Skeletal System Vocab and Identification
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
5 Functions of Skeletal System
-Support
-Protection
-Movement/Leverage
-Mineral Storage
-hemopoeisis
Osseous Tissue
Another name for bone tissue; a specialized connective tissue.
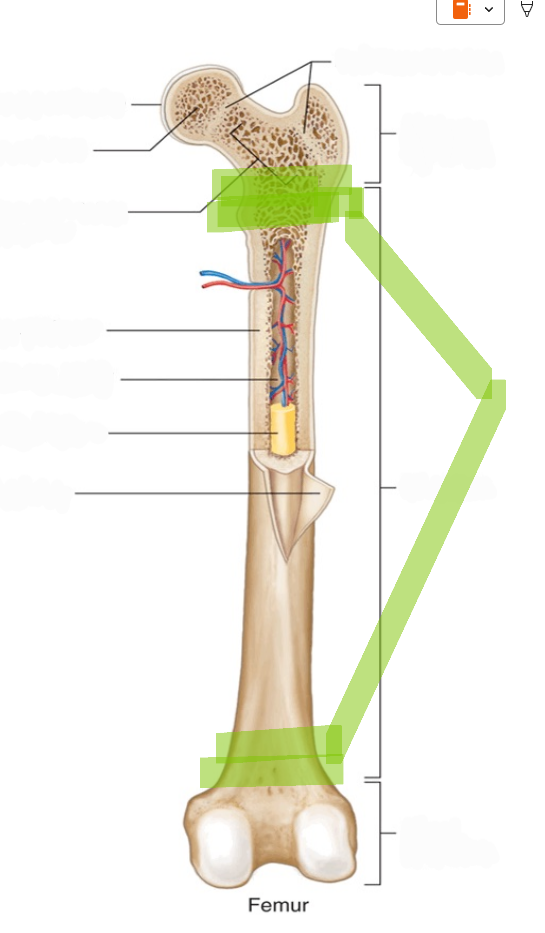
Long Bones
Bones that are longer than they are wide, with a shaft and two expanded ends (examples: femur, humerus).
Short Bones
Cube-shaped Bones
Flat Bones
Thin bones with large surface areas for muscle attachment and organ protection (examples: skull bones, ribs).
Irregular Bones
Bones with complex shapes that don't fit other categories (example: vertebrae).
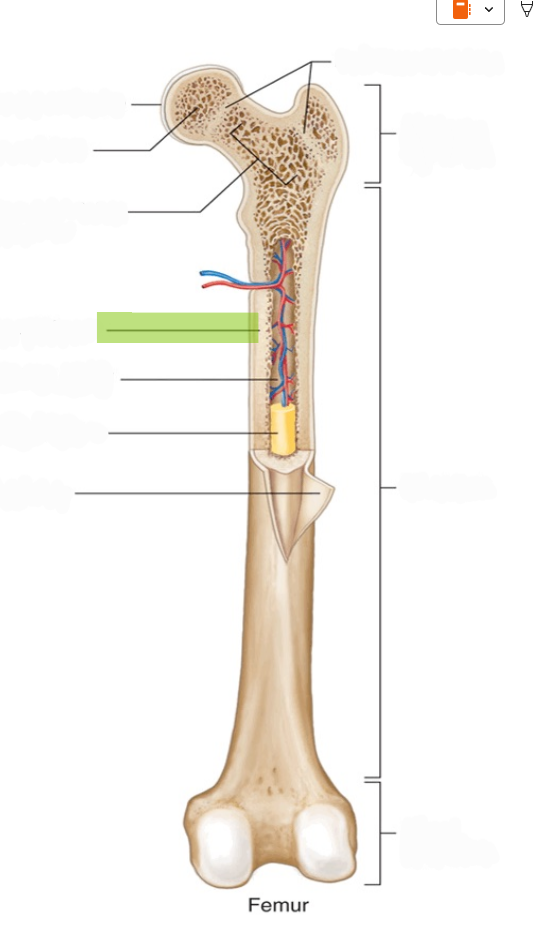
Diaphysis
The hollow, tubular shaft of a long bone located between the proximal and distal ends.
Diaphysis
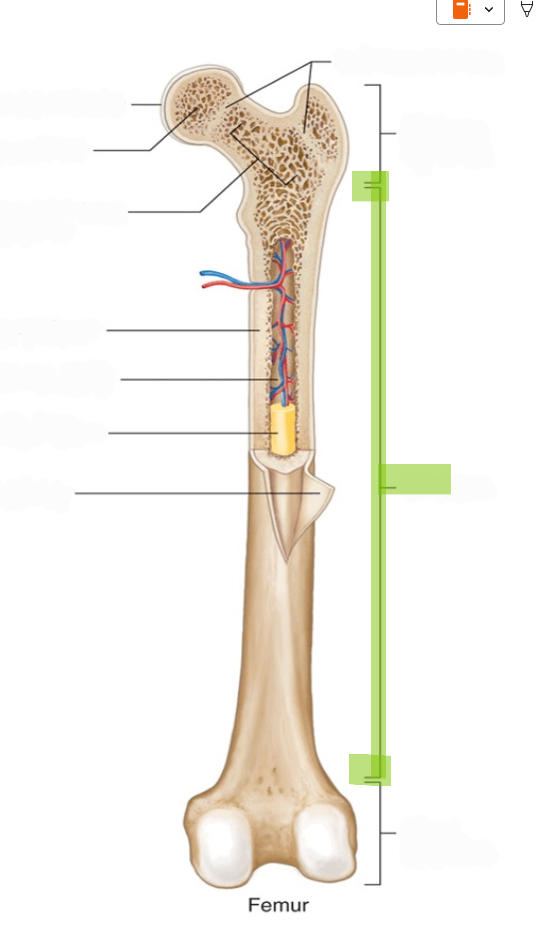
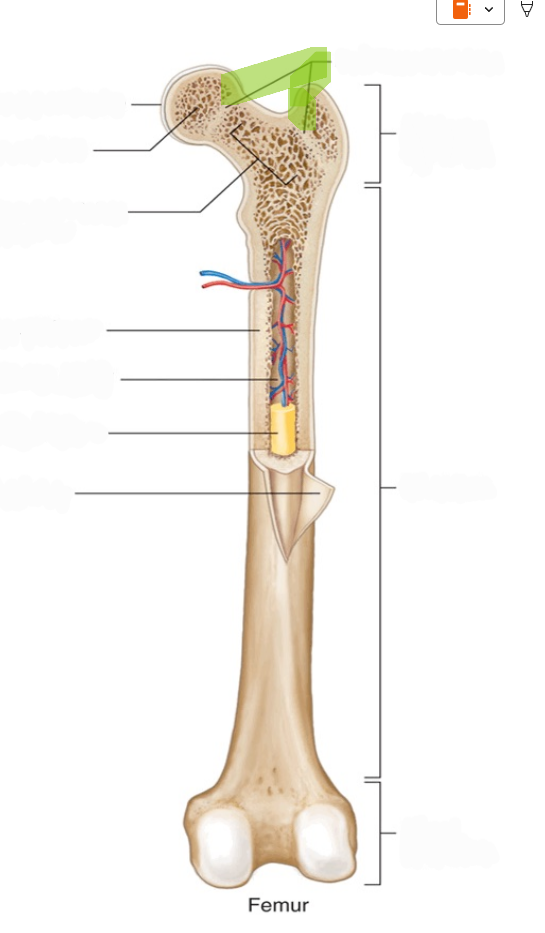
Epiphysis
The expanded end regions of a long bone, filled with spongy bone (plural: epiphyses).
Distal Epiphysis
Metaphysis
The region where the diaphysis meets the epiphysis; contains the growth plate in children.
Metaphysis
Medullary Cavity
The hollow space within the diaphysis, filled with yellow bone marrow in adults.
Medullary Cavity
Articular Cartilage
Smooth hyaline cartilage covering the ends of bones at joint surfaces.
Articular Cartilage
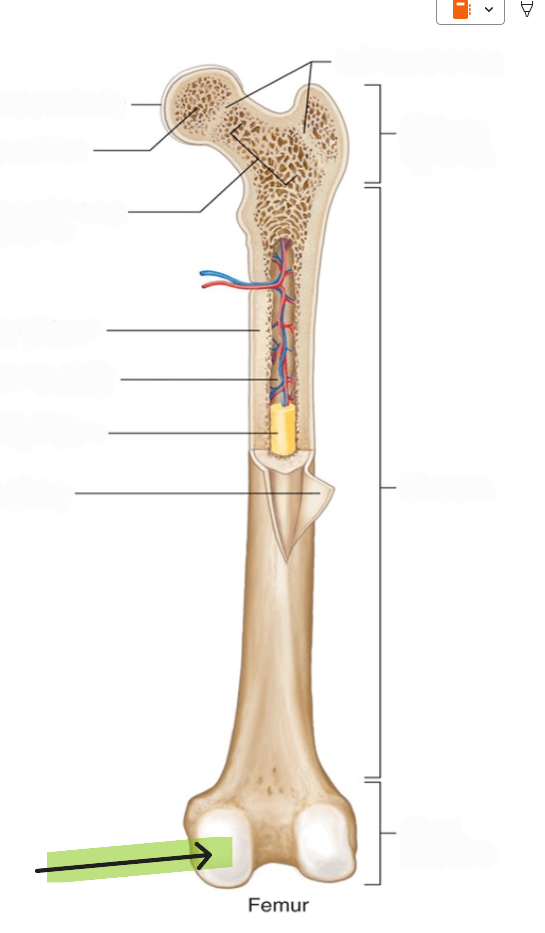
Periosteum
The tough, fibrous outer membrane covering bones, containing blood vessels and nerves.
Periosteum
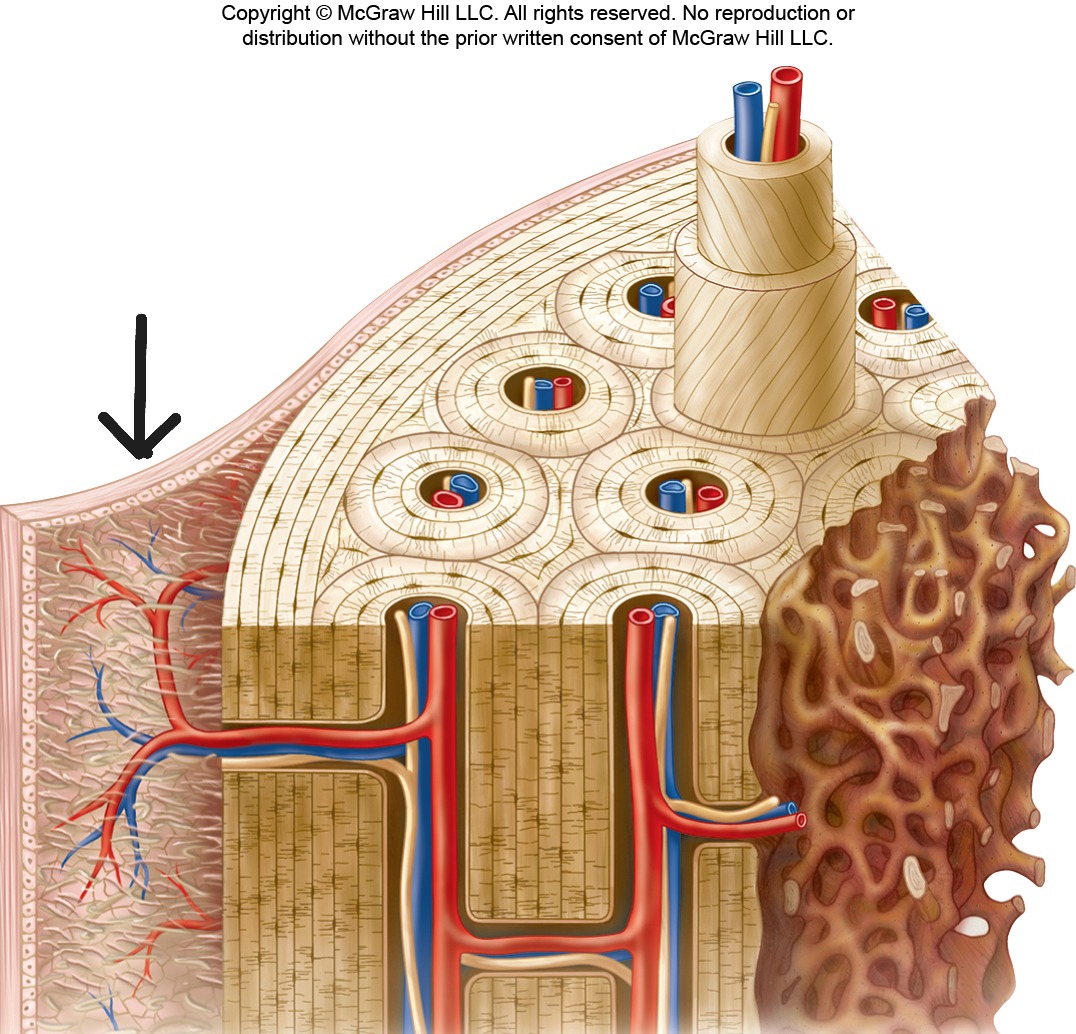
Periosteum
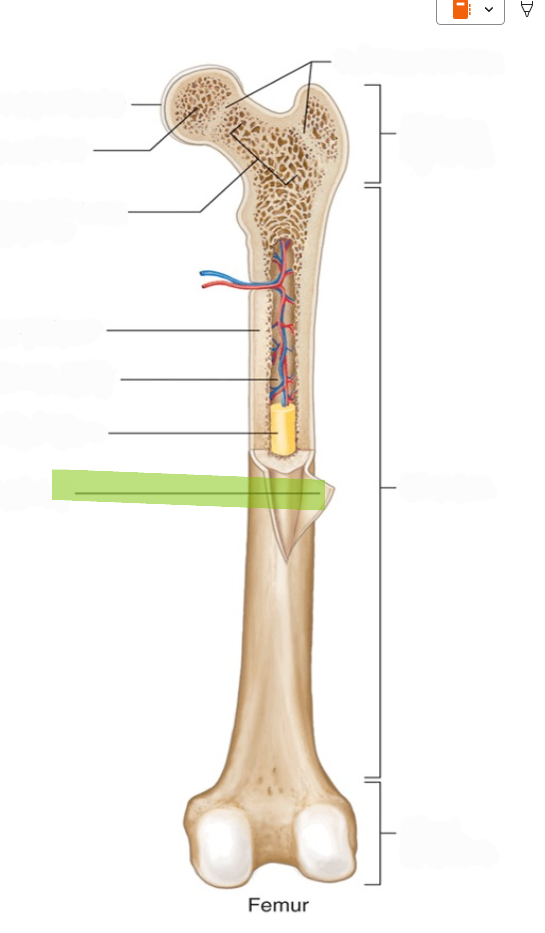
Endosteum
The delicate membrane lining the inner surface of the medullary cavity.
Endosteum
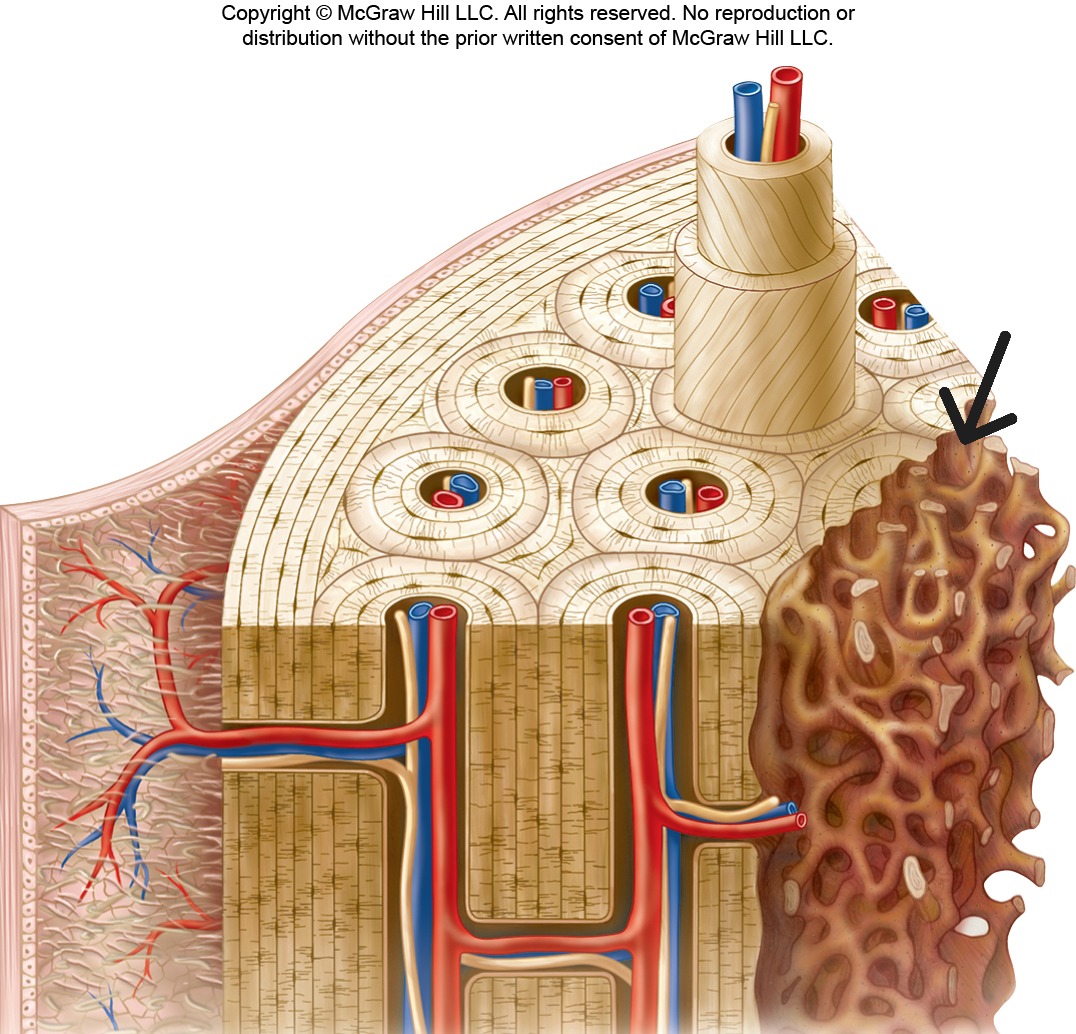
Compact Bone
Dense bone tissue organized into osteons (Haversian systems); forms the outer layer of bones.
Compact Bone
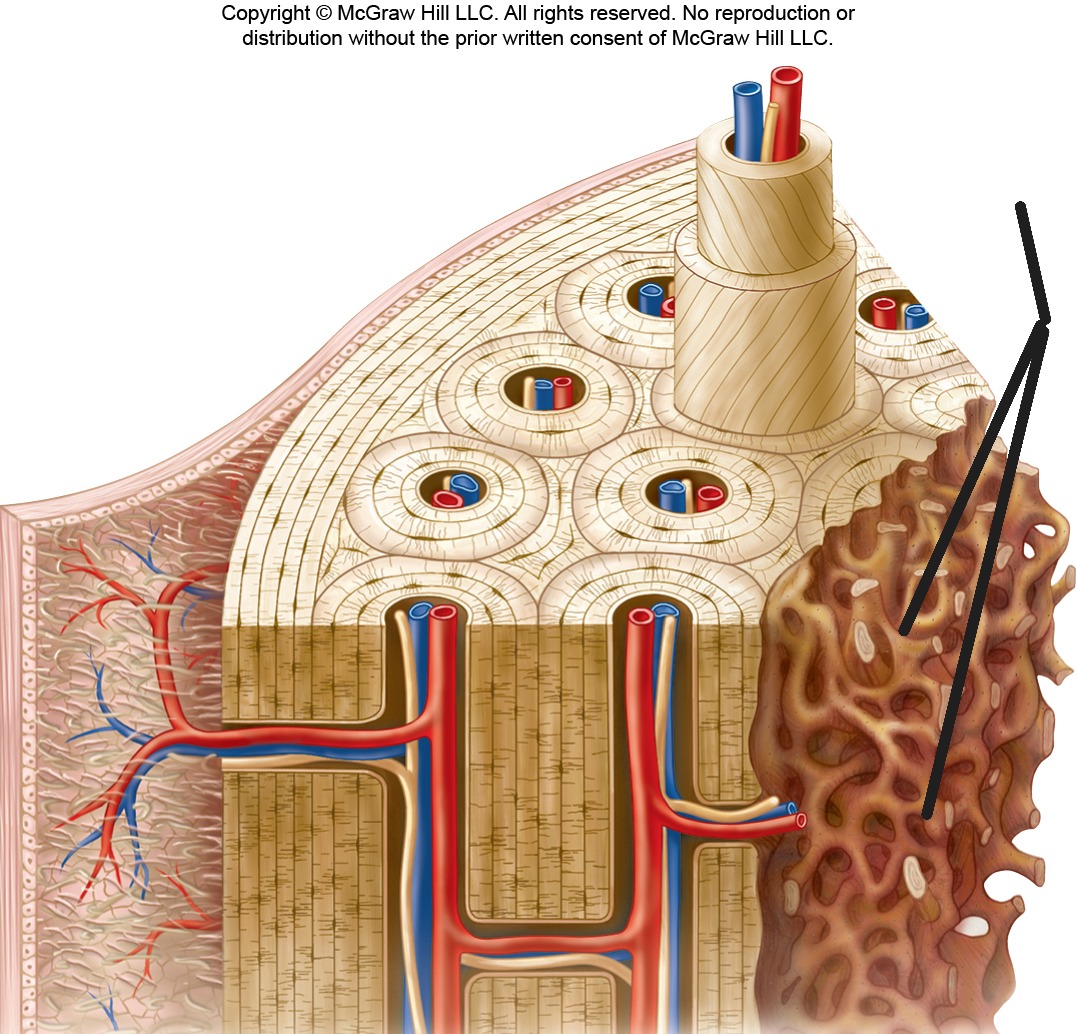
Spongy Bone
Lightweight bone tissue organized into trabeculae; also called cancellous bone.
Spongy Bone
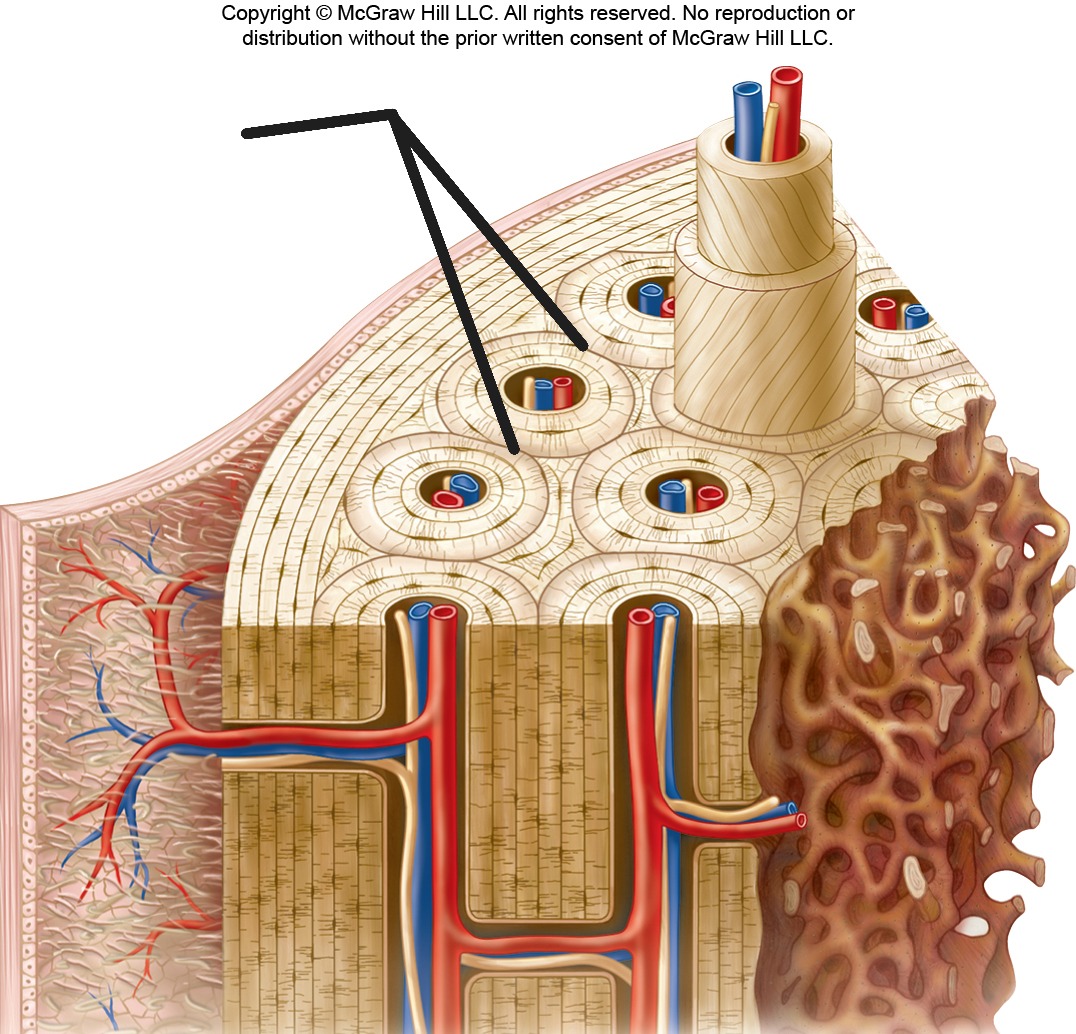
Trabeculae
The interconnected plates and bars that form the meshwork of spongy bone.
Trabeculae
Osteoid
The organic component of bone matrix consisting of collagen fibers and ground substance.
Collagen
Protein fibers in bone matrix that provide tensile strength and flexibility.
Hydroxyapatite
The crystalline form of calcium phosphate [Ca₁₀(PO₄)₆(OH)₂] that provides bone hardness.
Inorganic Material of Bones
Hydroxyapatite
Ground Substance
The non-fibrous component of bone matrix containing glycosaminoglycans and proteins.
Osteoblasts
Bone-building cells that secrete osteoid and facilitate mineralization.
Osteocytes
Mature bone cells trapped in lacunae that maintain the bone matrix and detect mechanical stress.
Osteoclasts
Large, multinucleated cells that break down and resorb bone tissue.
Osteoprogenitor Cells
Stem cells that differentiate into osteoblasts; also called osteogenic cells.
Osteon
The functional unit of compact bone; also called Haversian system.
Osteon
Haversian System
Another name for osteon; the circular structural unit of compact bone.
Haversian Canal
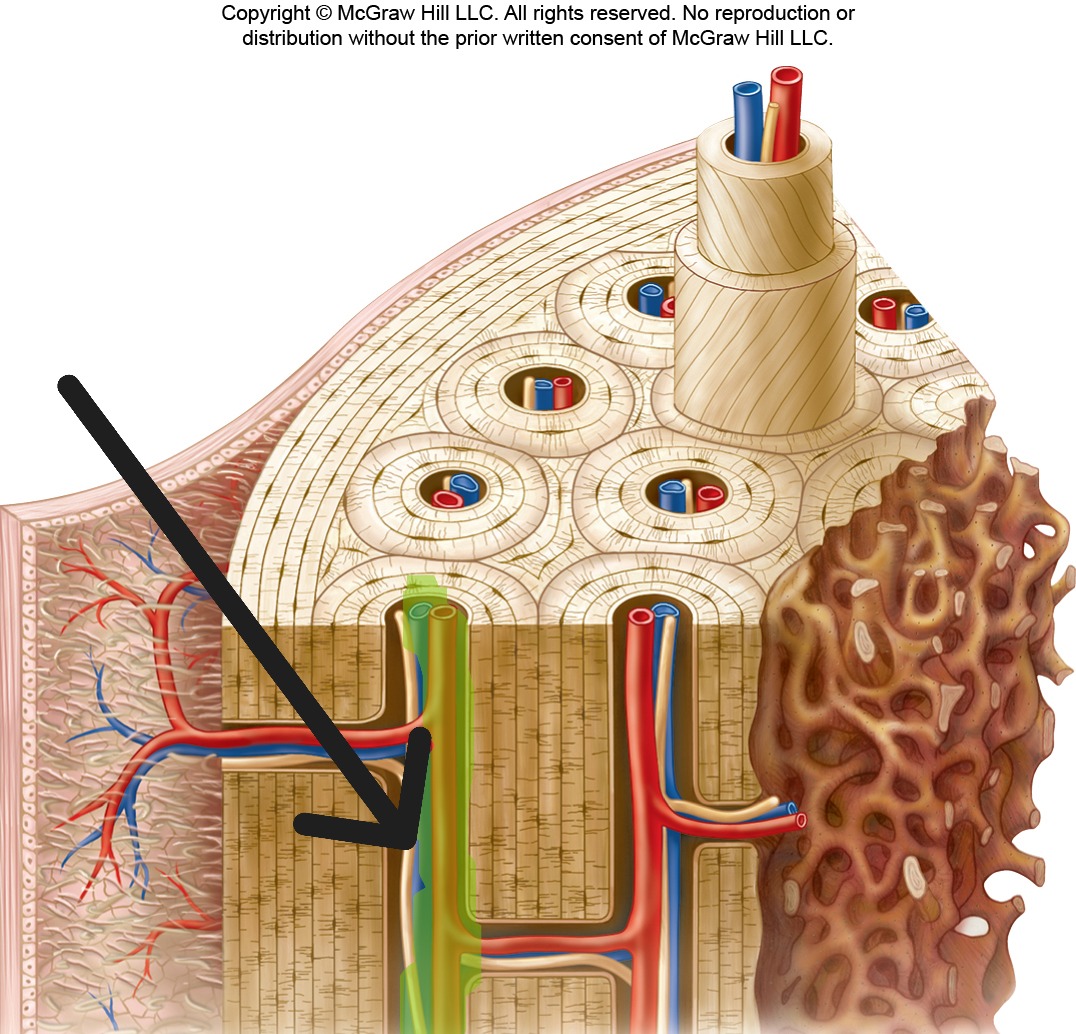
Central Canal
The channel in the center of an osteon containing blood vessels and nerves; also called Haversian canal.
Volkmann Canal
Lacunae
Small spaces in bone matrix that house osteocytes (singular: lacuna).
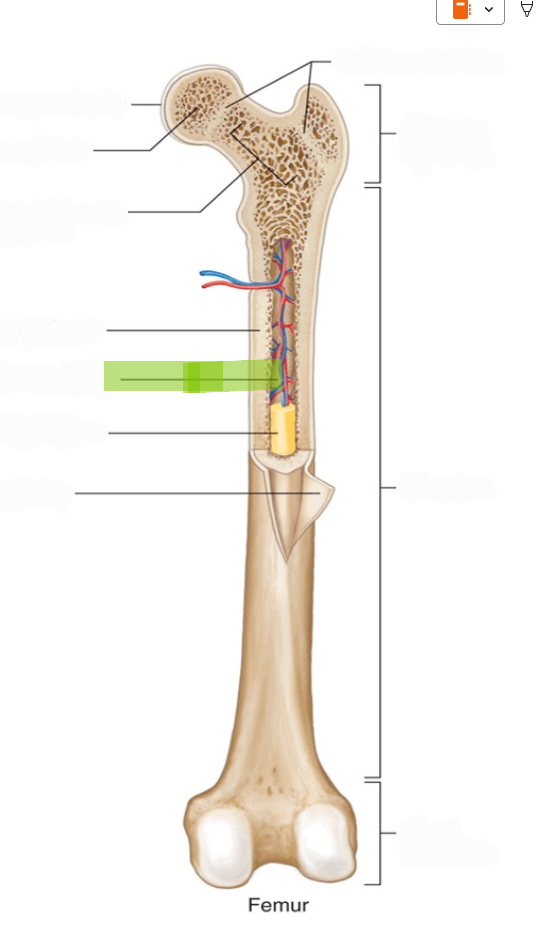
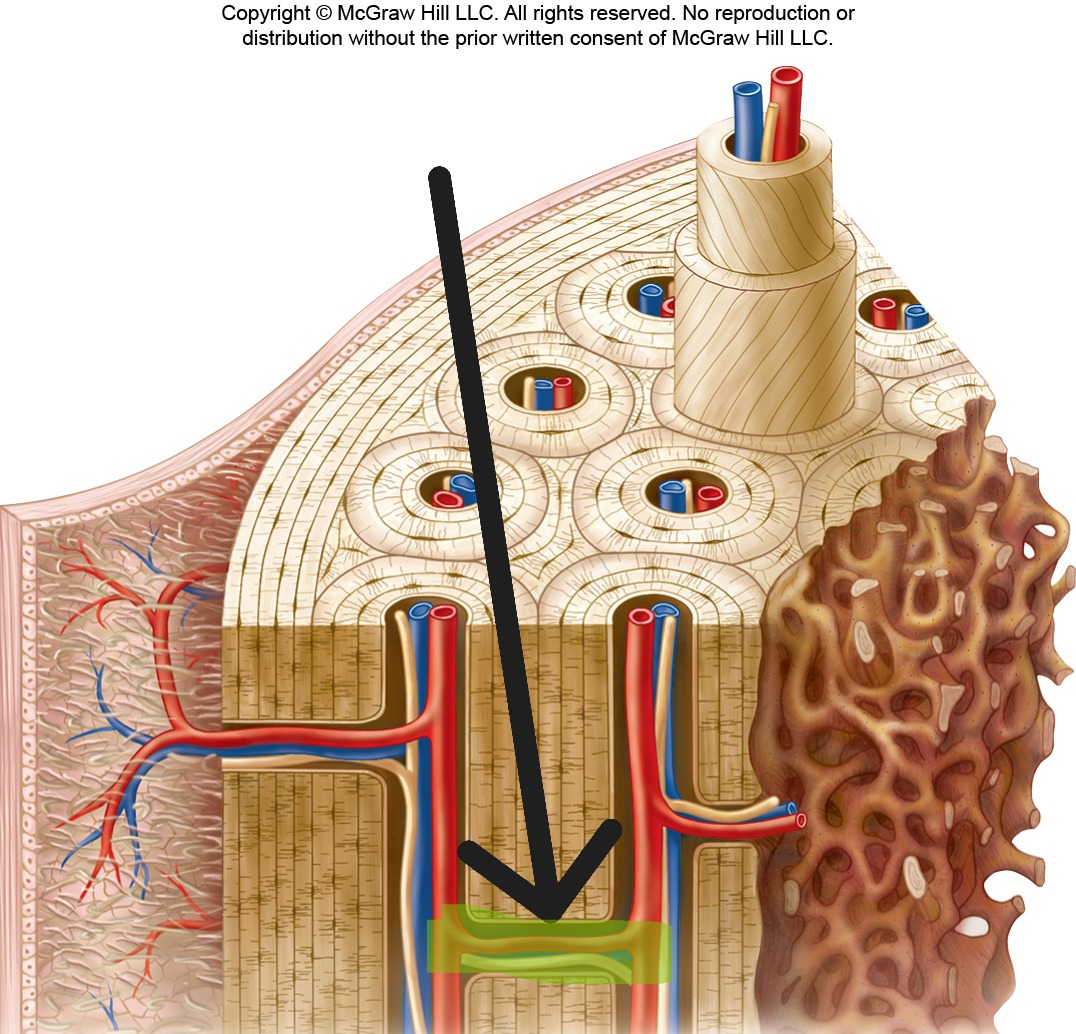
Red Bone Marrow
Hemopoietic tissue that produces blood cells; found in spongy bone of axial skeleton and proximal long bones.
Red Bone Marrow
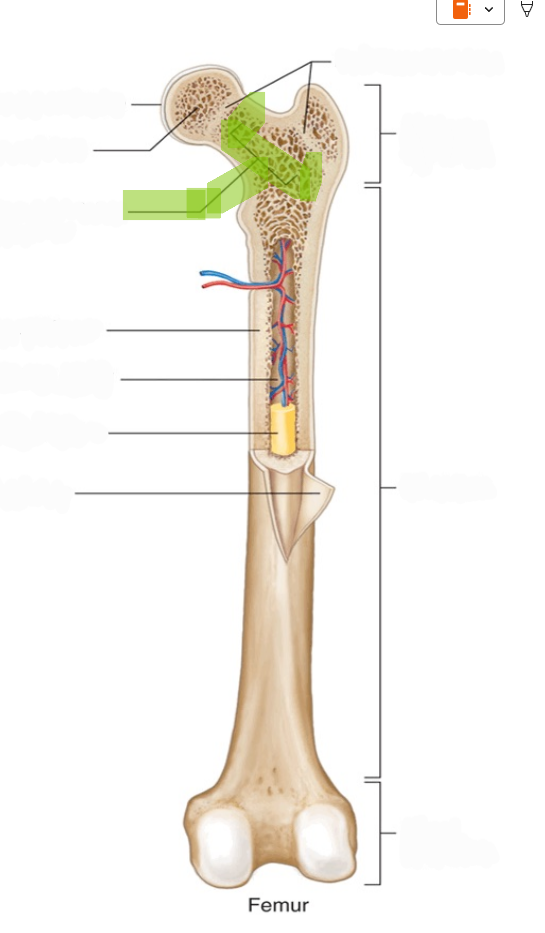
Yellow Bone Marrow
Adipose tissue that stores fat; found in the medullary cavity of adult long bones.
Yellow Bone Marrow
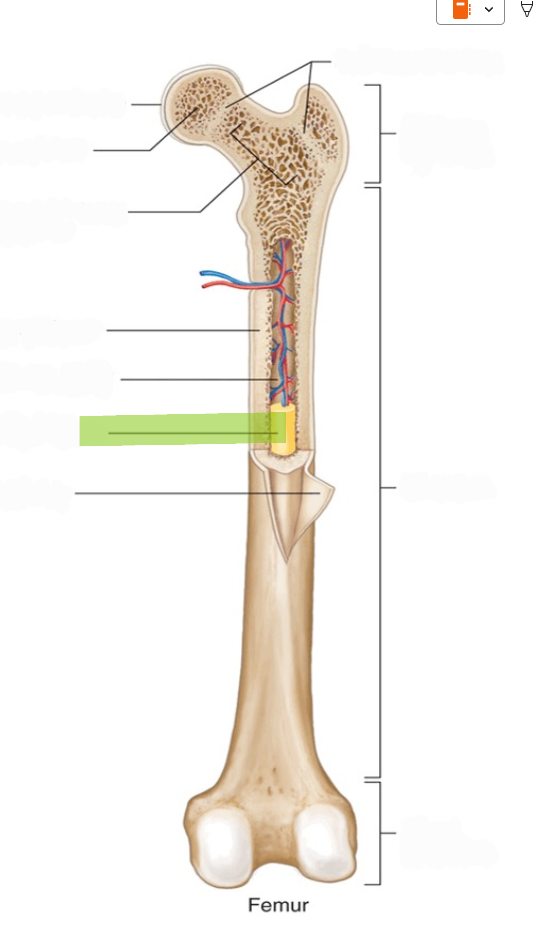
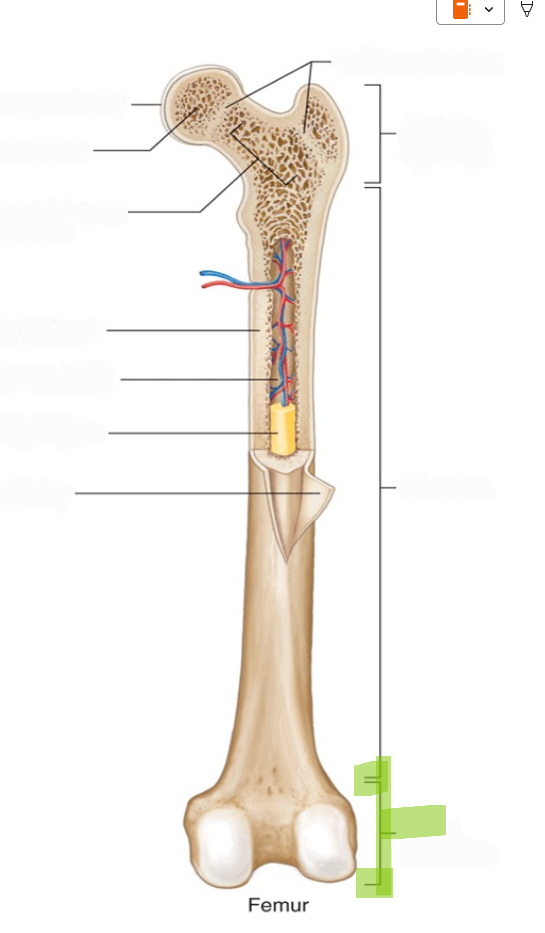
Epiphyseal Plate
The cartilaginous growth plate in children and adolescents that allows longitudinal bone growth.
Epiphyseal Plate
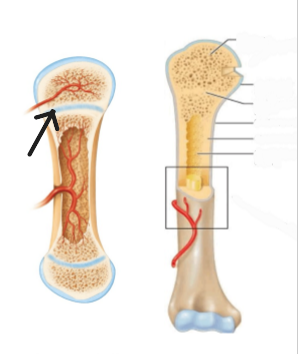
Growth Plate
Another name for epiphyseal plate.
Epiphyseal Line
The remnant of the epiphyseal plate in adults after growth has ceased.
Epiphyseal Line
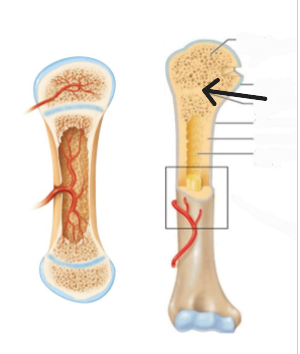
Endochondral Ossification
The process of bone formation from a cartilage template.
Epiphyseal Closure
The process when the growth plate stops functioning and becomes the epiphyseal line.
Bone Remodeling
The continuous process of bone breakdown and formation throughout life.
Osteolysis
The breakdown of bone tissue by osteoclasts.
Without Collagen
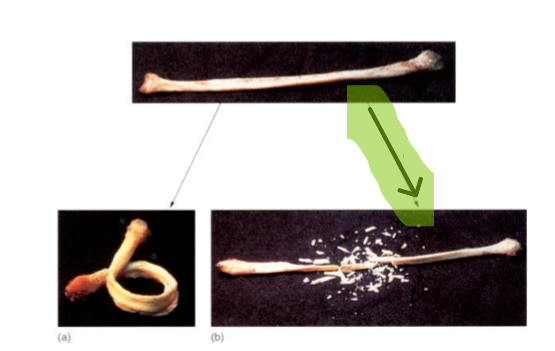
Growth Hormone
Hormone that stimulates bone growth and epiphyseal plate activity.
Without Minerals

Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
Hormone that increases blood calcium by stimulating osteoclast activity.
Calcitonin
Hormone that decreases blood calcium by inhibiting osteoclast activity.
Estrogen
Female hormone that helps maintain bone density; deficiency leads to bone loss.
Testosterone
Male hormone that helps maintain bone density.
Vitamin D
Essential vitamin for calcium absorption in the intestines; deficiency leads to weak bones.
Vitamin C
Required for collagen synthesis; deficiency impairs bone formation.
Vitamin A
Stimulates osteoblast activity; both deficiency and excess can harm bones.
Achondroplasia
Genetic disorder affecting the FGFR3 gene, causing impaired epiphyseal plate growth and short stature.
Osteoporosis
"Porous bone" disease characterized by decreased bone density and increased fracture risk.
Osteopenia
Mild bone loss that may progress to osteoporosis.
Bone Mineral Density
A measure of the amount of mineral content in bone tissue.
DEXA Scan
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry; a type of bone density scan.
Fetal Skeleton
The developing skeleton in utero, primarily composed of cartilage.
Cartilage Template
The cartilaginous model that serves as the framework for bone development.
Bone Age
A measure of skeletal maturity based on epiphyseal plate development.
Axial Skeleton
The bones of the skull, vertebral column, and rib cage.
Appendicular Skeleton
The bones of the arms, legs, and their attachments to the axial skeleton.