Chapter 9: Memory & Learning
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
PBSI 350
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
What does the explicit memory system do?
permits the conscious recollection of prior experiences and facts
What does the implicit memory system do?
allows past experiences to influence behavior without us realizing it
What does the declarative memory system do?
supports memory of "known" information that we can use in different situations
What does the procedural memory system do?
supports memory of "how" things should be done and allows us to learn/show skills
What memory system is this an example of: details about your last vacation
explicit memory system
What memory system is this an example of: skills or habits
implicit memory system
What memory system is this an example of: knowledge
declarative memory system
What memory system is this an example of: swimming, playing piano
procedural memory system
What is amnesia?
a loss of memory (including the ability to form new long-term memories) across modalities and materials
Amnesia results from damage to regions of the medial temporal lobe, including what regions?
hippocampus, dentate gyrus, subiculum, amygdala, and parahippocampal area
Information from a variety of different brain regions converges in the ________ to enter the hippocampus.
entorhinal cortex
After information converges in the entorhinal cortex, it then flows unidirectionally and exits either by returning to the entorhinal cortex or projecting to other brain regions via the ________.
fornix
What is retrograde amnesia?
impairment in recalling memories prior to the amnesia
What is anterograde amnesia?
impairment in forming new memories after the amnesia
What is episodic memory?
memories of events/episodes including autobiographical information of our experiences
What is semantic memory?
knowledge of facts and concepts that are not tied to personal experiences
What is working memory?
the ability to hold and process a limited amount of information over the short term
Working memory is ________ in individuals with amnesia.
unaffected
What is verbal working memory?
the ability to temporarily store and manipulate verbal information
What is visuospatial working memory?
the ability to temporarily store and manipulate visual and spatial information
What is Baddeley’s model of working memory?
explains how we temporarily store and maintain/manipulate information
According to Baddeley’s model of working memory, what regions are involved in working memory?
prefrontal cortex (specifically dorsolateral prefrontal cortex)
What are the four different stages of memory?
encoding, storage, consolidation, and retrieval
What brain regions are involved in the encoding stage of memory?
medial temporal lobe and prefrontal regions
In the encoding stage of memory, what information comes from the the retrosplenial cortex and the parahippocampal gyrus?
spatial information
In the encoding state of memory, what kind of information comes from the perirhinal cortex?
object information and their identities
In the encoding stage of memory, what happens to information in the entorhinal cortex?
it converges
What is the subsequent memory effect?
items we remember later trigger more brain activity in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex than items we forget
What does the ventrolateral prefrontal cortex do in memory?
selects information most relevant for encoding
What does the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex do in memory?
supports the structure of multiple pieces of information for later reordering
What is pattern separation?
distinguishing between similar items/scenes (ie., first date or second date at the same restaurant)
What does the hippocampus do in the encoding stage of memory?
ensures that similar and overlapping representations are encoded more distinctly
What does the hippocampus do in the storage and consolidation stages of memory?
supports memory consolidation
What is the consolidation theory of long-term memory?
a temporary memory is transformed into a more stable, long-lasting form
What is the multiple trace theory?
every time a memory is retrieved, the hippocampus creates a new trace and integrates any prior related episodes
How do the consolidation theory of long-term memory and the multiple trace theory differ from one another?
consolidation theory sees memories as stabilizing over time, while multiple trace theory sees them as evolving with each recall
What does the hippocampus do in the retrieval stage of memory?
participates in the retrieval of various long-term memories by allowing for pattern completion
What is pattern completion?
each smaller piece of information can be used to reconstitute the whole
In the retrieval stage of memory, what is recognition?
the use of thought to rely on a sense of familiarity
What brain regions are involved in recognition?
perirhinal cortex and dorsal medial nucleus
In the retrieval stage of memory, what is recall?
remembering something specific about an item
What brain regions are involved in recall?
hippocampus and midline diencephalic structures
What does the prefrontal cortex do in the retrieval stage of memory?
supports strategic and executive aspects of memory retrieval and suppresses unwanted memories
What does the parietal cortex do in the retrieval stage of memory?
contributes through its role in attentional control and integration across modalities
What is the role of the basal ganglia in learning and memory?
extracts regularities between a stimulus and the response or outcome with which it is associated
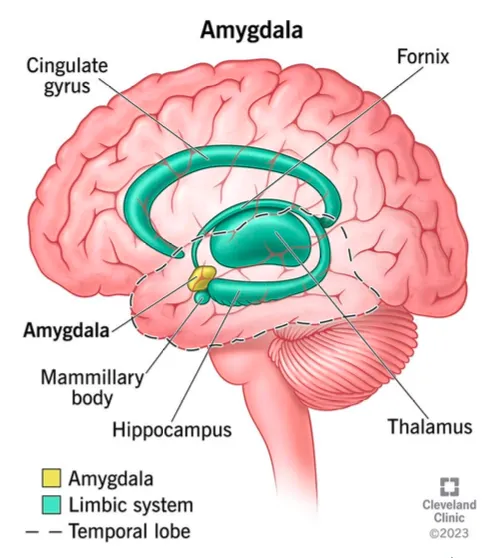
What does the amygdala do in memory?
allows emotional experience to modulate certain aspects of long-term memory (flashbulb memory)
What does the amygdala do in fear conditioning?
helps the learning and expression of emotional responses to stimuli with learned emotional significance
What happens if you have damages to the amygdala?
precludes a person from exhibiting a conditioned fear response