Theories of Acids and Bases
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Hydrogen atoms are made of what?
protons and electrons
What forms when Hydrogen Atoms lose an electron?
they form H+, made of a proton
What happens during a reaction for it to be a Bronsted-Lowry Reaction?
proton transfer
reactant loses H⁺
product gains H⁺
product needs a lone electron pair
How are acids defined in terms of the ions they produce in aqueous solutions?
Acids produce H⁺ ions
How are bases defined in terms of the ions they produce in aqueous solutions?
they produce OH⁻ (hydroxide) ions
What is neutralization in terms of ions?
a reaction where H⁺ ions and OH⁻ ions combine to form water, with the leftover cation and anion forming a salt
What is an acid in terms of H⁺ ions?
a proton donor
loses H⁺ ions
What is a base in terms of H⁺ ions?
a proton acceptors
gains H⁺ ions
What happens to H⁺ ions in water?
They react with water molecules to form hydronium ions, H₃O⁺(aq)
What do bases generally contain?
at least one atom with one or more lone pairs
The equation for the neutralization of sulphuric acid, with potassium hydroxide is shown below:
H2SO4 (aq) + 2 KOH (aq) → K2SO4 (aq) + 2 H2O (l)
Deduce the Bronsted-Lowry acid and base in the reaction
H2SO4 (aq) - acid
KOH (aq) - base
Why are acid-base reactions reversible?
The proton transfer can occur in either direction
How do acid-base pairs differ?
They differ by one proton, with the acid having one more than the base
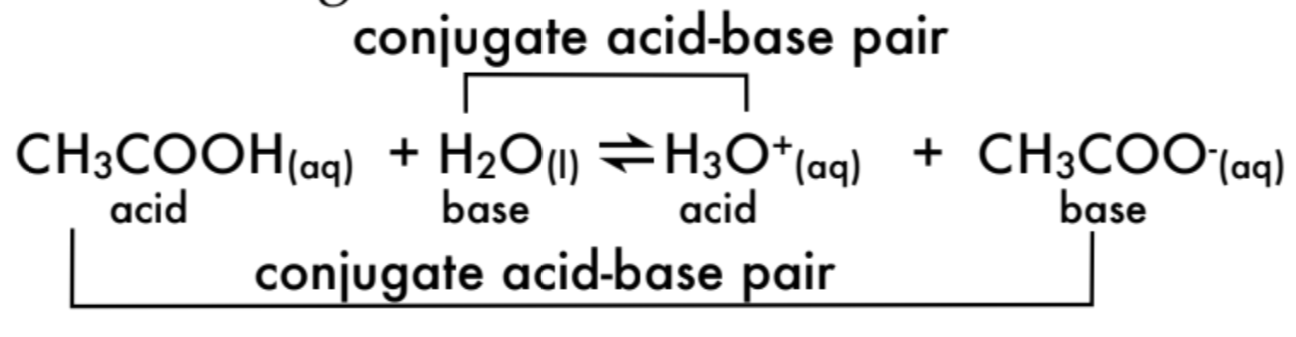
What is a conjugate acid-base pair?
A conjugate acid-base pair consists of a pair where one species acts as an acid (donates H⁺) and the other as a base (accepts H⁺)
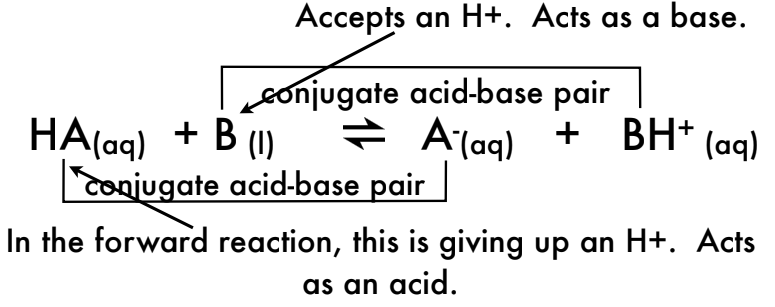
Label the conjugate acid-base pairs in the following reaction: CH3COOH (aq) + H2O (aq) H3O+(aq) + CH3COO-(aq)