Dentistry!
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Who gets antibiotic prophylaxis for bacterial endocarditis?
Patients with cardiac conditions (1. Prosthetic cardiac valve 2. Previous endocarditis 3. Congenital heart disease (a. unrepaired cyanotic congenital heart disease b. completely repaired congenital heart disease with prosthetic material or device during the 1st six months after procedure c. repaired congenital heart disease with residual defects at the site or adjacent to the site of a prosthetic patch or prosthetic device) 4. Cardiac transplantation recipients with cardiac valvular disease
When is BE prophylaxis recommended?
All dental procedures that involve manipulation of gingival [gum] tissue, periapical region of teeth or oral mucosa examples: extractions, cleanings, most fillings, root canal treatment, etc.
When is BE prophylaxis NOT recommended?
1. Routine anesthetic injection through noninfected tissue 2. Taking dental x-rays 3. Placement of removable prosthesis 4. Adjustments and placement of orthodontic appliances 5. Shedding of “baby teeth” 6. Bleeding from trauma to the lips or oral mucosa
What medication for BE prophylaxis?
Oral: Single dose 30-60 min. prior to appt. Amoxicillin: adult-2gm, child 50mg/kg. Clindamycin: adult 600mg, child 20mg/kg Clarithromycin: adult 500mg, child 15mg/kg IM or IV Ampicillin: adult 2g, child 50mg/kg Cefazolin: adult 1g, child 50mg/kg
Dental Caries
(tooth decay) Is an infectious microbiological disease of the teeth that results in localized dissolution and destruction of the calcified tissues.
Teeth, bacteria, carbohydrate (sucrose)
Three things that are absolutely necessary for dental caries
Microbiology of caries
Streptococcus Mutans, Lactobacillus, Actinomyces (Root caries), (Streptococcus Sanguis)
Streptococcus mutans
A small circular bacteria. It is a facultative anaerobe. It is an acid producer and acid tolerant (Acidogenic – aciduric) Has the ability to produce glucans from dietary sucrose. (sticky matrix). Glucans are sticky carbohydrates that act as a matrix for the bacteria on the enamel surface. Sucrose glucosyltranferase glucans.
Dental plaque
It is a gelatinous mass of bacteria adhering to the tooth surface. The accumulation of plaque on teeth is a highly organized and ordered sequences of events.
Dental plaque process
1. Bacteria produce acid 2. Acid dissolves enamel of tooth 3. Bacteria invade dentin 4. Dissolving of dentin 5. Invasion of pulp tissue 6. Irreversible infection of pulp tissue
Adhesion
This mixed streptococcal mat allows the adherence of other organisms, such as filamentous and spiral bacteria. S. sanguis is more efficient in adhering to tooth surfaces than S. mutans. As bacteria multiply in the dental plaque, the flora environment is more adequate to anaerobes. Thus the S. Mutans is creating an environment for itself via its by-products: acid and glucans.
Bacterian role
Teeth free from infection with bacteria, do not develop caries. Antibiotics are effective in reducing caries.. Oral bacteria can demineralize enamel in vitro. Specific bacteria can be isolated and identified from plaque over various carious lesions.
Lactobacillus
Is a rod shaped bacteria that is anaerobic, it produces acid as a by-product of sucrose metabolism and is acid tolerant (Acidogenic – aciduric). This bacteria plays more a role in later stage caries development .
Caries prevention
Fluoride (1. Topical treatment; toothpaste, gels, etc. 2. Water supply 3. Fluoride pills- no fluoride in water .5mg or 1mg chewable or liquid forms), chlorhexidine (rinse), xylitol
Fluoride action
1. Absorbed topically in enamel- aids recalcification and makes enamel less soluble in acid 2. Taken internally- becomes part of dentin and enamel matrix
Xylitol
a sugar alcohol, is derived mainly from birch and other hardwood trees. Short-term consumption is associated with decreased Streptococcus mutans levels in saliva and plaque. Aside from decreasing dental caries, may also decrease the transmission of S. mutans from mothers to children.
Chlorhexidine
antiseptic agent use of rinse in high riskpatients decreases bacterial count for hours.
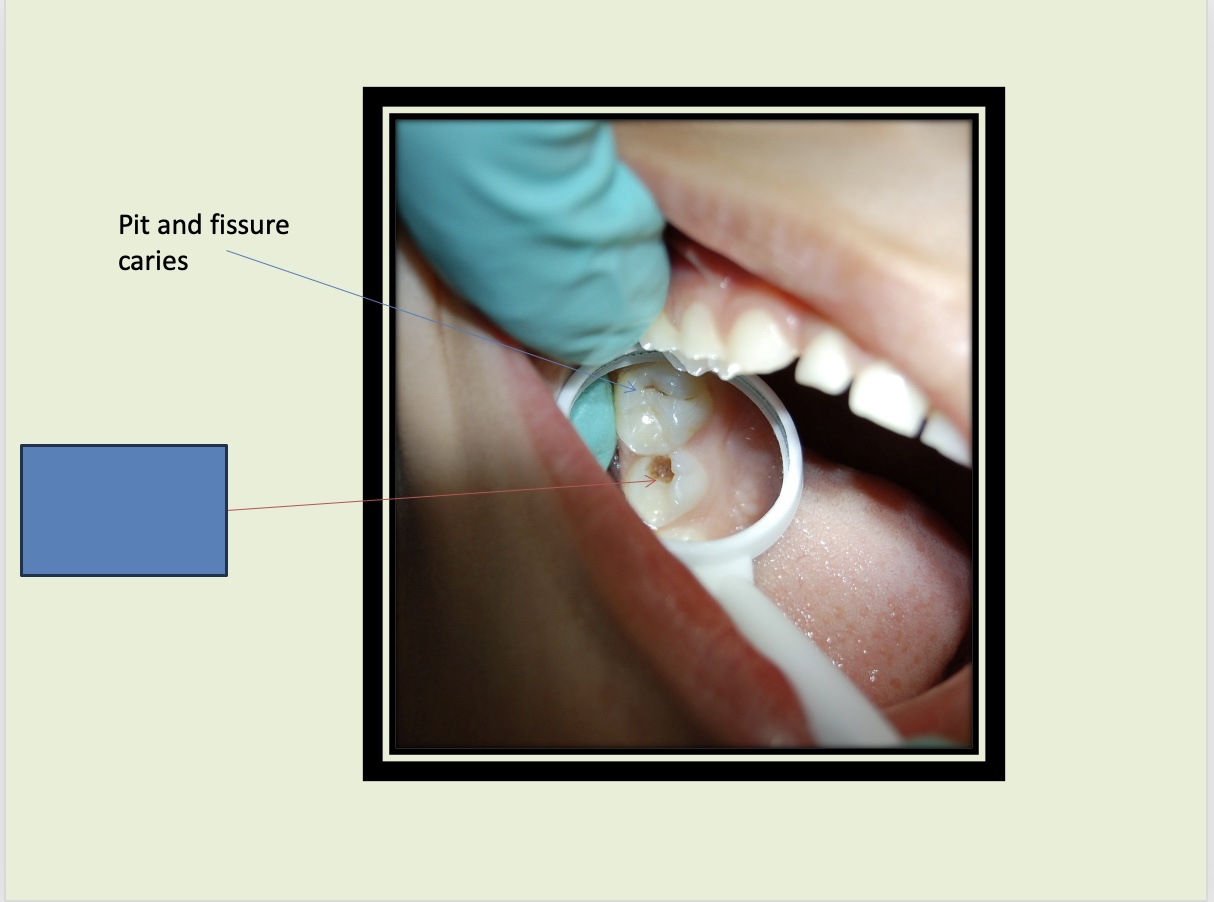
What is indicated by the blue box?
Pit and fissure caries
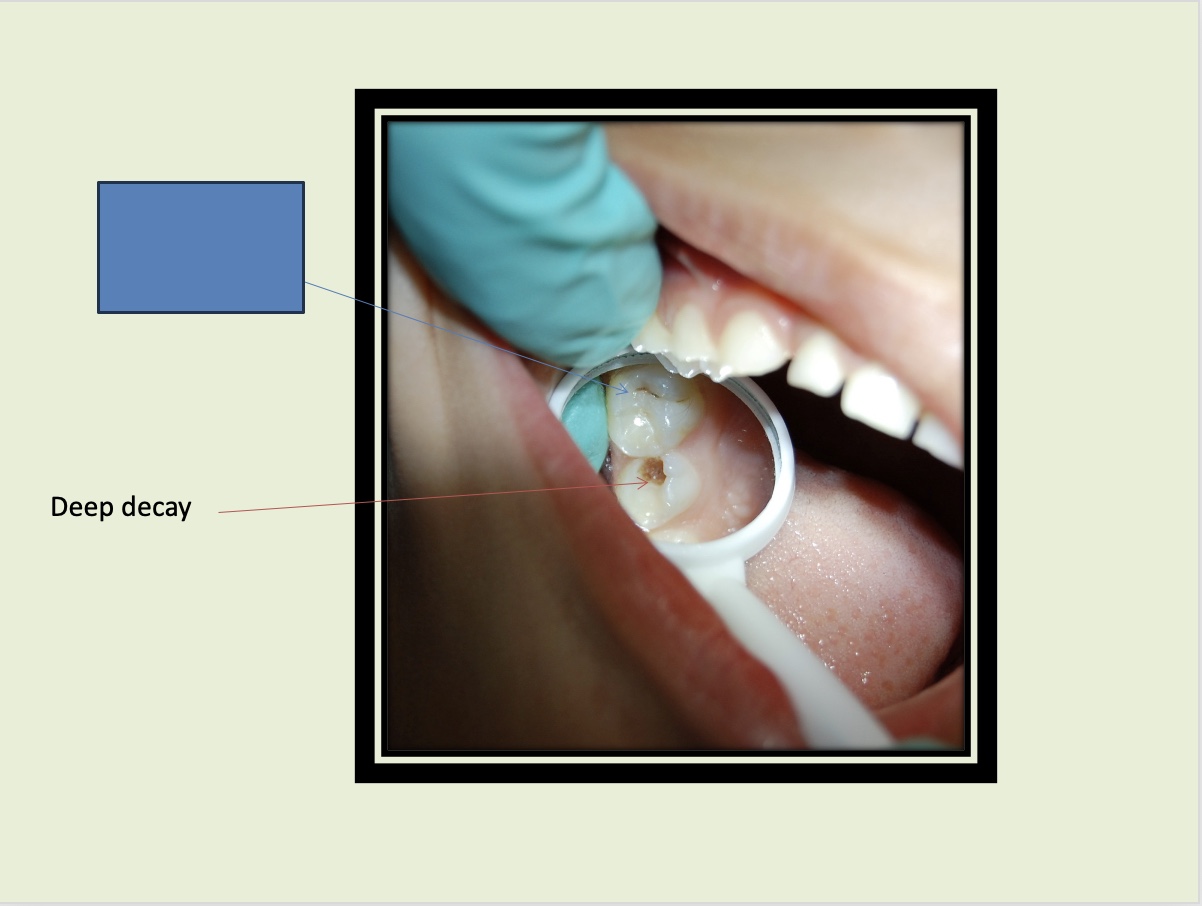
What is indicated by the blue box?
Deep decay
2-3
Decay is usually ____ times deeper than it appears
Deep caries with probably pulp involvement
What do these images show?
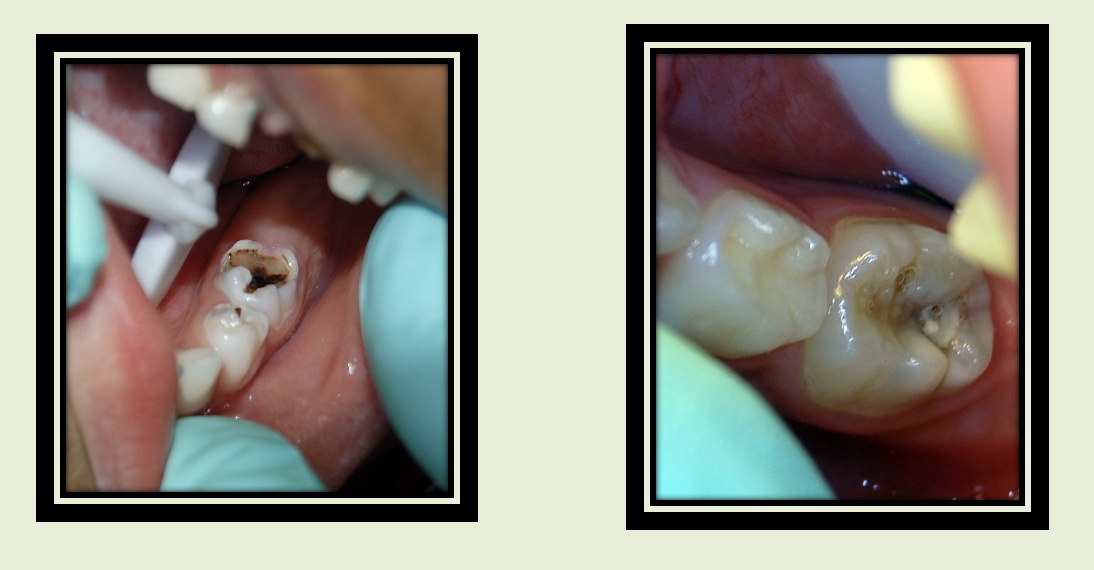
abscess
What is indicated by the blue box?
Root tip
What is indicated by the red box?
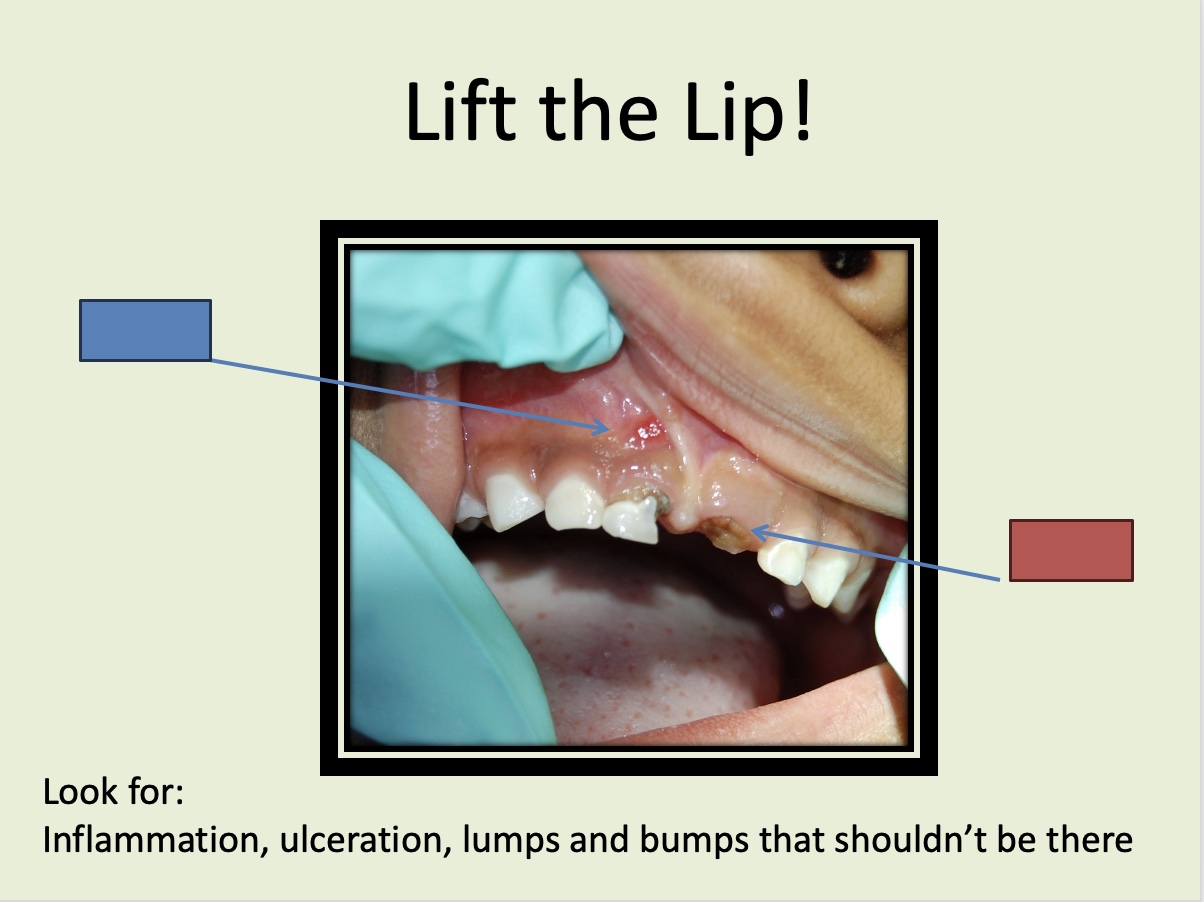
Healthy gums
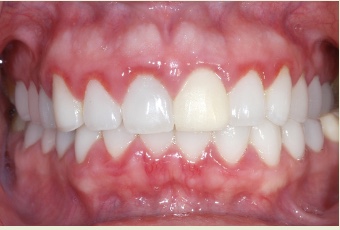
What is shown in this image?
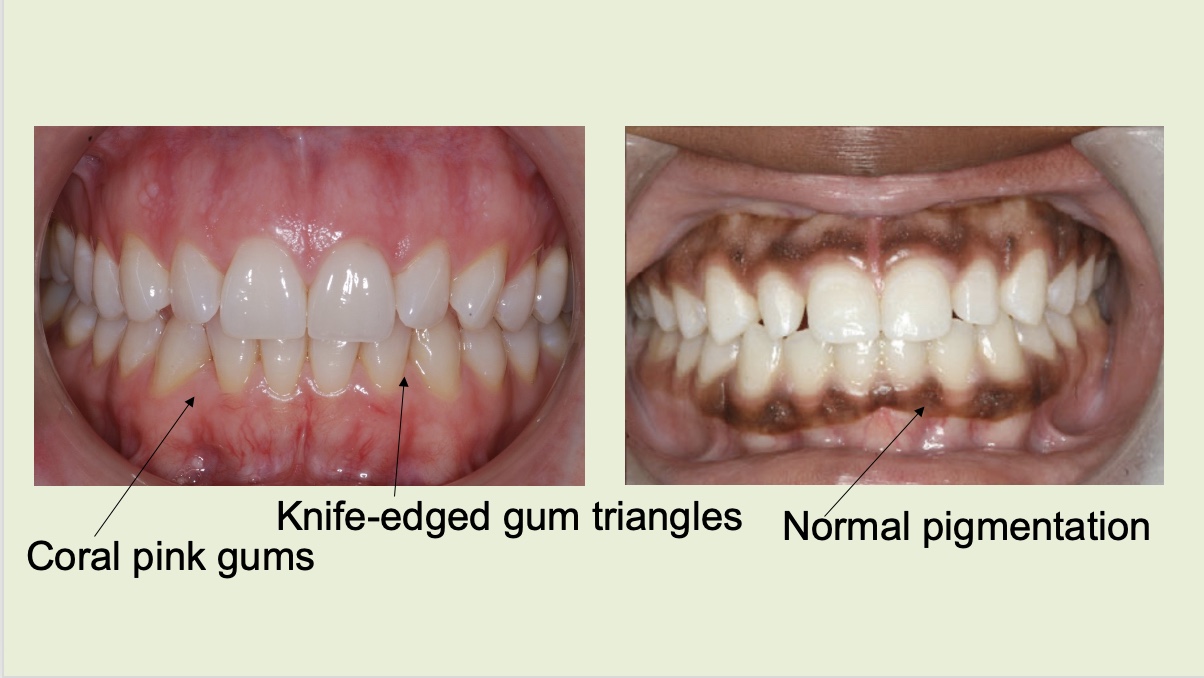
Healthy
Healthy
[Healthy/Unhealthy] Gums are coral pink or brown, and usually lack red areas which may indicate areas of gum irritation or inflammation. The gums are tight and firmly-attached to the underlying bone. The gums often appear ‘dimpled’ like an orange peel. When the gums are unhealthy and swollen, the dimpling may disappear.
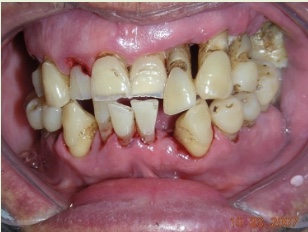
Periodontal disease
INFECTION OF THE TISSUES [GINGIVA] SUPPORTING TEETH. Classified by severity of disease: 1. Gingivitis- milder and reversible, only infects gingiva 2. Periodontitis- more severe infection of gingiva and alveolar bone [surrounds teeth]
Periodontal disease warning signs
1. Gums bleed easily 2. Red, swollen and tender gums 3. Receding gums 4. Persistent “bad breath” and/or bad taste in mouth 5. Permanent teeth that are loose and/or separating
Periodontal risk factors
1. Tobacco use 2. Systemic diseases, example diabetes 3. Some types of medications, examples steroids, calcium channel blockers, oral contraceptives 4. Defective restorations 5. Crooked teeth 6. Pregnancy [most of the time reversible]
Coronary Heart Disease [CHD]
In nine different studies periodontitis was associated with a 15% greater risk of developing _______. Many referenced articles are available on the American Dental Associations [ADA] web site.
Healthy teeth and gums
What is indicated by the black box?
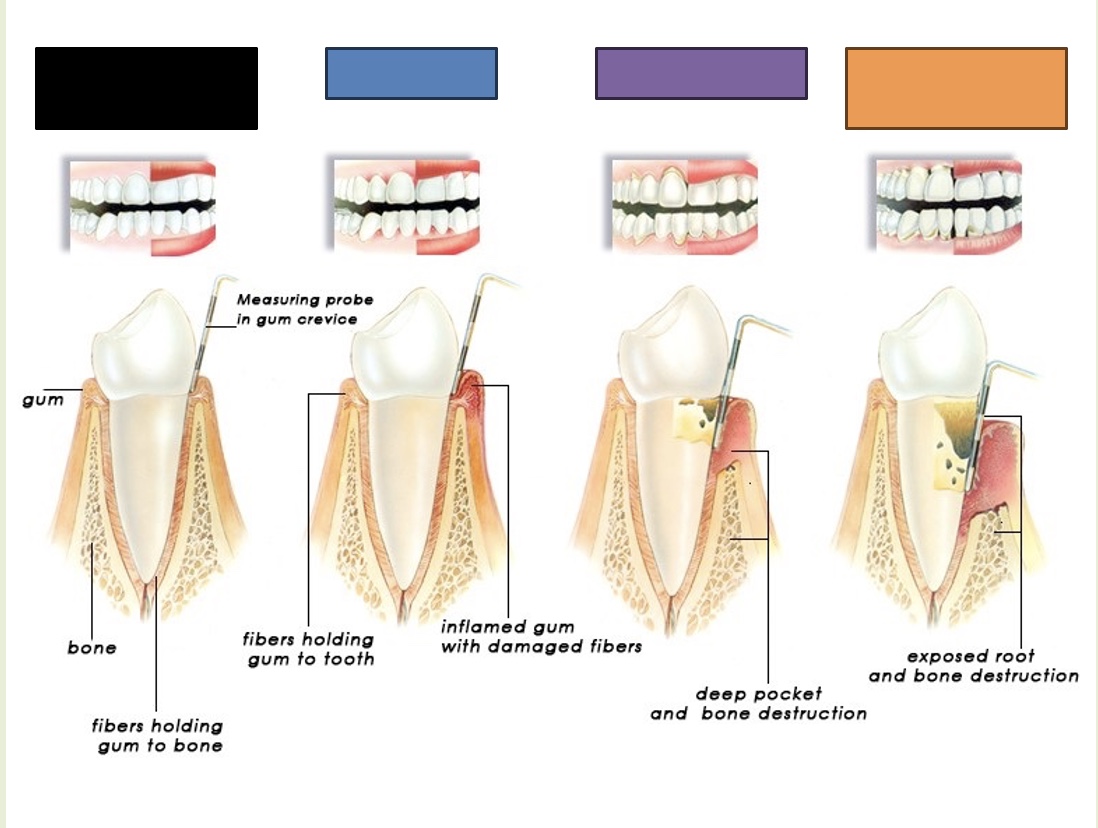
Gingivitis
What is indicated by the blue box?
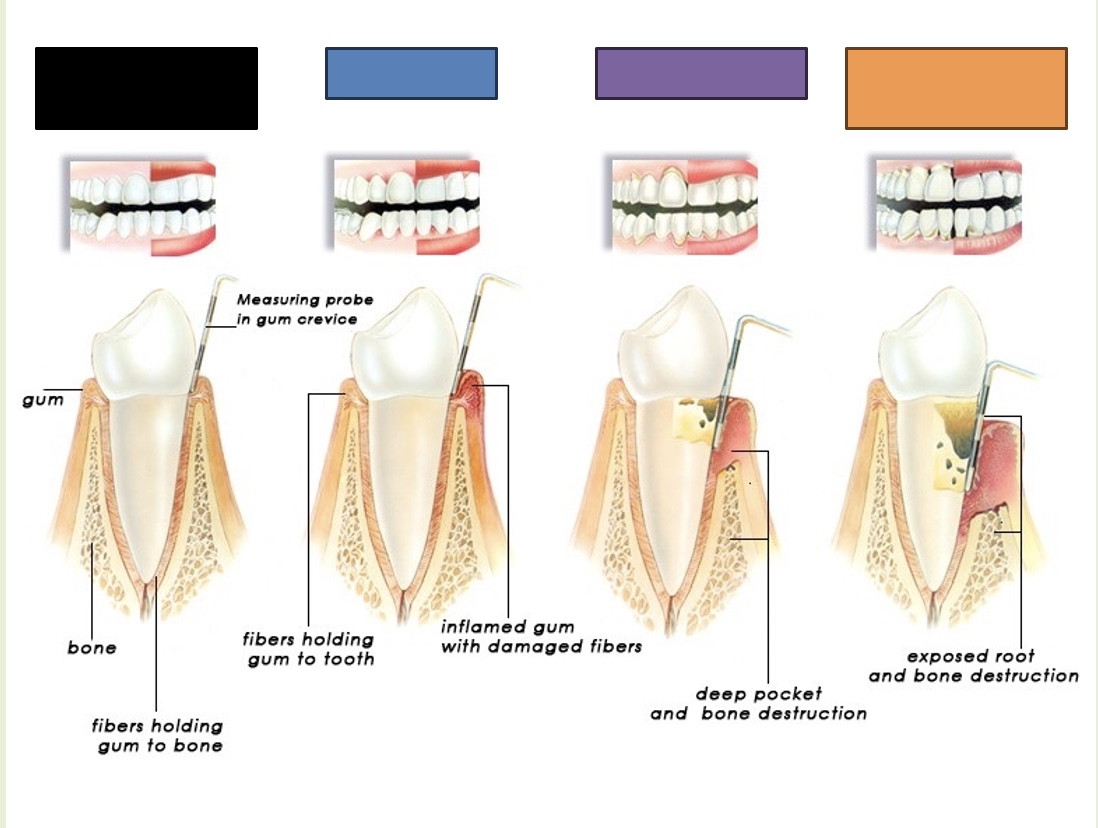
Periodontitis
What is indicated by the purple box?
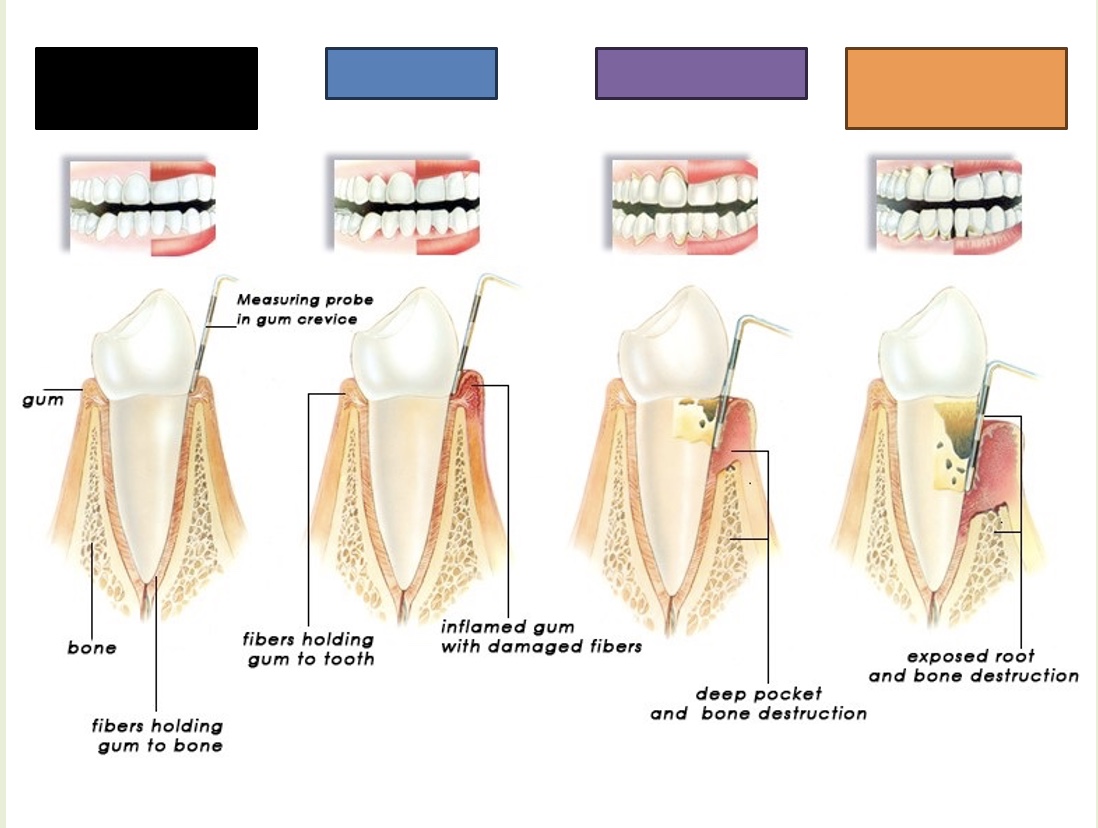
Advanced periodontitis
What is indicated by the orange box?
Plaque
a film which forms on the teeth. It is made up of food particles, bacteria, and saliva which remains on the tooth surface after eating.
Calculus (tartar)
is actually plaque that has hardened onto the teeth, especially at the gumline. Both plaque and tartar make the gums irritated and inflamed.
Gingivitis
a condition when the gums bleed easily. The borders where the gums and the teeth meet may look red. If the teeth are cleaned, and plaque and tartar are removed, the swelling and redness go away. Can be stopped from getting worse and its effects can be reversed.
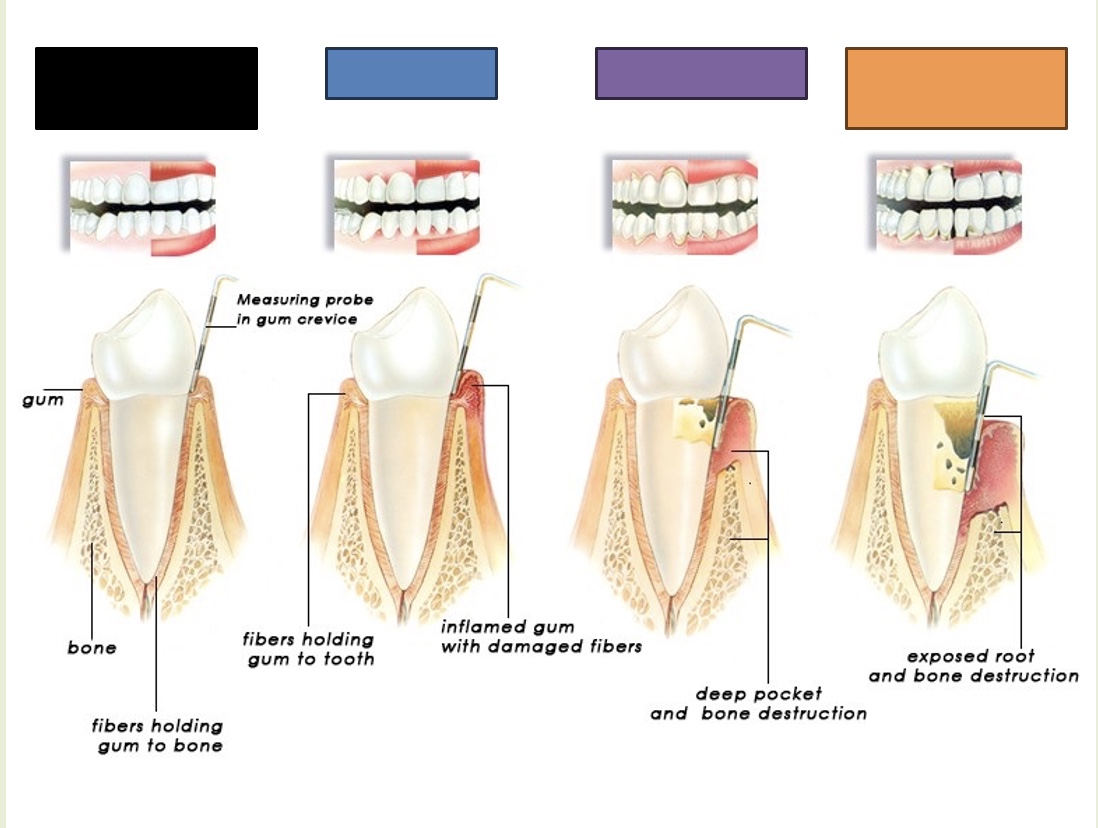
Periodontitis
Bone loss has occurred due to unstopped gingivitis. Teeth may appear longer. There may be spaces between teeth that were not there before. Teeth may become loose. Plaque and tartar may be visible. There can be draining pus.
Unhealthy
[Healthy/Unhealthy] gums Bleed easily because they are irritated and inflamed. Are swollen. This is because enlarged blood vessels bring more blood to the area in order to fight the germs in the plaque. It’s the plaque that covers the teeth and contacts and irritates the gums. ____ gums that are inflamed by plaque or tartar may initially bleed when brushed. Teeth should be brushed well even though gums may bleed easily at first. Brushing the teeth regularly and thoroughly will usually eliminate or reduce the cause of the bleeding.Pus may be draining from around the tooth due to localized infection.
Gum disease causes
Poor oral hygiene and failure to remove bacterial plaque and food material from teeth and gumlines. Oral bacteria. Medicines that Cause dry mouth, Cause gum overgrowth, or Have high sugar content, which promotes plaque build-up.
Gum disease treatment
1. Improved oral hygiene 2. Routine teeth cleaning 3. Medication: Peridex 4. Periodontal surgery 5. Removal of infected teeth
Gum disease prevention
ORAL HYGIENE: BRUSHING and FLOSSING (Disturbs dental plaque thus decreases acid production) PIT and FISSURE SEALANTS (Prevents nidus for plaque formation) ROUTINE DENTAL EXAMS (1. Early detection of possible decay 2. Fluoride treatment 3. Restorative intervention)
Sources of bad breath
Poor oral hygiene, Dry mouth, Gum disease, Frequent sinus infections, Digestive problems, Diabetes, Medicines, Fissured, or deeply grooved tongue
Dental pulp infection
IRREVERSIBLE INFECTION 1. Poor blood supply 2. Inability of increased blood flow to infected area SYMPTOMS 1. Swelling 2. Pain without stimulus 3. Pain due to hot stimulus 4. X-ray shows apical radiolucency
Causes of dental pulp infection
DECAY: Invasion of bacteria into pulpal tissue FRACTURE OF TOOTH: Exposure of pulp to oral floraTRAUMA: Disruption of apical blood supply to tooth
Dental pulp infection treatment
ENDODONTIC OR ROOT CANAL TREATMENT 1. Removal of pulp tissue 2. Replacement of pulp tissue with an endodontic filling material [gutta percha most popular]
Root Canal result
1. Keep tooth 2. Sometimes tooth becomes discolored [dark]3. Sometimes tooth becomes “brittle” 4. Tooth may need full coverage restoration [crown]
Dental abscess
Antibiotics should be prescribed with swelling. Drainage must be considered if the swelling is fluctuant. Drainage is best achieved by incision and extraction of the involved tooth. Swelling usually indicates a necrotic pulp with spread of inflammation into the soft tissue. Need to evaluate size and extent. Is it only intra-oral or is there an extra oral component? Has the swelling increased over the last 24 hours?
Treatment of odontogenic infections
Removal of the cause. Local drainage and debridement. Extraction of involved teeth (always with primary teeth) or root canal therapy for permanent teeth. Oral antibiotics if systemic involvement. Often extraction of the abscessed tooth alone will bring about resolution without antibiotic therapy in chronic infections. Mandibular infections which spread may compromise the airway. Presenting problems for a young patient may include pain and dehydration. It is important to ask whether the child has urinated during the previous 12 hours and assess their fluid intake.
Severe odontogenic infections
Hospital admission, Extraction of involved teeth, Drainage of any pus present. If mandibular swelling crosses the midline, extra-oral drainage should be considered. Swab for culture and sensitivity. Intravenous antibiotics. Penicillin or first generation cephalosporins if allergic. Maintenance fluids. Cholorhexidine gluconate rinses. Pain control.
reasons for dental pain
Dental Infection, Dry Socket, Post Dental Procedure
Best dental pain analgesic
Ibuprofen [200 mg] plus Acetaminophen [500 mg] q4-6h
Temporomandibular disorders
TM JOINT ONE OF THE MOST COMPLEX JOINTS IN THE BODY MOVEMENT - Combination of rotating and translocational when chewing and speaking. About 15% of American adults suffer from chronic facial pain. Experience Pain in or around ear, Tenderness of the jaw, Clicking and/or popping noises when opening mouth, Chronic headaches, Chronic neck aches
TMD diagnosis criteria
1. Damaged jaw joints are suspected when there are popping, clicking and grating sounds during jaw movement 2. Chewing may be painful 3. Jaw may lock or not open wide 4. Teeth may appear worn smooth 5. Ear symptoms very common and need to rule out infection of ear, sinuses and/or teeth
Hard tissue
During diagnosis, when examining _____ use dental x-rays or CT scanning
Soft tissue
During diagnosis, when examining _____ use magnetic resonance imaging
Acute pain
Treatment of _____ includes: 1. Jaw rest; bite guard, soft food, avoid chewing gum and avoid opening too wide to eat 2. Heat and ice therapy 3. Medications; a. anti-inflammatory medication; aspirin, ibuprofen b. muscle relaxants; valium c. certain situations local injection of cortisone preparations •4. Osteopathic manipulation 5. Physical therapy 6. Stress management 7. Occlusal therapy- custom made bite guard or splint 8. Correction of bite abnormalities- occlusal adjustments, orthodontic movement, etc. 9. Last resort; surgery
Avulsed tooth (knocked out)
Treatment of ____ includes: 1. Hold tooth by crown 2. Rinse off gently with water only if dirty 3. Do not scrub or remove attached tissue fragments 4. Gently insert tooth and hold in socket 5. If not possible place in cup of milk and go to a dentist
Causes of Cracked tooth syndrome
1. Chewing on hard object 2. Accident 3. Grinding or clenching teeth 4. Stress on tooth 5. Post endodontic “brittleness
Treatment of cracked tooth syndrome
Dependent upon size and location. 1. Placement of restoration [filling or crown] 2. Placement of bonding agent 3. Root canal treatment
xerostomia
Symptoms of ____: dry mouth, burning sensation, changes in taste, difficulty with swallowing and speech. Etiology: medications, rheumatic disease and radiation therapy, Sjögren's syndrome. Not enough saliva can promote tooth decay, gum disease, oral infections, and food retention in the mouth, and can make nutrition, swallowing, and psychological well-being more difficult
Managing xerostomia
Avoid using these products: Inciting medications, Irritants such as alcohol, caffeine, and tobacco, Sugar-containing drinks and candies. Suggest patients do the following: Take sips of water, especially during eating. Chew sugarless gum and mints. Use saliva substitutes. Try salivary stimulants such as pilocarpine. Prevent caries and periodontal disease by: Maintaining meticulous oral hygiene and Using increased strength topical fluorides such as 1.1% sodium fluoride
Xerostomia (dry mouth)
These medications can cause ______: Steroids, Antihistamines, Diuretics, Antihypertensives, Anticholinergics, Antidepressants
Gingival hyperplasia
These medications can cause ___: Phenytoin , methotrexate, Calcium channel blockers
osteonecrosis
These medications can cause ____: Intravenous Bisphosphonates
stomatitis and mucositis
These medications can cause ____: Cancer chemotherapy – Radiation Therapy
candidiasis
These medications can cause ____: steroids
periodontal disease
These medications can cause ____: Immunosuppressive – Nifedipine in Type II Diabetics
dental caries
These medications can cause _____: sugar containing medications
diabetics
Poor glycemic control is associated with a threefold increased risk of having periodontitis in diabetics versus controls. _____ with good glycemic control have no significant increased risk of periodontal disease. Chronic infection (like periodontal disease) worsens glucose control. Treatment of periodontal disease results in a 10–20% improvement in glycemic control. Decreased salivary flow and increased salivary glucose levels make patients with diabetes susceptible to fungal infection in the mouth.
Elders
80% of ____ have one or more chronic disease. 30% have three or more chronic diseases. 14% of those over 65 live in poverty. Most lack dental insurance. Many are homebound or institutionalized. 38% of those over 65 are disabled.
systemic
A _____ approach should be used in evaluating the mouth of elderly patients. All patients should receive a complete oral exam annually and more often if signs and symptoms are present. Assess symptoms suggestive of oral problems. Examine: Face and lips, Teeth, gums, and dentures, including level of hygiene, Mucosal surfaces and saliva, including soft and hard palate, Lateral borders and undersurface of the tongue, Posterior pharynx. Palpate: Neck, Temporomandibular joint, Floor of the mouth. Identify abnormal lesions. Offer anticipatory advice
Immediate attention
Conditions requiring _____: bleeding, avulsed tooth, swelling
Non-immediate attention
Conditions requiring ______: swollen or bleeding gums, mouth sores (aphthous ulcers, decay (cavities) on tooth surfaces, enlarged “overgrown” gums, oral candidiasis (yeast infections, “hairy” tongue, fistula or “gum boil”, broken tooth, discoloration
hairy tongue
when small elevated pads on the surface of the tongue have become long and may be colored black, white or brown due to bacteria growing on the surface of the tongue. May occur in people who: Breath through their mouths. Have poor oral hygiene. Take many medicines. It can be prevented by use of tongue scraper.
Fistula
(“Gum boil”) is a pimple-like opening on the gums near a swelling of the gums above or below the teeth. This occurs with chronic, long-term untreated tooth infections. It usually does not cause pain but may drain pus and leave a bad taste in the person’s mouth.
recent
Tooth discoloration from a ____ injury may appear pinkish or reddish due to bleeding inside the tooth.
Older
Tooth discoloration from a _____ injury may appear more as gray or brown in color due to the breakdown of blood in the tooth, much as a bruise on the skin appears black and blue.
unmet health need
Oral diseases, which range from cavities to oral cancer, cause pain and disability for millions of Americans each year. According to the Surgeon General's Report on oral health in 2000: Dental care is the most common _______. Oral disease can severely affect systemic health. Much oral disease is preventable or at least controllable. Profound disparities in oral health and access to care exist for all ages.
2.5
Dental Caries is the most common chronic disease of childhood yet children are _____ times more likely to lack dental coverage than medical coverage. Severe gum disease affects approximately 20% of the adult population ages 5 to 44. There are approximately 30,000 oral cancers diagnosed annually resulting in 8000 deaths a year, oftentimes due to late diagnosis.
tooth decay
_____ is the most prevalent chronic disease that is not self-limiting or amenable to short term course of antibiotics, experienced by children in the United States. This occurs in spite of the fact that dental caries are, for the most part, preventable
40
Children that have dental pain are unable to function in school. Almost 52 million school hours are missed annually by children because of oral problems. This is roughly 850,000 school days missed a year. ____0% of the children are affected by the time they enter kindergarten.
75 - 80
_____% of the most severe caries occur in only 20%- 25% of the children. These are often found in the lower socioeconomic groups and the caries commonly develop early in life, often at less than 2 years of age. Although a much greater percent of children with decay are found in those of lower socioeconomic and minority groups, do not take for granted those at higher socio economic groups. Parents do not want to upset child, use milk or bottle as a pacifier, boxes of juice, working parents, …
4 - 5 million
In the United States, between 4-5 million children suffer dental disease bad enough that they have functional impairments from dental pain, such as: not sleeping well, not eating well, chronic pain, problems concentrating on homework, Problems getting along with other people, and Poor self esteem. A lot of times the child may be called “cranky” “picky eater” or even being worked up for failure to thrive, when all along the problem may stem from being in pain and unable to eat due to poor oral health.