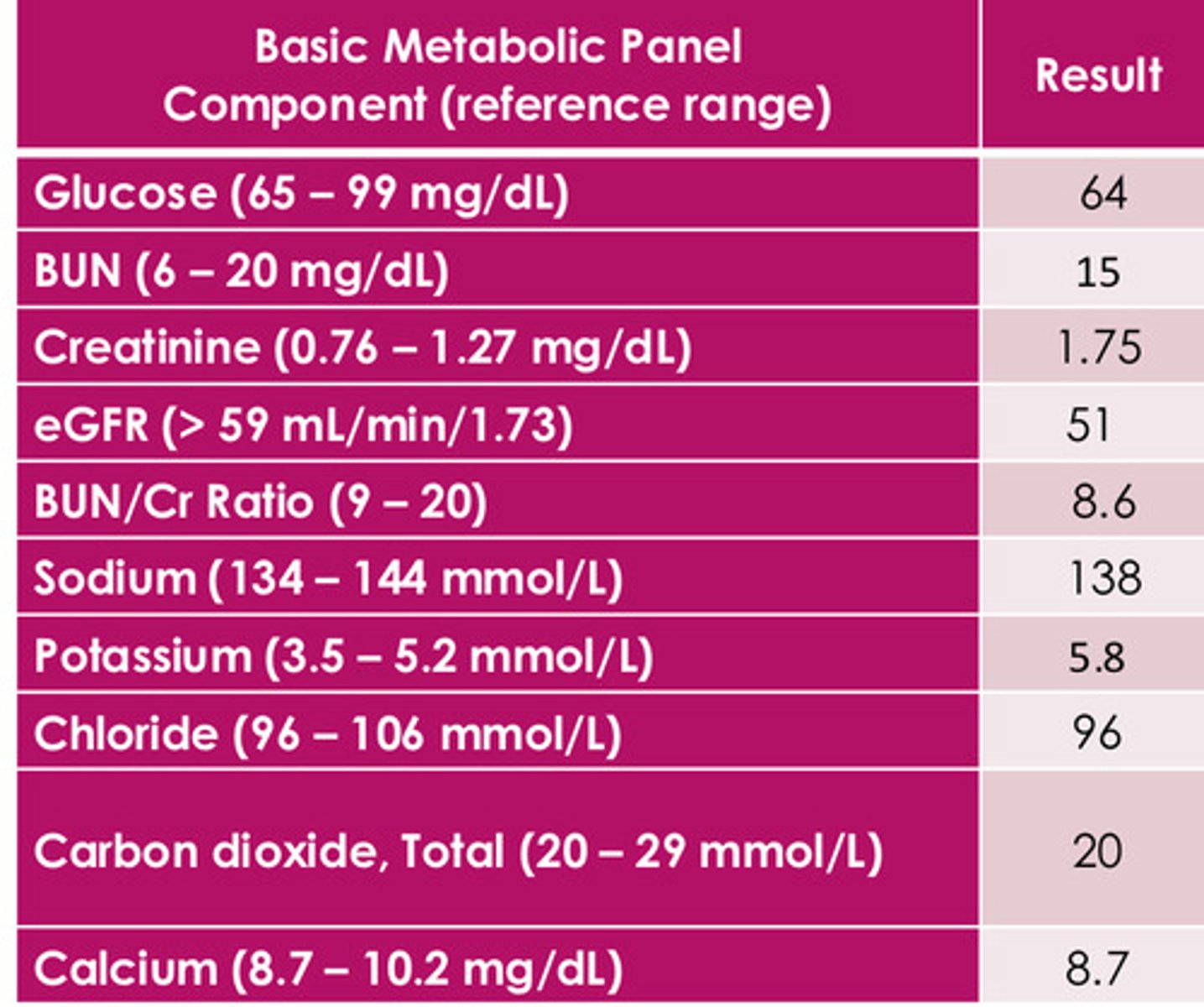
acute/chronic?
Does PT have diabetes, HTN, heart failure, acute illness, dehydration, autoimmune disease, etc.?
What is PTs baseline kidney function?
(concerned for RHABDOMYOLOSIS)
What are some important questions to be asking based on the results of this chart?
neuromuscular disease, cardiac function, bone metabolism, evaluate parathyroid function, renal disease, and some malignancies
What does calcium levels help us to assess?
Hypercalcemia
an abnormally high level of calcium in the blood (PT will be weak)
Hypocalcemia
an abnormally low level of calcium in the blood
hyperparathyroidism, malignancy, excessive Vit D intake, thiazide diuretics
When do we see hypercalcemia?
hypoparathyroidism, low Vit D, renal failure, Mg deficiency, massive transfusion, chemo, certain drugs (bisphosphonates)
When do we see hypocalcemia?
hypoalbuminemia (40% of Ca is bound to albumin), pH status (ionized Ca), prolonged tourniquet time
What are some things that can impact normal Ca levels (normal 9-10.5 mg/dL)?
electrolyte levels (extra-cellular anion -a negatively charged ion found outside of cells in the body's extracellular fluid)
What do chloride levels help us to assess?
Maintain electrical neutrality as a salt w/ Na+
Affects H2O balance - H2O moves w/ Na+ and Cl-
Buffer in acid-base balance - CO2 (cation) increases, bicarb (anion) moves from intracellular to extracellular space, Cl- will move back into cell to maintain electrical neutrality
What is the function of chloride?
excessive saline infusions (increase Cl levels)
What can impact normal Cl levels (normal 98-106 mEq/L)?
reflects bicarb - serum pH and electrolytes (major role in acid-base balance)
What do CO2 levels help us to assess?
Air (under-filling tube w/ blood), venous blood specimens not highly accurate - ABGs much more accurate for CO2 levels
What can impact normal CO2 levels (23-30 mmol/L)?
dissolved gas (mostly HCO3-, surrogate for bicarb)
CO2 on a BMP ≠ what?
inversely related (when one increases, the other decreases)
What is the relationship between CL and CO2?
assess fluid and electrolyte balance (MAJOR cation and electrolyte in extracellular space)
What do Na levels help us to assess?
dietary Na+ intake and renal excretion
What determines Na+ blood levels normally (normal 136-145 mEq/L)?
<120 or >160 (mEq/L)
What are the critical values for Na+?
aldosterone, natriuretic factor, and ADH
What three things work together to maintain appropriate levels of free water?
"Salt-retaining hormone" - promotes the retention/conservation of Na+ by the kidneys (decrease renal loss, increase BP)
Aldosterone
Hormones reducing blood volume (decrease Na+ reabsorption) and pressure - more urine output
Natriuretic peptides
controls water reabsorption in kidneys - increases water reabsorption in kidneys - decreases urine output (affects Na+ blood levels)
ADH (vasopressin)
Trauma, surgery, shock (increase levels - reduced renal blood flow)
What are some external factors that can impact Na levels?
high sodium in the blood (>150 mEq/L)
What is hypernatremia?
SLOWLY
Do we correct hypernatremia quickly or slowly?
increased morbidity (hemorrhages) and mortality
What happens as a result of hypernatremia?
dry mucus membranes, thirst, seizures, agitation, restlessness, hyperreflexia, mania, coma
What are some symptoms of hypernatremia?
rapid decrease of cerebral volume - cerebral vein rupture - hemorrhages
What happens as a result of acute hypernatremia?
less likely to induce neurological symptoms in the adult
slow correction in infants
what happens as a result of chronic hypernatremia?
- increase Na+ intake (dietary, IV)
- decrease Na+ loss (CUSHING SYNDROME - TOO MUCH ALDOSTERONE, HYPER ALDOSTERONISM)
- excessive free body water loss (GI loss, excessive sweating/burns, diabetes insipidus, osmotic diuresis)
- meds (steroids, estrogen, laxatives, OCP, cough meds)
In general, what can cause hypernatremia?
low sodium levels in the blood (<135 mEq/L)
What is hyponatremia?
weakness, confusion (change in mental status), lethargy, stupor, coma
what are some symptoms of hyponatremia?
- decrease Na+ intake (DIETARY, IV)
- increase Na+ loss (ADDISON'S DISEASE - INADEQUATE ALDOSTERONE and corticosteroid hormone levels, diarrhea, vomiting, nasogastric aspiration, diuretics, intraluminal bowel loss, etc.)
- increased free body water (hyperglycemia, CHF, pleural effusion, inappropriate/ectopic secretion of ADH (common), excessive oral/IV intake, peripheral edema etc.)
- meds (ACE, diuretics, heparin, NSAIDS, haloperidol, TCA, vasopressin)
In general, what can cause hyponatremia?
CARDIAC function, evaluate serious illnesses, maintenance of membrane electrical potential (neuromuscular tissue) - affecting HR and CONTRACTILITY
(MAJOR cation and electrolyte in intracellular space)
What do potassium, K levels help us to assess?
NO!!! (no renal absorption - excreted by kidneys)
Is potassium reabsorbed in the kidneys?
Aldosterone (increases renal loss of K)
Na reabsorption (K loss)
Acid Base balance (alkalotic states LOWER serum K levels, acidotic states INCREASE serum K levels - diabetic ketoacidosis)
tourniquet w/fist and hemolysis of blood (can increase K levels in blood)
What are some common factors that can affect K levels?
High potassium levels in the blood (>5.5 mEq/l)
What is hyperkalemia?
irritability, nausea/vomiting, GI cramping/colic, diarrhea
What are some symptoms of hyperkalemia?
ECG - PEAKED T WAVES (widened QRS, depressed ST), cardiac arrhythmias, paralysis, ascending muscle weakness (legs - trunk, arms)
What are some signs that someone is hyperkalemic?
- increase K intake (dietary, IV)
- Acute/chronic renal failure - inability of kidneys to excrete K (kidney disease)
- Addison's disease
- Hypoaldosteronism
- crush injury to tissues
- acidosis
- dehydration
- insulin deficiency (hyperglycemia, hyperosmolority)
- meds (BETA BLOCKERS, ACE-inhibitors/ARBs, digitalis overdose, aldosterone-inhibiting diuretics)
In general, what can cause hyperkalemia?
low potassium levels in the blood (<3.5 mEq/L)
What is hypokalemia?
decreased contractility, ECG - U waves, flattened T waves, cardiac arrhythmias, paralysis, ascending muscle weakness (legs - trunk, arms), cardiac sensitivity to digoxin
What are some signs that someone is hypokalemic?
- decrease K intake (DIETARY, IV)
- insulin administration - pushes K and glucose into cell (decreases serum K levels)
- diuretics
- burns
- GI (diarrhea/vomitting)
- hyperaldosteronism
- Cushing's Syndrome
- meds (amphortericin B (antifungal), barium intoxication, chloroquine intoxication, quetiapine and risperidone (antipsychotics))
In general, what can cause hypokalemia?