Analysing the strategic position of a business 3.7
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Non-financial measures of performance
Environment - how ethical + sustainable
Compliance regulation - how lawful
Health and safety - employee safety
Social media reach - numbers on socials
Net present value
Calculates the monetary value of the projects future cash flows.
Mission statement
Overriding goal and provides a strategic perspective.
Internal influences on corporate objectives
Business ownership
Attitude to profit
Ethical stance
Culture
Leadership
Strategic position
Stakeholder influence
External influences on corporate objectives
Short-termism
Economic environment
Political/ legal environment
Competition
Social/ tech change
Strategy
Long term, made by seniors
Tactics
Short term, supports achievements of targets and is usually delegated to juniors.
SWOT
Internal: Strengths/Weaknesses
External: Opportunities/Threats
Return on capital employed (ROCE)
The return the business has made on its resources being used.
Current ratio
Assess whether a business has enough cash or equivalent current assets to be able to pay its debts as they fall due.
Gearing
Measures the amount of borrowing that is done.
Payable days
Average time it takes a business to pay its debts
Receivable days
Average time it takes a business to receive its debts.
Inventory turnover
How often inventory is replaced during the year
Core competencies
Unique that a business has or can do strategically well that other business cannot copy.
Examples of Core Competencies
Collective learning
Ability to integrate skills and tech
Ability to deliver superior products/services
Ways a business is differentiated
Short and long term performance examples
Share price
Revenue growth
Gross and operating profit
Unit cost/ productivity
ROCE
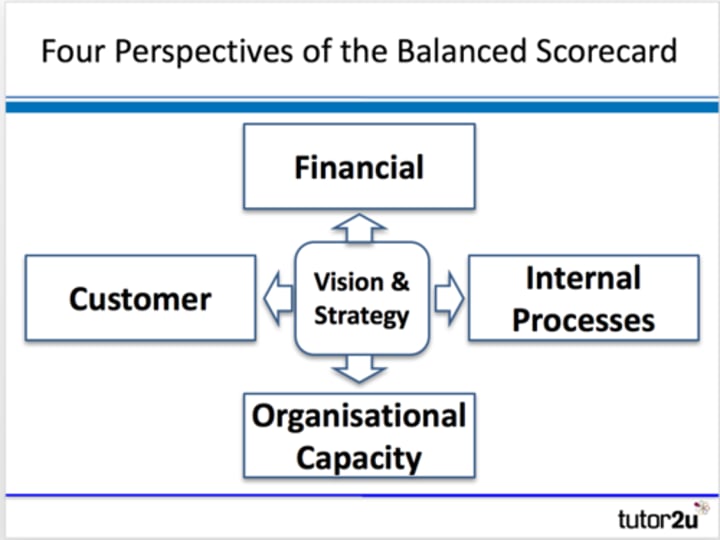
Kaplan and Norton's balanced scorecard
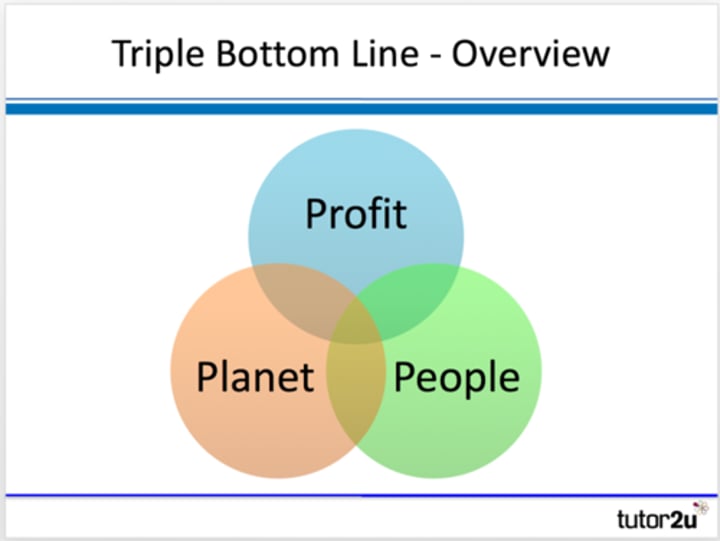
Elkington's triple bottom line
Regulators
Agencies that oversee enforcement of rules.
International trade
The exchange of goods and services between countries
GDP
Total market value of all goods and services produced annually in an economy
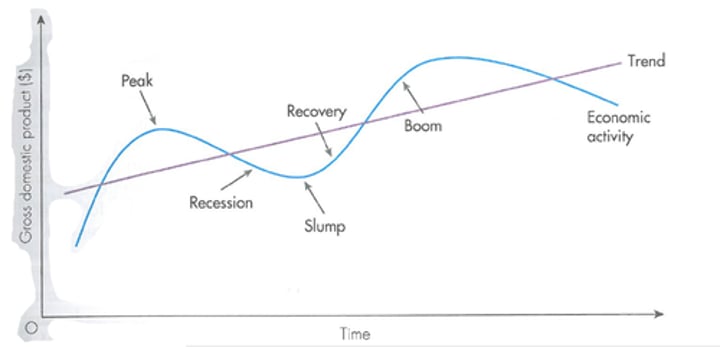
Business cycle
Exchange rate
How much one currency is worth in relation to another.
Inflation
Progressive increase in prices
Fiscal policy
Use of tax and spending to manage level of economic activity.
Monetry policy
Controlling money/interest rates within economy in order to achieve desired level of activity.
Open trade
Countries freely able to trade between each other with no tariffs or quotas.
Protectionism
Economic policy of shielding an economy from imports.
Economic factors
GDP
taxation
exchange rates
inflation
fiscal and monetary policy
more open trade v protectionism
Globalisation
The trend for many markets to become worldwide in scope
Emerging markets
Countries in the process of rapid growth and industrialization. Examples are BRIC(S) and MINT.
Reasons for greater globalisation of a business
Support of governments and major businesses.
Falling cost of international transport and communications.
Growth of global trading blocs and reduction of barriers to trade.
Growth of multinational companies.
Increasing global incomes and growing demand for goods and services.
Importance of globalisation for a business
Increased sales, revenue and profits
Cheaper resources
Economies of scale
Developing different products for different markets
Importance of emerging economies
Provide labour sources
Offer large markets
Rapid growth
Exclusive natural resources
Urbanisation
Increase in the proportion of the countries population living in towns and cities
CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility)
A business's concern for the welfare of society.
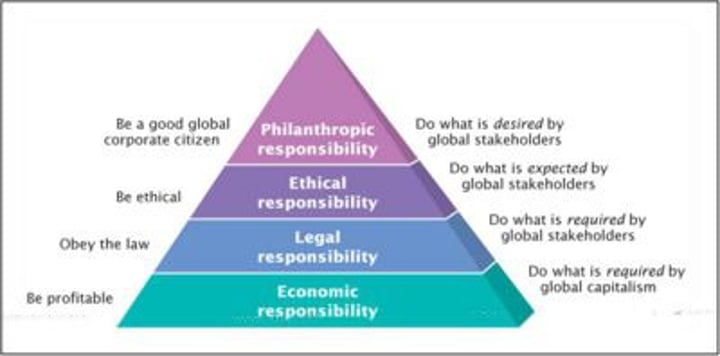
Carroll's CSR Pyramid
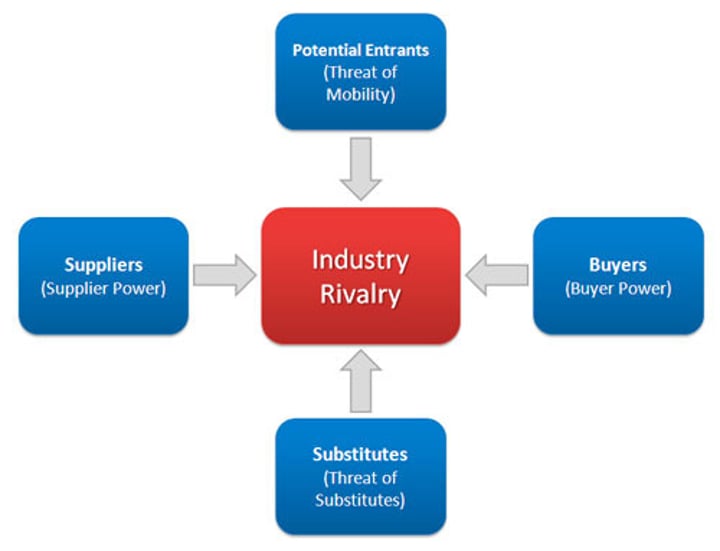
Porters five forces
Payback period
Time it takes for a project to repay its initial investment
Average rate of return
Looks at the total accounting return for a project to see if it meets the target return.