Statistics 1: Definitions
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
Statistic
information from a sample (subset of a population)
Parameter
the summary of a population
Descriptive statistics
organizing and summarizing data (numerical summaries, tables, graphs, etc)
Inferential Statistics
take results from a sample (descriptive portion) and sees how applies to the population; measures reliability
Qualitative/Categorical variables
characteristics or attributes (not usually numerical)
Quantitative variables
numerical measures; can be added or subtracted
Discrete variable
countable, limited possibilities (ex: the number of students in a class, cannot be partial)
Continuous variables
continuous, infinite possible values, any level of accuracy (ex: height, weight)
Nominal level of measurement
the name of an item
Ordinal level of measurement
items are arranged in a specific order
Interval level of measurement
usually numerical, differences between items, addition or subtraction make sense, zero doesn’t mean the absence of quantity (ex: temperature)
Ratio level of measurement
accounts for factors, multiplication and division make sense, zero does mean the absence of quantity. (ex: speed)
Observational Study
observing a group of individuals (no intervention) over time and drawing a conclusion (ex: unethical studies)
Designed Experiment
organizing and manipulating a group of individuals and records the value of the response variable
Response variable
the response to the experiment (dependent variable)
Explanatory variable
what causes the response (independent variable)
Confounding
when the effects of two or more explanatory variables are not separated, so the result doesn’t imply causation in experiment
Confounding variable
an explanatory variable that cannot be separated from the independent variable but impacts experimental results
Lurking variables
not considered in a study but impacts the response
Simple random sampling
pre-determining the individuals that you are selecting without seeing them
Random
every individual has an equal chance of being selected
Frame
a list of all individuals in the population
Systematic sample
select sample members from a larger population at regular intervals, starting from a randomly chosen point (no frame)
Stratified sample
separating the population into groups (nonoverlapping) that contain similar people, obtaining a simple random sample from each group
Cluster sample
selecting all individuals within a random collection of groups
Sampling without replacement
once an individual is chosen, they cannot be chosen again
Sampling with replacement
once an individual is chosen, they can be chosen again (go back into the pool)
Cross-sectional studies
observational study at a specific point in time
Case-control studies
observational study that is retrospective (looking back at previous actions compared to now)
Cohort Studies
observational study that follows a large group for a period of time (prospective = future)
Bias
if the sample is not representative of the population
Sampling bias
when sampling tends to favor one part of the population leading to undercoverage/overcoverage of some groups
Nonresponse bias
when people don’t respond to a survey leading to missing possible data
Response bias
when people on a survey are not honest
Response bias: Interview error
interviewer must be trained to get truthful responses
Response bias: Misrepresented answers
questions result in responses that are untrue
Response bias: Wording of questions
questions must be balanced and worded neautrally
Response bias: Order of questions
responses that are affected by prior questions
Response bias: types of questions
open allows the respondent to choose, closed limits the respondents choice
Response bias: data entry error
type of nonsampling error, error in recording
Nonsampling error
result of undercoverage, nonresponse bias, response bias, or data-entry error
Sampling error
using a sample that doesn’t accurately represent the population and occurs because the sample gives incomplete information about a population
Treatment
any combination of values of the factors of an experiment
Experimental unit/subject
well-defined item upon which a treatment is applied
Control group
baseline treatment, used to compare
Placebo
something that mimics the treatment, but doesn’t actually include the treatment, used to filter out personal bias
Blinding
nondisclosure of treatment
Single-blind experiment
participant doesn’t know if their getting a placebo or the treatment
Double-blind experiment
neither the participant nor the researcher knows what the participant is receiving
Raw data
data that is not organized
Frequency distribution
list of each category of data and the # of occurrences for each (a count)
Relative frequency
percent of observations within a category (frequency/sum of all frequencies)
Relative frequency distribution
lists each category of data with relative frequency
Bar graph
graphical representation of a frequency distribution
Pareto chart
a bar graph where bars are drawn in order of frequency or relative frequency
Side-by-side bar graph
compares data for two different time zones, should use relative frequencies bc of different population sizes
Pie chart
sectors are proportional to frequencies of the categories
Classes
categories of data
Lower class limit
smallest value within class
Upper class limit
largest value in class
Class width
difference between consecutive lower class limits
Histogram
bar graph where bars are connected, implies a connection between data
Convenience sampling
individuals in the sample are easily obtained
Self-selected/voluntary responses
self-explanatory, participants may not be telling the truth
Multistage sampling
using more than one sampling method in large-scale surveys
Class midpoint
the sum of the consecutive lower class limits divided by 2
Cumulative frequency distribution
total number of observations that are less than or equal to the category (running count of all data)
Cumulative relative frequency distribution
percentage of observations less than or equal to the category (running count of percent of data)
Time series data
if the value of a variable is measured at different points in time
Uniform distribution
frequency of each value are evenly distributed (straight across)
Bell-shaped distribution
highest frequency is in the middle and tail off to the right and left (equally)
Skewed right distribution
tail to the right is longer than the tail to the left
Skewed left distribution
tail to the left is longer than the tail to the right
Dispersion
the degree to which the data is spread out
Population standard deviation
the square root of the sum of squared deviations about the population mean divided by the number of observations in the population (N)
larger = more varied
smaller = less varied
Sample standard deviation (s)
the square root of the sum of squared deviations about the sample mean divided by n – 1, where n is the sample size
Range
Difference between max and min values
Variance
square of the standard deviation
Empirical rule (for bell-shaped curves)
68% of data will fall within 1 standard deviation of the mean
95% of data will fall within 2 standard deviations of the mean
99.7% of the data will fall within 3 standard deviations of the mean
Chebyshev’s Inequality
guarantees only 1/K² values will be found within a specific distance from the mean of a distribution
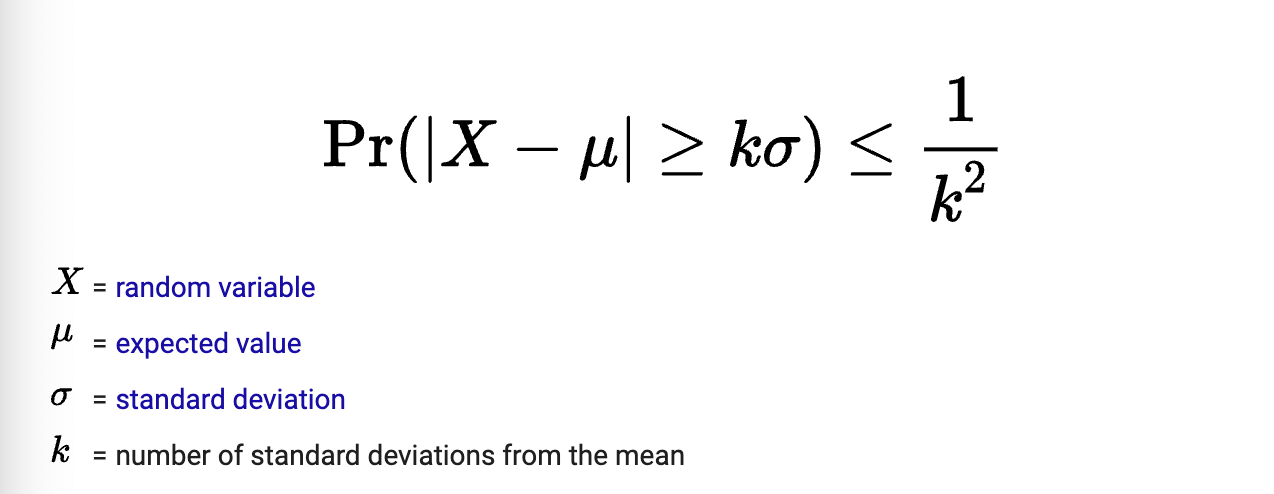
Z-score
(data point - mean)/standard deviation
Percentile
P(k) = percent of observations less than or equal to k
Quartiles
Q1 = 25% of the data is less than this = 25th percentile
Q2 = 50% of the data is less than this = 50th percentile
Q3 = 75% of the data is less than this = 75th percentile
IQR
middle 50% of observations -> Q3 - Q1
Fences
cutoff values for determining outliers
Upper fence: Q1 - 1.5(IQR)
Lower fence: Q3 + 1.5(IQR)
5 Number Summary
min, Q1, M, Q3, max
Boxplot
Number line long enough to include max and min values with vertical lines at Q1, M, and Q3
Upper and lower fences labeled
Whiskers: lines from Q1 to smallest value and Q3 to largest value minus the outliers
Outliers marked with asterisk
Median is in the middle of box if data is not skewed
Explanatory Linear (positive)
increase in x -> increase in y
Explanatory Linear (negative)
increase in x -> decrease in y
Explanatory Nonlinear
some pattern, but not linear
Explanatory No Relation
almost random
Positive association
increase in x -> increase in y
Negation association
increase in x -> decrease in y
Linear correlation coefficient + rules
measure of strength and direction of the relationship of two variables
The linear correlation coefficient is always between –1 and 1, inclusive. That is, –1 ≤ r ≤ 1.
2. If r = + 1, then a perfect positive linear relation exists between the two variables.
3. If r = –1, then a perfect negative linear relation exists between the two variables.
4. The closer r is to +1, the stronger is the evidence of positive association between the two variables.
5. The closer r is to –1, the stronger is the evidence of negative association between the two variables.
Line of best fit
a line which is drawn from two points that best express the data
Residual
the difference between the observed value of y and the predicted value of y
Scope of the model
the range of values that the data set applies to based on what makes sense