River Management: Geography WJEC: GCSE (9:1)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
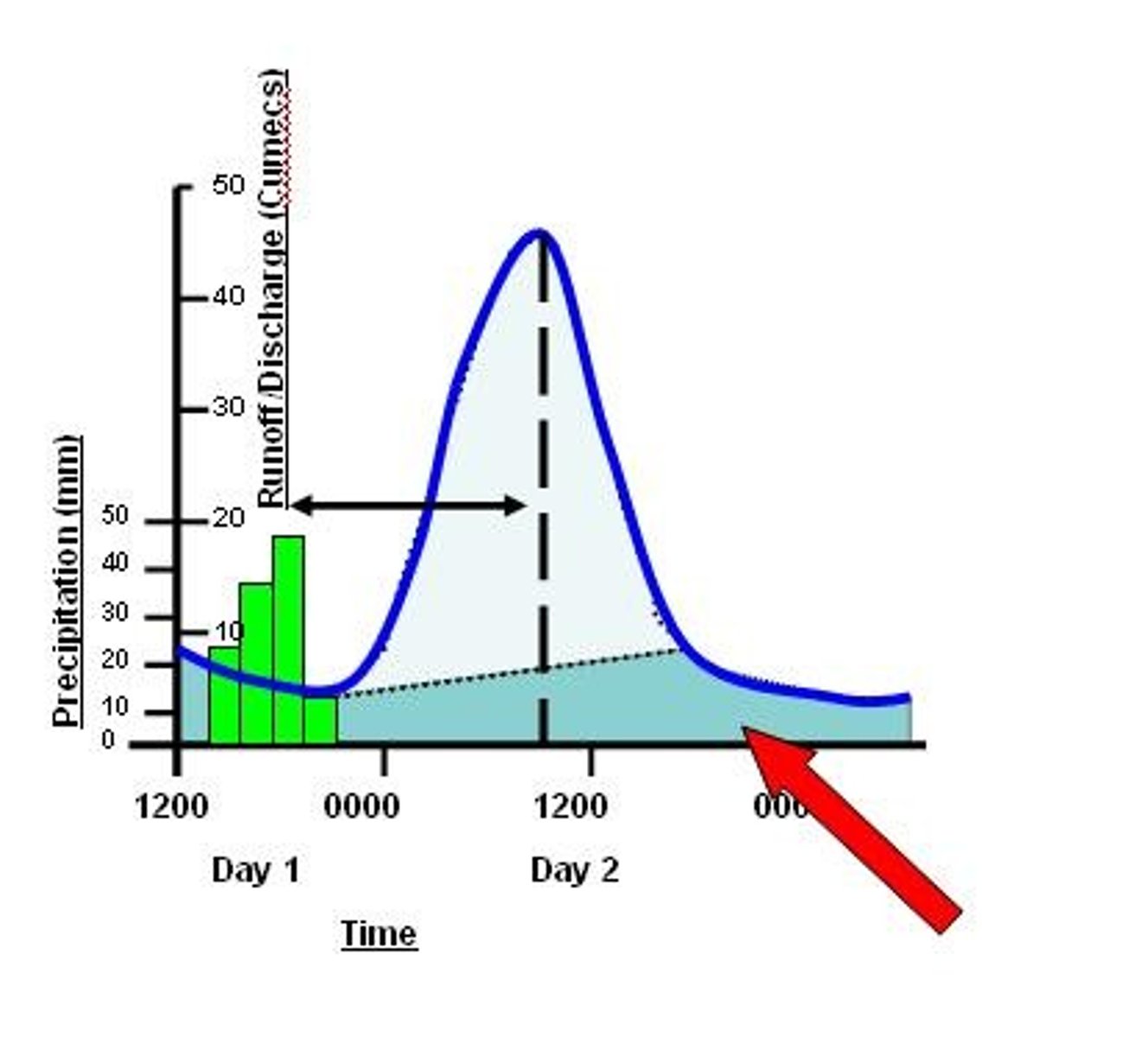
Flood hydrograph
Graph of stream discharge over a time period for a specific place
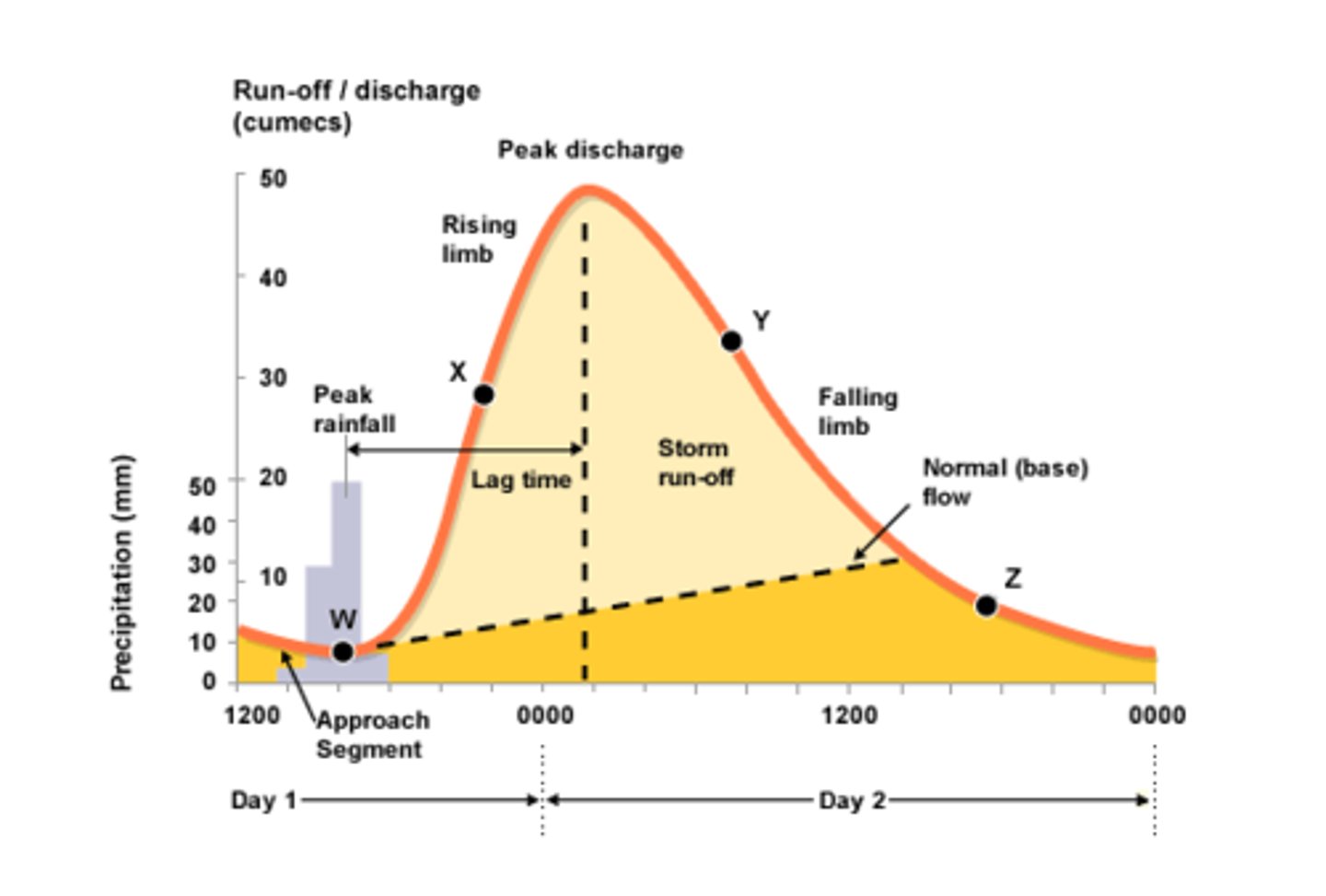
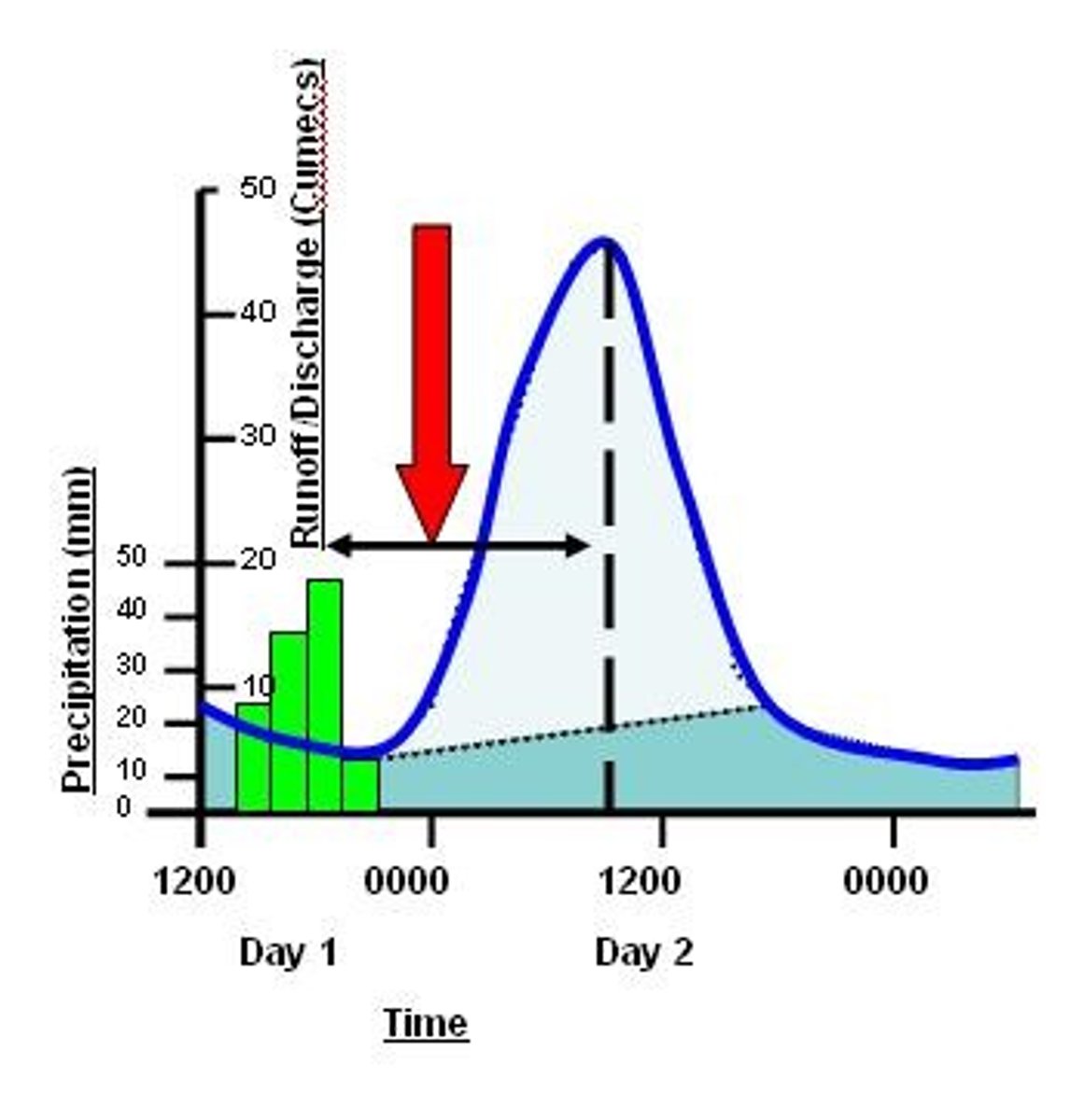
Peak rainfall
The greatest amount of rainfall that falls in a storm.
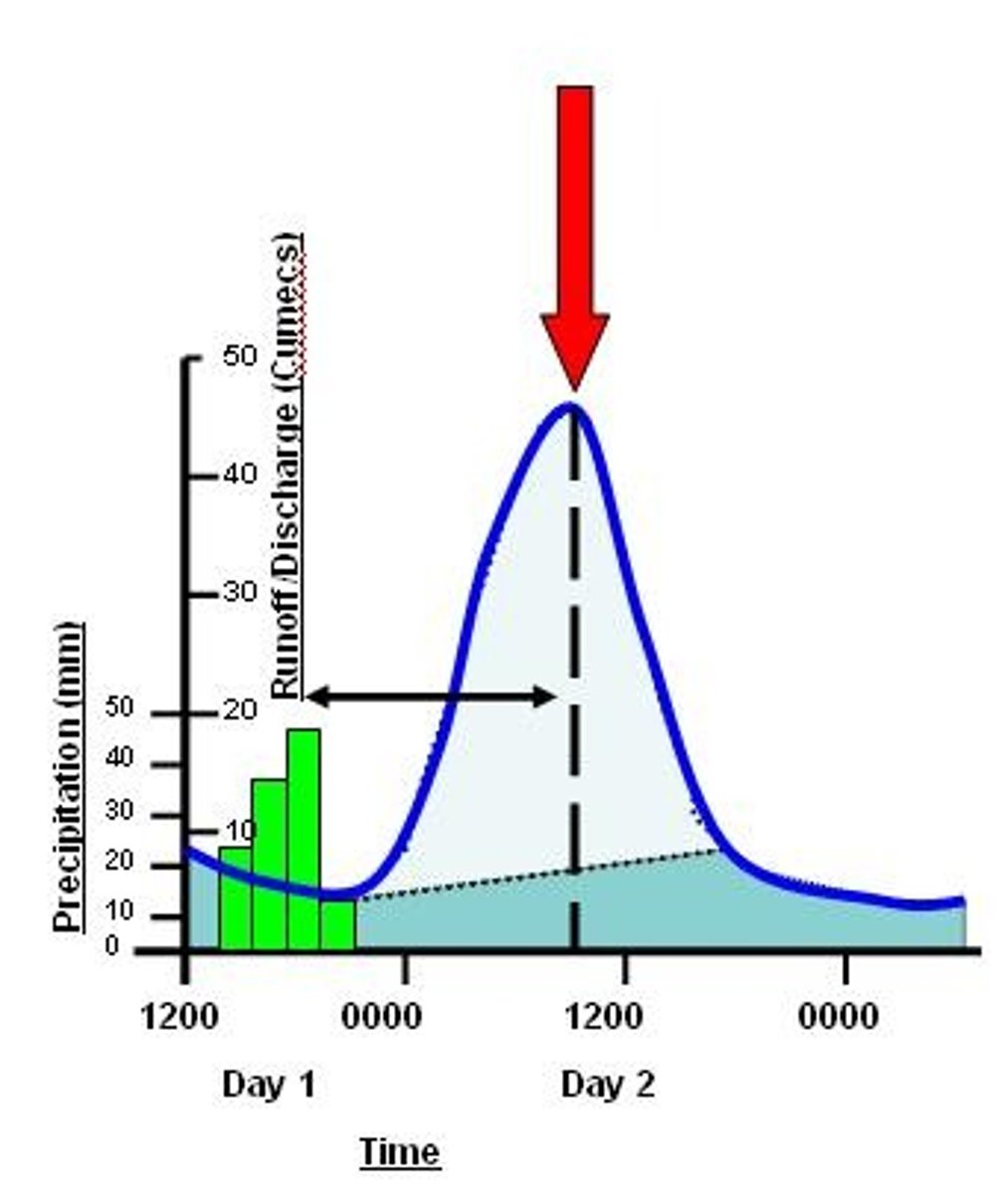
Peak discharge
The greatest volume of water that flows in the river at a given time.
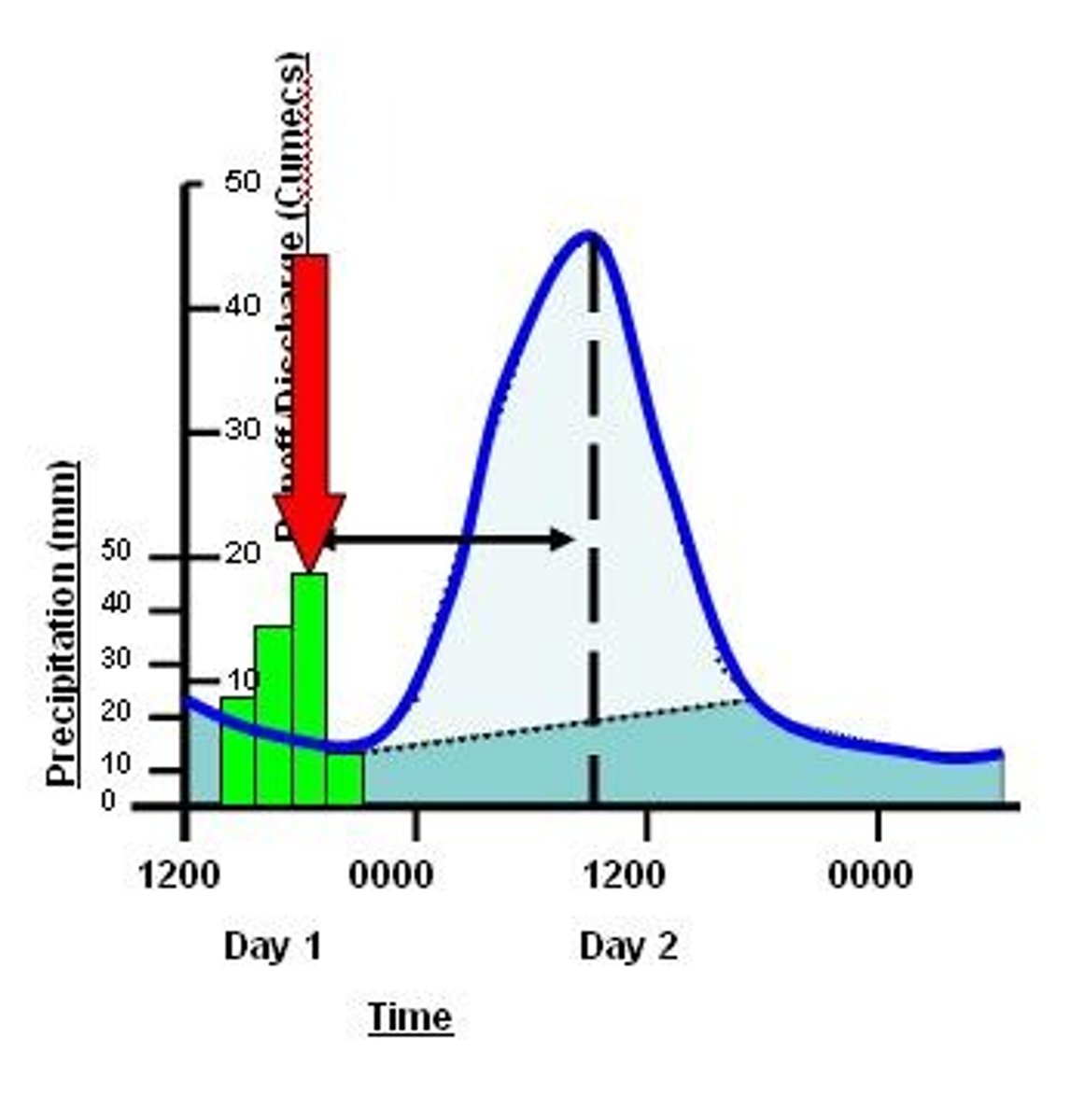
Lag time
Time between peak rainfall and peak discharge.
Rising limb
The period of rising river discharge following a period of rainfall.
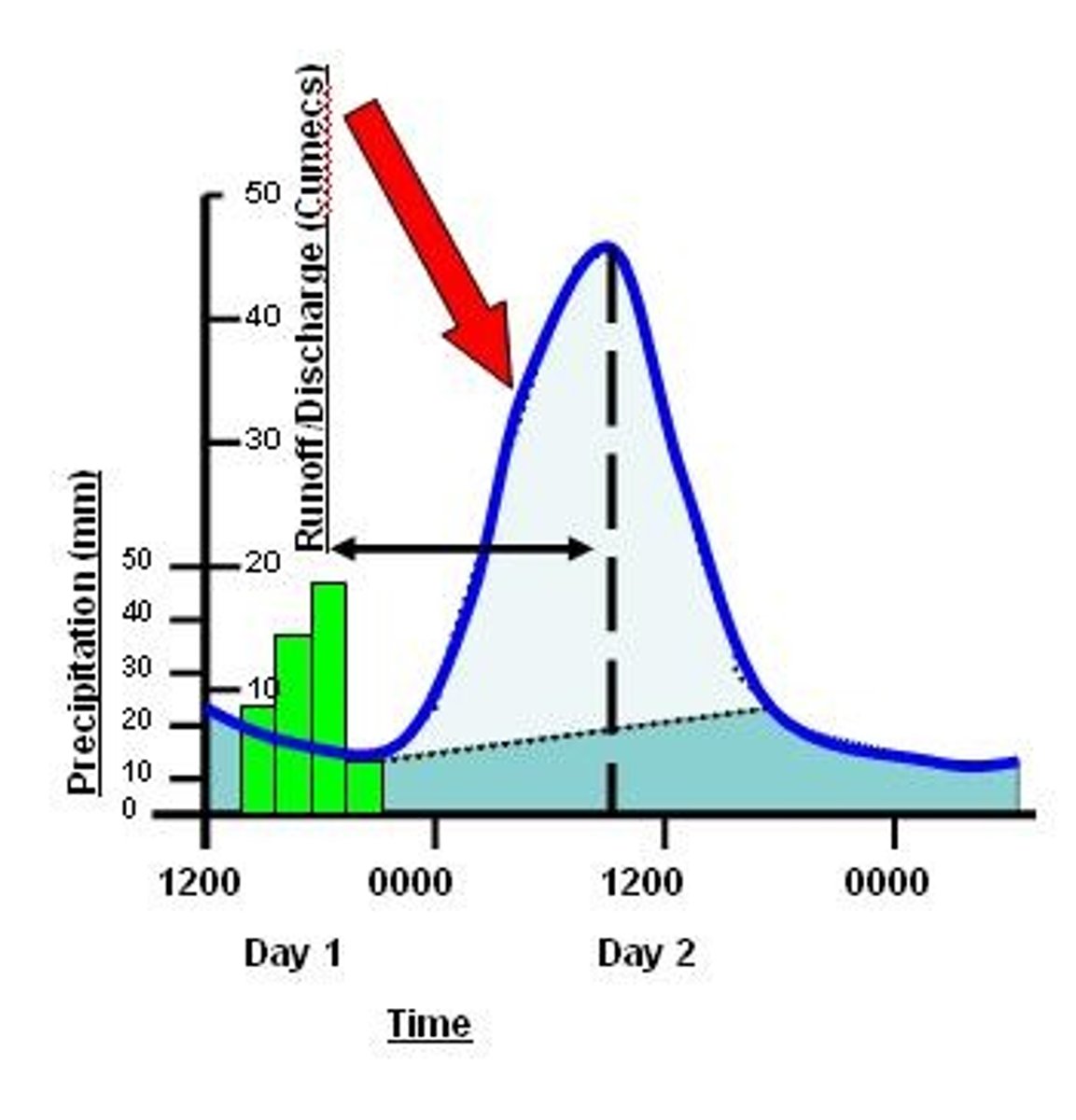
Falling limb
The decrease in river discharge as the river returns to its normal level.
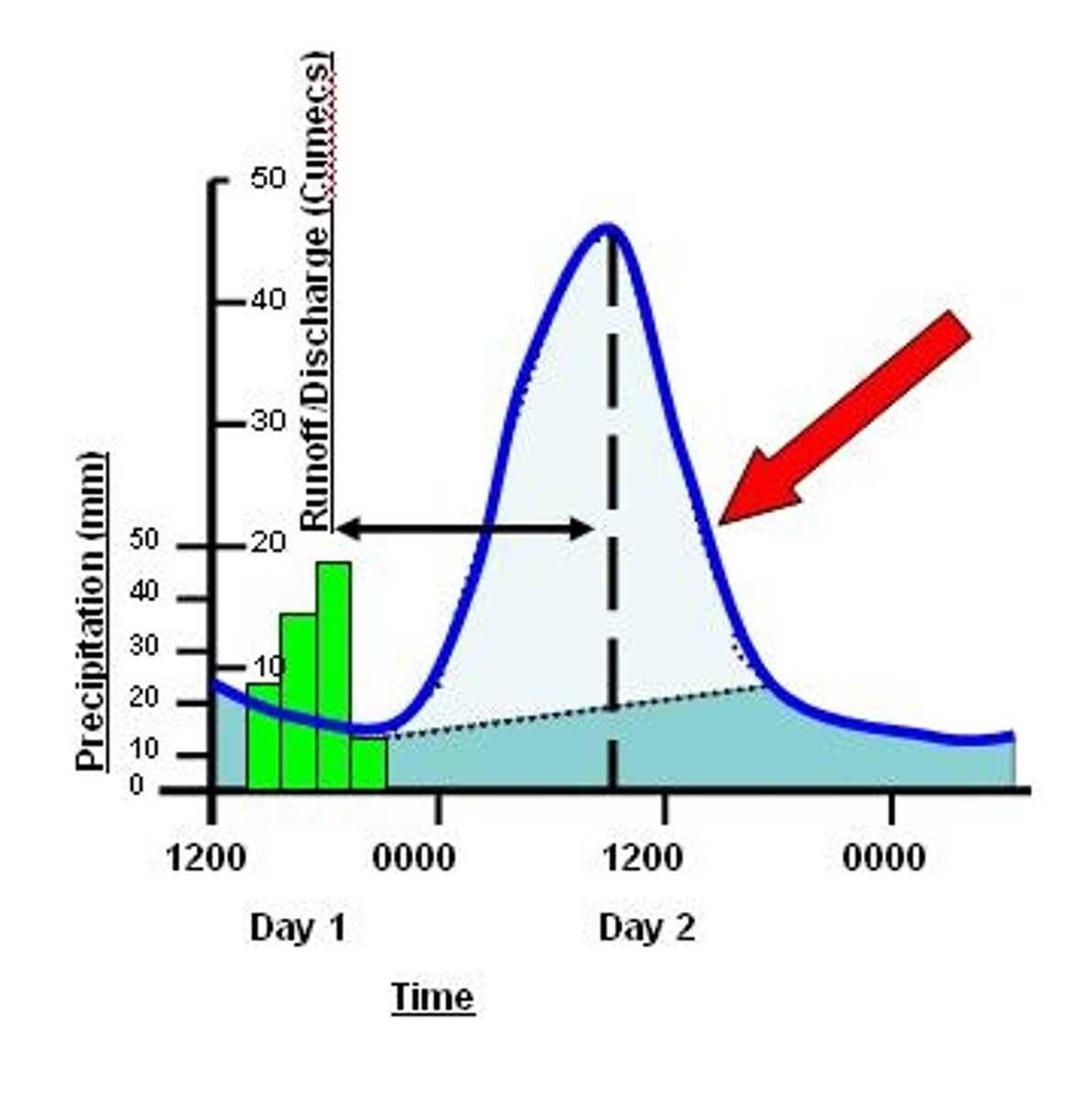
Base flow
Normal discharge of the river.
Hard engineering
The use of concrete and large artificial structures by civil engineers to defend land against natural erosion processes.

Dam
A structure built across a river to control the river's flow.

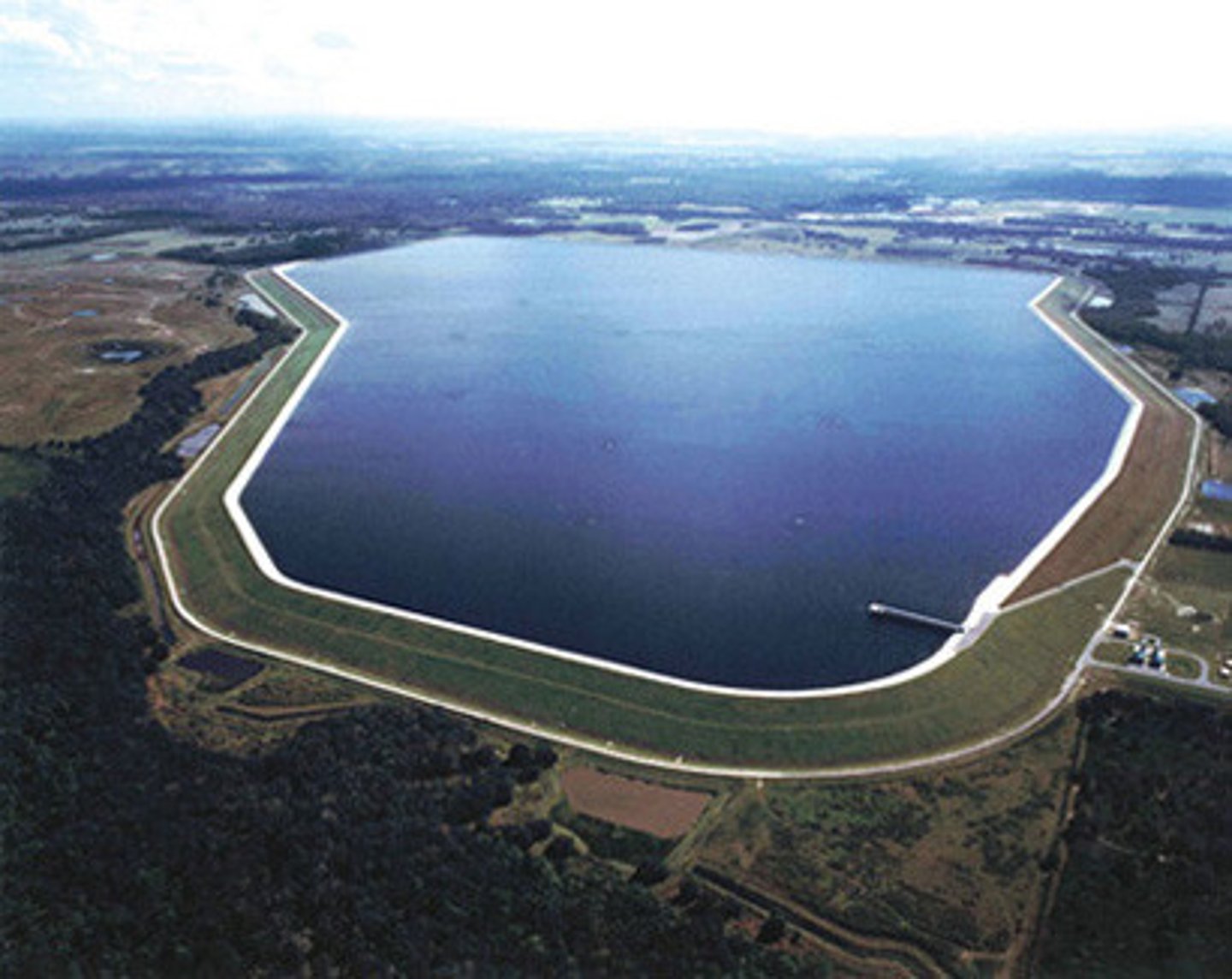
Reservoir
A large natural or artificial lake used as a source of water supply that builds up behind a dam.

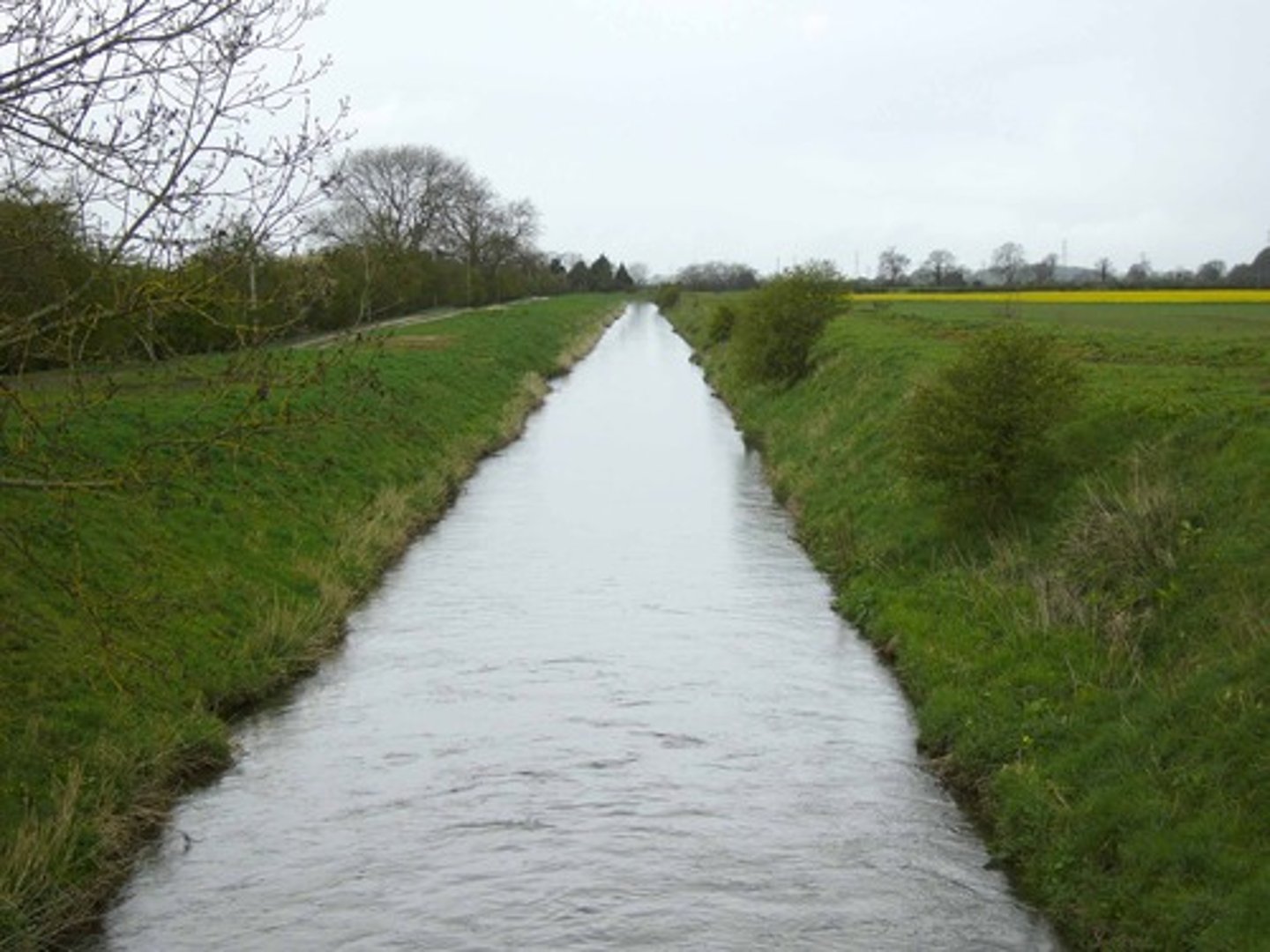
River straightening
Blocking off meanders, also known as channelisation.

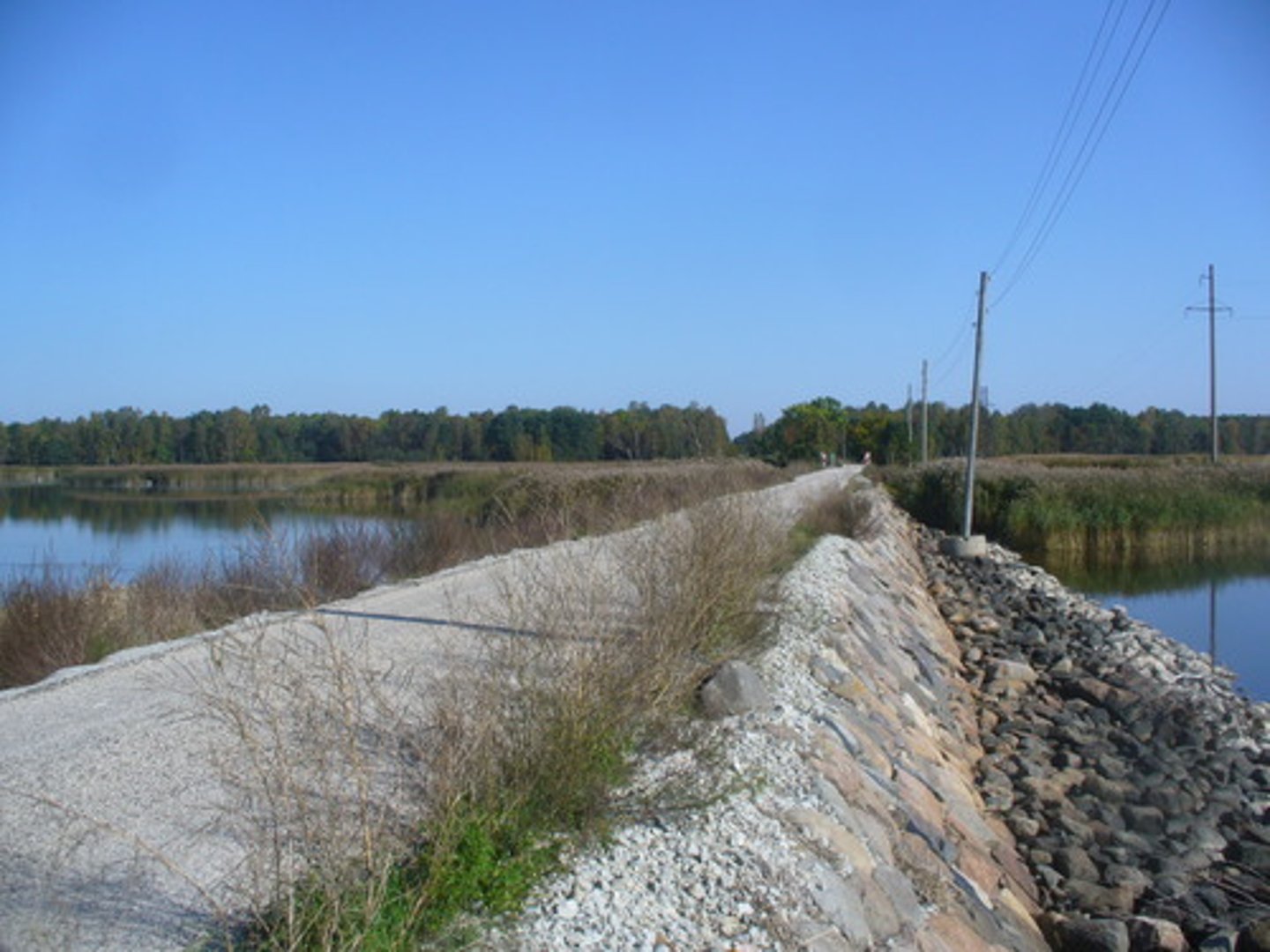
Embankments
Raised banks constructed along the river; they effectively make the river deeper so it can hold more water.

Flood relief channels
Building new artificial channels which are used when a river is close to maximum discharge.

Soft engineering
A sustainable approach to managing the river system without using artificial structures
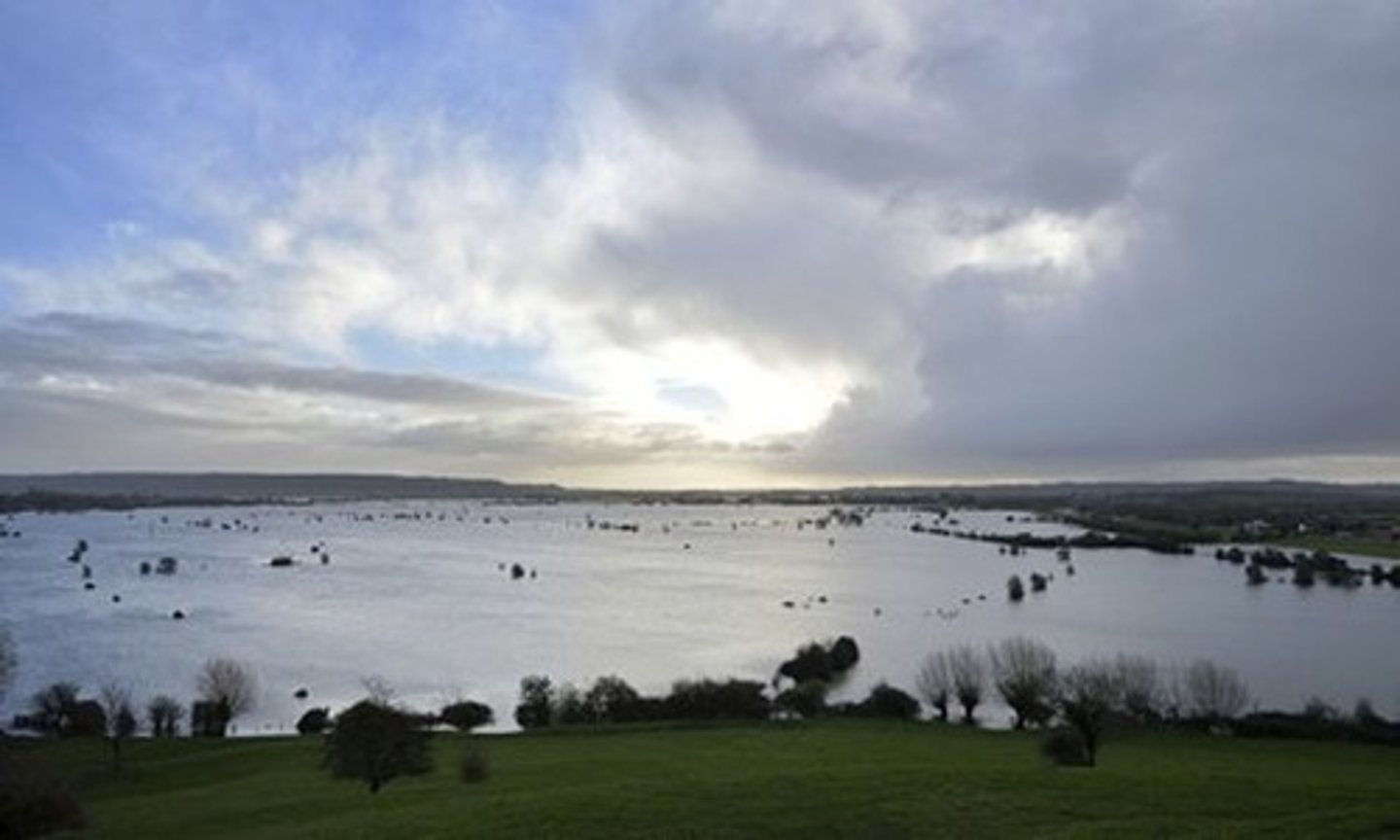

Flood warnings
The Environmental Agency providing reliable advance information about possible flooding.

Preparation
Using sandbags or removing valuables to a safe area away from rising flood waters.

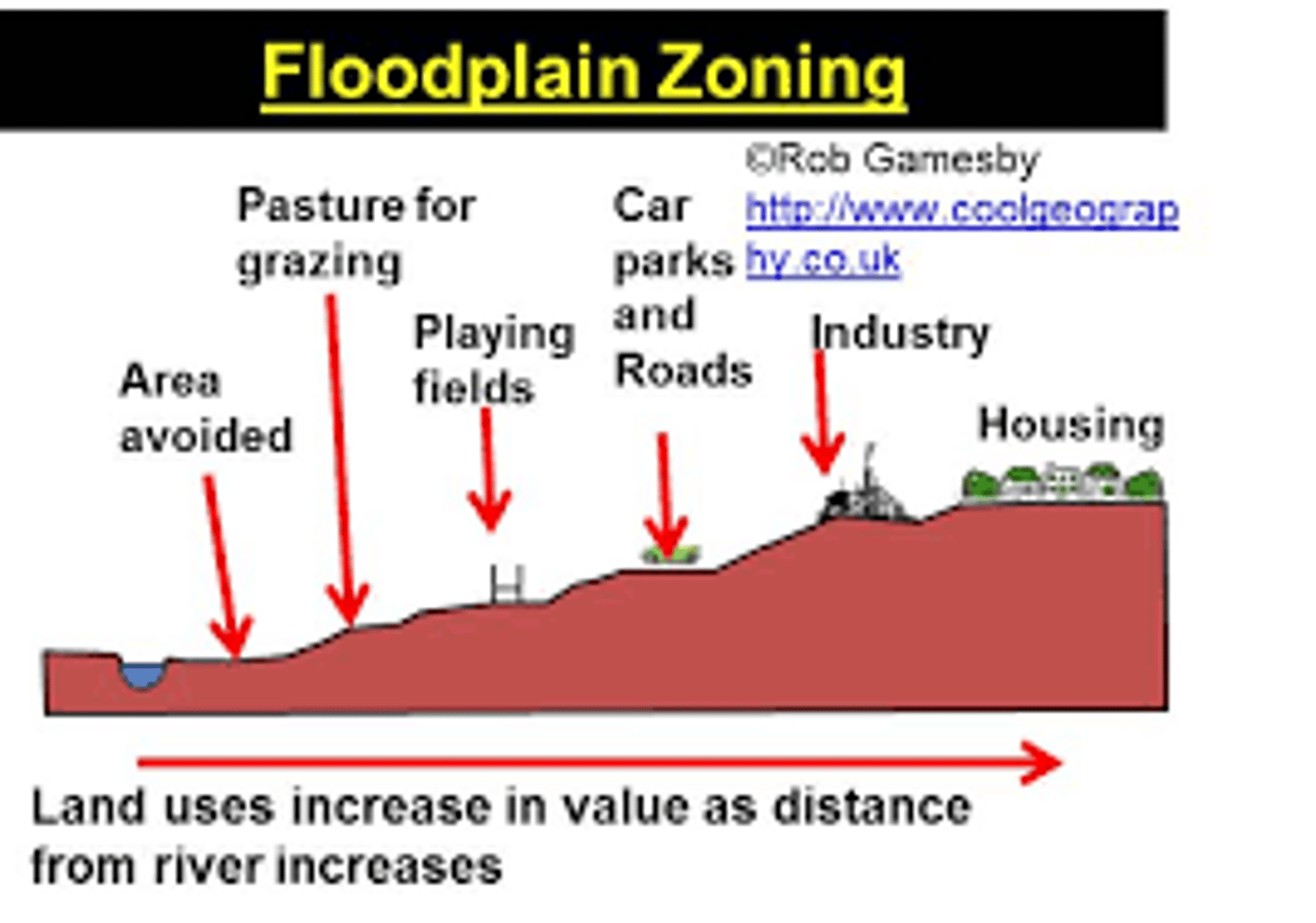
Flood plain zoning
This attempts to organise the flood defences in such a way that land that is near the river and often floods is not built on.
Planting trees
This increases interception and increases the lag time and decreases the flood risk.

River restoration
Modifying the course of a river to return it to its natural state
