Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis (10/23-10/25)
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Recommended: Learn mode but only with Flashcards
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
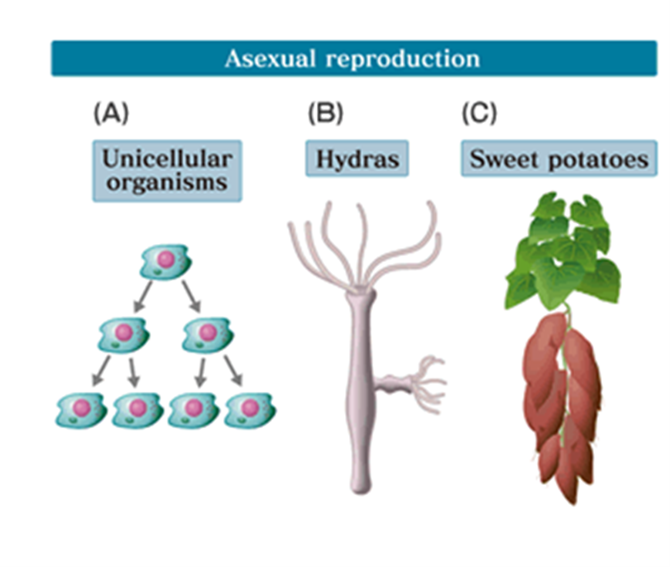
Asexual Reproduction (Hint: 3)
Single individual passes on all of its genes to its progeny
Progeny are genetically identical to the parent- a clone
Genetic differences rarely occur
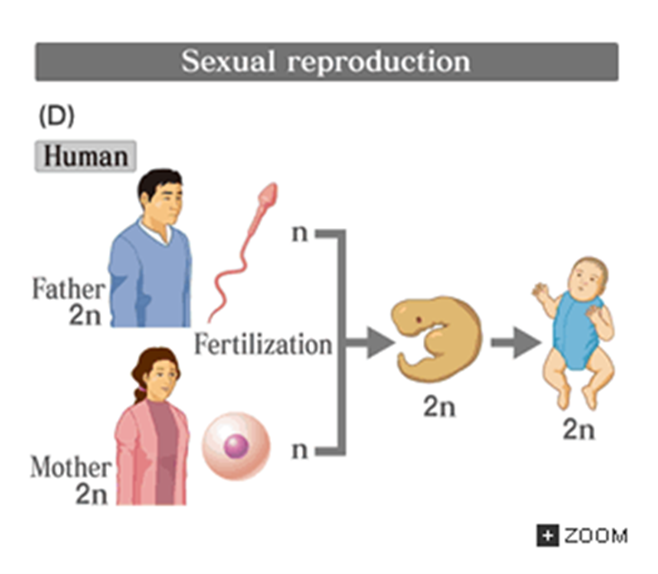
Sexual Reproduction (Hint: 4)
2 parents give rise to progeny
Each passes on half of its DNA
Progeny have a unique combination of DNA
Greater genetic variation in the resulting population
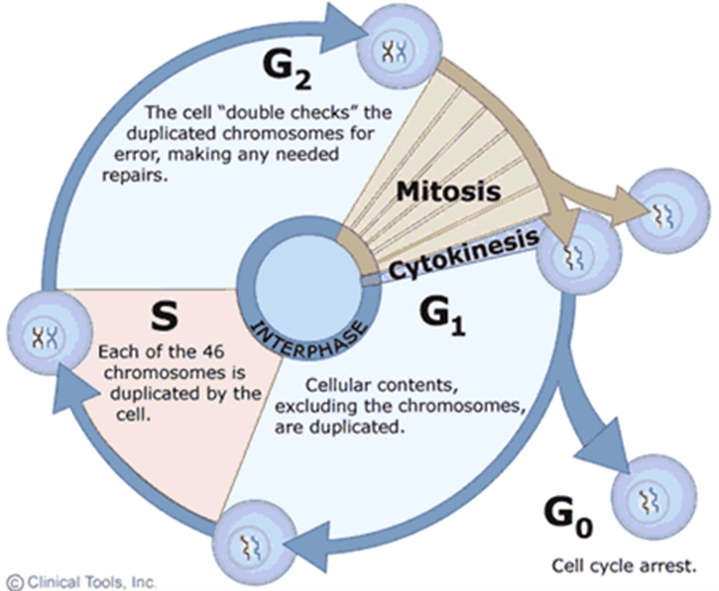
The Cell Cycle (Hint: 2)
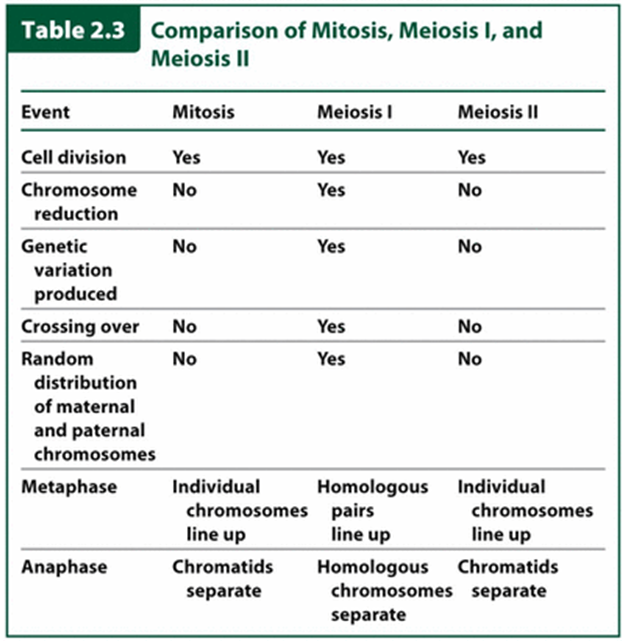
The process by which cells replicate their chromosomes and separate them into 2 new cells
The resulting cells contain the same genetic material as the original
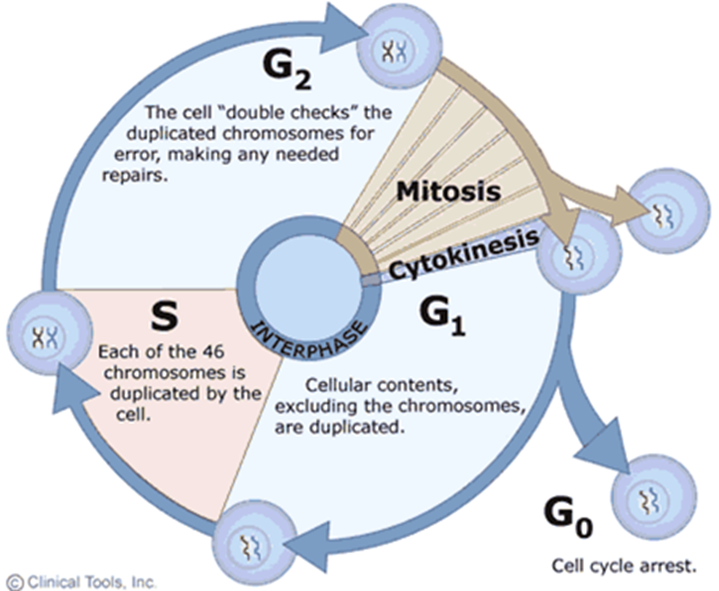
Interphase (Hint: 2)
What happens before mitosis
G1, G0, S, and G2
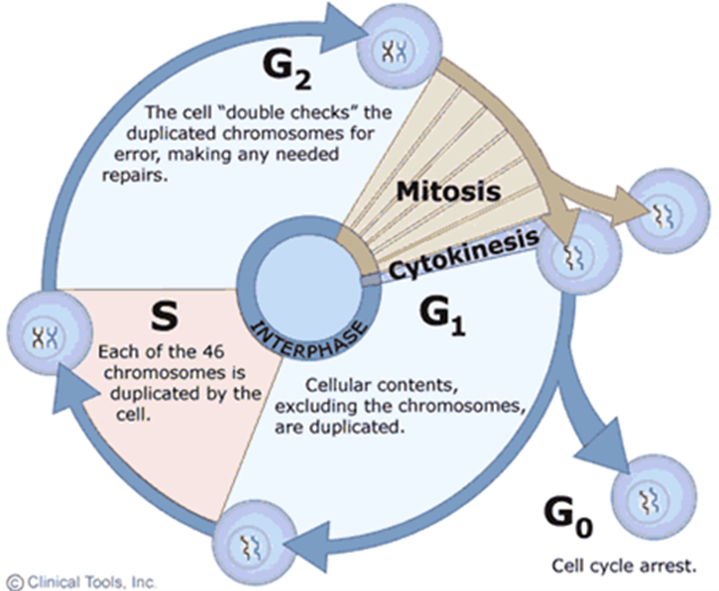
G1 Phase (Hint: 2)
Gap (growth) phase
Normal cellular function/preparation for S
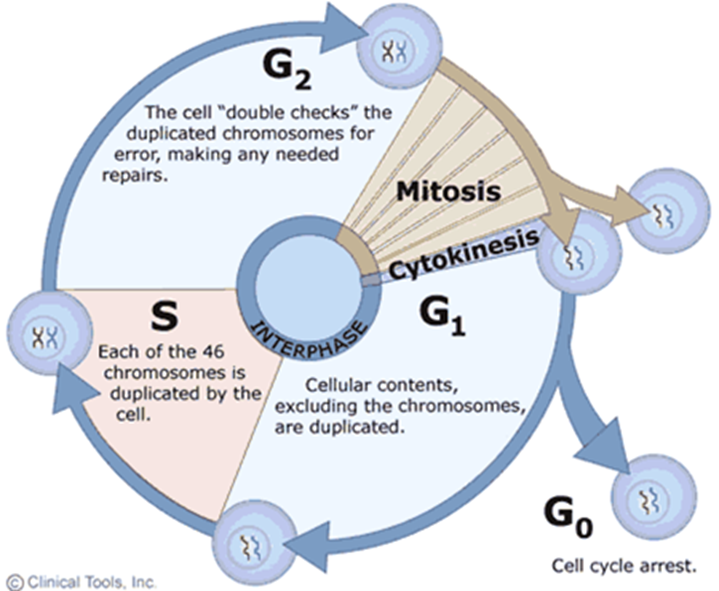
S Phase (Hint: 3)
Synthesis
DNA replication
Always go through, regardless of type (aka mitosis vs. meiosis)
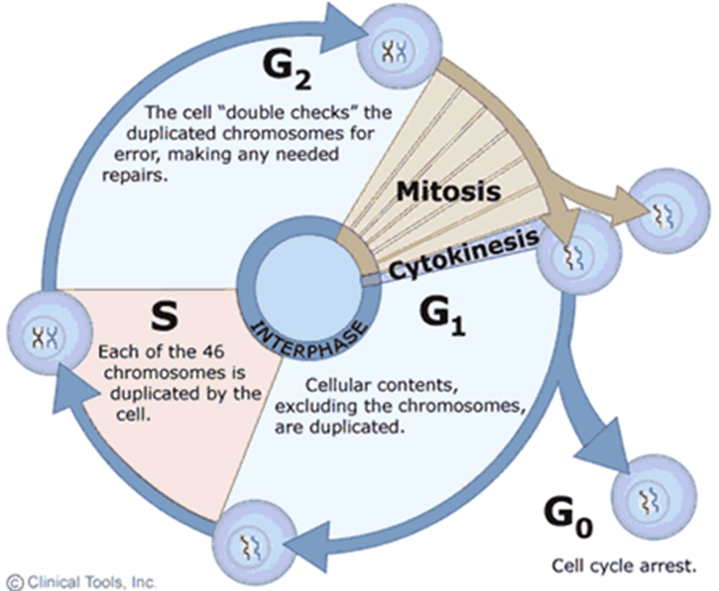
G2 Phase (Hint: 2)
Gap (growth) phase
Preparation for M
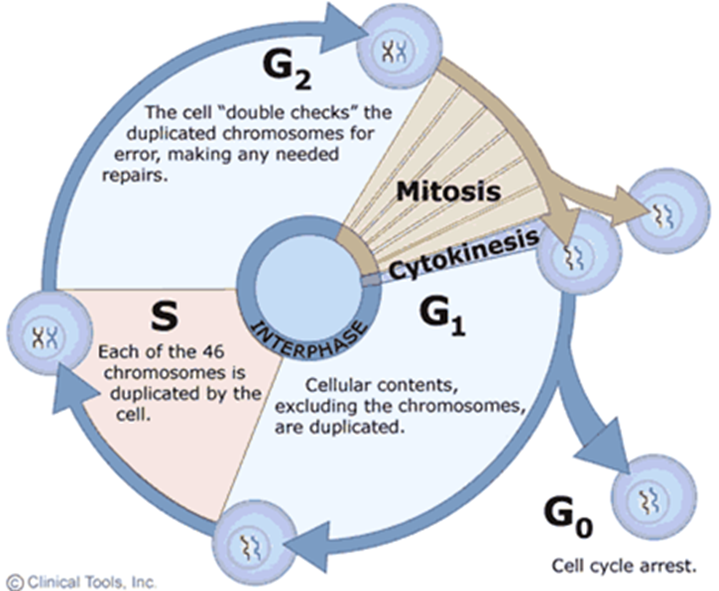
Mitosis/M-Phase (Hint: 2)
Division of the nucleus
Cytokinesis
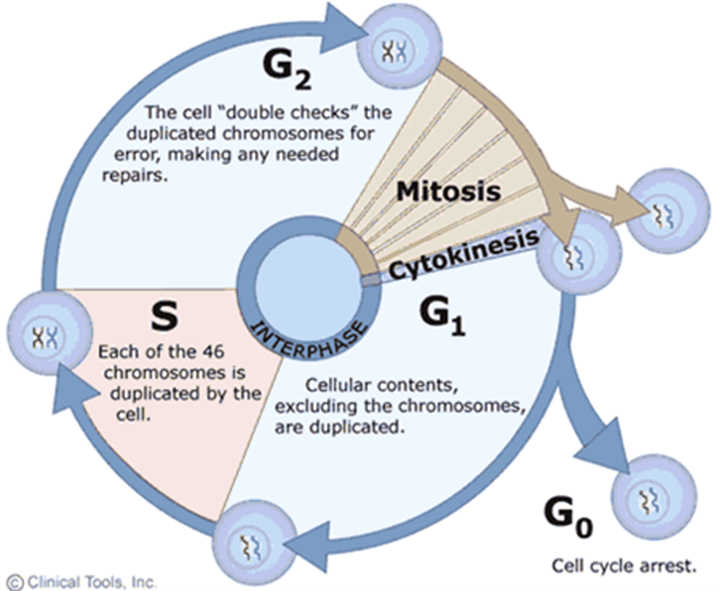
Cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm
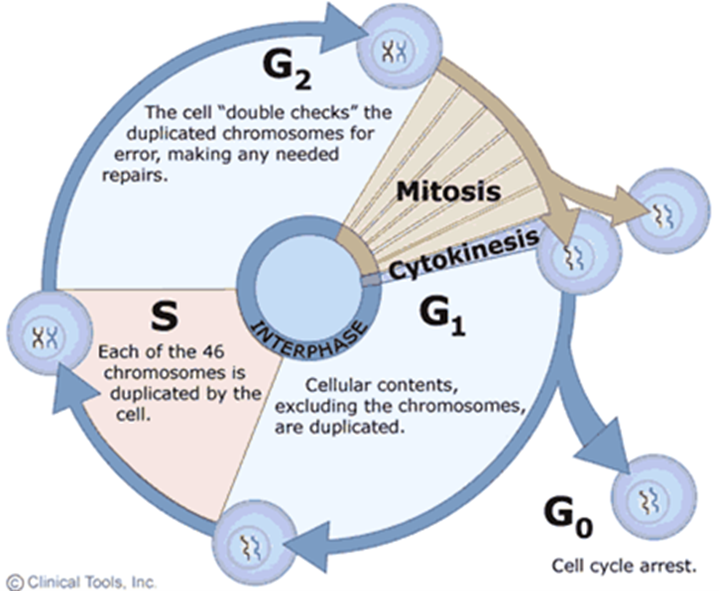
G0 Phase (Hint: 2)
Cell cycle exit (arrest)
Cells go about normal function without dividing
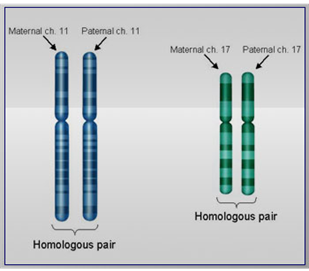
Homologous Chromosomes (Hint: 2)
A pair of the same chromosome
Eukaryotic cells generally contain a pair of each chromosome (one maternal and one paternal)
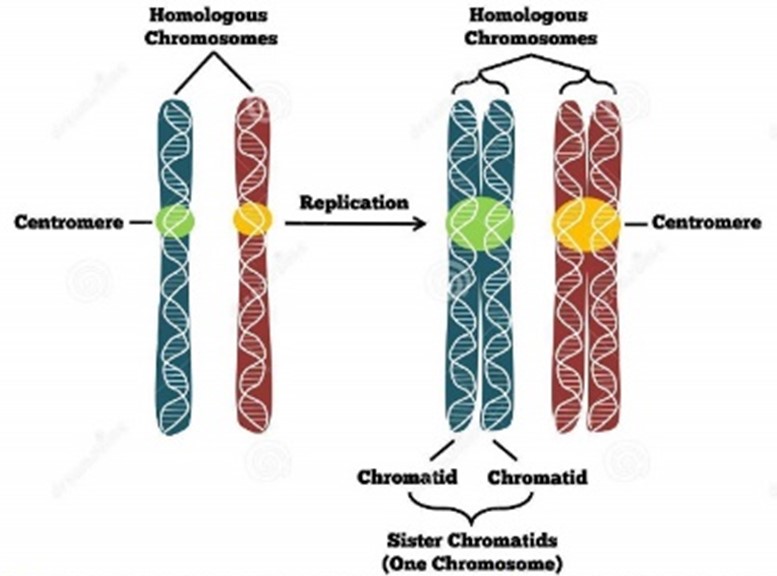
Monad
1 DNA molecule and 1 Chromosome
Dyad
2 Sister chromatids, 2 DNA molecules, and 1 Chromosome
Sister Chromatids
Identical copies of a chromosome that are joined together by a centromere and are formed during DNA replication
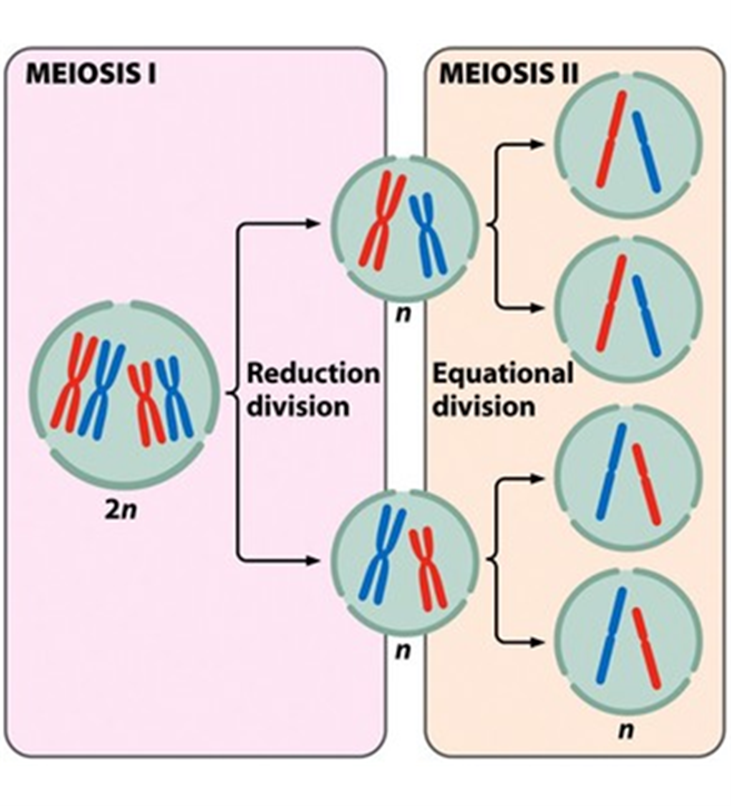
Meiosis (Hint: 4)
A form of cell division that produces the haploid gametes
Start with a diploid cell
Involves 2 cell divisions
Known as reductive division
Gametes (Hint: 2)
Sex cells
Sperm and egg
Haploid (Hint: 3)
n
Carry 1 set of chromosomes
Humans: 23 chromosomes
Diploid (Hint: 4)
2n
Carry 2 sets of chromosomes
1 maternal/1 paternal
Humans: 46 chromosomes
Meiosis I (Hint: 2)
Homologous chromosomes are separated into 2 new cells
Reductive division, but still dyad
Meiosis II (Hint: 2)
Sister chromatids are separated into 4 new cells
Very similar to mitosis (separate dyad)
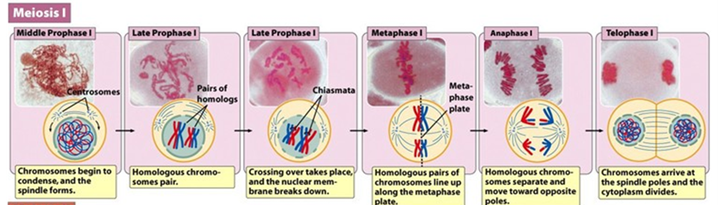
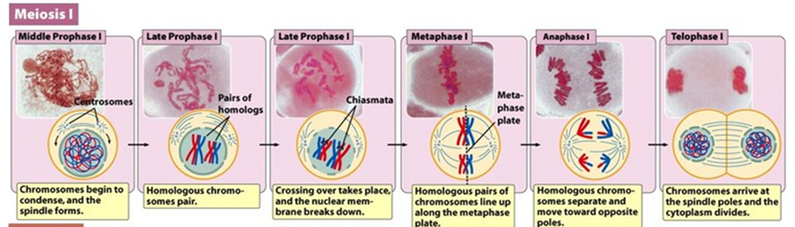
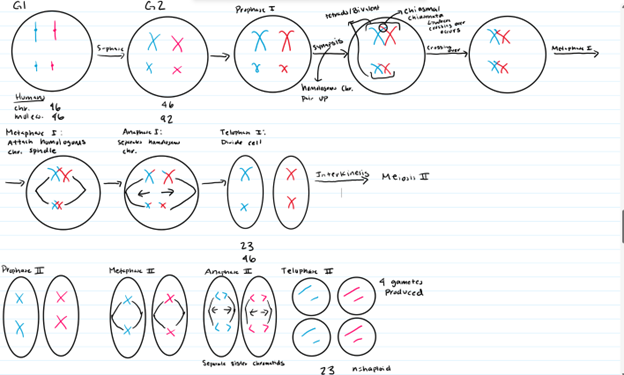
Prophase I
Chromosomes condense and nuclear envelope disintegrates
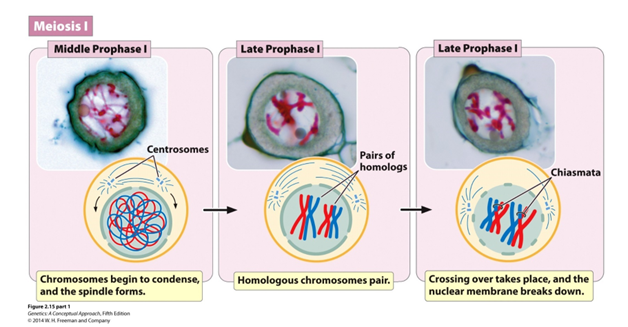
Synapsis (Hint: 4)
Homologous chromosomes pair with each other
Unique (only happens here)
Paternal and maternal chromosomes pair up
Called a bivalent or tetrad
Crossing Over (Hint: 4)
Occurs late in prophase I
Only happens here
Forms a structure called the chiasmata
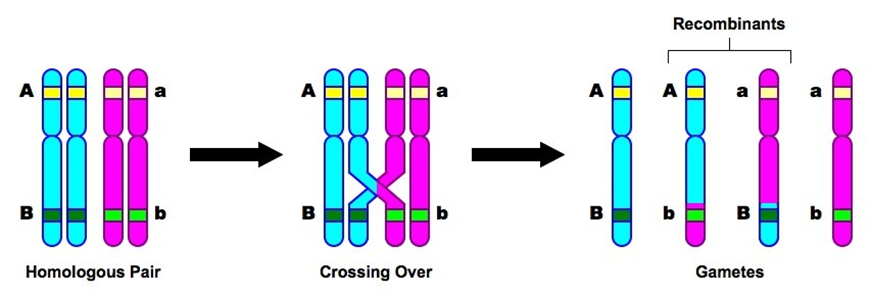
Chiasmata (Hint: 2)
Specialized chromatin structures that link homologous chromosomes together until anaphase
Where crossing over occurs
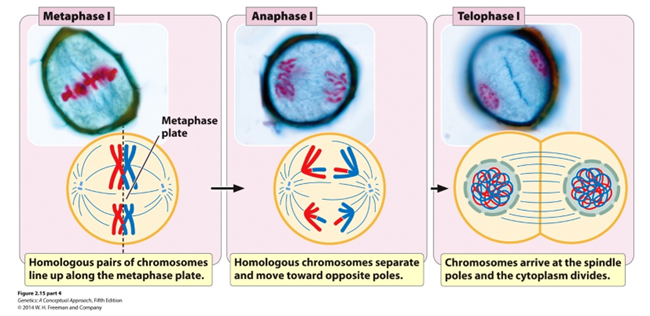
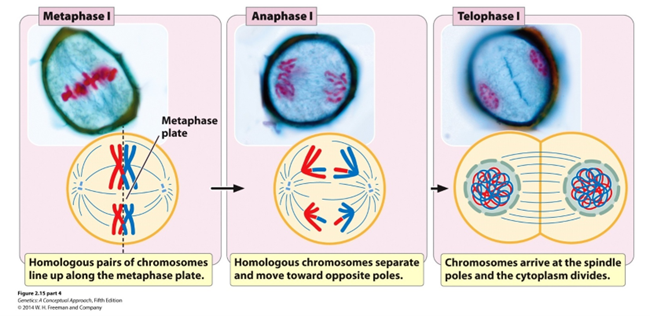
Metaphase I (Hint: 2)
Homologous chromosomes line up on metaphase plate
Homologous chromosomes attach to meiotic spindle
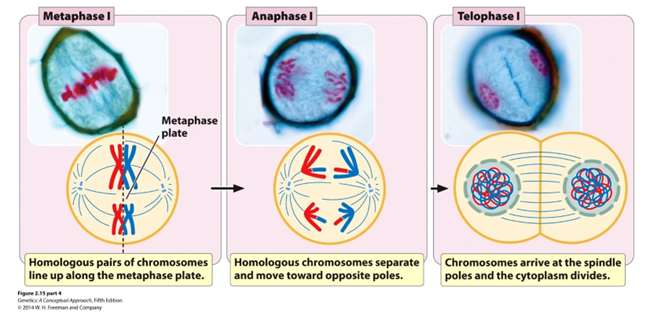
Meiotic Spindle
A microtubule-based structure that separates chromosomes during meisosis
Cohesin In Mitosis (Hint: 3)
Holds the sister chromatids together
Cleaved by separase at anaphase
Allows chromatids to separate
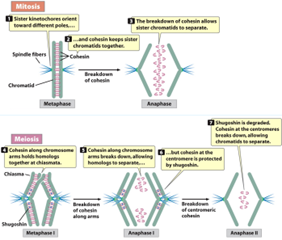
Cohesin in Meiosis (Hint: 3)
Cohesins on the arms hold homologs together at the chiasmata
Protected by shugoshin (not cleaved by separase)
By Meiosis II, shugoshin destroyed and separase cuts cohesins and separates sister chromatids
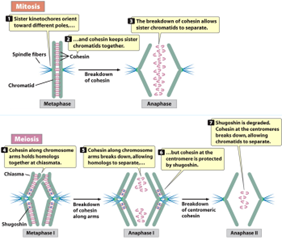
Anaphase I
Homologous chromosomes are separated
Separase
Cuts cohesion and allows the sister chromatids to separate
Shugoshin (Hint: 2)
Protects the cohesins at the centromere during anaphase I
Degraded in anaphase II and separase can cleave the cohesins and the sister chromatids separate
Telophase I (Hint: 3)
Cell divides to form 2 cells and nuclei reform
Number of chromosomes per cell = 23 (humans)
Number of DNA molecules per cell = 46 (humans)
Interkinesis
The period between meiosis I and meiosis II
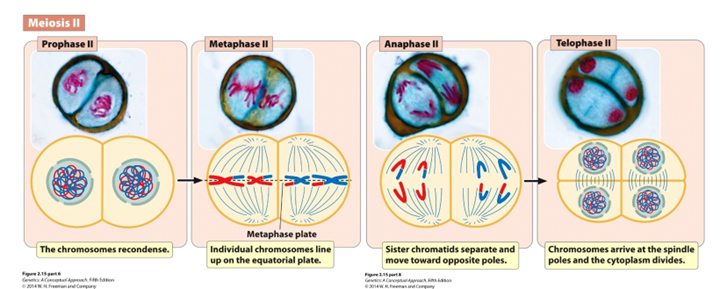
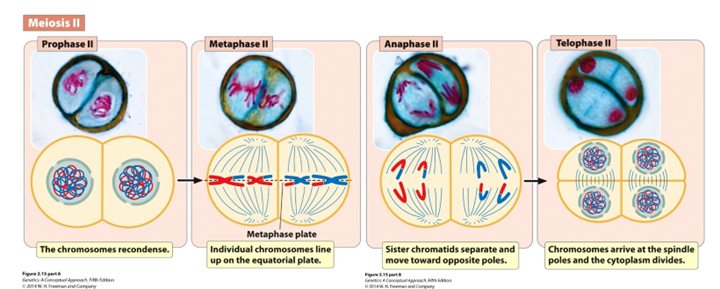
Prophase II
Chromosomes condense and nuclear envelope disintegrates
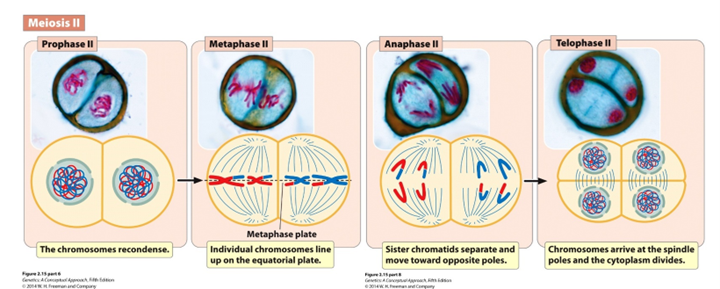
Metaphase II
Individual chromosomes line up on the equatorial plane
Equatorial Plane
The imaginary plane that runs directly through the center of a dividing cell, where all the chromosomes line up during the metaphase stage of mitosis or meiosis
Anaphase II
Sister chromatids separate and are pulled to the poles
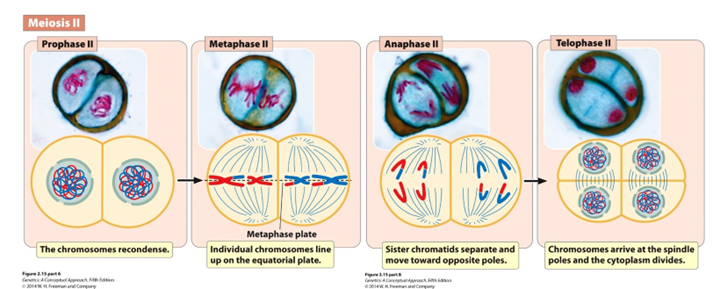
Telophase II (Hint: 3)
Cells divide to form 4 haploid gametes
Number of chromosomes per cell = 23 (human)
Number of DNA molecules per cell = 23 (human)
Recombination (Hint: 2)
How crossing over happens
The process that makes 2 chromatids from a bivalent pair swap portions of DNA
Random Separation of Homologous Chromosomes (Hint: 4)
2haploid number of chromosomes
During meiosis I the homologous pairs of chromosomes line up randomly and are separated
The sister chromatids are separated in meiosis II
The resulting gametes will have a random assortment of chromosomes
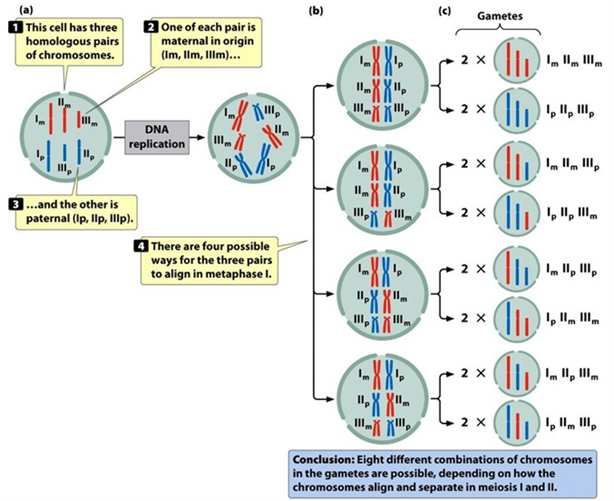
Independent Assortment
A genetic principle that describes how genes separate independently during the development of reproductive cells
Gametogenesis
Production of the haploid gametes
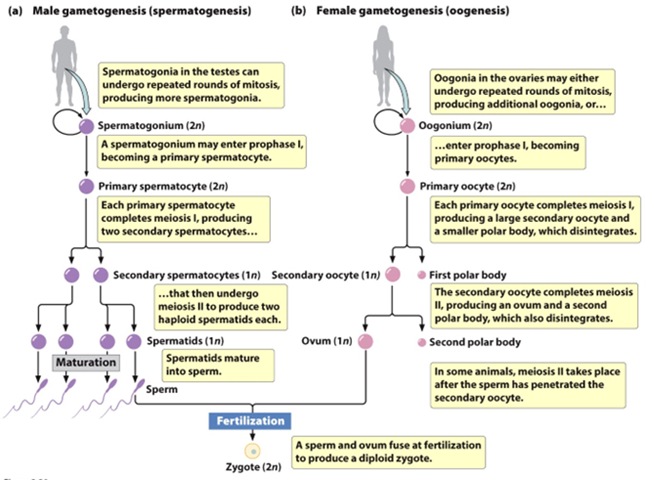
Fertilization
Fusion of the sperm and egg to form a diploid zygote
Zygote
A fertilized egg cell that contains the genetic information for a new individual organism
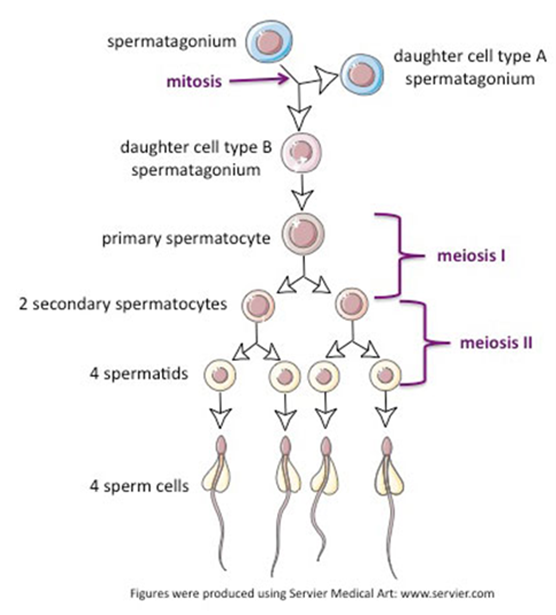
Spermatogenesis (Hint: 2)
The generation of sperm cells
Occurs in the testes
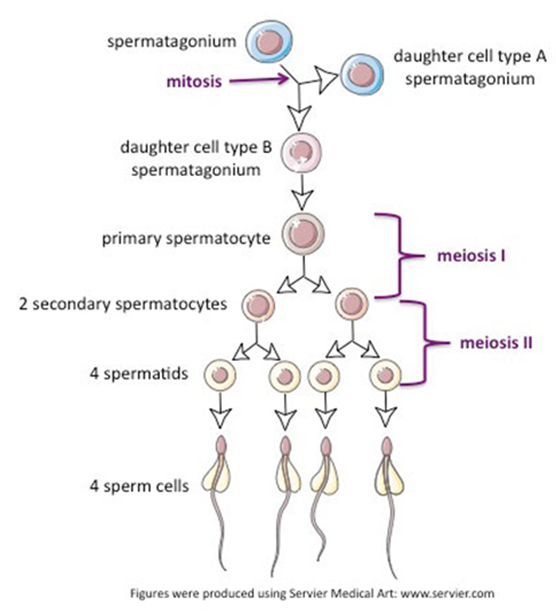
Spermatogonium (Hint: 2)
Starting cell
Can produce more spermatogonia by mitosis
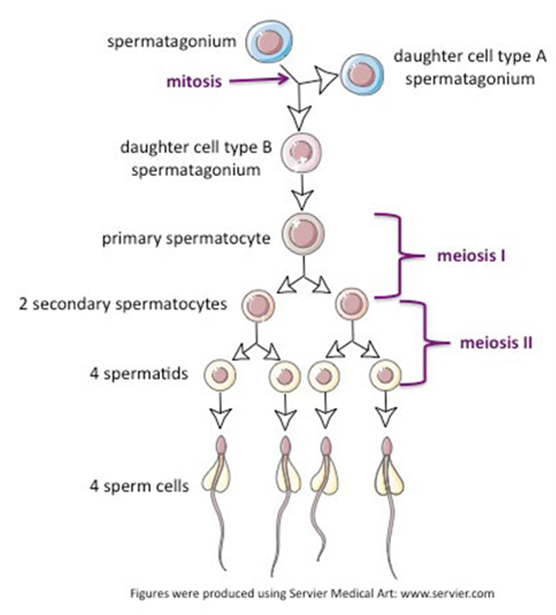
Primary Spermatocyte
Enters meiosis I
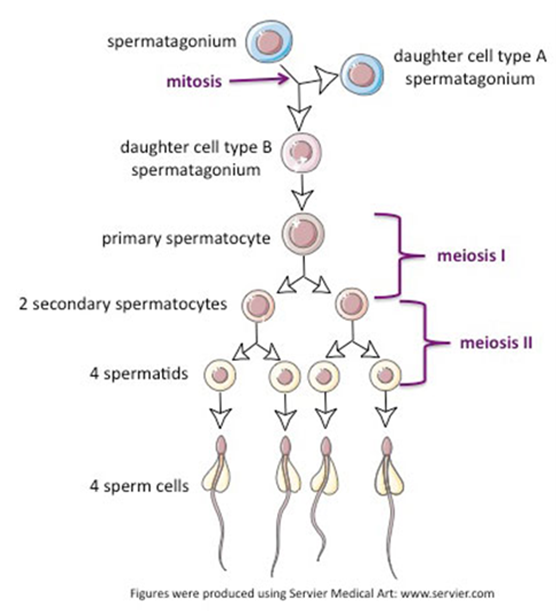
Secondary spermatocyte
After meiosis I
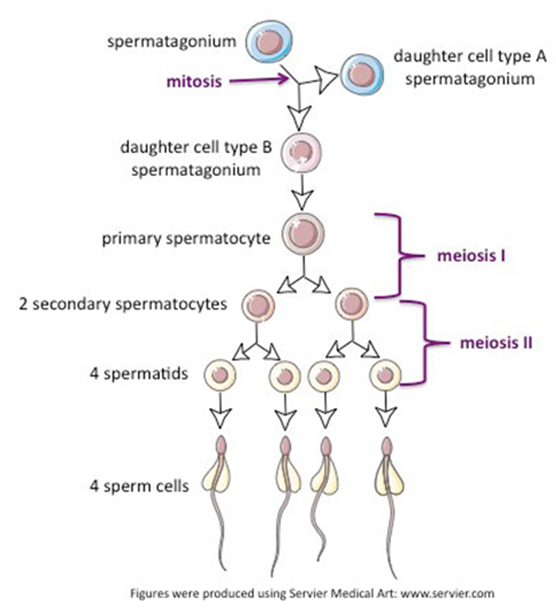
Mature sperm cells
Developed from spermatids
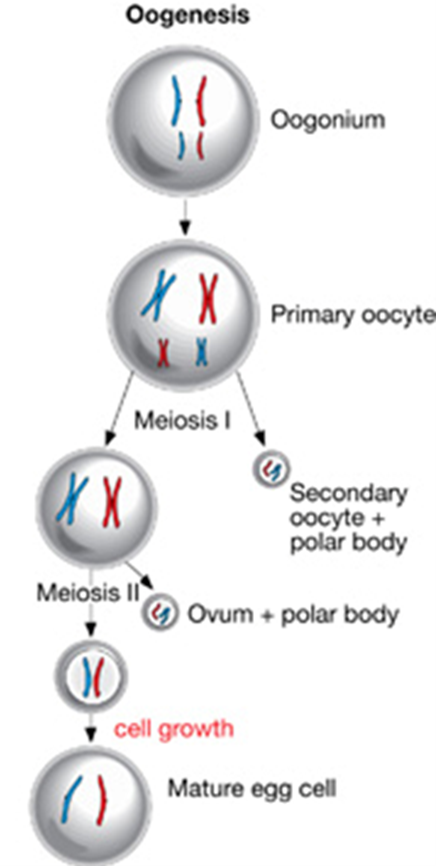
Oogenesis (Hint: 2)
The generation of an egg cell
Occurs in the ovaries
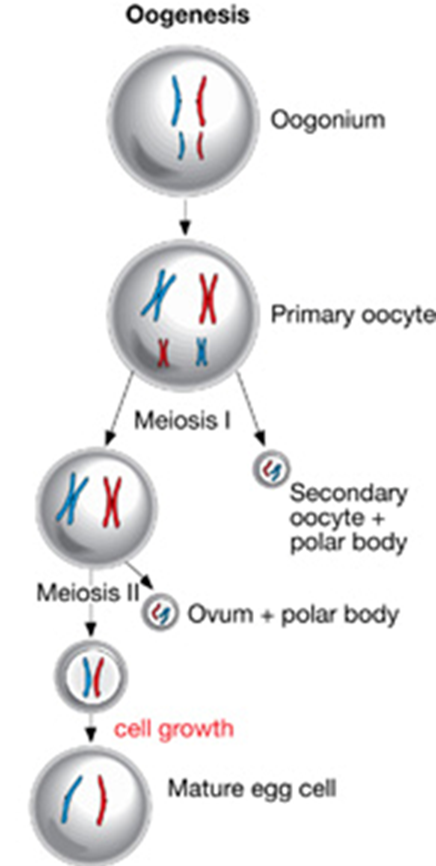
Oogonium (Hint: 2)
Starting cell
Can produce more oogonia by mitosis
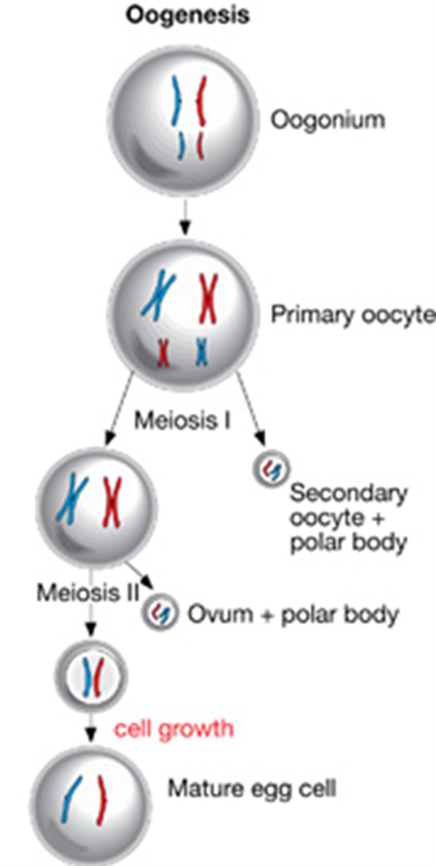
Primary oocyte (Hint: 4)
Enters meiosis I
Occurs in utero
Cell remains arrested in prophase I until puberty
Cell division is unequal- produces a secondary oocyte and a polar body
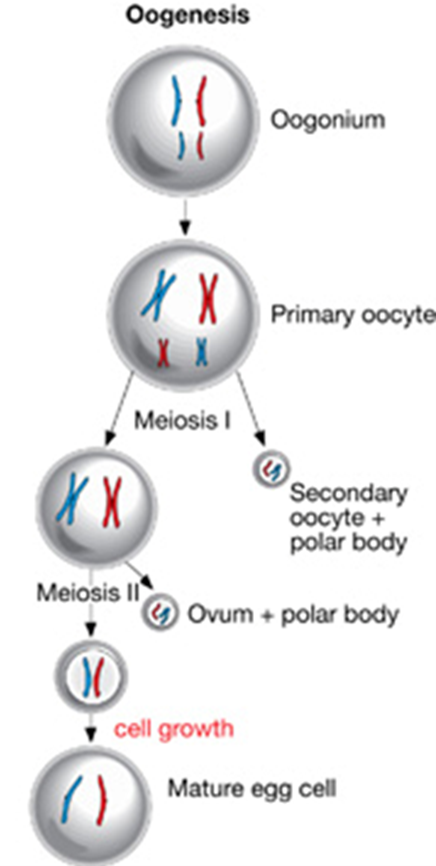
Secondary Oocyte
Produced in meiosis I by a primary oocyte because the cell division is unequal
Arrests at metaphase II until the egg is fertilized
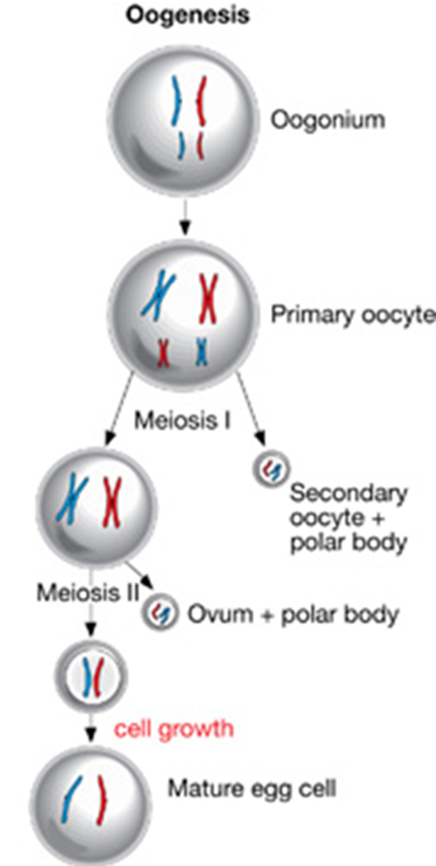
Ovum (Hint: 2)
Mature cell that is created
Unequal division produces only 1 ovum and 1 polar body
List the 3 advantages of sexual reproduction
High genetic variability
Facilitates adaptation
“Speeds” up evolution
List the 3 disadvantages of sexual reproduction
Energy costly
Courtship is time/resource consuming
Usually sacrifices the fitness of one sex to the other
List the 3 advantages of asexual reproduction
Save energy
Courtship is a non-issue
Greatest increase in fitness for each individual
List the 3 disadvantages of asexual reproduction
Low genetic variability
Adaptation to environment is difficult
Slows down evolution
Describe Meiosis in its entirety
List the similarities and differences between mitosis and meiosis
What are the 2 sources of genetic variation during meiosis?
Crossing Over
Random Separation of Homologous Chromosomes