Test 1 & Haworth/Fischer Projections
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Molecular Chaperones
Proteins that fold other proteins into their 3D shape during synthesis
Amphiphilic
Molecules that contain both hydrophobic and hydrophilic portions
Acidosis
Increased CO Leads to Increased Concentration of H+; pH goes down
Metabolic (Exercise)
Respiratory (Choking)
Alkalosis
Decreased CO Leads to Decreased Concentration of H+; pH goes up (basic)
Respiratory (Rapid Exhalation)
Isoelectric Point (PI)
pH where a molecule exists as a zwitterion
Secondary and Tertiary Structure
Secondary = 3D structures of Parts of Proteins
Tertiary = 3D structure of the entire protein
Zwitterions
Partial Negative, Partial Positive, Overall Neutral Charge
Why do different proteins have the same secondary structure?
Secondary structure (a-helices and B-sheets) arise from hydrogen bonds between amide groups; all proteins are poly-amides (all amino acids have amide groups)
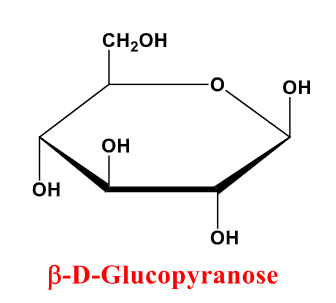
D-Glucose
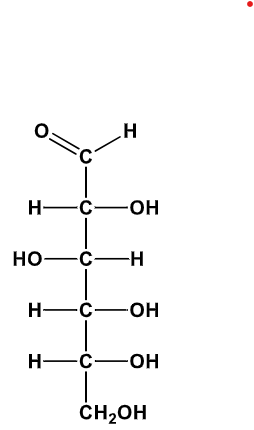
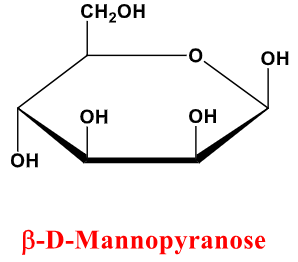
D-Mannose
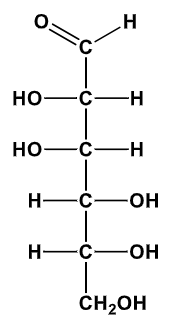
D-Galactose
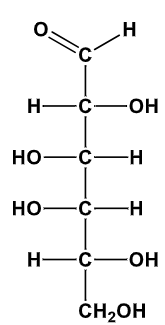
D-Fructose
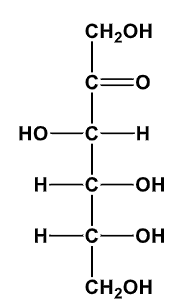
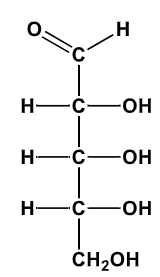
D-Ribose
B-d-Glucopyranose
B-D-Mannopyranose
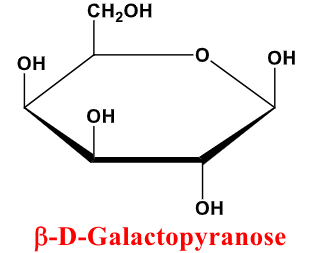
B-D-Galactopyranose
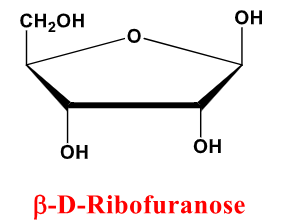
B-D-Ribofuranose
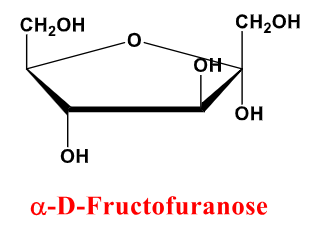
A-D-Fructofuranose