Klebsiella
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
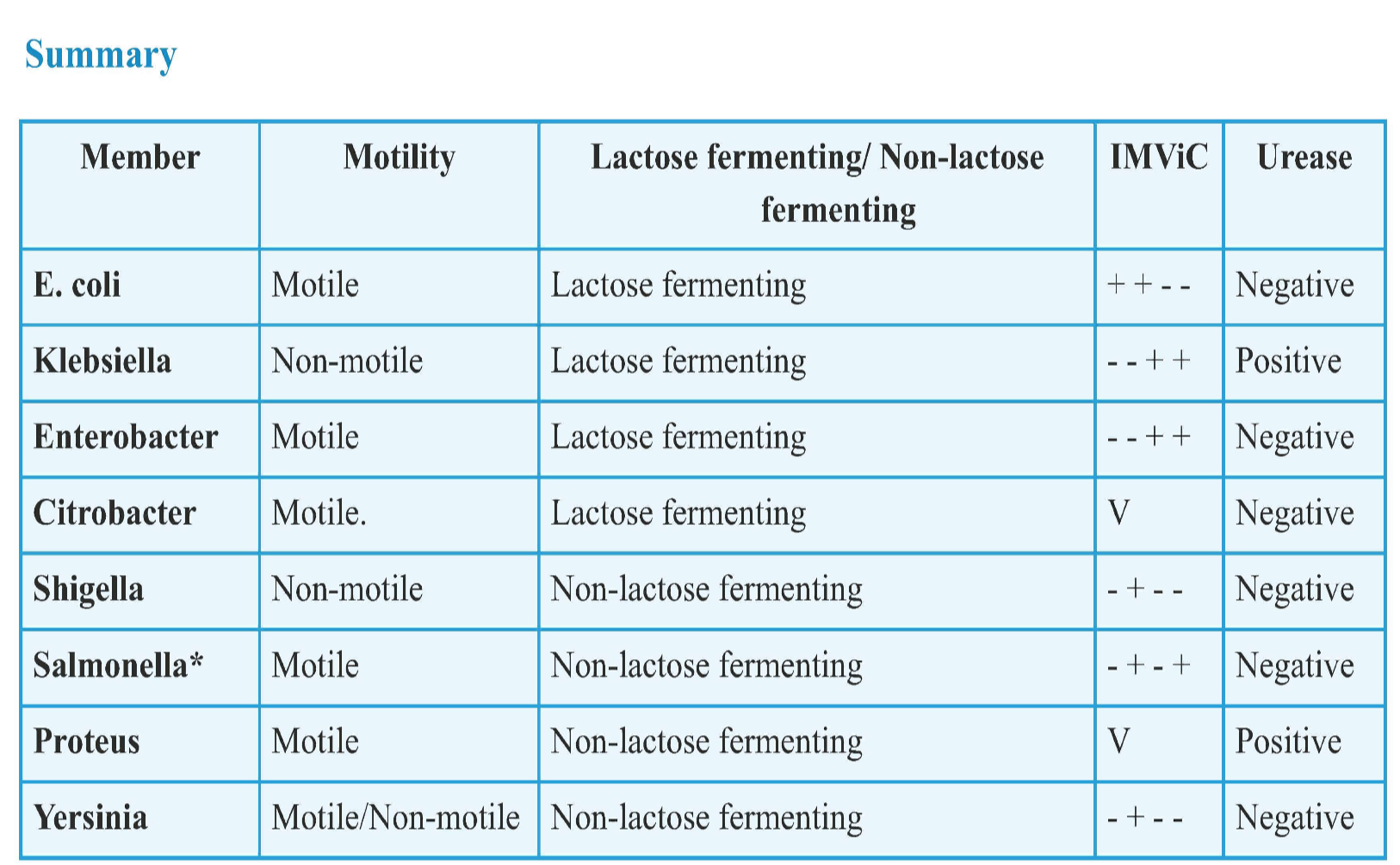
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Tribe Klebsiella
Klebsiella
• Serratia
• Enterobacter cloaca
• Hafnia alvei
• Pantoea agglomerans
Types
K. pneumoniae or Friedlander's bacillus
• Pneumonia (CAP, HAP, VAP)
• Red currant jelly
K. ozaenae
• Ozaenae/ Atrophic rhinitis:
• Foul-smelling discharge
• Anosmia
K. rhinoscleromatis
• Rhinoscleroma (woody nose/hebra nose)
K. granulomatis
• Painless genital ulcers.
• Also known as Donovanosis/Granuloma Inguinale (Donovan bodies).
Klebsiella Pneumonia
Community-acquired, Hospital-acquired or Ventilator-acquired Pneumonia.
• Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) → Superadded infection.
• Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI).
• Septicemia
Important Information
Recent strain → Hyper-viscous, Hyper-virulent strain of K. Pneumoniae.
• Causes community-acquired pneumonia, meningitis and sepsis.
• Resistant to treatment.
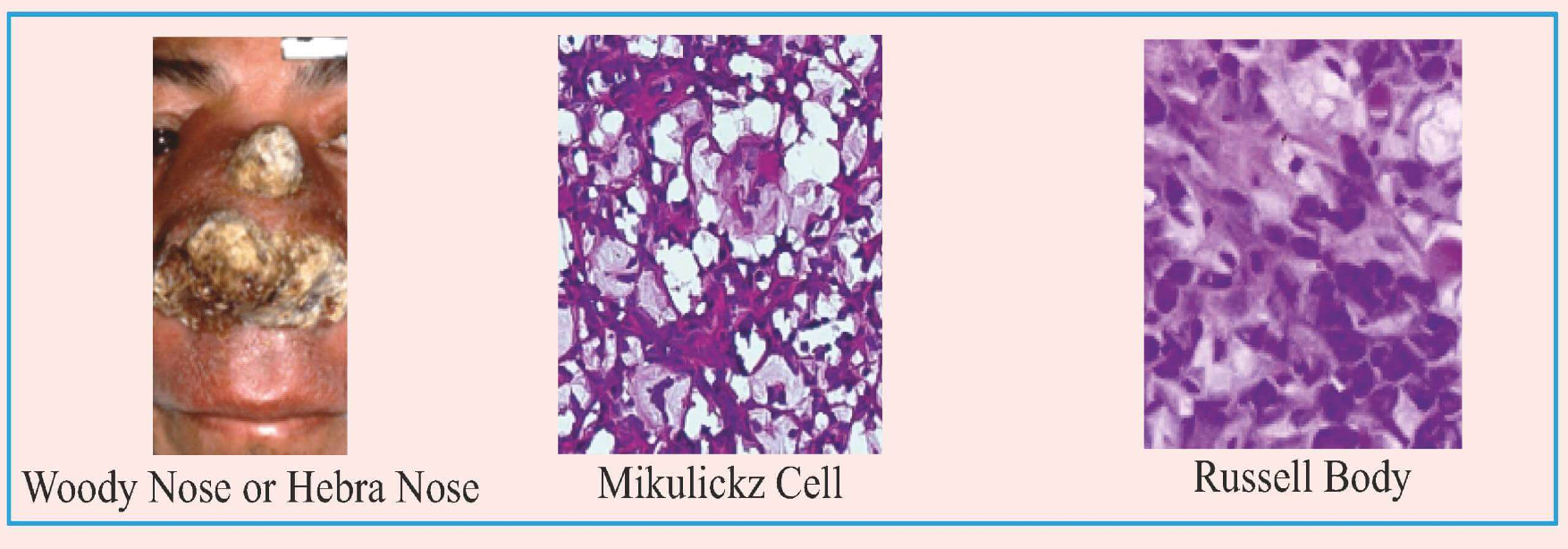
Rhinoscleroma
Gross findings
• Woody nose or hebra nose
• Microscopic findings
• Mikulickz cell → Foamy cell
• Russell body → Immunoglobulin production
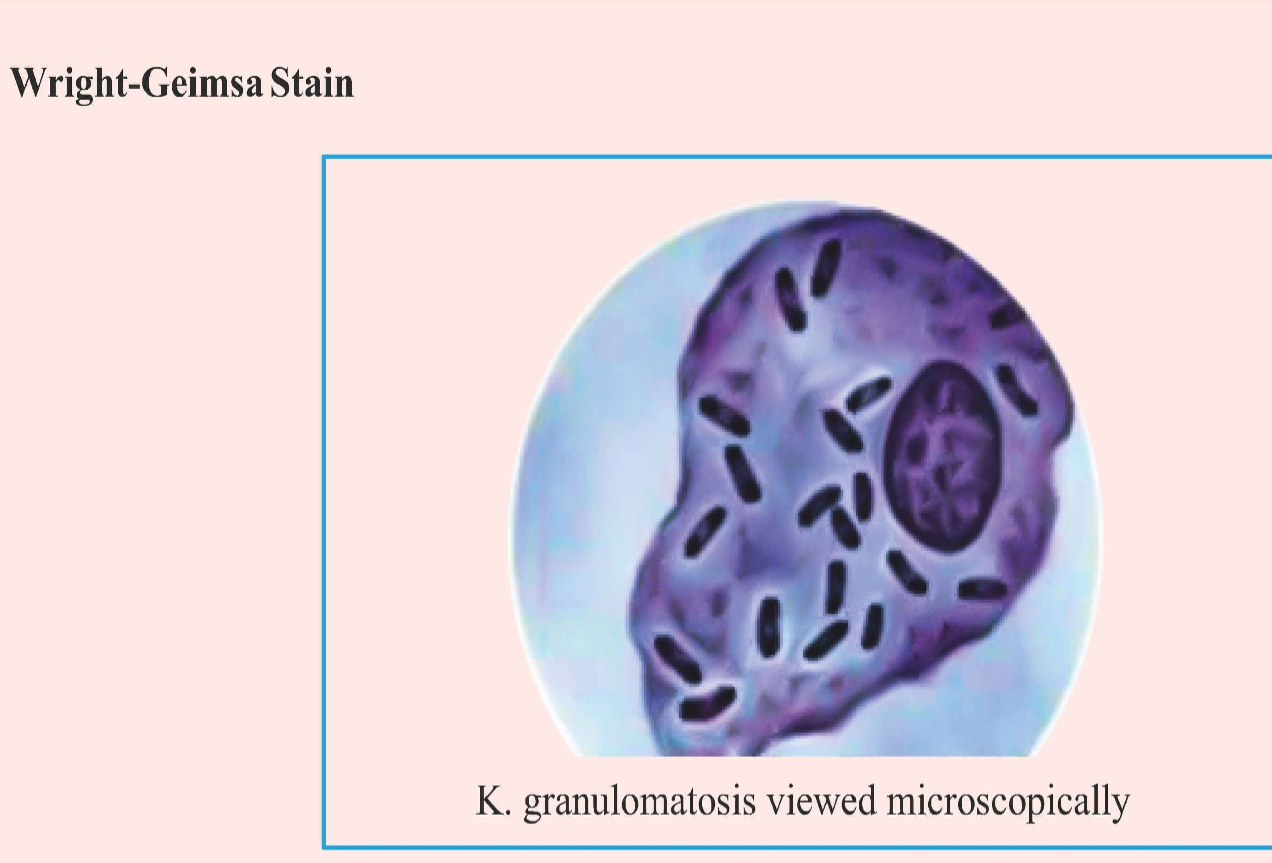
Wright- Geimsa stain
Donovan bodies - Pund cells (Mononuclear cells).
• Safety pin appearance of Donovanosis.
• Bipolar staining
Urease Positive Organisms
(Mnemonic Punch Kiss)
• Proteus
• Ureaplasma
• Nocardia
• Cryptococcus
• Helicobacter
• Staphylococcus Saprophyticus
• Staphylococcus Epidermidis
Klebsiella Pneumoniae
Morphology
Non-motile rod
• Mucopolysaccharide capsule seen as a halo around the organism.

Diagnosis & Treatment
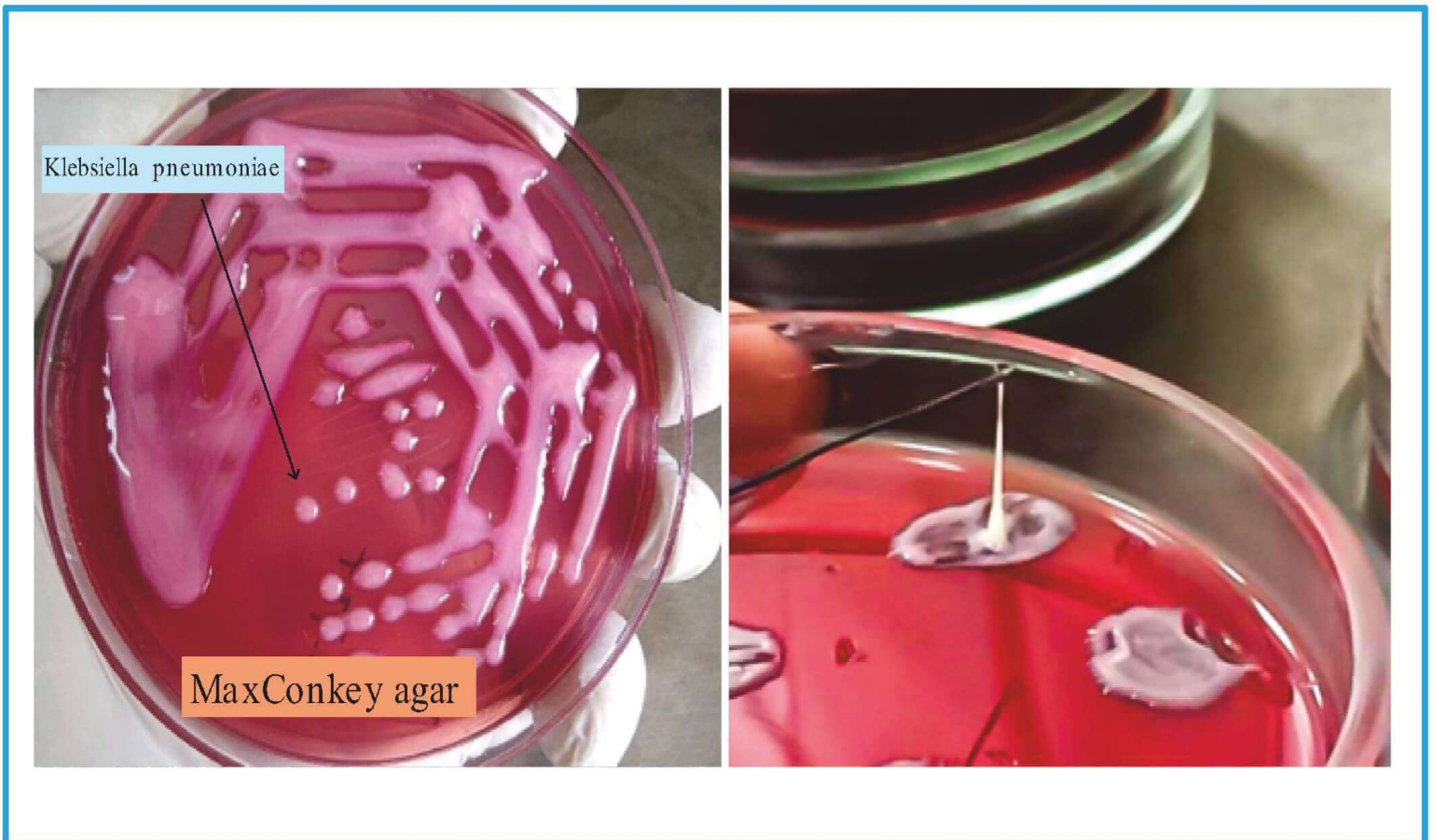
MacConkey Agar:
Positive lactose fermenter.
Pink color after fermentation.
• Pink color also seen in E. coli.
• Capsule presence in K. pneumoniae can be used to differentiate it from E. coli.
Mucoid colony
String test positivity
Biochemical Tests
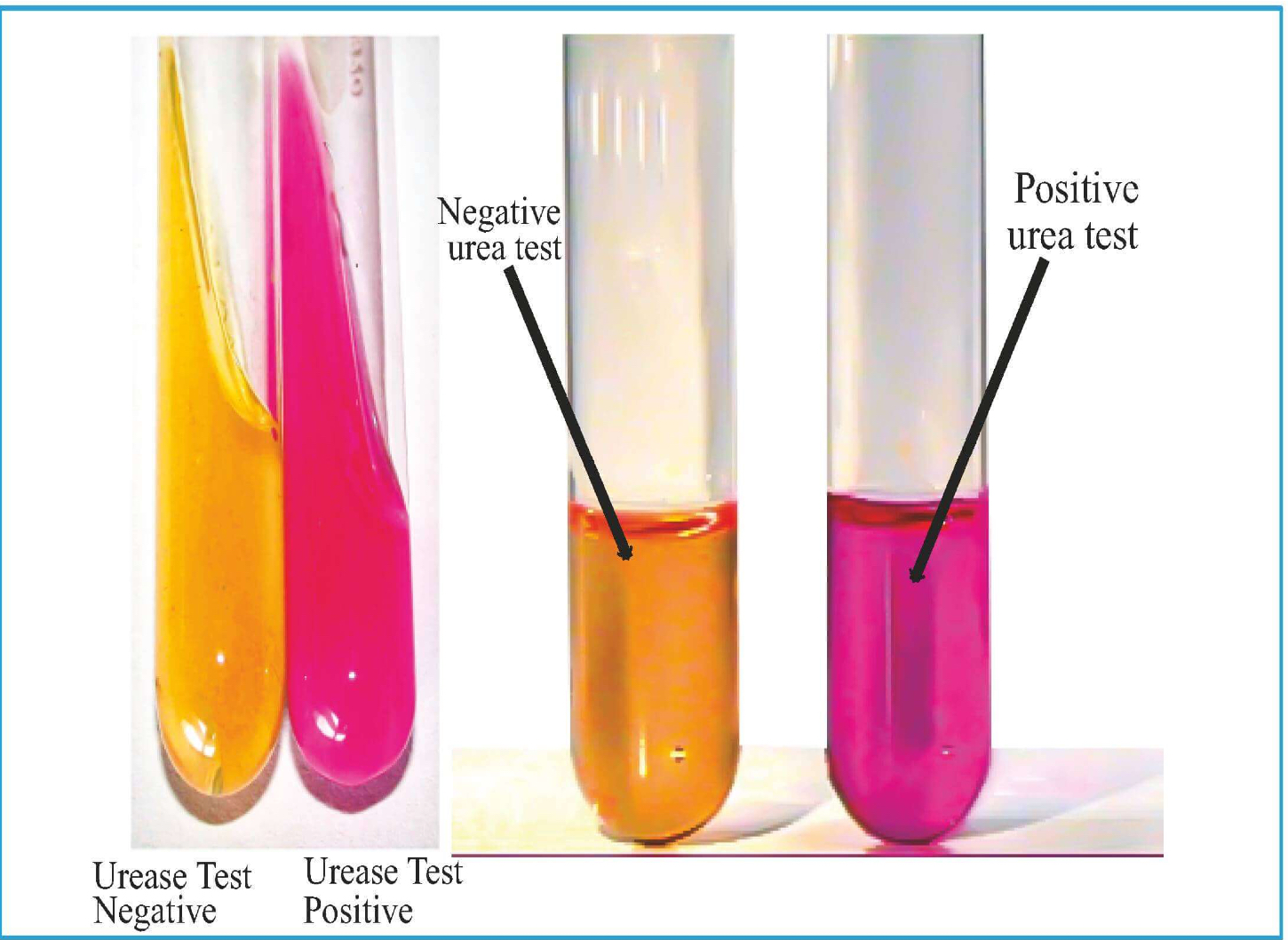
• Urease positivity: Pink color
• IMVIC testing →--++
• Ferments all sugars with production of acid and gas.
Treatment
• Piperacillin + Tazobactam.
• Extensively drug-resistant (XDR) strains → Colistin or Polymyxin (Very expensive).
• Depends on Antibiotic Sensitivity Test
Tribe proteeae
PPA reaction: Phenylalanine acted on by phenylalanine deaminase to produce PPA.
Phenylalanine →→→(PhenylalanineDeaminase)→→→ Phenyl pyruvic acid
Proteus
• Urease positive
• Phenyl Pyruvic Acid (PPA) positive
Providencia
• Urease negative
• PPA positive
Morganella
• Urease positive
• PPA positive
Proteus
Pleomorphic bacillus → Any shape
• Gram negative bacilli
• Non-capsulated
• Fishy odour
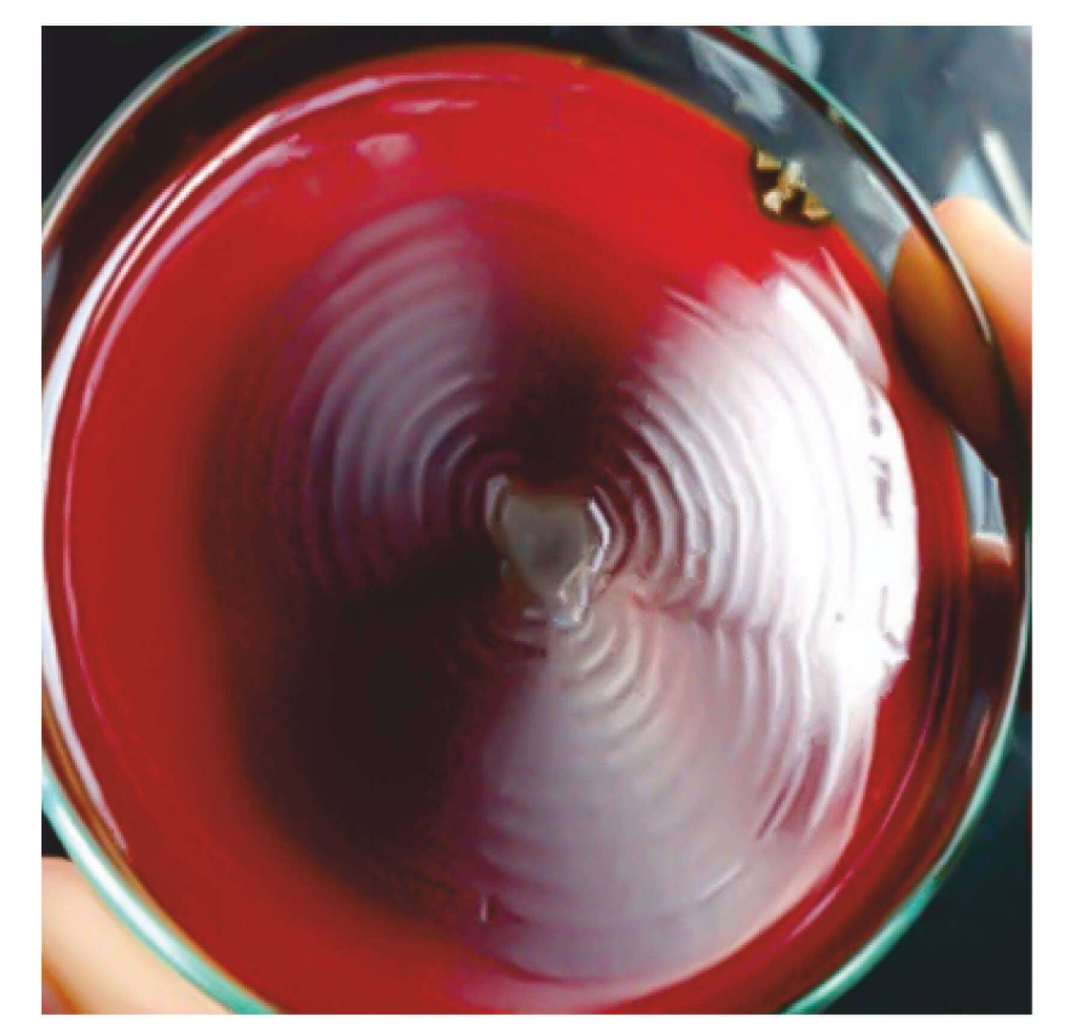

Swarming Growth or Motility
Concentric growth
Seen in:
• Proteus
• Vibrio Parahaemolyticus
• Vibrio Alginolyticus
• Clostridium Tetani
• Bacillus Cereus
• Serratia
Inhibited by:
• Firm agar (5-6% agar) (Normal concentration of agar is 2%).
• Chemicals e.g. boric acid and chloral hydrate.
• MacConkey agar due to taurocholate bile acid present.
Epidemiological typing
• To determine strains in different patients.
• Same strains: Merging of swarming.
• Different strains: Line of demarcation.
• Known as Diene's Phenomenon.
• Should not be confused with Diene stain done for Mycoplasma.
Use & Treatment for proteus
Uses of Proteus
• Non-motile strains especially Proteus mirabilis: OX 2, 0X 19, 0X K strains used in the Weil-Felix test for rickettsia.
Treatment
• Highly resistant bacteria.
• Antibiotic sensitivity testing required.
• P. Mirabilis → Ampicillin and Cephalosporin sensitive.
Salmonella
Salmonella Two types:
• Typhoidal
• Non-typhoidal
Kaufmann and White Scheme
• Used to classify salmonella.
A - S. Paratyphyi A.
B
S. Paratyphyi B.
S. Typhimurium.
C1 - S. Paratyphyi C.
C2 - S. Muenchen.
D -
S. Typhyi.
S. Enteritidis.
E2 - S. Anatum.
Antigens
O (Somatic)
• Complex made up of Polysaccharide, Protein and Lipid.
• Boivin Antigen (Extracted from cell by Trichloroacetic Acid).
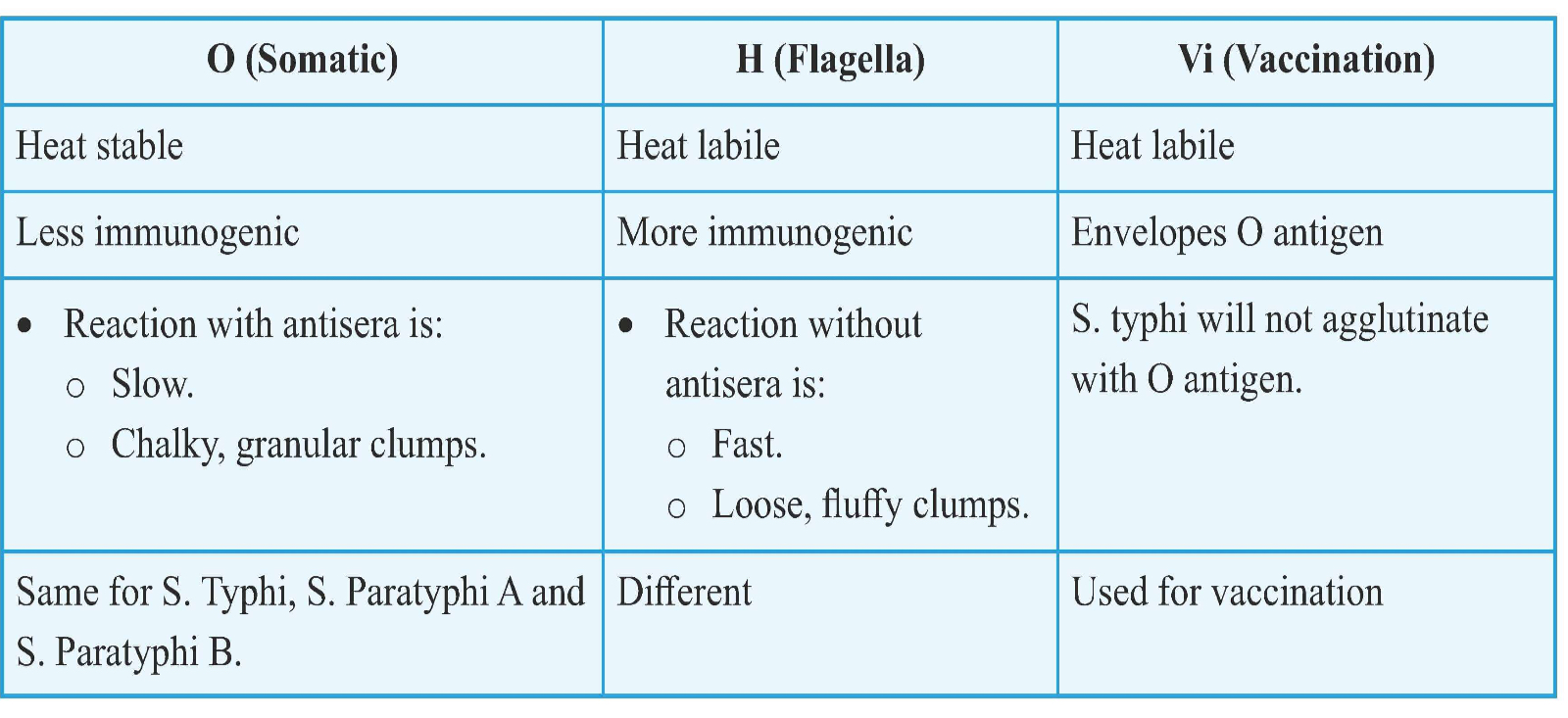
Antigenic Variation
Loss of H antigen - Loss of flagella
Loss of Vi antigen
• V antigen (agglutinable with Vi antiserum) changes to W antigen.
• Intermediate forms (VW).
Loss of O antigen
• Smooth to rough variation of cell wall.
• Loss of virulence.
New tests
These are card based tests.
Typhidot: IgM/IgG against outer membrane proteins.
Dot blot: IgG against flagellar membrane proteins antigen.

Culture
Enrichment Media
• Selenite F broth
• Tetrathionate B broth
Selective Media
• Xylose lysine deoxycholate (XLD).
• Deoxycholate agar (DCA).
• Salmonella-shigella agar (SS).
• Hektoen enteri agar (HE).
Biochemical Tests
• IMViC-+=+
Bacteriophage Typing
• S. Typhi phage A, E1.
• S. Paratyphi type 1 and 2.
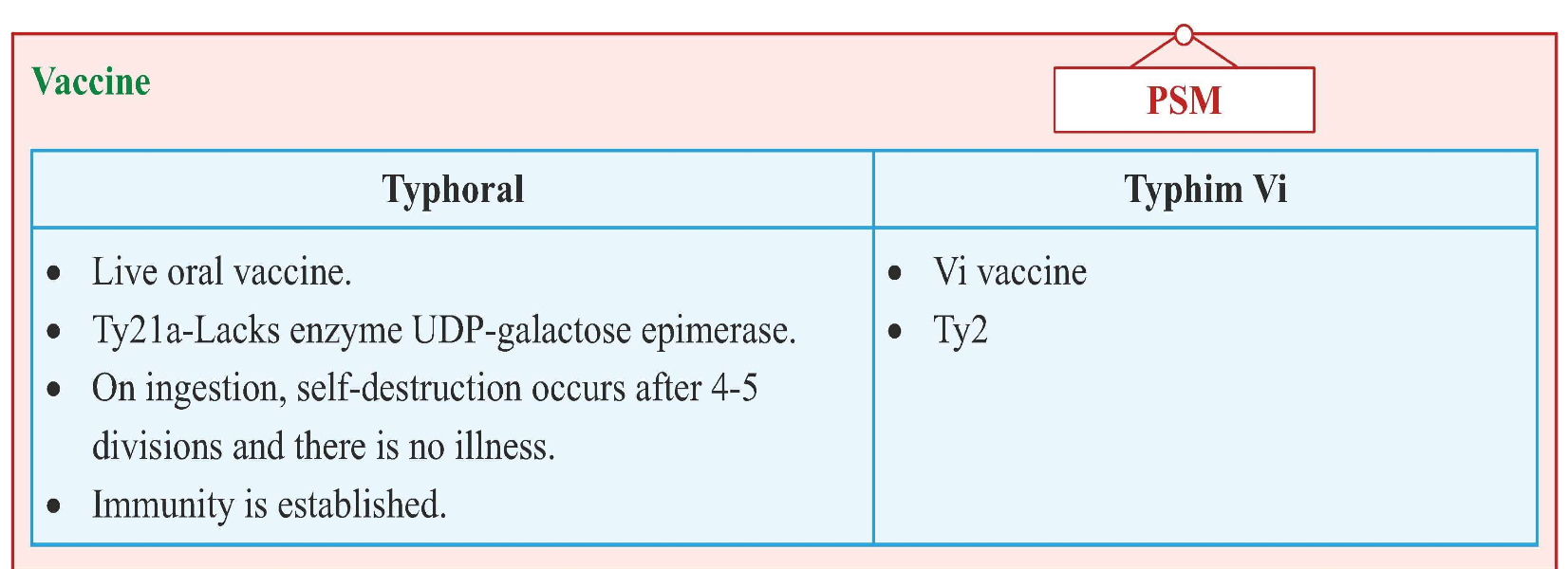
Salmonella Gastroenteritis
• Non-typhoidal salmonella.
• Most common cause:
• S. Typhimurium > S. Enteritidis.
• Source: Food e.g. meat and milk.
• Incubation period: < 24 hours.
Clinical Features
• Fever
• Vomiting
• Invasive diarrhoea
Treatment
• Usually supportive.
Salmonella septicemia
Caused by S. Choleraesuis.
Clinical features
• Endocarditis
• Pneumonia
• Osteomyelitis
Fatality rate of 25%
Important Information
• Salmonella has non motile members
• S. Gallinarum
• S. Pullorum