Biology Unit 1 (Reproduction)
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
Cleavage
-Cell division without growth
-Composed of three stages
-Happens so fast the cell doesn’t have time to replicate cytoplasmic contents
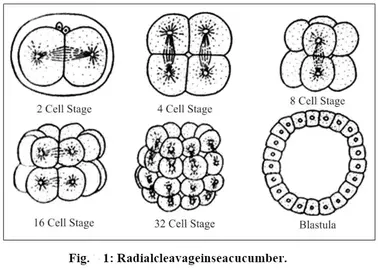
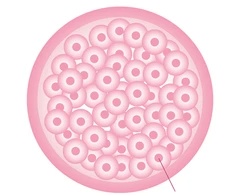
Morula
When the zygote has 16 cells
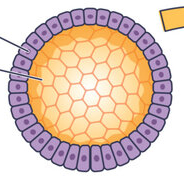
Blastula
embryo of the stage of implantation
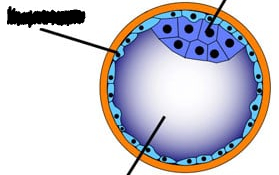
Trophoblast
Forms placenta and secretes HCG
Human Growth Hormone
secretes estrogen + progesterone to maintain endometrium + prevent ovulation
Gastrulation
The formation of 3 primary germ layers
Gastrula
The developing embryo
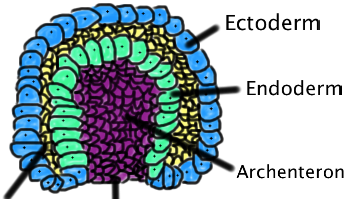
Primary Germ Layers
The first layers of the cells that form during embryonic development
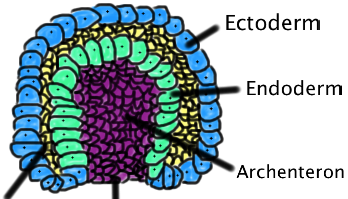
Ectoderm
-Outer germ layer
-Forms skin, nervous system (brain + spinal cord), sense organs
-Ectodermal cells form the neural tube
Mesoderm
-Middle germ layer
-Forms muscles, bones, and cartilage, components of blood
-Mesodermal cells will form the notochord- the backbone
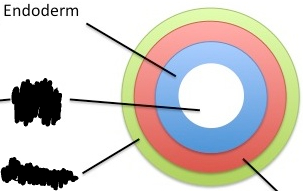
Endoderm
-Inner germ layer
-Lining of the respiratory system and digestive system
Differentiation
The process that allows specialization of cell function. All future tissues and organs systems of the body will develop from the cells of the germ layers
Neurulation
-Development of the brain and spinal cord
-At two weeks, neurulation begins
-The developing embryo becomes a neurula
Germ layer
A group of cells that are going to differentiate collectively
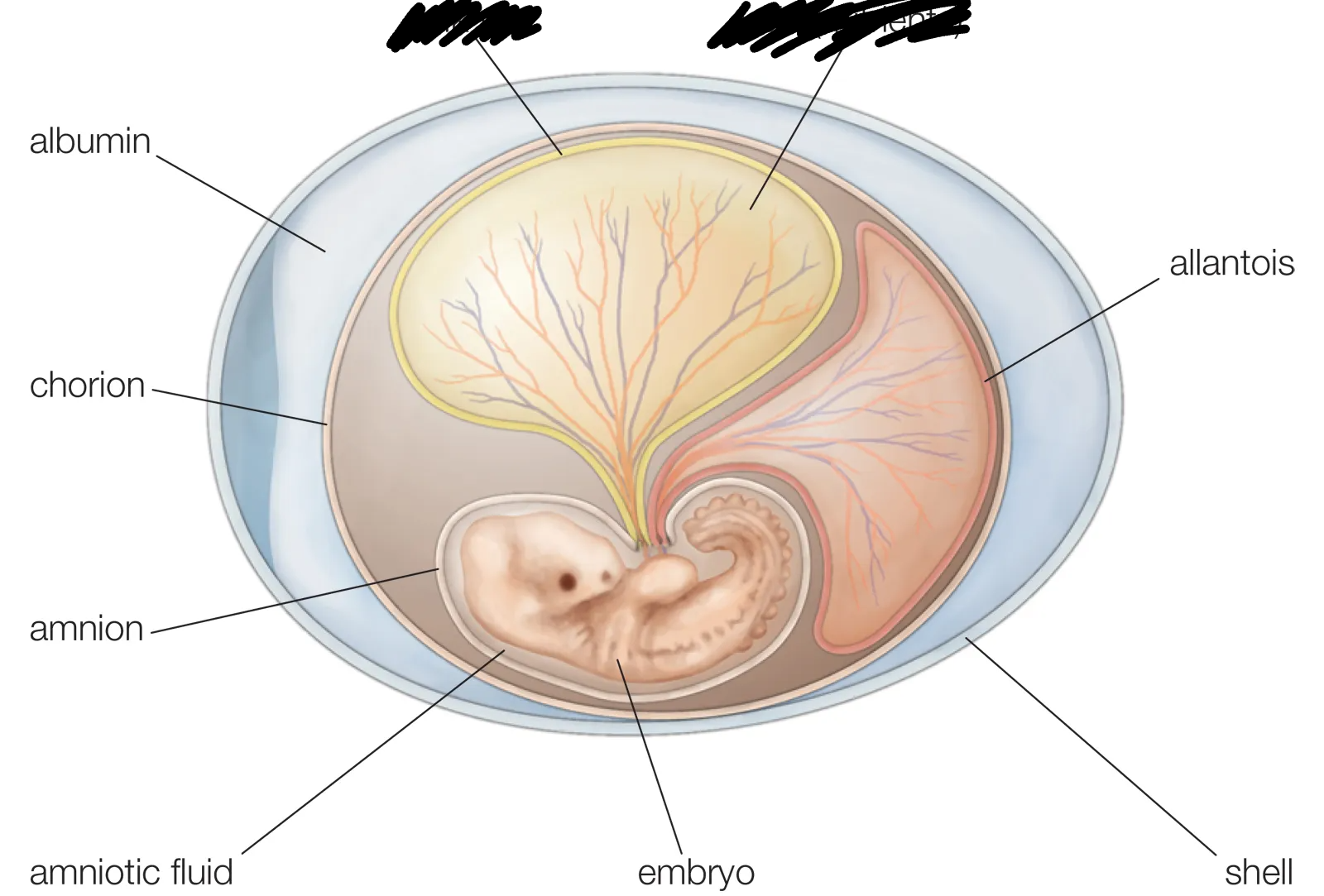
Extra-embryonic membranes
System of membranes external to the embryo,. used for protection, nutrition, respiration, and excretion
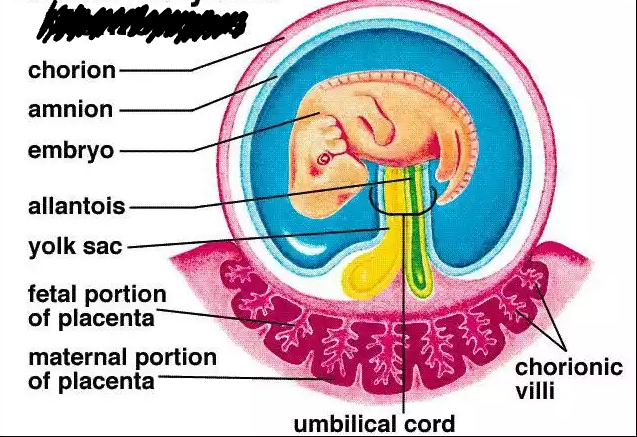
Allantois
Forms the umbilical cord
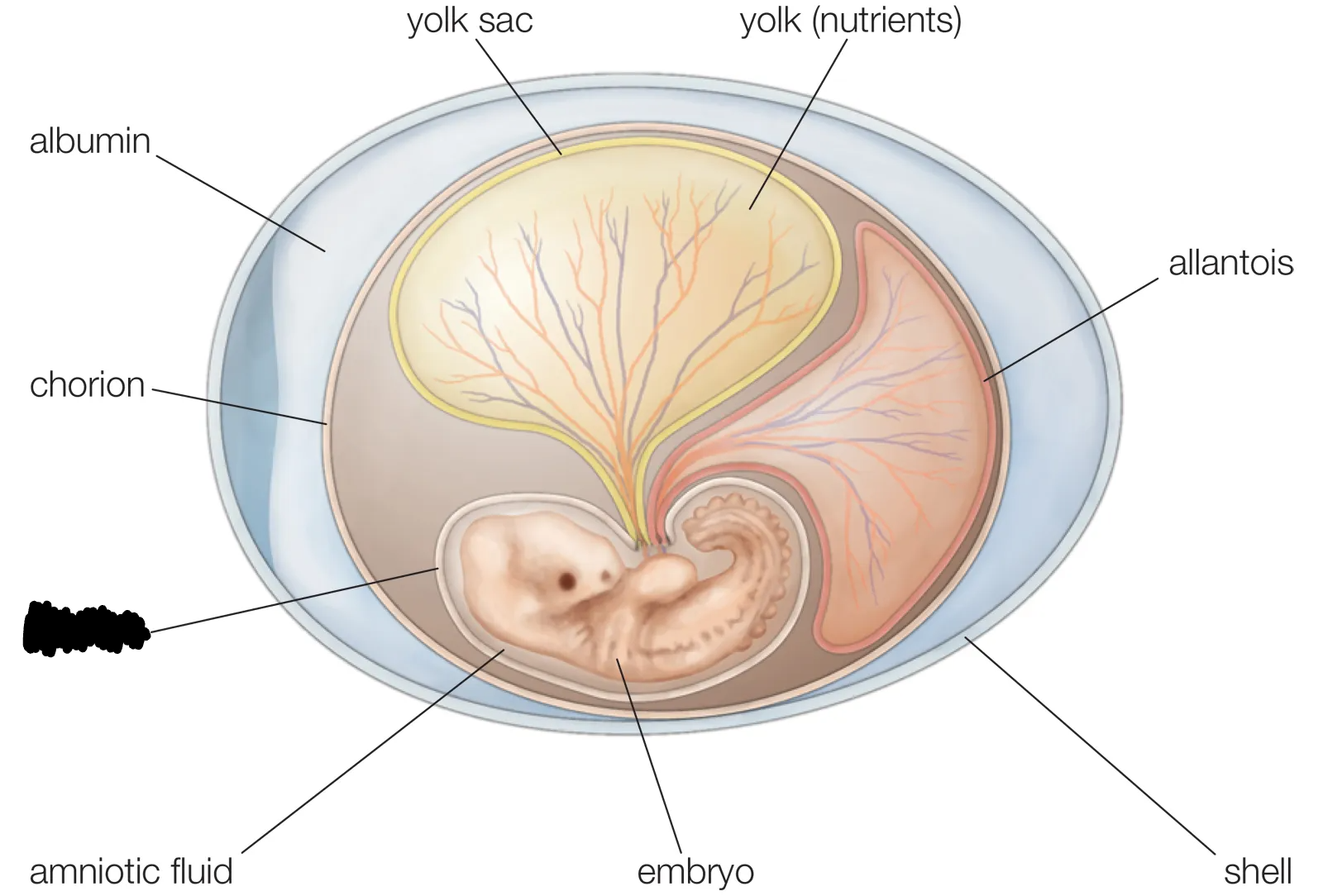
Amnion
Fluid-filled sac used for protection
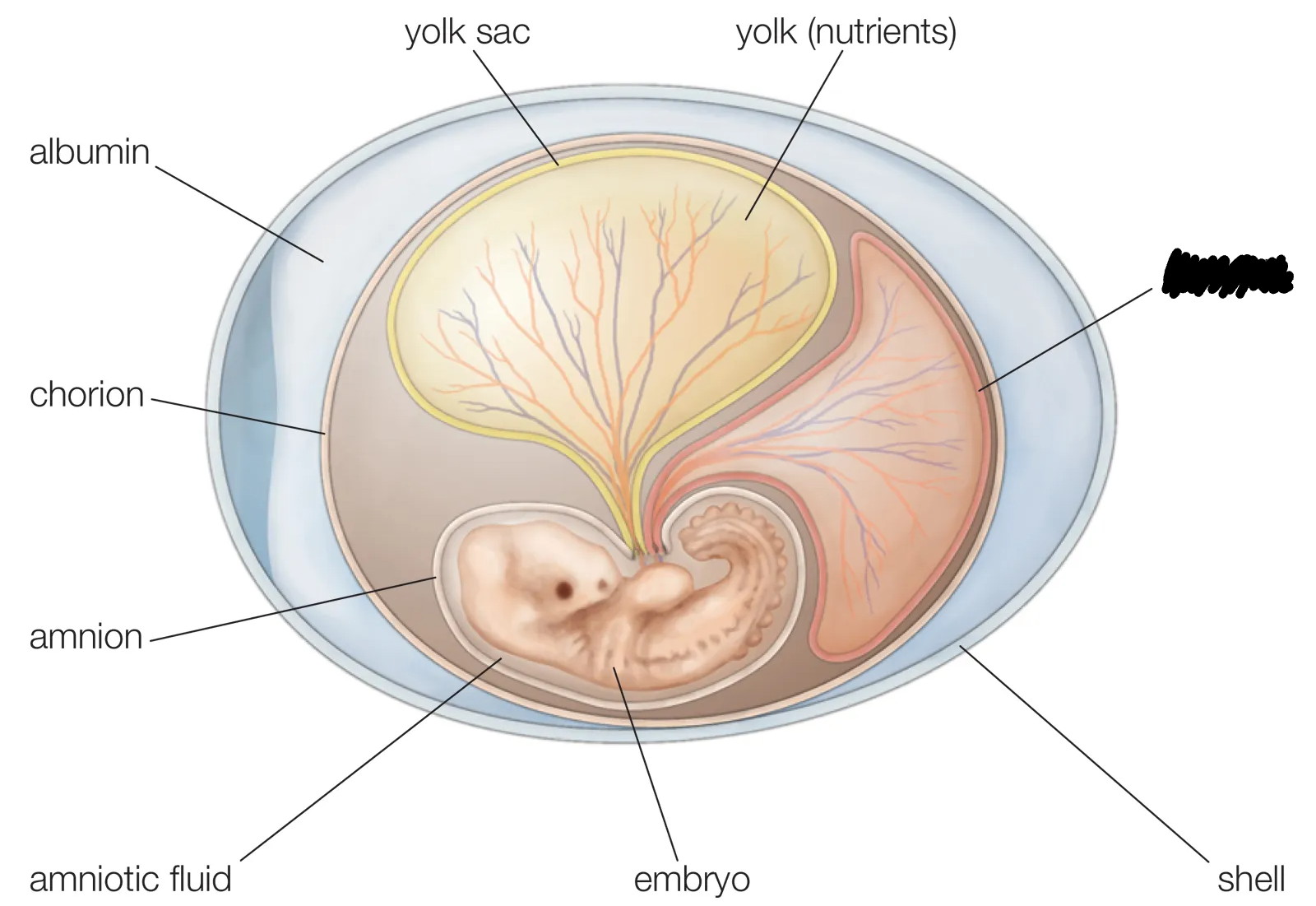
Chorion
Forms the placenta
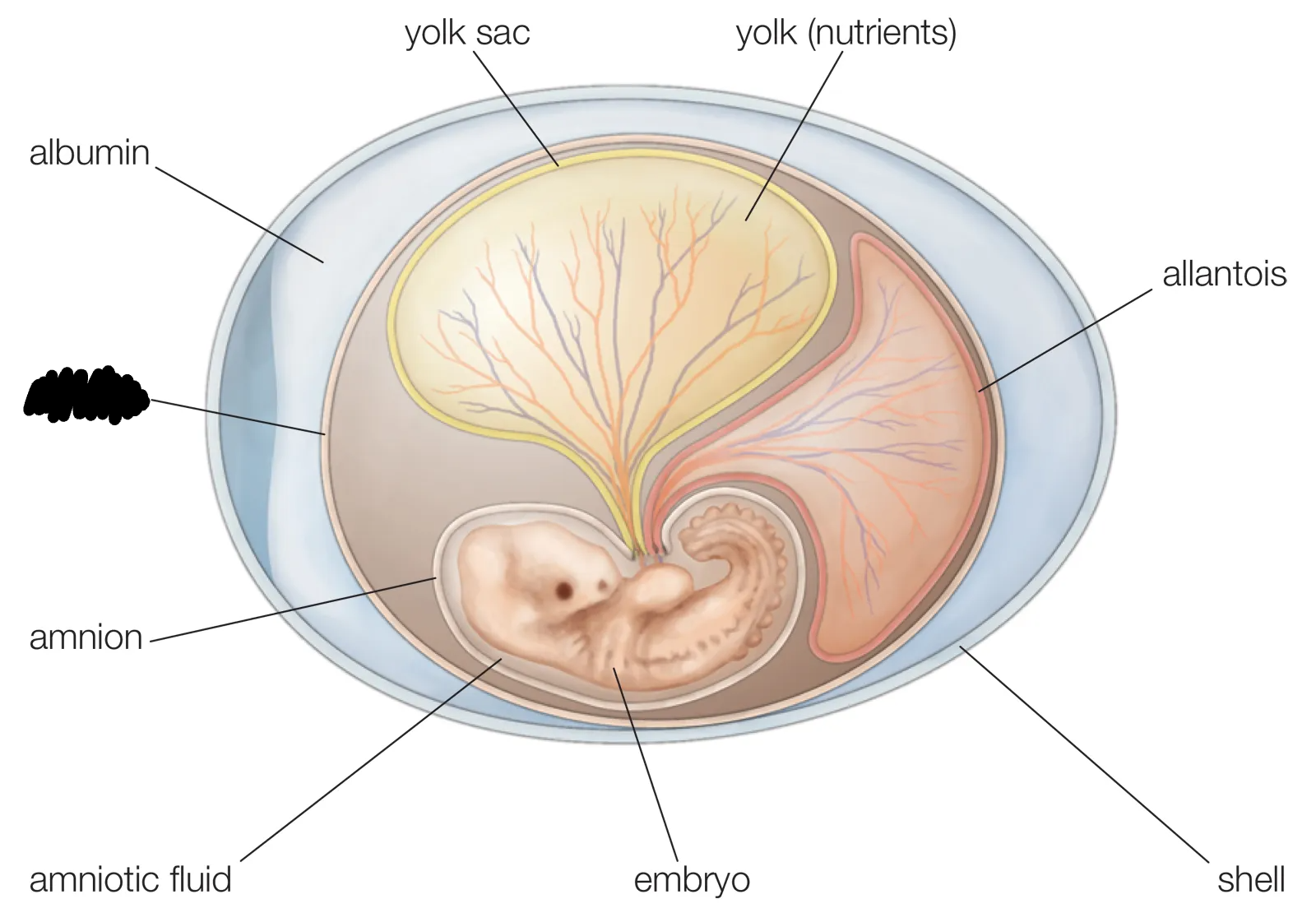
Yolk Sac
Site for the first blood cell production
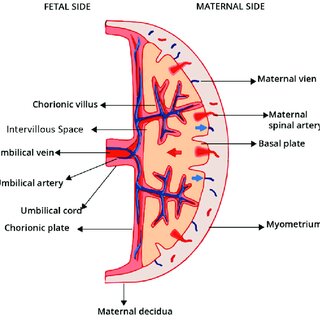
Placenta
-Formed from the chorion, it attaches the fetus to the uterine wall
-Nutrients and oxygen diffuses from the mother’s circulatory system to the baby and waste products leave that baby’s circulation
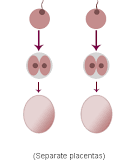
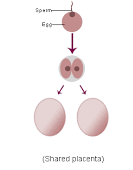
Fraternal Twins
-Dizygotic Twins
-Two eggs, two sperm, two separate fertilizations
-Twins are not genetically identical
Identical Twins
-Monozygotic Twins
-One egg, one sperm, one fertilization
-The zygote splits
-Twins are genetically identical
Parturition
The process of giving birth
Dilation
-Birth contractions cause cervix to dilate
Expulsion
-The baby is born
-It pushes through the cervix to the birth canal
Placental
After the birth, the placenta and umbilical cord (afterbirth)
Partuition Feedback Control
-Positive Feedback Mechanism
-Oxytocin released by pituitary gland
-Causes uterine contractions
-Cervix dilates and uterus to secrete prostaglandins
-Continues until birth
Lactation
-Positive Feedback Mechanism
-Caused by prolactin
-The suckling reflex
Teratogens
-An agent that causes a structural abnormality of a fetus due to exposure
-Worse during the first trimester
Home Pregnancy Test
Checks for HCG hormone in urine
Maternal Blood Test
Used to measure hCG levels, test for gestational diabetes, and evaluate chromosomal abnormalities
Ultrasound
Uses sound waves to create an image of the fetus, provides information about physical abnormalities, and is non-invasive
Amniocentesis
-A needle is used to draw amniotic fluid from the uterus
-Done at 14 weeks
-Used to check for chromosome abnormalities
-Highly Invasive
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS)
-Cells are taken from the chorion to create a Karyotype
-Around 9 weeks of pregnancy
-Used to check for chromosome abnormalities
-Highly invasive
Karyotype
An individuals complete set of chromosomes
Cell-free DNA prenatal screening
-A blood test is done to look for DNA fragments in the placenta
-Non-invasive but a positive test result must be confirmed with an invasive method
Fetoscopy
A procedure where a small instrument (laparoscope) is inserted into the uterus in order to see the fetus and placenta
Sterile
Inability to have kids
Infertile
Difficulty conceiving (Tryiing for 1+ years)
Male Infertility
-Obstruction in ductus deferens
-Low sperm count
-High # of non-viable sperm
-Inability to achieve erection
Fermale infertility
-Blocked oviducts
-Failure to ovulate
-Endometriosis
-Damage eggs
Artificial Insemination
-Sperm are collected and concentrated before being place in uterus
-Usually male infertility (cryopreservation)
Invitro Fertilization
Follicles that are closed to ovulation are identified and placed in glassware with sperm
In Vitro Maturation
Immature follicles are taken out of ovaries and are treated in the lab to avoid risks of stimulating ovaries
Gamete Intrafallopian Transfer (GiFT)
Sperm and egg are brought together in oviduct
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)
1 sperm is injected into an egg
Surrogate Mother
May be used by a infertile couple or a high risk mom
Super Ovulation
-Hormone treatment to cause ovulation of multiple eggs
-Women who have irregular cycles
-Increases chance of multiple births
Surgical Sterilization
-Vasectomy, tubal ligation and hysterectomy
-0% chance of pregnancy
Hormonal Contraceptives
Form of Reducing Reproductive Potential using hormones
Physical/Chemical Barriers
Form of reducing reproduction that includes barriers
Natural Methods
Form of reducing reproduction that can include ovulation tracking
Centrioles
During cell reproduction they produce microtubules that will eventually pull the chromatids apart
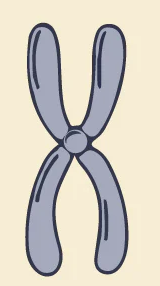
Chromosome
Short and fat DNA
Chromatid
Duplicated DNAthat is joined to its sister chromatid at the centromere and is separated during cell division.

Chromatin
-Long and thin DNA
-Stable form of DNA
Carbohydrates
Sugars
Monomer: Saccharide
Lipids
Monomer- Glycerol + Fatty Acids
Proteins
Monomers-Amino Acids
Nucleic Acids
Monomers-Nucleotide
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
Made of individual units called Nucleotides
G1 Phase (Interphase)
In this phase the new (baby) cell undergoes rapid growth and development
Synthesis Phase
During this stage DNA replicates (semi conservative DNA replication)
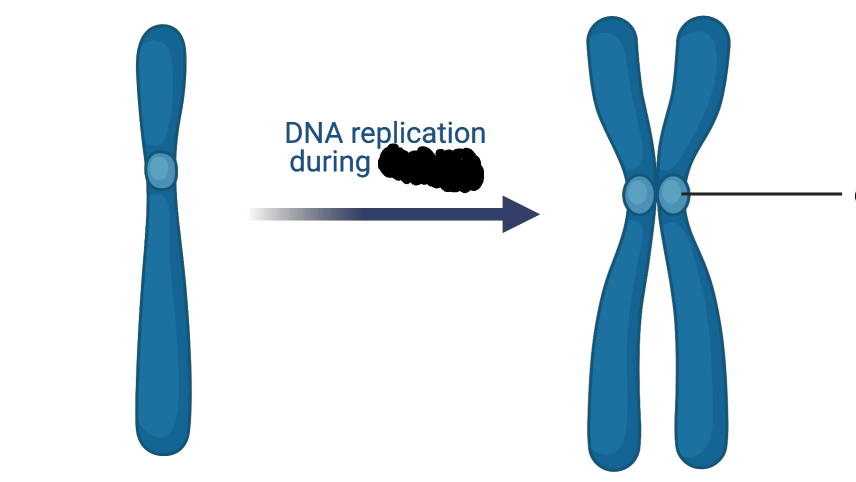
Centromere
A protein that holds two chromatids together; found all DNA
G2 Phase
Preparation for Mitosis
The centrioles replicate and move to opposite poles of the cell
2 centrioles replicate themselves
Prophase
-the nuclear membrane disintegrates
-the chromatin condense to become chromosomes (shorten and thicken)
-the centrioles produce spindle fibres
-the nucleolus disappears
Metaphase
-the alignment phase
-during metaphase the chromosomes align at the center (equator0 of the cell
-the spindle fibres attach to the centromeres of each chromosome
Anaphase
-the seperation phase
-during this stage the spindle fibres pull the chromatids apart
-they retract towards the poles of the cell
Telophase
-the spindle fibres disintegrate
-the nuclear membrane reforms around each set of DNA
-the chromosomes elongate and become chromatin (stable form of DNA)
-the cell membrane begins to invaginate
-the nucleolus reappears
Cytokinesis
-this is the last stage of the cell cycle
-the cell invaginates at the center to form two new identical daughter cells
Homologous chromosomes
-these are the chromosomes that have the size, shape, and genetic content
-they differ only in their alleles
Seminal Vessicle
-produces sugar and prostaglandins
-the sugar provides energy for the sperm
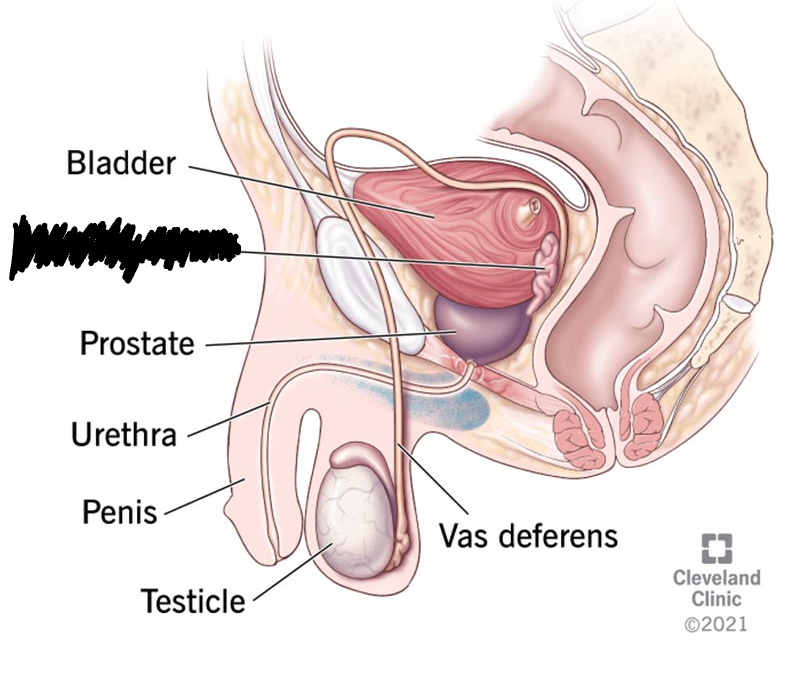
Prostate Gland
produces an alkaline base that reduces the acidity of the vagina
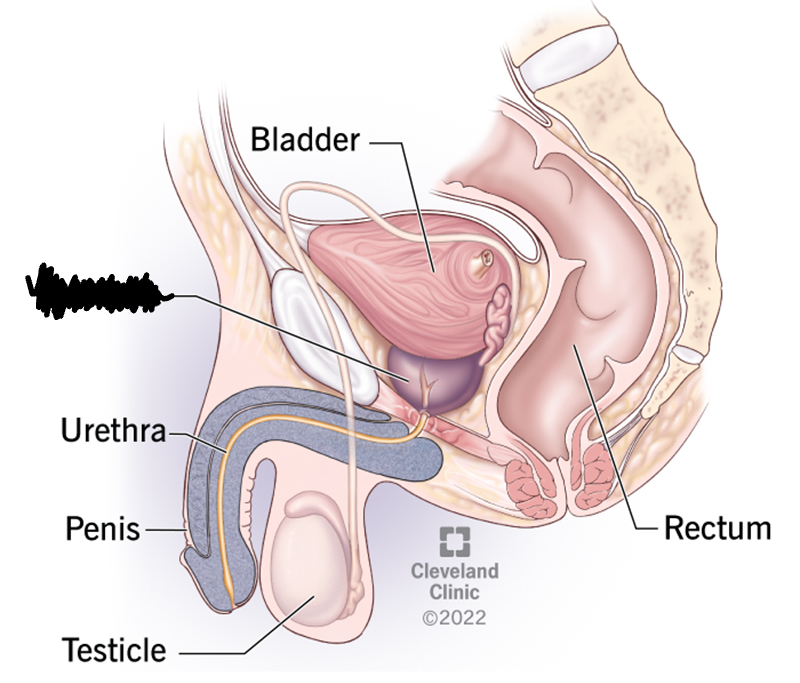
Cowper’s Gland
-provides a prejaculatory fluid
-it lubricates and provides a medium for sperm to swim
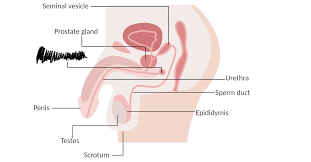
Vagina
An entrance for the erect penis to deposit sperm during sexual intercourse and an exit for the fetus during childbirth
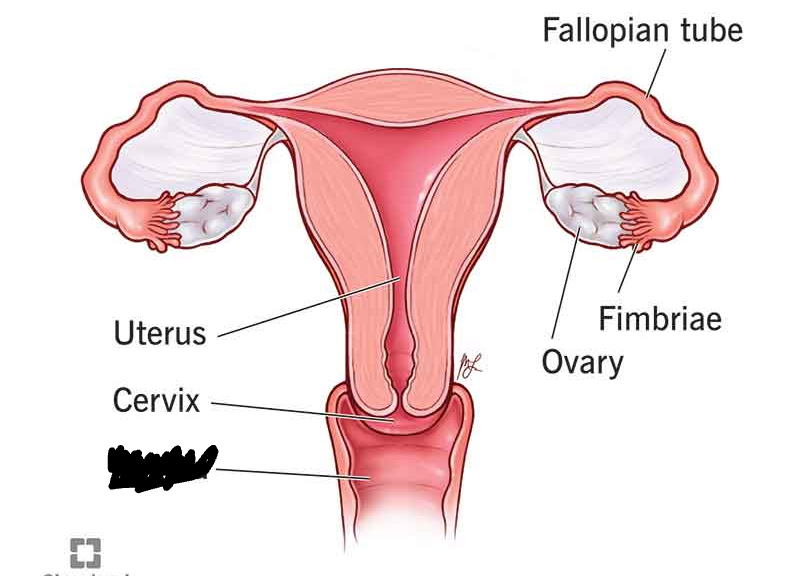
Cervix
An opening/exit to the uterus, a thick-walled muscular organ hat expands to six times it’s size to accommodate a fetus
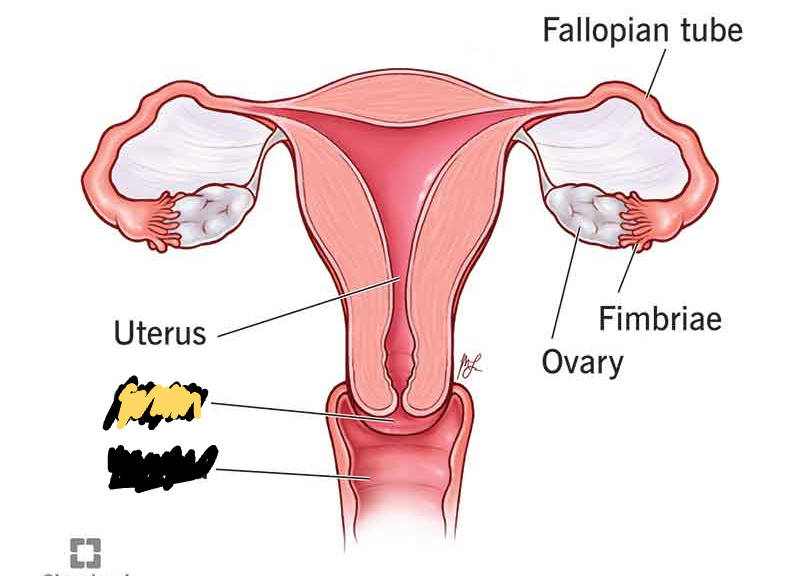
Endometrium
The lining of the uterus that is richly supplied with blood vessels to provide nutrients to a developing fetus. The - is affected by the changing hormone levels of the menstrual cycle

Myometrium
The external part of the uterus. Contains the muscle.
Follicle
Each follicle will eventually produce an egg
Oviducts
transfer an ovum from the ovary to the uterus. The lining of each tube is ciliated to create a current that moves the ovum toward the uterus
Fimbriae
finger like projections in the openings of the oviducts which sweep over the ovaries. The fimbriae are ciliated to sweep an ovum into an oviduct for it’s trip to the uterus
Glanol
Secretes chemical substances for use in the body or for discharge out of the body
Hormone
Chemical signals that are sent to many parts of body through the bloodstream
Negative Feedback Mechanism
regulatory system in the body that works to return the body to it’s normal internal state
Positive Feedback Mechanism
regulatory system in body that DOES NOT return the body to it’s normal internal state
Stages of the Menstrual Cycle
Follicular Stage
Ovulation
Luteal Stage
Menstruation