BIOCHEM LAB
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Urine
To aid in the diagnosis of diseases
Composition of Urine
95% water, 5% analytes
Organic Components
urea, creatinine, uric acid,
ammonia, undetermined nitrogen, others
Inorganic Components
Cl-, Na+, K+ P, Ca2+, phosphates, sulfates
First Morning
Most concentrated urine
24 Hour
For protein & creatinine
12 Hours
Addis count
Fasting
Diabetic
Refrigeration
Prevents bacterial
growth for at least 24
hours; preserves
organized sediments;
Acidic pH
Amorphous Urates
Basic pH
Amorphous Phospate
Phenol
Does not interfere with
routine tests
Odor
Bacterial
multiplication
or breakdown
of urea to
ammonia
pH
Bacterial
breakdown of
urea to
ammonia/ loss
of CO2
Nitrite
Multiplication
of
nitrate-reducin
g bacteria
Clarity
Bacterial
growth and
precipitation of
amorphous
material
Glucose
Glycolysis and
bacterial use
Ketones
Volatilization
and bacterial
metabolism
Bilirubin
Photooxidation
to biliverdin
-when exposed
to light it will be
decreased
(sensitive to
light)
Urobilinogen
Oxidation to
urobilin
Cells & Casts
Disintegration
in dilute
alkaline urine
Toluene
Does not interfere with
routine tests;
Thymol
Preserves glucose and
sediments well;
Formalin
Excellent sediment
preservative
Sodium Floride
Prevents glycolysis
Boric Acid
Preserves protein and
formed elements wel
Saccamano Fixiative
Preserves cellular
elements
Color
Oxidation or
reduction of
metabolites
Average daily output
1,200-1,500 mL
Polyuria
abnormal increase in urine output (diabetes mellitus, diabetes insipidus)
Oliguria
abnormal decrease in urine output (dehydration, renal insufficiency, poorly compensated heart disease, calculi formation, kidney tumors)
Anuria
total suppression of urine
production (severe acute nephritis, Hg poisoning, obstructive uropathy, kidney failure)
Nocturia
excretion of more than 500 mL urine at
night
Diuresis
transitory increase in urine volume
Straw (colorless)
recent fluid consumption
Pale yellow
dilute random sample
Dark yellow
concentrated random sample
Orange
bilirubin
Green
bacterial infection
Pink
RBCs are present
Red
Hemoglobin
Black
Melanin/ melanogen
Benzidine Test
Used to detect blood
Blood
Transports Oxygen from lungs to tissues,
clears Carbon dioxide, transports macromolecules
and moves waste to the liver and kidneys.
RBC
Anucleated cells with Hemoglobin
Appears pink to red
Measures 6 to 8um
Hemoglobin
WBC
Protects host from infection and injury
Types of WBC
→ Neutrophils - Bacterial infection
→ Eosinophils - Allergic/parasitic infection
→ Basophils - Hematologic dieases
→ Lymphocytes - Viral infection
→ Monocytes - Immune response
Platelets
Measures 2 to 4µm
Appears round, oval and anucleate
Controls Hemostasis
Hemin Test
Used to detect blood traces
Guaiac Test
Test for occult blood test in fecal samples
Confirmatory Test
Highly flammable and explosive Used
to detect blood
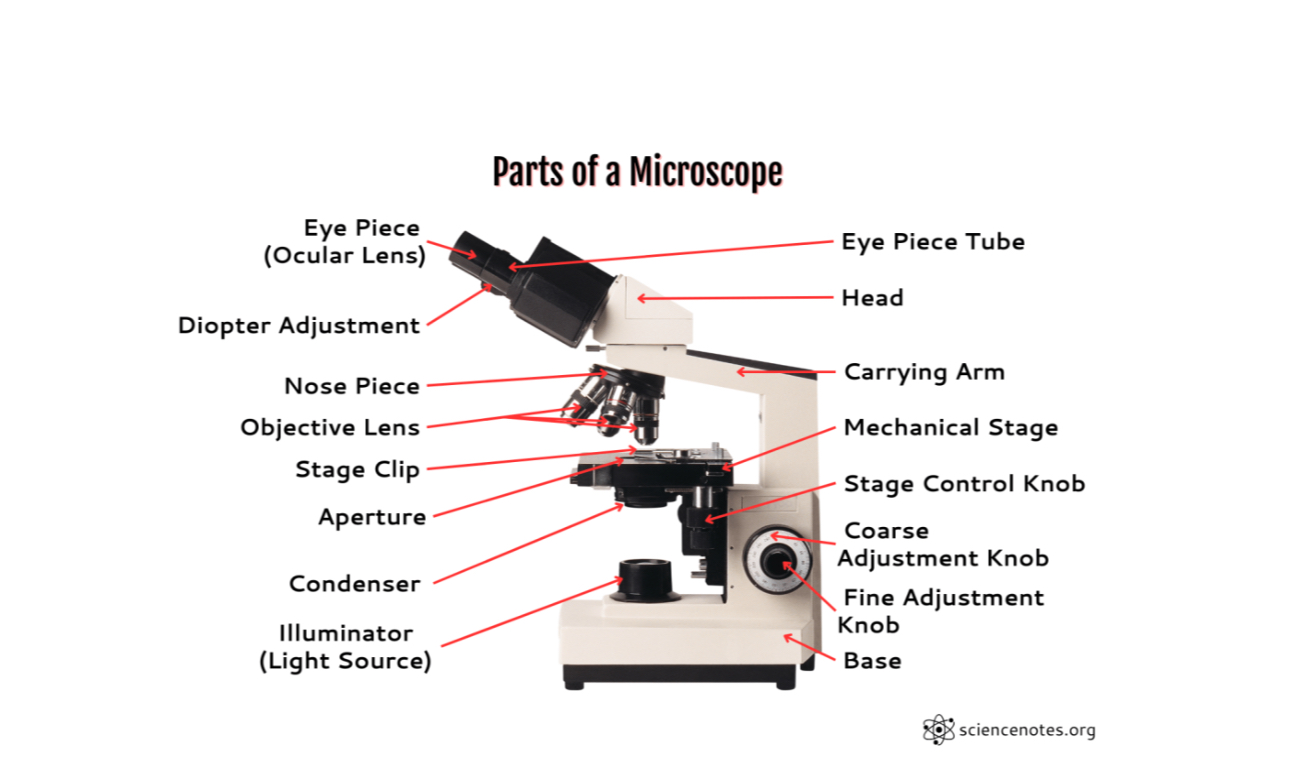
Parts of Microscope
1st Stop
Aspirate
2nd Stop
Dispense