Conduction, convection and radiation
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Energy is transferred by ___ and ___ via the processes of
conduction
convection
radiation
heating and radiation
What is thermal conduction? What about electrical conduction?
Thermal conduction is the transfer of thermal (heat) energy through a substance (usually in solids) by the vibration of the atoms within the substance
The substance itself DOESN’T move
Electrical conduction is the movement of electric charge through matter
Conduction is the main method of energy transfer by heating in solids
What are good conductors of heat? What is the name for a bad conductor?
Metals
Insulator
Explain the process of heat energy transfer by conduction
When a substance is heated, the atoms start to vibrate more in that area because they have more kinetic energy
These particles containing more energy bump into neighbouring particles and transfer some of this energy to them
The process repeats
IMPORTANT: this process takes place in all materials
What is the order of best thermal conduction between the three states of matter? Explain
Best are solids, then liquids and then gases
The particles in a liquid/gas are further apart than solids. This means that the frequency of collisions is reduced so less heat energy is being transferred to neighbouring particles in a fixed time in gases/liquids compared to solids.
More frequent collisions increase the rate of transfer
Why are metals good conductors of heat?
First they are solids so the particles are close together in a lattice so particles collide more frequently through vibrations
They have delocalised electrons that absorb heat energy and so gain KE so move faster
as they move through the metal, they collide with the ions, transferring energy much faster than atomic vibrations alone
Practical: investigate how well different metals conduct heat
Describe a method
Attach ball bearings to the ends of each metal strip at an equal distance from the centre, using a small amount of wax
The strips should then be turned upside down and the centre heated gently using a bunsen burner so that each of the strips is heated at the central point where they meet
When the heat is conducted along to the ball bearing, the wax will melt and the ball bearing will drop
Time how long this takes for each of the strips and record in a table
Repeat the experiment and calculate an average of each time
The first ball bearing to fall will be from the rod that is the best thermal conductor
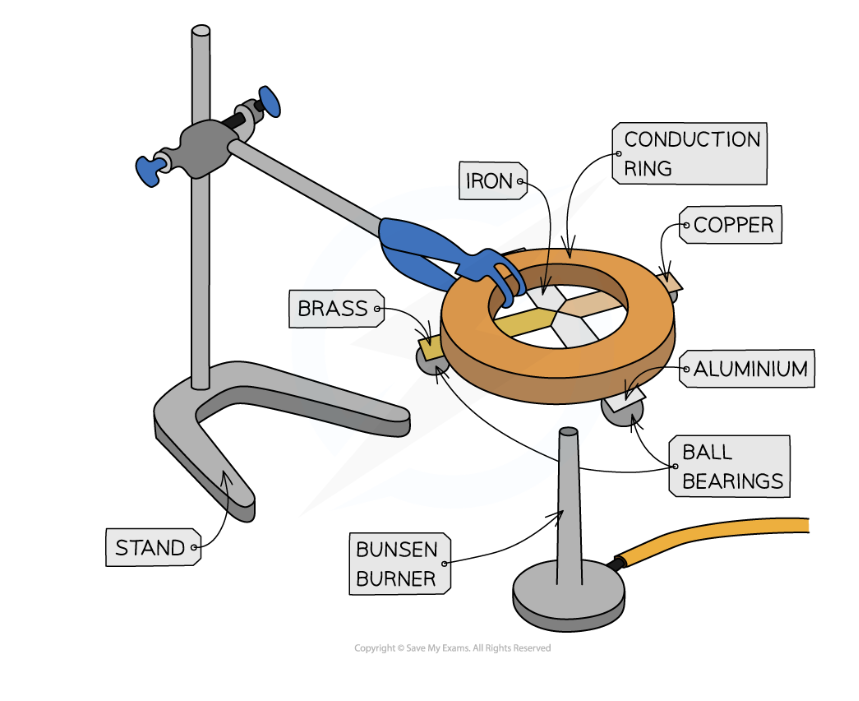
Variables?
What should you do to ensure a valid test?
Independent: type of metal
Dependent: rate of conduction
Control: length and thickness of metal rods, amount of wax used, identical ball bearings
Allow the rods to cool to room temperature before heating so that they all begin at the same temperature
What is convection?
Convection is the transfer of thermal energy through fluids (liquids and gases) by the upward movement of warmer, less dense regions of fluid
Convection ONLY occurs in fluids
Explain convection: what happens when a fluid is heated? What is this called?
Heat is initially transferred through the glass wall of the beaker by conduction (if in liquid)
The molecules push each other apart, making the fluid
This makes the hot fluid less dense than the surroundings
The hot fluid rises, and the cooler (surrounding) fluid moves in to take its place
Eventually, the hot fluid cools, contracts and sinks back down again
The resulting motion is called a convection current


Can you explain why, when a piece of card is set over the chimney that is not above the candle, the candle quickly goes out?
The rising warm air above the candle is not replaced by any air. Oxygen does not reach the flame and so it goes out.
How do temperature difference at the Earth’s surface occur?
If there are different surfaces such as land and sea
What happens during daytime? Which direction does the breeze flow?
Al revés during nighttime
Breeze towards the shore
During daytime, the land heats up quicker than the sea water
Air above the land is heated, expands and begins to rise
The rising air is replaced by cooler air drawn in from the surface of the sea
This is why it can be cooler by the coast while further inland the temperature is higher
Explain the difference between heat and temperature
Heat is the total amount of energy
Temperature relates to the average kinetic energy of particles
A 20 degree pool contains more heat than a 60 degree cup of coffee.
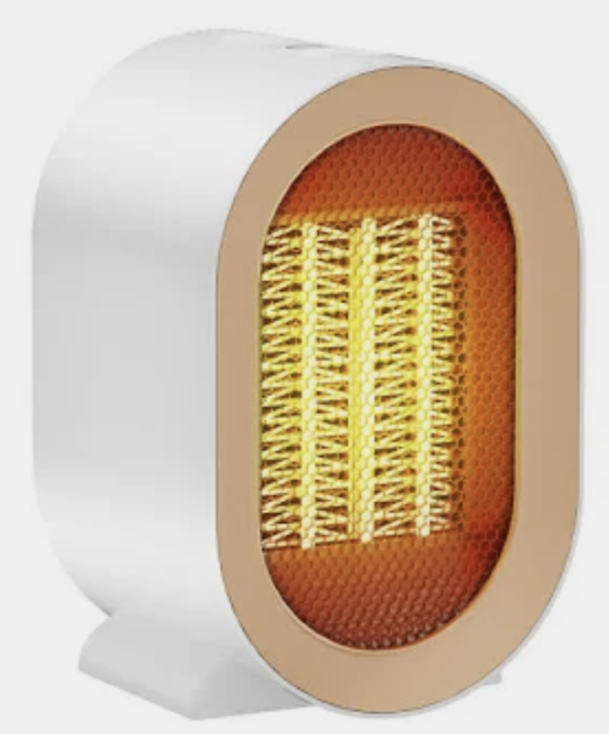
When you turn on a bathroom heater you feel the warmth instantly. Why is it not conduction nor convection?
It is not conduction bc conduction doesn’t occur that fast + air is a bad conductor
It is not convection either because it would result in heated air floating upwards on colder, denser air
How is heat energy travelling in this example? How would we know apart from the fact that it is really quick?
As infrared waves (heat waves)
The heat is travelling from the heater in a straight line
The design of the bathroom heater includes a specially shaped very shiny reflector, similar to the reflector behind a fluorescent light or in a torch
What is thermal radiation?
The transfer of energy by infrared waves.
Remember that we are talking about heat transfer — this is thermal radiation not nuclear radiation!
All objects ____
emit IR radiation (no matter what temperature)
Why is thermal radiation quicker than conduction?
Infrared waves have same properties as the other EM waves therefore:
radiation transfers heat via IR waves traveling at the speed of light
while conduction relies on slower molecular collisions.
What is a notable difference between conduction/convection and radiation? Evidence of this?
Conduction and convection require particles while radiation can take place in a vacuum
That is why the Earth can be heated up by the Sun even though it is in space and so far away
The sun radiates across the entire em spectrum but its peak output to Earth is the visible light and infrared parts, with small amounts of UV
Just like visible light, objects can ____ and ____ infrared waves.
Reflected and absorbed/emitted
Good emitters/radiators are good ___ of IR
Good reflectors are poor ___ of IR
Absorbers
Absorbers
Factors affecting radiation
Colour:
black — good absorber/emitter
white — bad absorber/emitter
Finish:
dull — reasonably good absorber/emitter
shiny — very poor absorber, it reflects it and also bad emitter
Surface area:
high SA — good absorber/emitter
low SA — bad absorber/emitter
How hot it is:
hotter — good emitter
cooler — bad emitter
The hotter an object, the ___
more infrared radiation it radiates in a given time
What changes occur as you increase the temperature of an object?
The hotter an object, the more infrared radiation it emits per unit of time
The nature of the EM waves also changes:
At low temperatures, most of the radiated energy is in the form of IR waves (invisible to the human eye).
As temp increases radiated waves shift to higher frequencies and shorter wavelengths, meaning more energy is emitted, moving from invisible infrared towards visible light (glow dull red, then orange, yellow, white)
This effect is the same as that of planets (astrophysics)
When talking about energy absorbed/emitted/reflected always say THERMAL RADIATION (not heat)
When will objects stop releasing heat?
Objects will continue to lose heat until they reach thermal equilibrium (equal temperature) with their surroundings
For example, a mug of hot coffee will cool down until it reaches room temperature
Why would you want to reduce rate of thermal energy loss?
It can become expensive
Production of energy using fossil fuels produces greenhouse gases, which contribute to global warming
Conduction is the main way thermal energy dissipates to the surroundings. How can we reduce energy transfer by conduction?
What would you take into account when choosing these materials when building a house? What is a good example material to build houses with?
Insulating materials should be used
They should be strong, durable and at a sensible price
Brick
How can we reduce energy transfer by convection?
Convection currents must be prevented from forming. Therefore the fluid that forms the currents must be prevented from moving
When talking about convection ALWAYS mention convection currents
Insulation reduces energy transfer from both conduction and convection.
What does the effectiveness of an insulator depend upon? Explain
Thermal conductivity of a material: the lower the conductivity, the less energy transferred
The density: the more dense the insulator, the more conduction can occur
in a denser material, the particles are closer together
The thickness: the thicker the material the better it will insulate
How is thermal energy loss reduced in houses?
Roofs and walls are made from insulating materials reducing thermal energy lost by conduction
Cavity wall insulation (fiberglass) prevents loss of energy by conduction and convection. This traps air between the fibres which prevents convection currents from forming in the wall cavity and transferring thermal energy from the inner layer to the outer layer.
The panels can be covered with shiny aluminium foil which prevents loss by radiation as it reflects IR radiation
Double glazed mirrors reduce loss by conduction (mirrors made of insulator glass) and convection by trapping air preventing convection currents from forming
Other ways include: reduction of draughts around doors preventing air currents + carpets which prevent thermal energy loss by conduction
They all reduce the rate of energy transfer from the home
What would happen if the layer of air between the glass panels in double glazed windows were too thick or thin?
Too thin and its insulating property would be reduced
Too thick and it would allow convection currents forming and transfer thermal energy from the hotter surface to the cooler one
Why do wool fleeces keep us warm? What would happen is we were to get oven mittens wet? What about wetsuits?
Air gets trapped in the fibres preventing convection currents from forming
Air is an thermal insulator preventing conduction
The trapped air is heated by your body and forms an insulating layer that stops you from losing heat
You might burn yourself because water is a better conductor of heat than air
Same thing but traps water next to the diver’s skin
A large proportion of body heat is loss from the ___
head, wear a hat
How does wind cause rapid heat loss from out bodies? What is a term for this? How can we prevent this?
It does this by forces convection. Makes cool air circulate close to the body surface
Causes sweat to evaporate quicker causing rapid cooling
The cooling effects of wind contributes to the wind-chill factor. To reduce the wind-chill effect, a piece of wind-proof outer clothing should be worn
When people do loose body heat at great rate they become hypothermic. When people are rescued from e.g mountains, they are wrapped in a thin reflective blanket
Other things to watch out for:
Heat does not rise (only hot gases or liquids rise)
Shiny things do not reflect heat (they reflect thermal radiation)
Black things do not absorb heat (they absorb thermal radiation)