L5 Child Abuse
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key terms and definitions from the child abuse lecture.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Types of child abuse
Psychological, physical, sexual abuse and neglect
Physical Abuse
Hitting with a closed hand or object, beating, shaking, burning, pinching, hair pulling, biting, kicking
Sexual Abuse (Kelly et al., 1991)
Some form of penetration or coerced/forced masturbation where the abuser was at least 5 years older, or unwanted interaction under 18.
Physical Neglect
Organization of the physical and temporal environment, overcrowding, household furnishings, personal hygiene, clothing, household sanitation
Psychological Neglect
Emotional and verbal responsivity of the mother, avoidance of restriction and punishment, maternal involvement with the child, opportunities for variety in daily stimulation
Child Abuse Statistics in NZ
NZ 3rd highest child death rate from childhood maltreatment of children to age 14. Also crazy high levels of child poverty (maori kids twice as likely to be abused or neglected)
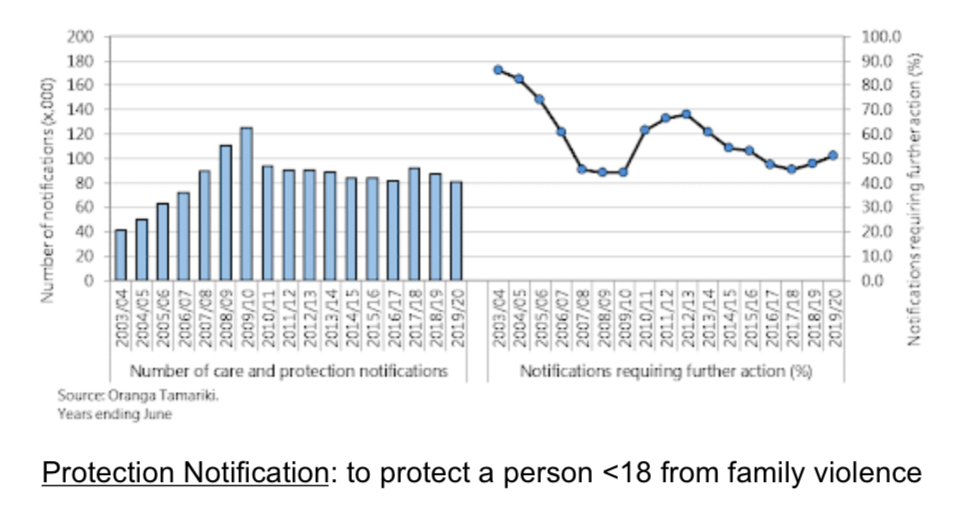
Oranga tamariki protection Notification
Trend increasing toll 2009 then decreasing. There was a culture of non-reporting before.
Children of substance abusers in USA are…
3x more likely to be abused, 4x more likely to be neglected. 2/3rds of people treated for drug abuse were physically or sexually abused as children (showing a cycle)
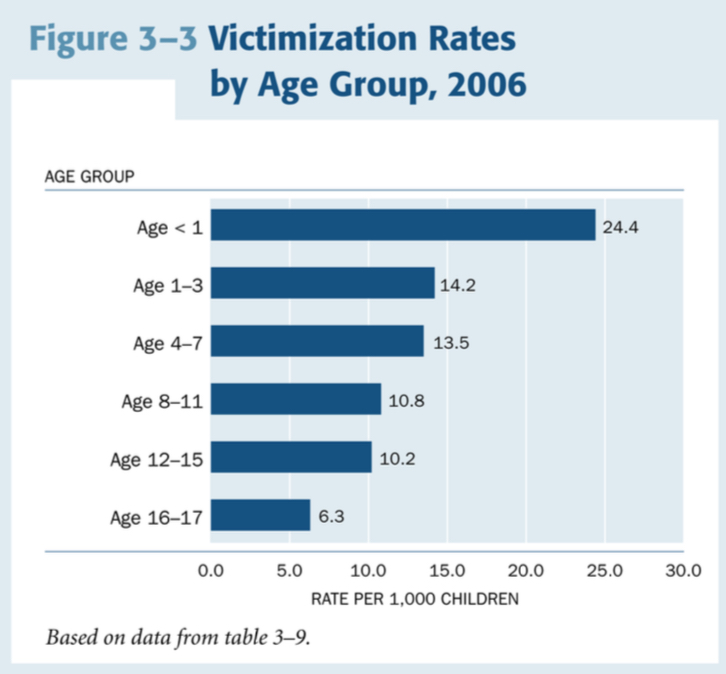
Age Group with the Highest Victimization Rates in U.S.A. (2006)
Children under 1 year old. Aged 16-17 is lowest.
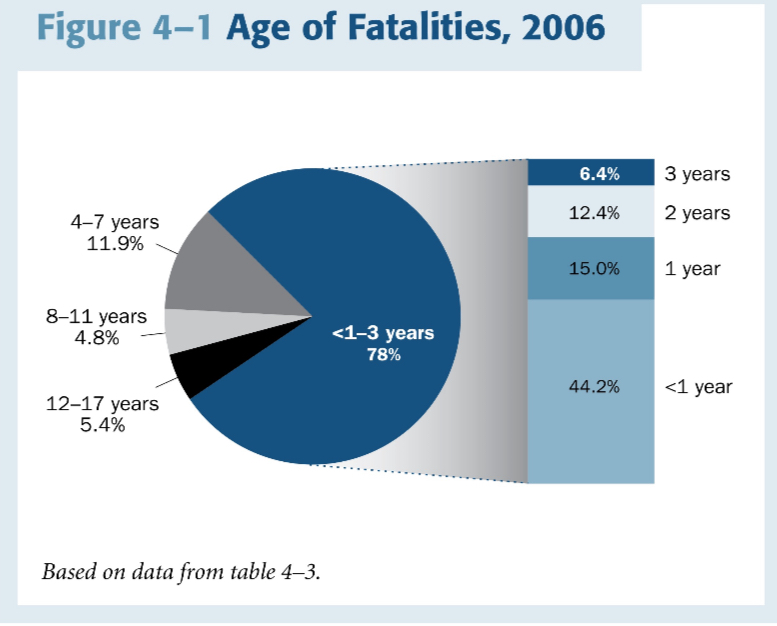
Most common age of fatalities of victims of child abuse
Under 1 to 3 years old
Most Common Maltreatment Type in Child Fatalities (2006)
Neglect, most uncommon is sexual abuse.
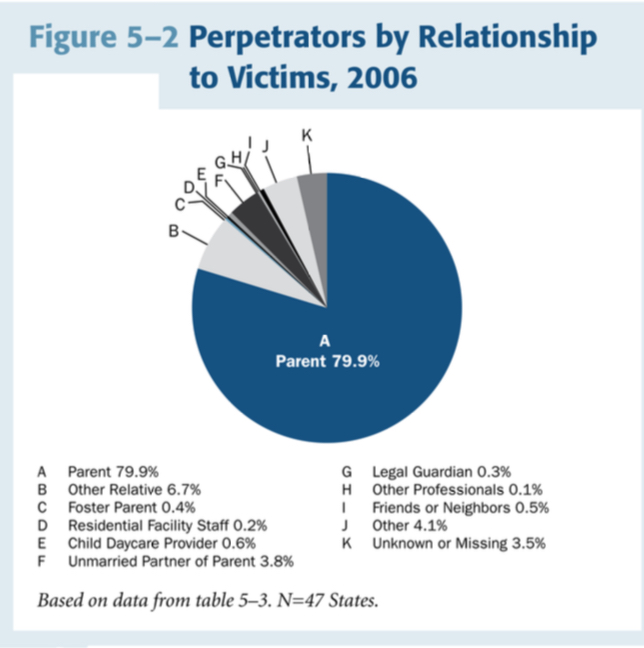
Most Common Perpetrator Relationship to Victims (2006)
Parent
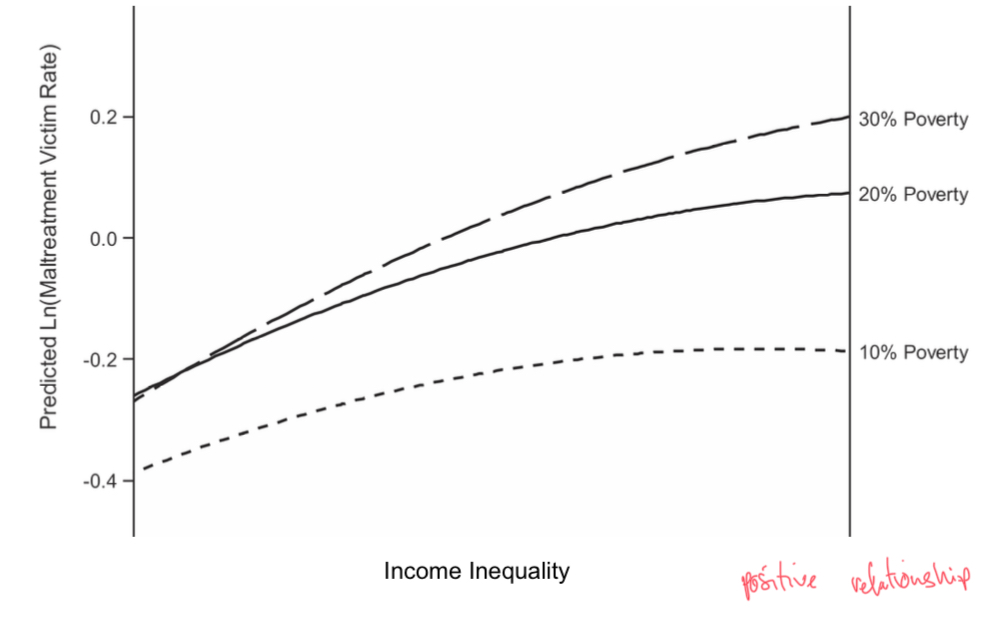
Child Abuse and the Income Gap
The bigger the income gap the bigger the maltreatment victimization rate (positive gradient) and the stronger the relation.
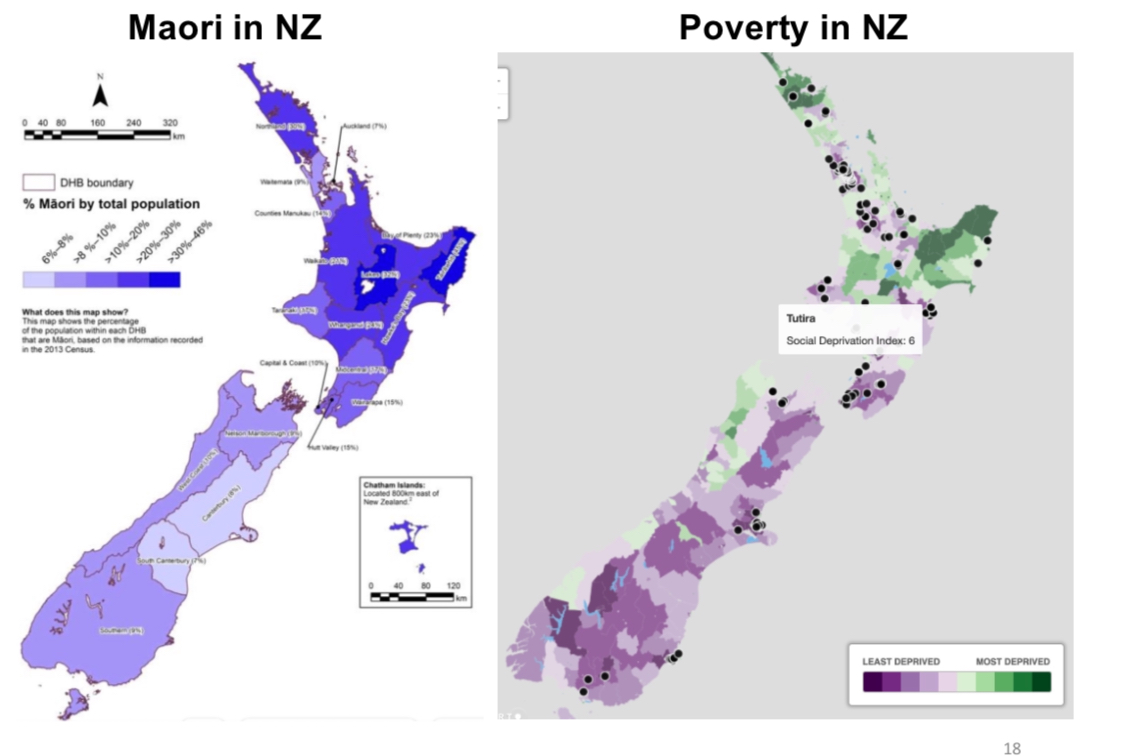
Comparimng Maori in NZ to poverty
Clear relationship between Maori, poverty, and child abuse. Maori are overrepresented in child abuse stats because they are overrepresented in poverty stats. Same pattern applies for other countries.
Outcomes of physical abuse on functioning at 21 (compared to control to show difference)
Males- Major deppresion, PTSD, antisocial, drug abuse, internalising and externalising behaviour. Pretty similar for females except they have more suicide attempts and less internalising behaviour.
Sexual abuse on functioning in 21 year females
Major depression, PTSD, antisocial, alcahol abuse, suicidal ideation and attempts.
Abuse relation to health issues (mid life effects)
More likely to develop a huge number of medical problems.
Shaken Baby Syndrome
Brain injury when baby violently shaken, brain bounces back and forth causing bruising, swelling, and tissue damage. Can cause permanent brain damage. Usually done to make child be quiet.
Prognosis of Shaken Baby Syndrome
Blindness, it’s much worse than accidental brain damage and majority of infants have mental disability (evident in later years)
Shaken Baby Syndrome stats
Accounts for up to ½ of child abuse deaths. Usually cases have history of baby shaking (older brain damage). Permanently disables 1/3rd of victims.
Costs of Child Abuse (New York)
Expenditure on child abuse $104 million. Total cost of child abuse $2424 million.