LM17| The Evidence for Evolution
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What is Evolution ?
A change in the heritable traits of a population over time.
What is Macroevolution?
Large scale changes that take place over extended time periods, such as the formation of new species and groups (speciation)
What is Microevolution ?
Small scale changes that affect just one or few genes and happen in populations over a shorter time period
(anatomy) What are homologous structure?
Species can have similar structure/physical features because the feature was present in a common ancestor but have different functions.
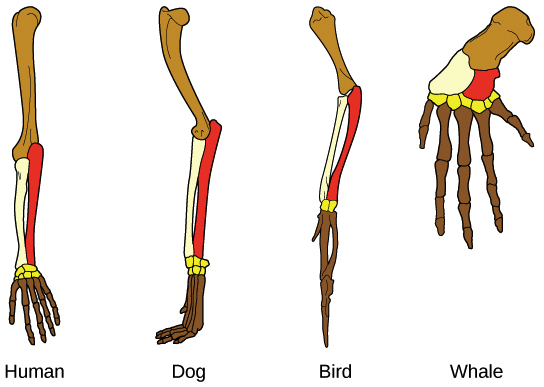
(molecular biology) How does molecular biology support the theory of evolution and that we have a common ancestor?
The same genetic material (DNA)
The same, or highly similar, genetic codes
The same basic process of gene expression (transcription and translation)
The same molecular building blocks, such as amino acids
Direct observation showcases evolution in action, such as antibiotic resistance in bacteria.
How do (fossils)serve as evidence for evolution?
Fossil records (though incomplete) provides information about what species existed at particular times on earths history and we find intermediate species which support evolution.
What are Vestigial Structures?
physical features (structures) in organisms that have lost their original function through evolution.
What are analogous features ?
Not all physical features that look alike are marks of common ancestry. Instead, some physical similarities are analogous: they evolved independently in different organisms because the organisms lived in similar environments or experienced similar selective pressures. This process is called convergent evolution. (To converge means to come together, like two lines meeting at a point.)
All living things are ?
Related and share a common ancestor
Evolution is powered by ?
Natural processes
How does embryology provide evidence for evolution?
(embryology)Similar stages of development in the embryo re-affirm evolution and that all living organisms share a common ancestor
what are homologous/ orthologous genes ?
Two species have the "same" gene because they inherited it from a common ancestor this observed through comparing sequences of related genes found in different species.
Ex: Humans, cows, chickens, and chimpanzees all have a gene that encodes the hormone insulin, because this gene was already present in their last common ancestor.
Also the more DNA differences in homologous genes (or amino acid differences in the proteins they encode) between two species, the more distantly the species are related