Social Studies 30-2
1/233
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
234 Terms
identity
A person's idea of who he or she is. A person's beliefs and values help create identity.
Ideology
A set of beliefs and values that is held by a society.
These are key beliefs around which a political or economic system is centered.
Factors that influence Ideology
-Common Good
-Culture
-Language
-Media
-Relationship to Land and Environment
-Gender
-Religion
-Spirituality
Individualism
The goals of the individual are more important than the goals of society. Capitalists and Liberalism believe in Individualism

Renaissance Period
This is where individualism developed from. During this period the importance of the individual overtook the importance of a class or group.
Age of Enlightenment
Philosophers began to write about the importance of the individual. People realized that each person is important, that reason should be the source of
knowledge, and that individuals could govern themselves.
Collectivism
A value held by supporters who believe that the goals of society are more important than the goals of the individual. Collectivism believes that individuals depend on each other within society. Indigenous societies believe in collectivism.

Interpretations of History
History is about how we got to be who we are and what society was like in the past. When a nation looks at its history, their understanding of their history becomes a part of their ideology.
Beliefs about Human Nature
It involves looking at what is the physical, emotional, and social (how people interact with each other) makeup of human beings.
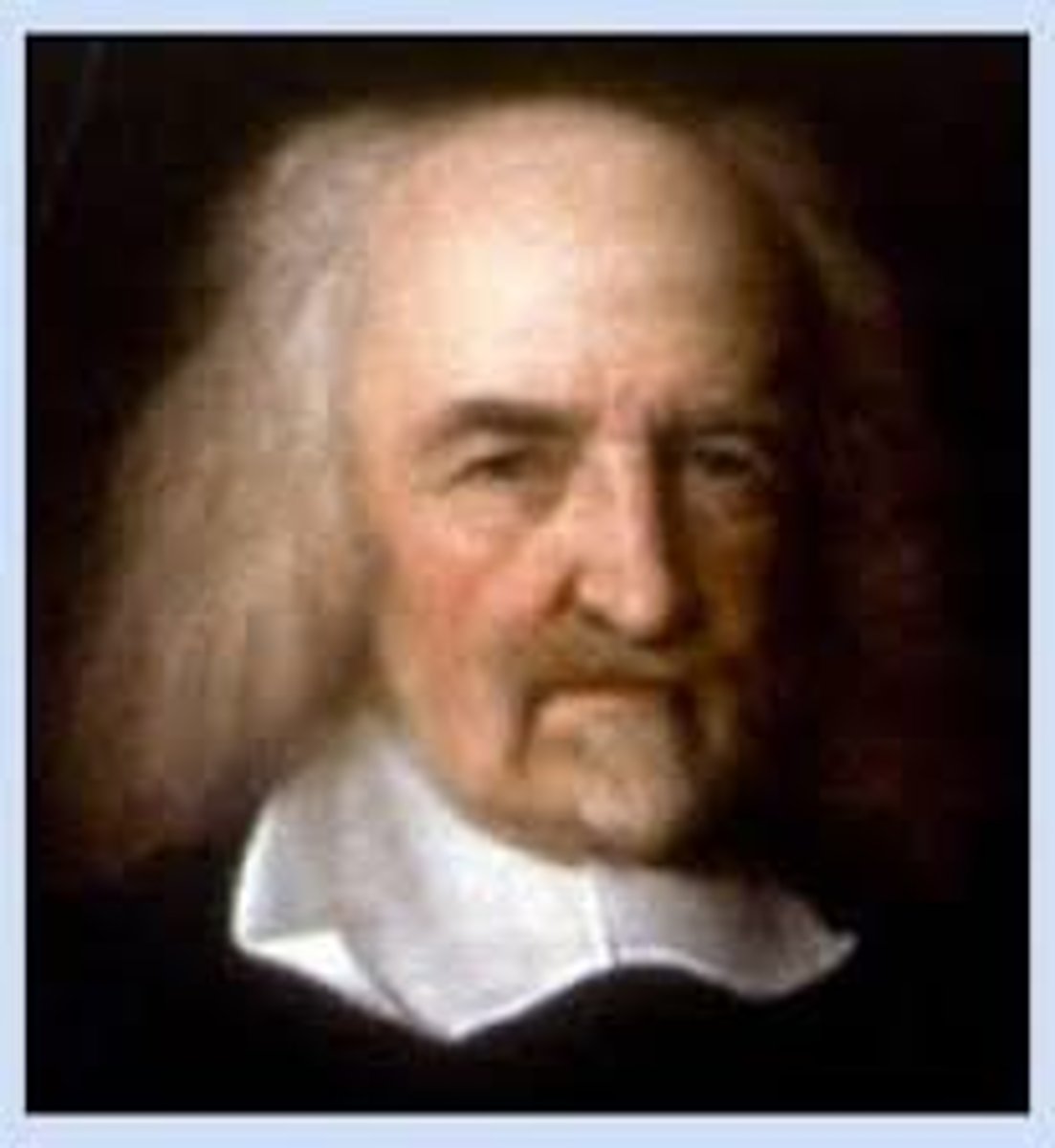
Thomas Hobbes
Believed that we need to have security more than we need to have freedom. Believed human nature involves fear, violence, and dangerous self-interest. Hobbes believed that extreme individualism involved only looking out for themselves and hurting anyone who get in their way.

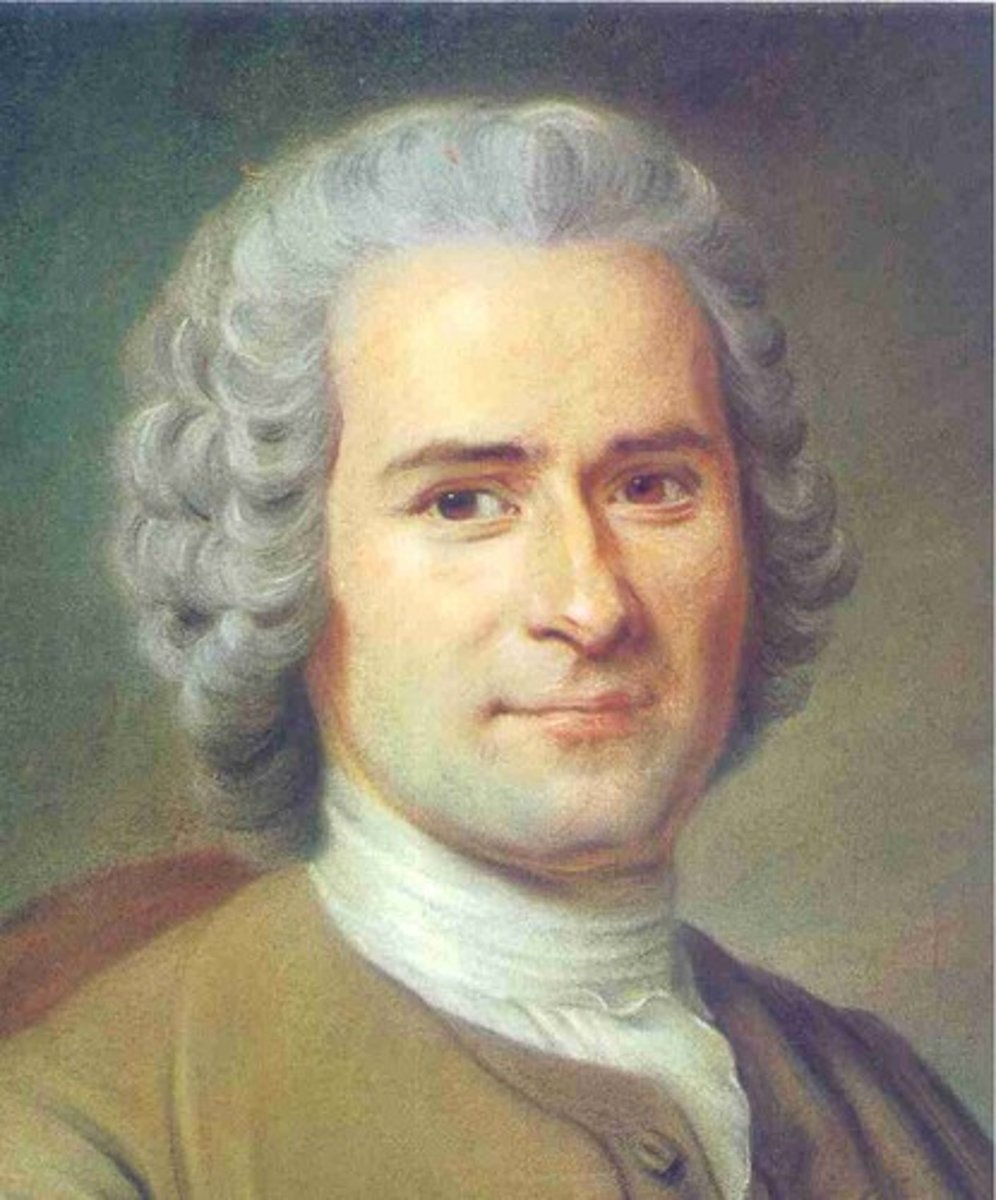
Jean-Jacques Rousseau
Believed people are naturally good however become corrupted by society. He believed humans are free and equal. Rousseau saw that when an individual owns private property they become selfish and lose compassion for others. He believed that the people should make the decisions themselves instead of electing people
to represent them in government (Direct Democracy)

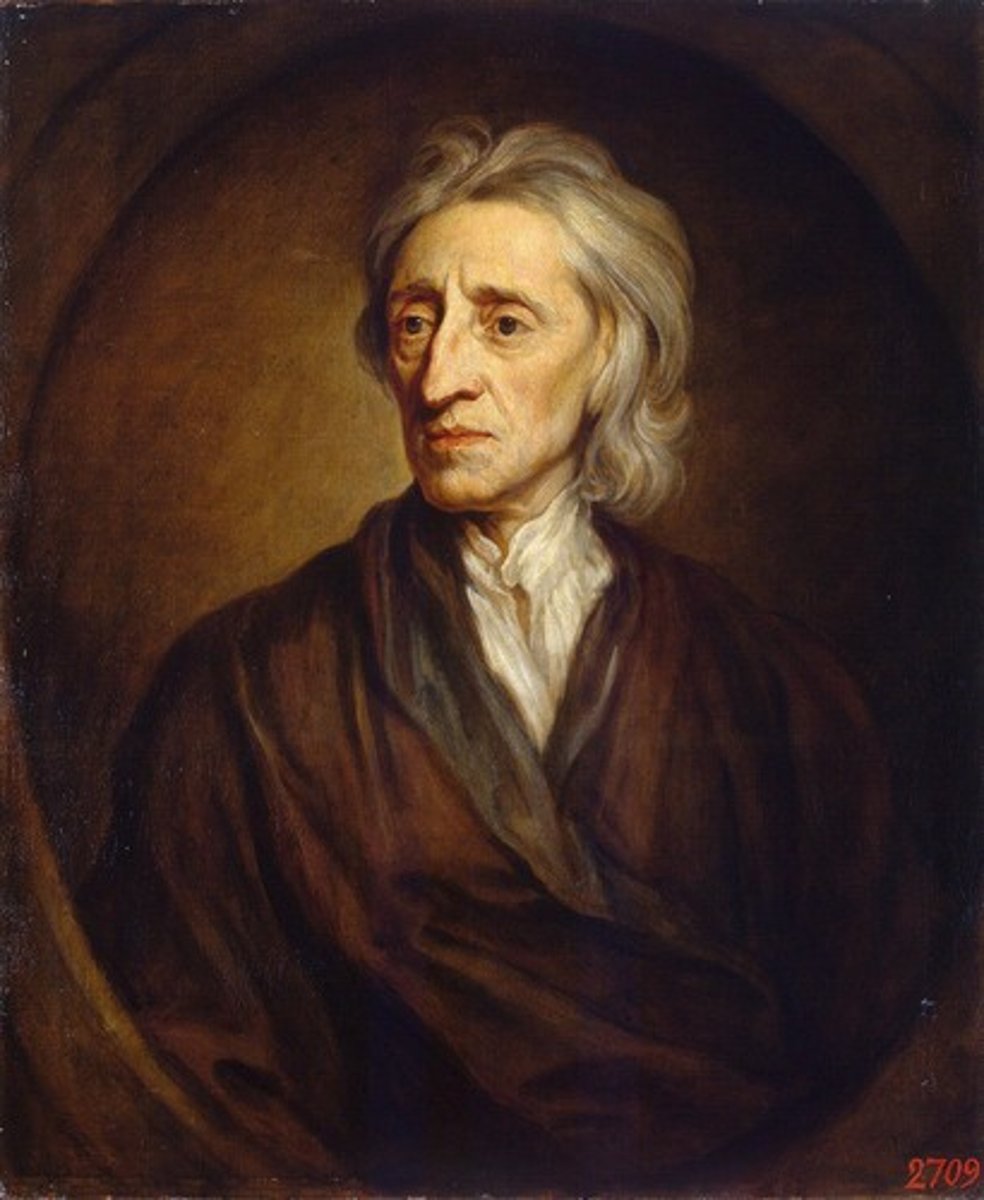
John Locke
Believed that people are rational, smart, and realistic. Locke believed that power came from the people and those who should have power must be appointed by the people. Governments are in place to protect life, liberty, and property and that any action the government takes must be approved by the majority of the people. (Representative Democracy)

Beliefs about Society
Ideologies are the base that society is built upon. All societies must decide between individualism, collectivism, or a mix of both. Even though a society might be individualist there can be laws that promote collectivism.
Beliefs about the Structure of Society
Structure of society is built upon beliefs and values. Therefore, society will change when beliefs and values change. There are three main parts to the structure of society including social, economic, and political structures.
Social Structures
Unwritten rules in society about how people should act like respecting the elderly people. Social structures also involve how people interact with each other.
Economic Structures
How decisions regarding the economy are made. A society must choose between a centrally planned/command (collectivist) economy or a free
market/capitalist (individualist) economy.
Free Market Economy
An economic system where the government does not interfere in business activity in any way. Follows supply and demand and competition.

Capitalism
an economic and political system in which a country's trade and industry are controlled by private owners for profit, rather than by the state.
Command/Centrally Planned Economy
A centrally planned economy is an economic system in which the state or government makes economic decisions rather than the these being made by the interaction between consumers and businesses. ... State-owned enterprises undertake the production of goods and services.

Mixed Economy
an economic system combining private and public enterprise (crown Corporation's and social programs)Example: Canada
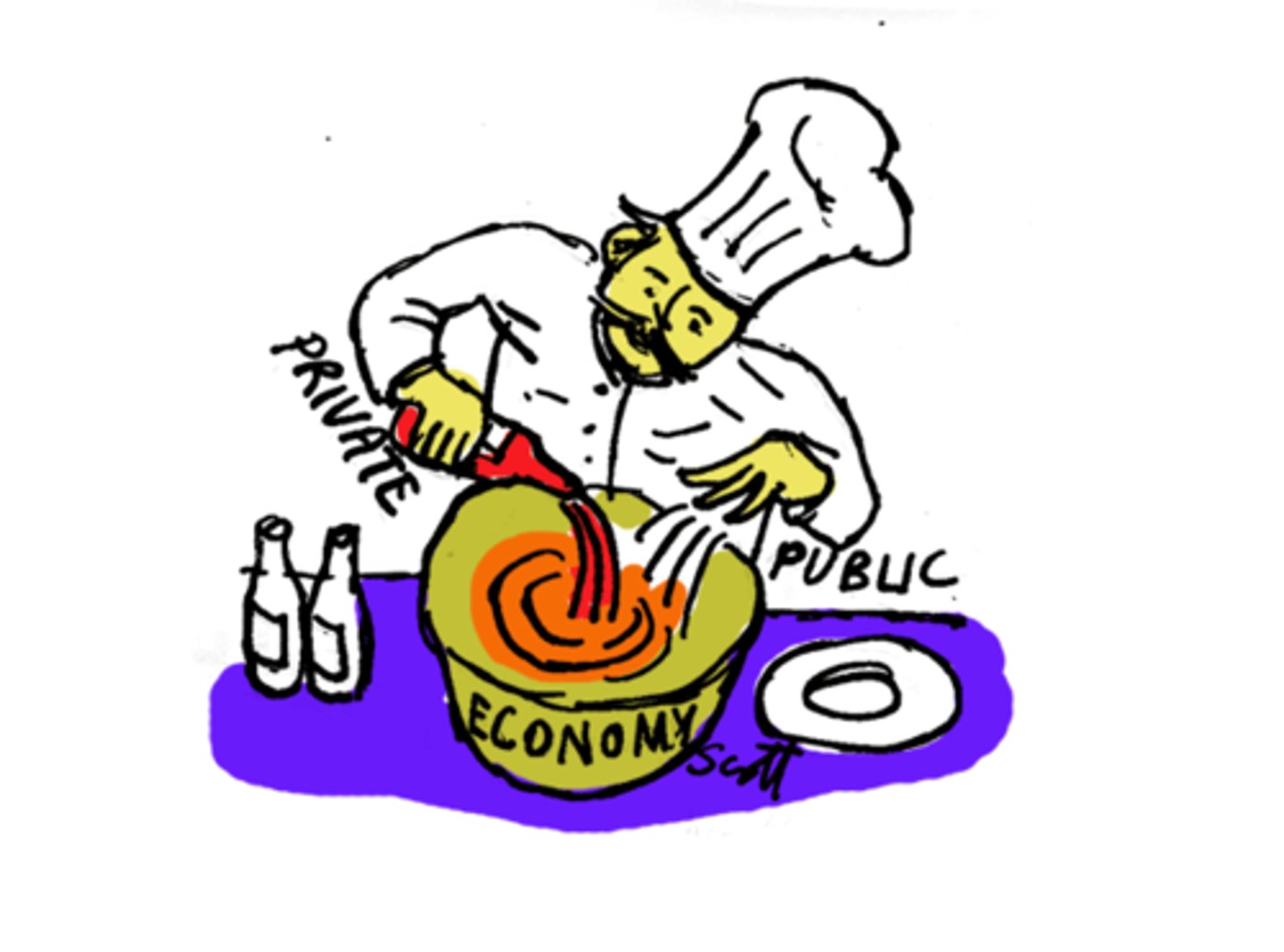

Political Structures
How political decisions in a society are made. A society can have a democracy where decision-making power is divided up between many people or a dictatorship where all power is with one person.
Democracy
A political system in which the supreme power lies in a body of citizens who can elect people to represent them

Dictatorship
A form of government in which the leader has absolute power and authority. A political system where society is governed by and ruled by one totalitarian and/or authoritarian dictator.

Authoritarian Dictatorship
A political system in which one person assumes total constitutional power under his/her authority. The dictator places all power within themselves.

Absolute Monarchy
A king or queen is given the right to rule
because of tradition or religious beliefs.

Military Dictatorship
Military leaders control all key political positions
and usually gain power by overthrowing the previous government.

Oligarchy
A form of dictatorial government directed and controlled by a few influential members. Most dictatorships are actually oligarchies.

Minority Tyrannies
A small group of people have political control over the majority of the population.
Totalitarian
A political system where the government has complete control over the actions of the citizen. An authoritarian government can become totalitarian once all political opposition is banned and forces the citizens to surrender their rights to the leader.

anarchy
An ideology where people believe that society would benefit with no leadership and government. Anarchists believe the government should be eliminated because people could live in total freedom through cooperation. Many anarchists use violence as a way of achieving their goals.

Visions for the Future
Ideologies have beliefs of what society should look like in the future. These future images all involve making life better for the people of that society.
Themes of Ideologies
-Nation
-Class
-Environmentalism
-Religion
Liberalism
Rights and Freedoms of the individual. Liberalism also respects the freedom of an individual to control their decisions and lifestyle. There are two main types of liberalism, classical and modern.
Political Roots of Liberalism
The American and French Revolutions are the roots of Liberalism. The Declaration of Independence (United States) and Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen (France) both recognized the rights of the individual.
Classical Liberalism
Focuses on individualism. Classical liberalism includes the respect for people`s rights and freedoms, private ownership, and the pursuit of life, liberty (freedom), and pursuit of happiness.
Modern Liberalism
Allows for the government to get involved with the economy and society to help promote more freedom and justice for the common good of citizen. Focuses on the rights of minorities and attempts to make sure all people can have a good standard of living (social welfare programs). It also promotes more freedom to make personal choices, concerns for the environment, humanitarian efforts, and political correctness.
Rule of Law
The idea that the 'law' has the greatest power in society and that all individuals must follow those laws. No individual is greater than the law, no matter how much power they have. If an individual breaks the law they are to be penalized for their
actions.
Social Contract
An idea where each individual of society agrees to be governed so that they can gain the benefits of living in that society.

Individual Rights and Freedoms
Are an important value of individualism and democracy. Nations that support liberalism pass charters to ensure that all citizens have the same legal freedoms and rights. Governments decide what the individual rights are as well as the limits on these rights. An example of this is the Charter of Rights and Freedoms, created with the Canadian Constitution the Charter of Rights and Freedom protect the privileges Canadians citizen have.
Economic Roots of Liberalism
Individualism focuses on the private property, self-interest, freedom, competition, and that laws affect everyone equally. However the economic roots of Liberalism come from the idea of mercantilism.
Mercantilism
Mercantilism believed that a country should export more goods than import, accumulate gold and silver, and protect their economy by taxing and setting quotas on imports and oppression of the workers.
Values of Individualism
-Self Interest
-Competition
-Privatization
-Economic Freedom
-Private Property
Values of Collectivism
-Collective Responsibility
-Collective Interest
-Public Property
-Economic Equality
-Nationalization
Crown Corporations
Businesses and industries owned by the Canadian government.

Haudenosaunee Confederacy
Involved membership of six Indigenous nations. Each nation of the confederacy had their own chief and council, these representatives would address the internal affairs of each nation. The leaders of these six nations worked together to promote peace and harmony.
The Great Law of Peace
Known as the constitution of the Haudenosaunee Confederacy, outlined the path to harmony and unity among the warring nations, divided power between different levels of government, and established equal participation of people. It also guaranteed rights of speech, rights to religion, and rights to the individual.
Fur Trade
Indigenous fur trade promoted business between Indigenous and the European settlers. Both groups benefited from mutual trade and this is an early example of a modern day market economy where buyers and sellers meet to exchange goods and services.

Indigenous Voting Rights
As a result of the Indian Act of 1876 if Indigenous wanted to vote they had to deny their Indigenous heritage and become Canadian however in 1960. Indigenous were given the right to vote without having to lose their identity. This is an important step for the Indigenous desire for equal rights and freedoms.
The Red Paper
the Red Paper is the Indigenous response to the Canadian government policy of assimilation stated in the White Paper wanting for a return to traditional land ownership for Treaty Indian as well as a demand for Indigenous rights and freedoms.
Métis, First-Nation, and Inuit Self-Determination
After receiving rights and freedoms from the government, Indigenous groups are currently working to attain the ability to make their own laws, policies, and decisions that are in the best interest of their group (self-determination).
Adam Smith
-Father of Capitalism
-Supported Classical Liberalism
-Competition is important to the economy
-Wrote the book The Wealth of Nations
-Rejected Mercantilism which led to monopolies
-Supporter of supply and demand and consumer sovereignty.
-ideas of Invisible Hand and Laissez-Faire Capitalism:

Laissez-faire capitalism:
An economic theory developed by Adam Smith that states that economies function best when the government does not become involved in the economy. This idea involves free markets, low taxes and regulations, as well as private ownership of property.

Invisible Hand (Trickle down theory)
An economic theory developed by Adam Smith in which individuals, acting their own self-interest, will benefit the common good of society.
This is a characteristic of free market economies.

John Stuart Mill
-supported Classical Liberalism
-wrote an essay On Liberty
-Believed that the government's role was to preserve rule of law, protect private property, and ensure that individual rights are secured.
-believes in individual freedom and choice, freedom of speech, freedom of the press and freedom to protest (dissent)

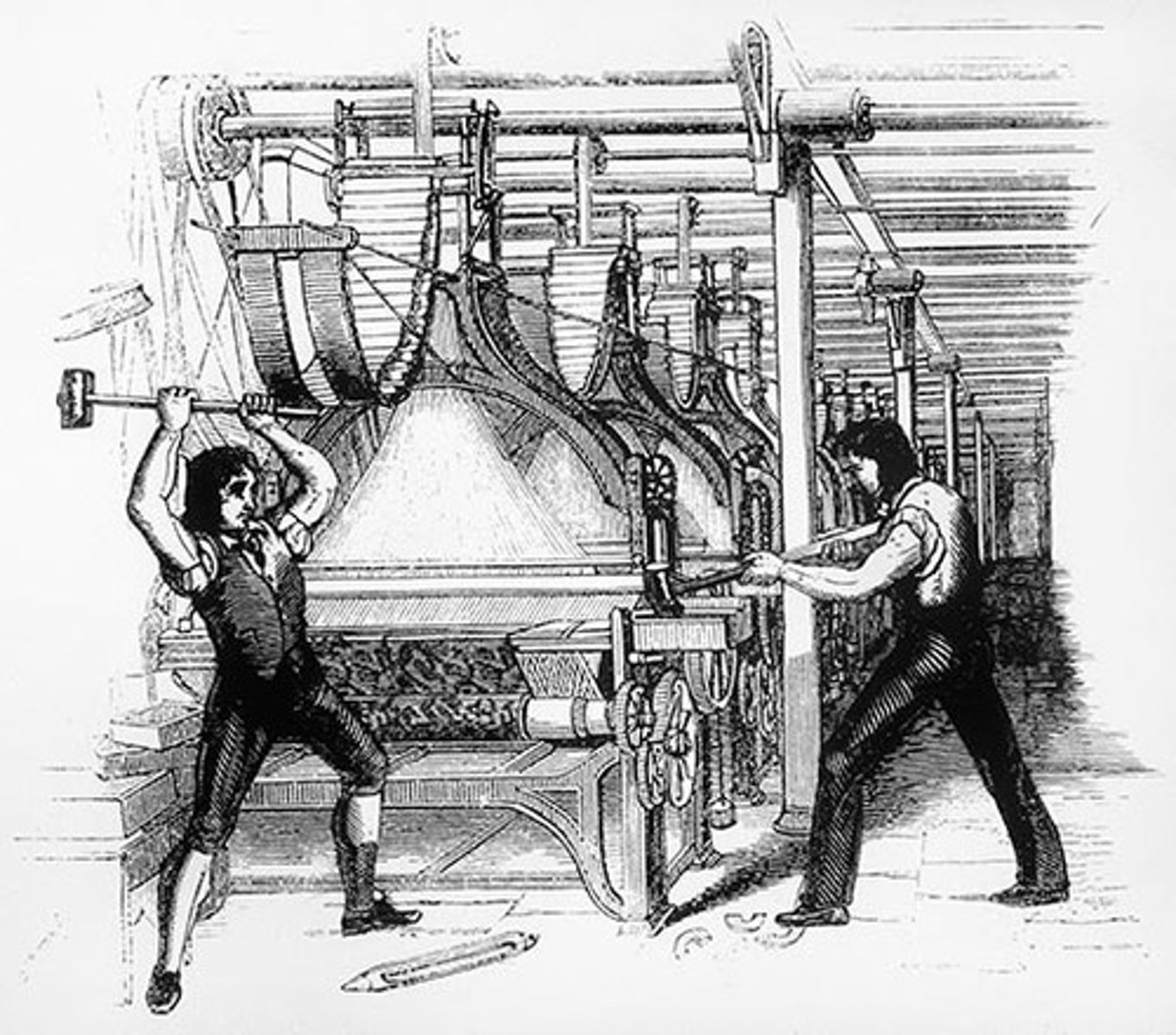
Industrialization
Moving from an agricultural and hand-made production to machine-driven mass production in factories. Known as the Industrial Revolution.

Luddites
These individuals broke into factories, destroyed machinery, and attacked business-owner because skilled workers were losing their jobs and the new technologies threatened their livelihood.
disparity
Division between rich and poor

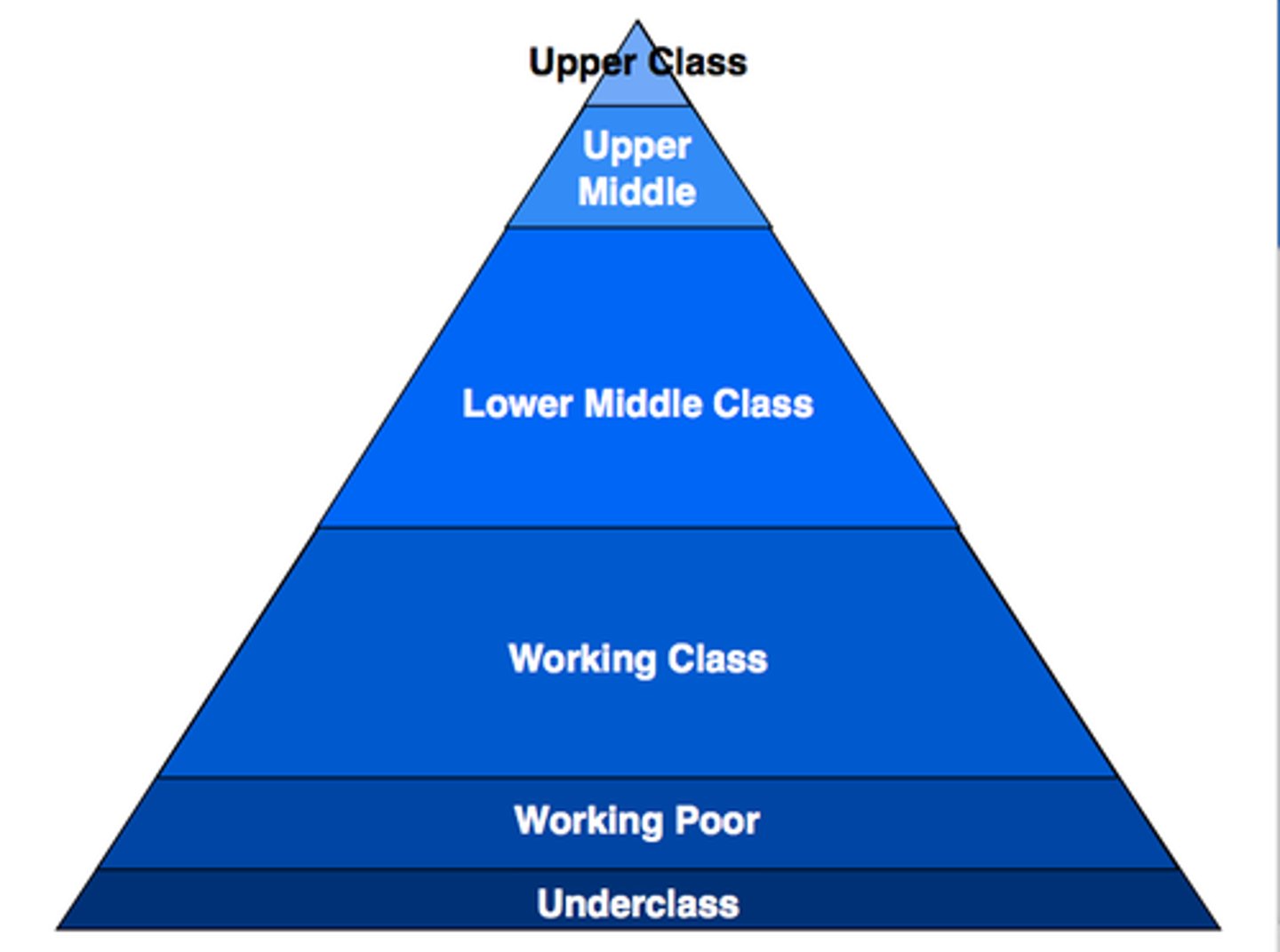
Class System
Most class systems have upper, middle, and lower classes based on wealth and power.
Factory Acts
A series of laws passed to make better and fairer working conditions for workers especially women and children. Examples of laws include the cleaning of the workplace, how long a child could work for in one day, and the education children must receive. The laws promoted liberalism by protecting the rights of all workers.
Labour Unions
Created to secure good wages for workers, protect against child labour, and prevent human rights violations. Unions often use strikes or work stoppages to bring about changes.

Welfare State
When a country looks after its citizens through programs like health care, employment insurance, old-age retirement plans, etc...

universal suffrage
voting rights for all adult citizens, regardless of race or gender

Feminism
The belief that women should have economic, political, and social equality with men

Desire for Change Spectrum
____________________________
1 2 3 4 5
1. Radical - wants a great degree of change, may support the use of violence
2. Liberal - wants some change, interested in improvement
3. Moderate - are open to changes if necessary
4. Conservative - wants to keep the status quo, the way it is now
5. Reactionary - would like a change back to the way it was, may support the use of violence
Socialism
Believes in state ownership and management of the economy (collectivism) as well as a society built on equal opportunities for all individuals (equality). There are two main types of socialism; democratic socialism, and communism/Marxism.
Communism
involves a class struggle (rich vs. poor people) that brings about a change in society, a revolution where the workers would overthrow the rich. Public ownership of resources as well as a classless society with no separation between the rich and poor.

Democratic Socialism
change could occur without a violent revolution. They felt change could occur through elections and reform. Many key industries were government owned and controlled however there was also the ability for individuals to own some private ownership of business. In democratic socialism the government would also provide social programs like employment insurance, health care, and education.
Robert Owen
Felt it was the responsibility for the business owners to operate productive workplaces as well as take care of their employees. He recognized the
importance of the worker, no workers means no products.

Charles Fourier
He felt society should be arranged small
communities that could take care of themselves through careful planning and regulation.

Karl Marx
Regarded as the most important socialist. He wrote the Communist Manifesto with Freidrich Engels. Marx's ideas lead to the idea of Marxism. He believed in economic equality and a classless system.

Fredrich Engels
Marx's partner in writing the Communist Manifesto

Utopian Socialism
A society that is focused on cooperation as opposed to competition. Robert Owen and Charles Fourier were strong believers in utopian socialism. "Perfect Society"

The Great Depression
Brought economic hardships with high unemployment during the 1930s. Many felt the reason for the Great Depression was an economy had no government guidance. These hardships brought a call for a more equal and fair society and many felt the best way to correct the economy and solve the hardships was for the government to get more involved with the economy.
Tommy Douglas
Premier of Saskatchewan and leader of the federal NDP, first leader to propose universal health care in Canada

Propaganda
Used to influence the opinions and behaviors of citizens. This is usually accomplished through indoctrination.

Controlled Participation
Citizens feel that they contributing to the nation by
attending rallies, preparing for the war effort, becoming a part of the secret police,etc... anything to feel they are contributing to the country.
Scapegoating
Pacing blame on a specific group of people.

pageantry
Highly colorful, splendid, and stately displays or ceremonies to show off the government. This is usually accomplished through military parades and rallies.
Rise of Socialism in Russia
Russia was ruled by a tsar who controlled all
social, political, and economic aspects of the country. Russia experienced a gap between the rich and poor. Many workers were upset over their working conditions and looked for changes. In 1898, the Russian Socialist Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) was created to demand changes in Russian society. Members of the SDLP included Vladimir Lenin, Leon Trotsky, and Joseph Stalin. The RSDLP would be the driving force behind the Russian Revolution of 1917.
Vladimir Lenin
-Leader of the Bolsheviks, a communist party
-Slogan "Peace, Land and Bread"
-"Father of the Soviet Union" because he joined republics with Russia.

Lenin's Red Terror
A time period in which Lenin used force and terror to maintain political control within Russia.
Lenin's Cheka
secret police force to police labour camps, torture and execute political opponents, as well as put down rebellions or riots by workers or peasants.
Gulags
slave labour camps

Lenin's War Communism Policy
the government has complete control over all aspects of society including mass state controlled farms and heavy industry. War Communism was unsuccessful after the peasants, specifically the
Kulak farmers, revolted due to mass famine and high production quotas.

Lenin's New Economic Policy
allowed for some private ownership and individualism.
Joseph Stalin
-Stalin was a totalitarian dictator
-communism
-led with oppression and fear
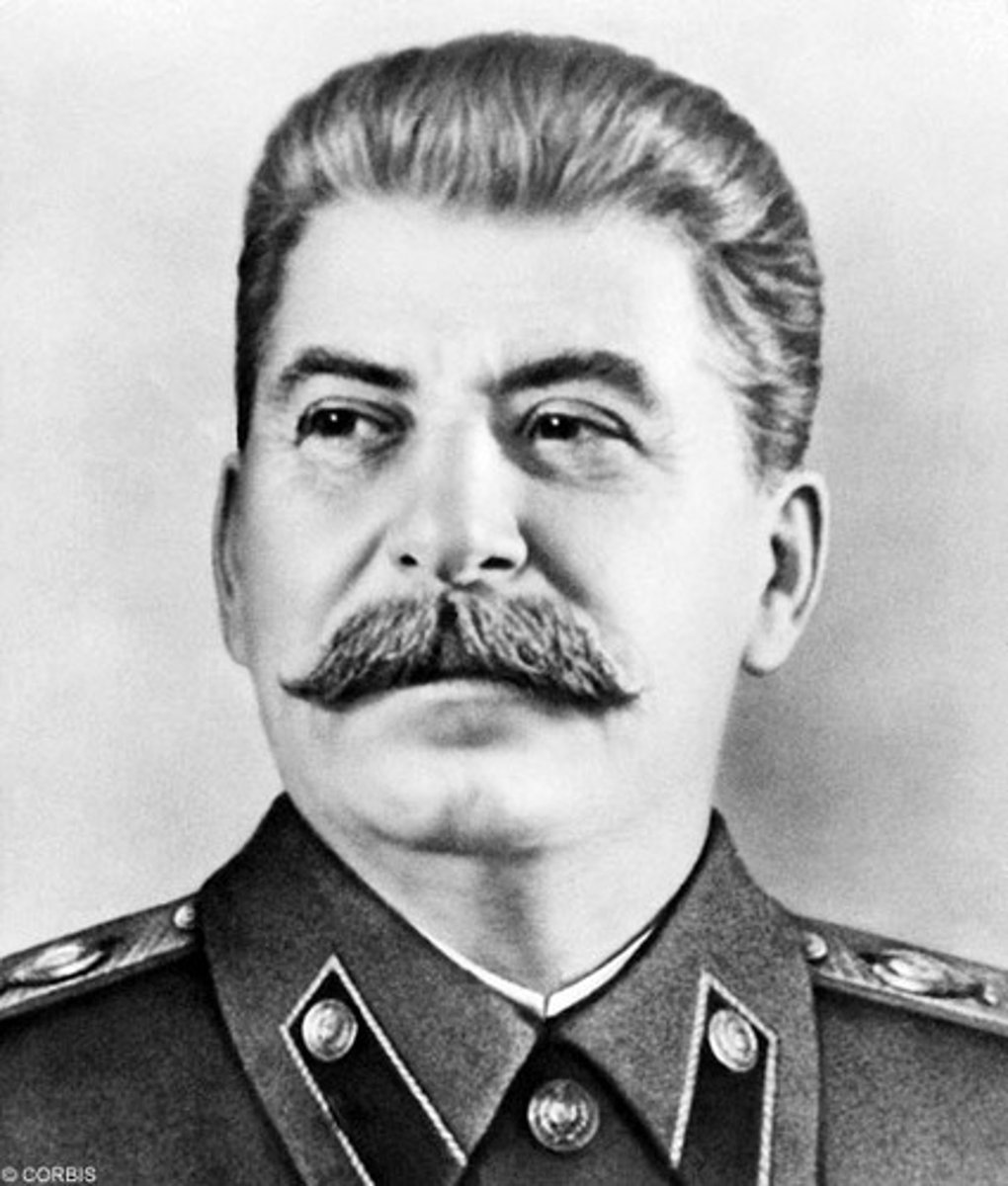

Stalin's Great Purges
to get rid all political opposition in the Communist Party and armed forces including Trotsky who was eventually exiled and assassinated in Mexico.
Stalin's NKVD
secret police force to enforce his control over
Soviet society and carry out the Great Purges, and police the Gulags
Young Pioneers
organization to indoctrinate youth toward Communist ideas suppressing differing perspectives.
Stalin's Scapegoating
He placed blame on Trotskyists, Capitalists, and the Kulak farmers.
Stalin's 5 year plans
Focused on industrializing the USSR by increasing oil, coal, steel, and iron production in the USSR through quotas. Also used to increase the military strength in preparation for war.
Stalin's Collectivization
created a large state owned collective farming system

Fascism
one party in power and is led by a totalitarian dictator. it believes that democracies are weak, unstable, and unable to solve problems in society. society should focus on their nation-state and must dominate all other nations. allows for private ownership economically however business owners, although they are allowed to make a profit for themselves, must produce goods for the good of the state.associated with racism and hatred of non-white ethnic groups.
Social Darwinism
"survival of the fittest" individuals or groups achieve power and advantage over other because
they are stronger and fitter.

Fascism in Germany
After the Germans were defeated in World War I, the victors forced the Weimer Republic (German government) to sign the Treaty of Versailles placing blame for the war solely on Germany. The Treaty led to economic chaos where many people were unemployed. These economic problems also caused political problems as many people lost support in the German government. These economic and political problems, combined with the fear and hatred of communism, opened the door for Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party to gain power.
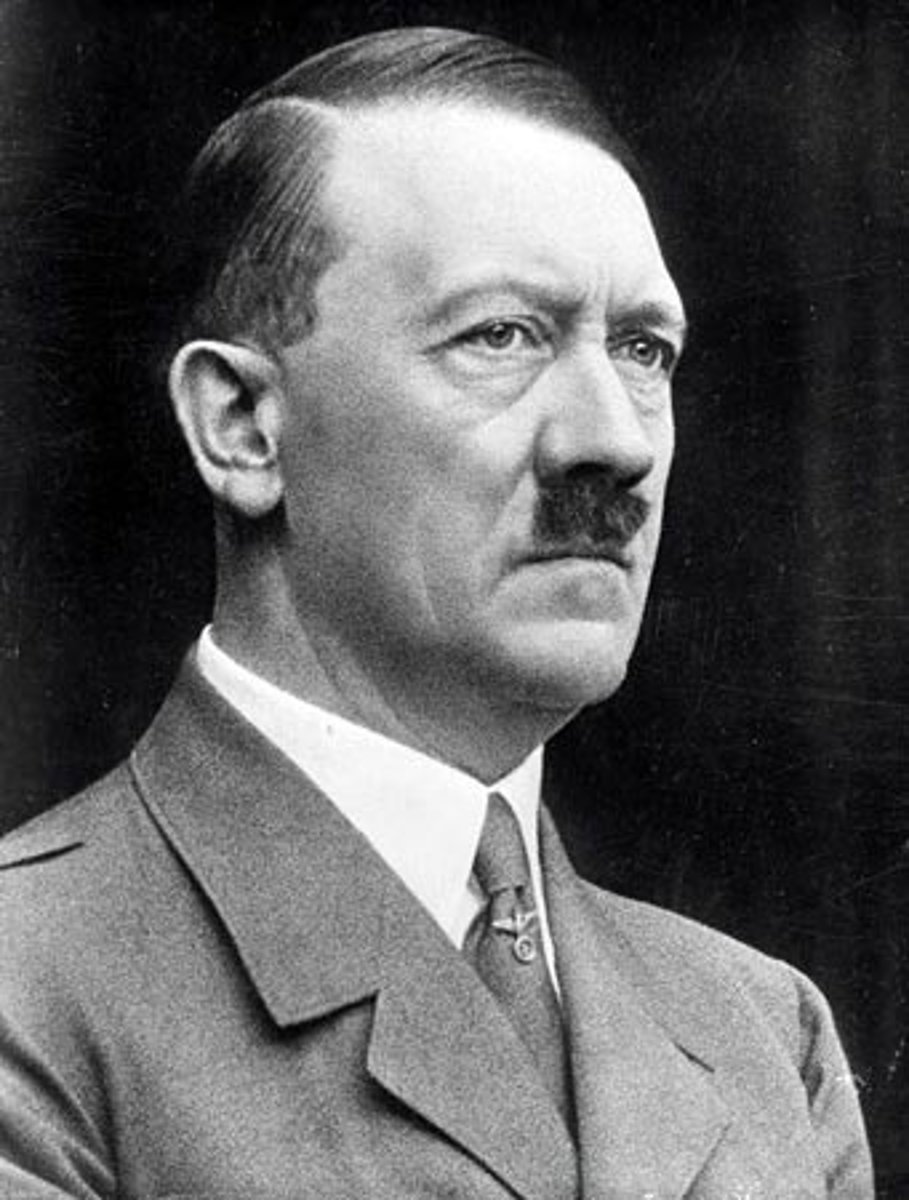
Adolf Hitler
-elected into power
-promised economic change and revenge for the Treaty of Versailles.
-Fascist Dictator
-Master Race (Aryan race)
-used propaganda, youth movements,
the elimination of any opposition, force and terror with his secret police (the SA storm-troopers and later the SS)
-persecuted undesirables in society including the Jews, homosexuals, people with mental or physical disabilities, and gypsies.

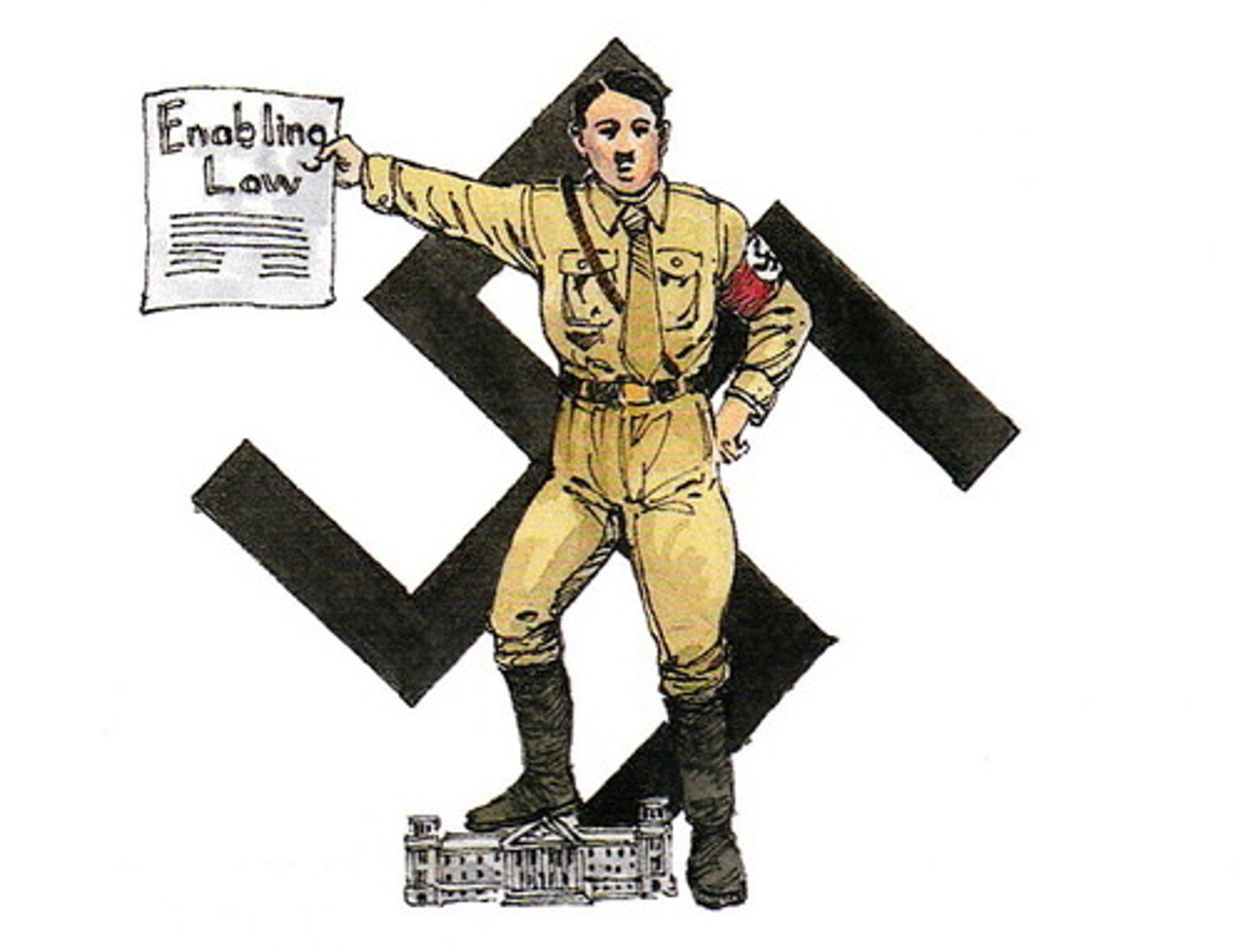
Hitler's Enabling Act
This act gave the leader of the Nazi Party absolute decision-making power and the ability to ignore German constitution for four years. The Enabling Act also removed many individual rights and freedoms. It enabled Hitler to turn Germany from a Democracy into a Dictatorship.

Hitler's scapegoats
communists, Jewish population, Treaty of Versailles and the Weimar government.

Nuremberg Laws
identify who the Jewish people were and how to ensure the purity of the 'master race' (Aryan race).
Kristallnacht (Night of Broken Glass).
persecution of the Jews occurred in 1938 when Jewish businesses, homes, synagogues were vandalized as well as 91 Jews killed and 30000 sent to concentration camps.