Digestive System
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:00 PM on 3/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
1
New cards
Why do we eat?
\-food provides nutrients needed for building tissues and maintaining needed chemical reactions (food is a source of energy for every cell)
2
New cards
What does the digestive system do in general?
breaks food down into usable form = nutrients
3
New cards
What are the (5) specific functions of the digestive system?
1. ingestion
\
2. movement of food via peristalis (squeezing) using smooth muscle
\
3. digestion
\
4. absorption
5. defecation
4
New cards
Describe ingestion.
\- mouth - entry to digestive system
5
New cards
Describe digestion.
breaking food down into nutrients
6
New cards
What are the two types of digestion?
mechanical and chemical
7
New cards
Describe mechanical digestion.
physical breakdown (example: teeth grinding up food)
8
New cards
Describe chemical digestion.
chemical breakdown (example: enzymes)
9
New cards
What are the main biomolecules being digested?
protein, carbohydrates, lipids
10
New cards
Describe absorption.
nutrients to tissues
11
New cards
Define defecation.
eliminating indigestible residues (pooping)
12
New cards
What us the gastro-intestinal tract?
\- 10 m continuous tube from mouth to anus
\-accessory structures along the way to help with digestion, but food doesn’t pass through them
\-accessory structures along the way to help with digestion, but food doesn’t pass through them
13
New cards
What are the 4 main layers in the tube?
1. mucosa
2. submucosa
3. muscularis
4. serosa
14
New cards
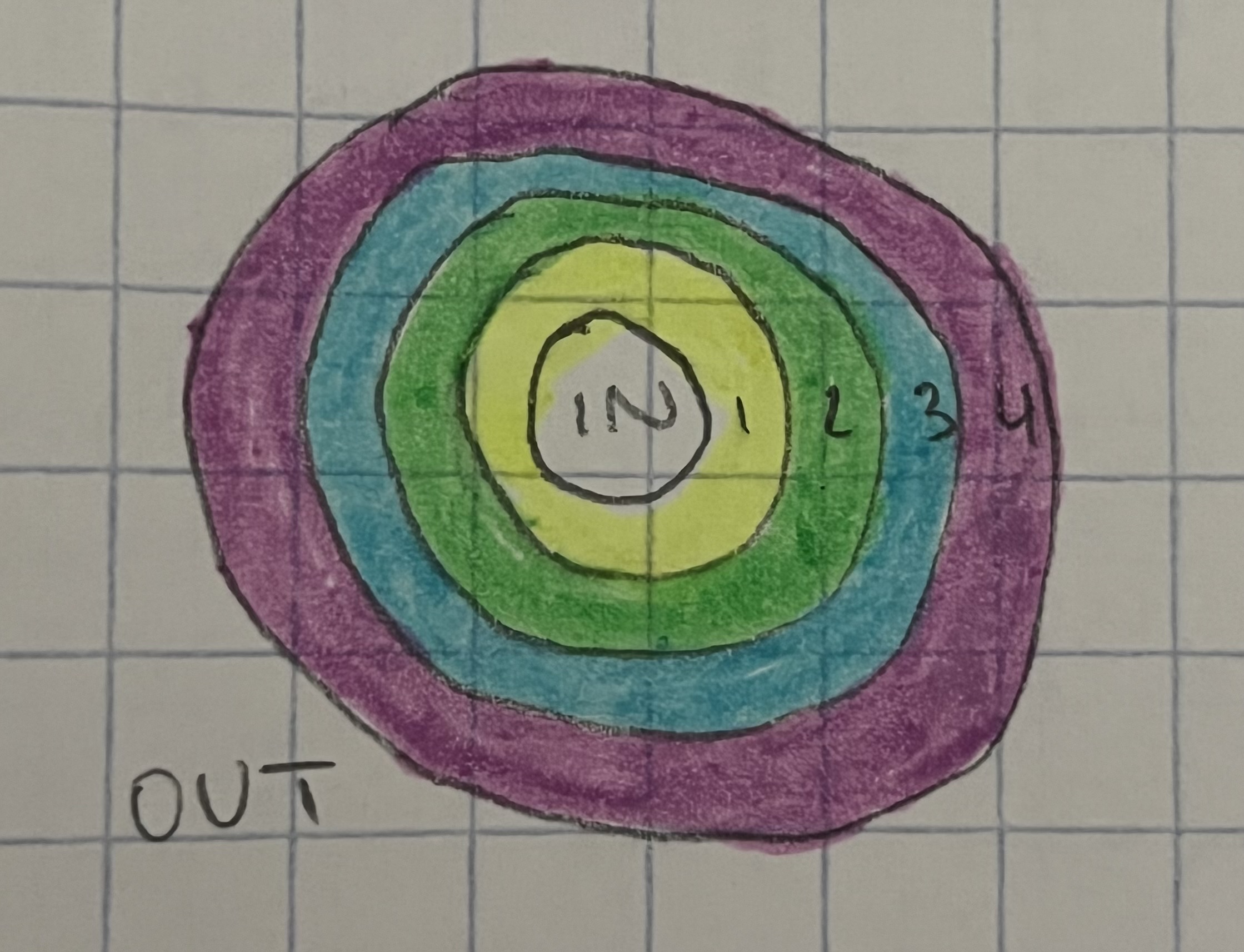
Draw a diagram of the 4 layers of the gastro-intestinal tract.
yellow = mucosa
green = submucosa
blue = muscularis
purple = serosa
green = submucosa
blue = muscularis
purple = serosa
15
New cards
Describe mucosa.
\-contains epithelial tissue
\
Where is mucosa simple?
\-in areas of high diffusion like small intestine
\
Where is mucosa stratified?
\-in areas of high wear and tear like mouth or anus
\
Where is mucosa simple?
\-in areas of high diffusion like small intestine
\
Where is mucosa stratified?
\-in areas of high wear and tear like mouth or anus
16
New cards
Describe muscularis.
\-contains muscle
\-mostly smooth
\
Where is muscularis skeletal (voluntary)?
\-in areas where you need to choose like pharynx for swallowing or anus for pooping
\-mostly smooth
\
Where is muscularis skeletal (voluntary)?
\-in areas where you need to choose like pharynx for swallowing or anus for pooping
17
New cards
Name all the structures food must pass through.
mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, duodenum, jejunum, ileum, cecum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, rectum, anus
18
New cards
What is food called when it passes through the pharynx (swallowed)?
bolus
19
New cards
What is food called when it goes to the stomach?
bolus turns into chyme
20
New cards
What is food called when it passes through the large intestine?
chyme turned into feces
21
New cards
What are the parts of the mouth (oral cavity)?
\-gingivae
\-palate
\-uvula
\-tongue
\-teeth
\-palate
\-uvula
\-tongue
\-teeth
22
New cards
What are the gingivae?
gums
23
New cards
What is the palate?
hard and soft roof of mouth
24
New cards
What does the uvula do?
lifts when swallowing to keep food out of nose
25
New cards
What are the structures on the tongue? Describe their purpose.
\-papillae
\-bumps on tongue that contain taste buds
\-bumps on tongue that contain taste buds
26
New cards
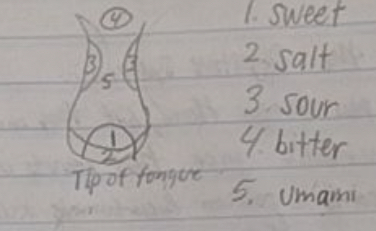
Draw a diagram of the tongue and label which parts of the tongue can taste sweet, salt, sour, bitter, and umami.
27
New cards
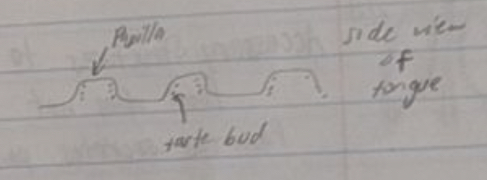
Draw a diagram of the side view of the tongue and label a papilla and a taste bud.
28
New cards
Name the different tooth types.
incisors, cuspids, bicuspids, molars
29
New cards
What is the function of the incisors?
cut
30
New cards
What is the function of the cuspids?
rip/tear
31
New cards
What is the function of the bicuspids?
rip/tear
32
New cards
What is the function of the molars?
grinding
33
New cards
Name the tooth parts.
crown, neck, root, layers
34
New cards
What are the layers made up of?
enamel (hardest substance in body), dentin, pulp cavity
35
New cards
Which tooth types do herbivores have?
only molars and incisors for grinding and cutting plants
36
New cards
Which tooth types do omnivores have?
all tooth types
37
New cards
Which tooth types do carnivores have?
all tooth types, but all are pointy
38
New cards
What is the pharynx?
common space for air and food
39
New cards
What is the esophagus?
\-food tube
\-muscular (peristalsis) and collapsable
\-muscular (peristalsis) and collapsable
40
New cards
What is the stomach?
\-mixing area and reservoir
\-4 parts
\-has rugae
\-4 parts
\-has rugae
41
New cards
What are the 4 parts of the stomach?
cardia, fundus, body, pylorus
42
New cards
What is the rugae?
folds for stretching and to increase surface area for secretion
43
New cards
What is the small intestine?
\-most absorption of nutrients occurs here via diffusion
\-very long and has folds called villi to increase surface area
\-3 parts
\-very long and has folds called villi to increase surface area
\-3 parts
44
New cards
What are the 3 parts of the small intestine?
duodenum, jejunum, ileum
45
New cards
What are the parts of the large intestine?
cecum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, rectum, anus
46
New cards
What are the accessory structures to the digestive system?
pancreas, liver, gall bladder
47
New cards
What does it mean when something is an accessory structure?
food does not pass through it, but it aids in digestion
48
New cards
What is the function of the pancreas?
\-secretes pancreatic juice
\-has pancreatic islets
\-has pancreatic islets
49
New cards
What does pancreatic juice consist of?
water + salts + sodium bicarbonate + digestive enzymes
50
New cards
What is the purpose of sodium bicarbonate in pancreatic juice?
for neutralizing stomach acids
51
New cards
What are pancreatic islets?
secrete glucagon and insulin to control blood sugars
52
New cards
What is the liver?
\-heaviest gland in body
\-functions in metabolism and the removal of toxin (sinusoids)
\-functions in metabolism and the removal of toxin (sinusoids)
53
New cards
What are sinusoids?
blood pods in the liver, so can be detoxified
54
New cards
What is the gall bladder?
\-stores bile that was secreted by liver
\-releases bile into duodenum to emulsify fats when needed
\-releases bile into duodenum to emulsify fats when needed
55
New cards
What is a diet?
what you eat