1.2 B Receptive Region and Graded Potential
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Dendrites
short unmyelinated processes branching off cell body
receive input and transfers these signals to cell body
cell body
aka soma
contains nucleus and organelles
receives signals and transfers them towards the axon hillock region
axon
conducts action potentials from axon hillock region to the axon terminal
may be myelinated by neuroglial cells
neurotransmitters are released from the axon terminal synaptic knob region in response to action potentials reaching this area
axon hilock
contains the initial segment where summation of inputs occurs to determine if threshold is met
if threshold is met an action potential in initiated in this region and conducted down the axon
are dendrites myelinated or unmyelinated
unmyelinated
do dendrites receive or provide a response
receive input
what is at the end of axons
synaptic knobs
receptive/receiving segment
binding of neurotransmitters released from presynaptic neurons
production of graded potentials
can be excitatory or inhibitory
initial segment
in between condductive segment and receptive segment
summation of graded potentials
initiation of action potential
conductive segment
voltage gated channels
propagation of action potential
transmissive segment
action potential causes the release of neurotransmitter
neurons at rest
ions are unevenly distributed across the plasma membrane
due to action of pumps
sodium leak channels are always open
potassium leak channels are always open
how are the concentrations of ions unevenly distributed across plasma membrane in resting neurons
na+, cl- and ca+ are at higher extracellular concentration
k+ higher intercellular concentration
resting membrane potential rmp
-70mv in most neurons
this is an electrical charge difference from inside and outside of cell
how is rmp maintaijned
througgh leak channels and pump action
where are k+ and na+ leak channels located
all regions of the neuron
is there a greater # of k+ or na+ leak channels… hjow does this affect rmp
greater # of k+
more k+ is leaked than na+ is gained
results in net negative charge…. -70mv
Na+ and k+ pumps
unequal movement of ions… 3 positive charges out 2 positive in,,,, net negative
maintains concentration gradient for these ions
how much energy does the na+ and k+ account for
75%
receptive segment
at post synaptic membrane
change in membrane potential due to opening of chemically gated channels
small localized change in membrane potential
signals vary in both direction of change and strength of signal
signals are multidirectional and weaken with distance
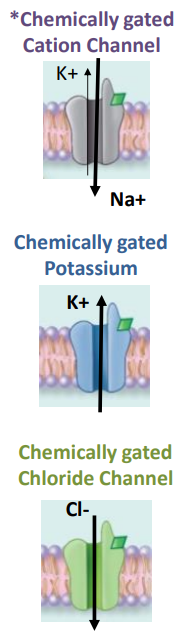
chemically gated cation channels
na+ comes in
k+ goes out
more na+ comes in than k+ goes out
DEPOLARIZE - makes the inner membrane more positive
depolarization
make more positive
chemically gated potassium
net efflux of k+
HYPERPOLARIZATION - makes inner membrane more negative
hyperpolarization
make more negative
efflux
leave
chemically gated chloride channel cl-
net influx of cl-
hyperpolarization
Postsynaptic potentials
graded potentials that change the membrane potential
rest in either depolarization or hyperpolarization of the membrane
signals vary in strength and decrease with distance and over time
depolarization postsynaptic potentials
ion movement due to open receptors causes the inside to be relatively more positive (+)
hyperpolarization
ion movement due to open receptors causes the isde to be relatively more negative (-)
steps in generation of an excitatory postsynaptic potential EPSP
excitatory neurotransmitter is released from the synaptic knob of a presynaptic knob of a neuron and diffuses across the synaptic cleft
the neurotransmitter binds to a chemically gated cation channel causing them to open resulting in a net influx of sodium into the neuron
EPSP is established as the inner face of the plasma membrane becomes depolarized…. more positive
moves towards the threshold to send out an action potential
EPSP weakens as it moves from where it was initiated towards the initial segment where summation occurs
what does the presence of calcium ions cause
synaptic cesivles to bind to the membrane allowing neurotransmitters to be released
voltage gated calcium must travel across synaptic cleft
steps in the generation of an inhibitory post synaptic potential (IPSP)q
inhibitory neurotransmitter is released from the synaptic knob
neurotransmitter binds chemically gated k+ channels or chemically gated cl- channels causing them to open
allows for specific ions to flow through the gradient.
results in inner face of membrane being more NEGATIVE
IPSP is established as the inner face of the plasma membrane and hyperpolarizes (becomes more NEGATIVE)
IPSP weakens as it moves from initiated point towards the initial segment where summation occurs
Temporal summation
SAME presynaptic neuron initiates postsynpatic potentials rapidly within a narrow period of time
not as effective as spatial summation
ONLY APPLIES TO A SINGLE SYNAPSE
Spatial summation
DIFFERENT presynaptic neurons initiate postsynaptic potentials within a narrow period of time
APPLIES TO 2 OR MORE SYNAPSES OCCURING SIMULTANESOUSLY
summation
cumalative impact of all simultanesously received graded potentials upon the intial segment
threshold
15 mV from RMP
determines if action potential is initiated
action potential
all or none event
generated and propagated down axon without any loss in intensity
voltage gated na+ channel
immediate
na+ influx
depolarization (+)
voltage gated k+
delayed
k+ efflux
hyperpolarization