Chapter 14 Study Quiz
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
A DNA nucleotide consists of:
phosphate-deoxyribose-base
There are 4 different kinds of nucleotide bases in DNA. How many bases are in a DNA molecule (such as an entire chromosomes)?
millions or billions
How many DNA base pairs are in a typical gene? G
hundreds or thousands
The bases bond to the _________ in the backbone of DNA.
Sugar
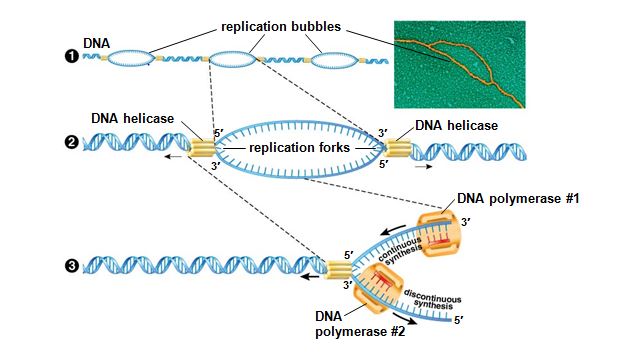
This figure represents the duplication of DNA. Which enzyme is breaking the double-stranded DNA molecule into single-stranded segments at the replication fork?
DNA Helicase
The hereditary material present in all cells is:
DNA
What two scientists won the nobel prize in science for their discovery and description of the DNA double helix?
Watson & Crick
In the comparison of a DNA molecule to a twisted ladder, the uprights (sides) of the ladder are:
alternating deoxyribose bonded to phosphates
If a DNA base sequence of GGCTTCG is mutated to GGATTCG, this type of mutation is considered a:
point mutation
In the structure of DNA, to what part do the nitrogen-containing bases covalently bond?
deoxyribose
In DNA, phosphate groups bond to:
the deoxyribose sugar
Watson and Crick are credited with the discovery and description of the DNA:
Double Helix
When chromosomes replicate:
the two DNA strands separate and each is used as a template for synthesis of a new strand
When does DNA replication occur?
During S of interphase
In the comparison of a DNA molecule to a twisted ladder, the steps of the ladder are:
nitrogenous bases linked together
The sequence of subunits in the DNA "backbone" is:
sugar-phosphate-sugar-phosphate
What is the relationship among DNA, a gene, and a chromosome?
A chromosome contains hundreds of genes, which are composed of DNA.
If a DNA base sequence of ACGTTCG is mutated to ACCGGTTCG, this type of mutation is considered a:
Insertation mutation
During DNA replication, what is the name of the enzyme that matches the nucleotide base in the original parental DNA strand with its complementary partner?
DNA Polymerase
T or F: "In eukaryotic cells, chromosomes consist of both DNA and proteins."
True
T or F: The number of subunits in a DNA molecule is more important to its function than the sequence of these subunits.
False
During DNA replication, what is the name of the enzyme that separates the parental strands of DNA?
DNA Helicase
In DNA, complementary base pairs are held together by:
hydrogen bonds
Where does DNA replication occur in eukaryotic cells?
the nucleus
Where does DNA replication occur in prokaryotic cells?
the cytoplasm
How many different kinds of nucleotide bases are in DNA?
four
There are 4 different kinds of nucleotide bases in DNA. How many bases are in a DNA molecule (such as an entire chromosomes)?
millions or billions
________________ discovered DNA in 1869 and called it "nuclein," showing it was in the nucleus of cells.
Friedrich Miescher
_____________ discovered the process of transformation in 1928, showing that genetic material could be transferred between bacteria.
Frederick Griffith
In 1944, they identified DNA as the "transforming principle," proving that DNA is the molecule responsible for heredity
Oswald Avery, Colin Macleod, and Maclyn McCarty
In 1952, they confirmed that DNA, not protein, is the genetic material using experiments with viruses (bacteriophages).
Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase
discovered in 1950 that in DNA, the amount of adenine equals thymine (A = T), and guanine equals cytosine (G = C).
Erwin Chargaff
used X-ray diffraction in the 1950s to produce images of DNA, revealing its helical structure.
Rosalind Franklin
in 1953, proposed the double helix structure of DNA, based on Rosalind Franklin’s X-ray data.
James Watson and Francis Crick
The four nitrogen-containing bases are:
adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine
The sugar in the nucleotide is:
deoxyribose
the phosphate group is attached to the _____ in each nucleotide.
deoxyribose sugar
In the DNA double helix, the two strands run in _________ directions. One strand runs 5' to 3', and the other runs 3' to 5'.
antiparallel
The order of nitrogenous bases (A, T, C, G) in the DNA sequence determines…
the genetic information, which is used to build proteins
DNA in a eukaryotic cell is wrapped around proteins called ______, forming nucleosomes.
histones
DNA in a eukaryotic cell is wrapped around proteins called histones, forming __________.
nucleosomes
DNA replication is __________________, meaning that each new DNA molecule consists of one old strand and one newly synthesized strand.
semi-conservative
_____________ unwinds the DNA double helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs.
DNA helicase
______________ bind to the separated DNA strands to prevent them from re-joining during replication.
Single Strand Binding Proteins
______ adds short RNA primers to the DNA template to start the process of replication.
Primase
____________ adds complementary nucleotides to the growing DNA strand and also proofreads the newly synthesized DNA strand, correcting any errors in base pairing to reduce mutations.
DNA polymerase
_______________ are the building blocks that DNA polymerase uses to form the new DNA strand.
Free nucleotides
____________ seals the gaps between Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand, joining the fragments into a continuous strand.
DNA ligase
____________ adds repetitive DNA sequences to the ends of chromosomes (telomeres) to prevent loss of important DNA during replication.
Telomerase
A gene mutation is:
a change in the sequence of nucleotides in the DNA
A point mutation is:
a change in a single nucleotide in the DNA sequence.
A frameshift (insertion and deletion) mutation occurs when:
nucleotides are added or removed from the DNA sequence
A translocation mutation occurs when:
a segment of one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosome