5.1 & 5.2 The Photoelectric Effect
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Photons
Packets of radiation with energy proportional to their frequency and INVERSELY proportional to wavelength
Equations to find E
E = hf and E = hc/λ
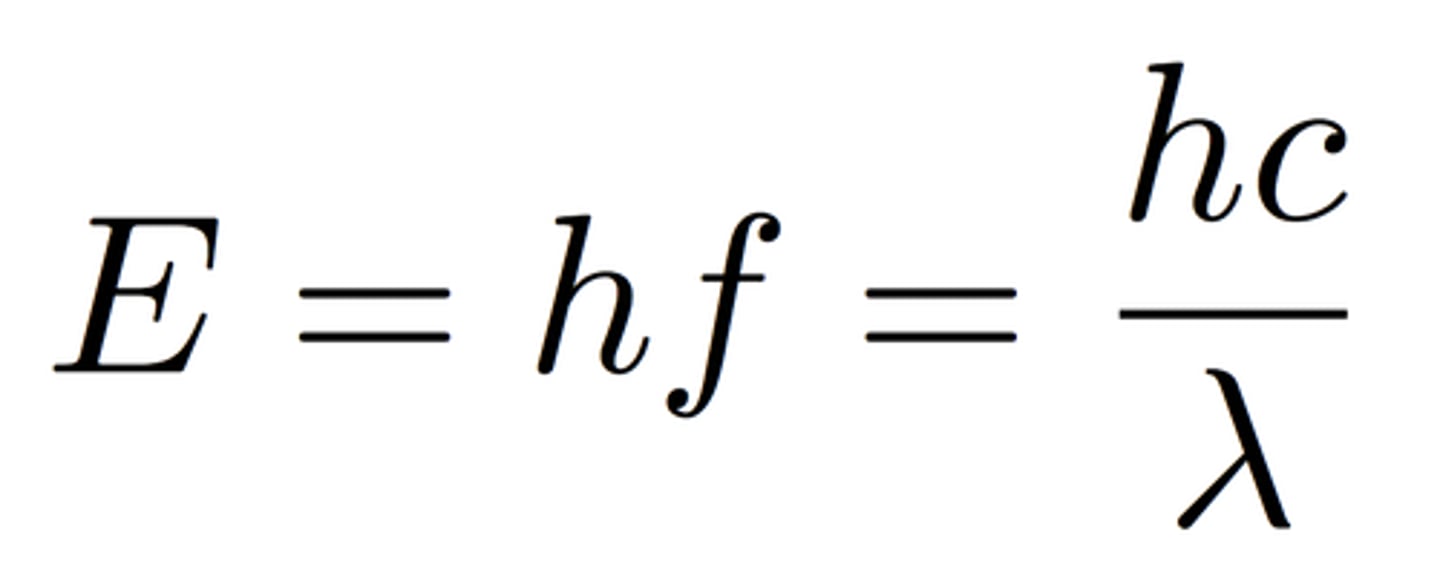
What is the value of h?
6.63 x 10^-34 Js
What do we measure energy of a photon in?
Joules
The Photoelectric Effect
The photoelectric effect is when light above a particular frequency hits a metal surface, causing electrons to be emitted from the surface.
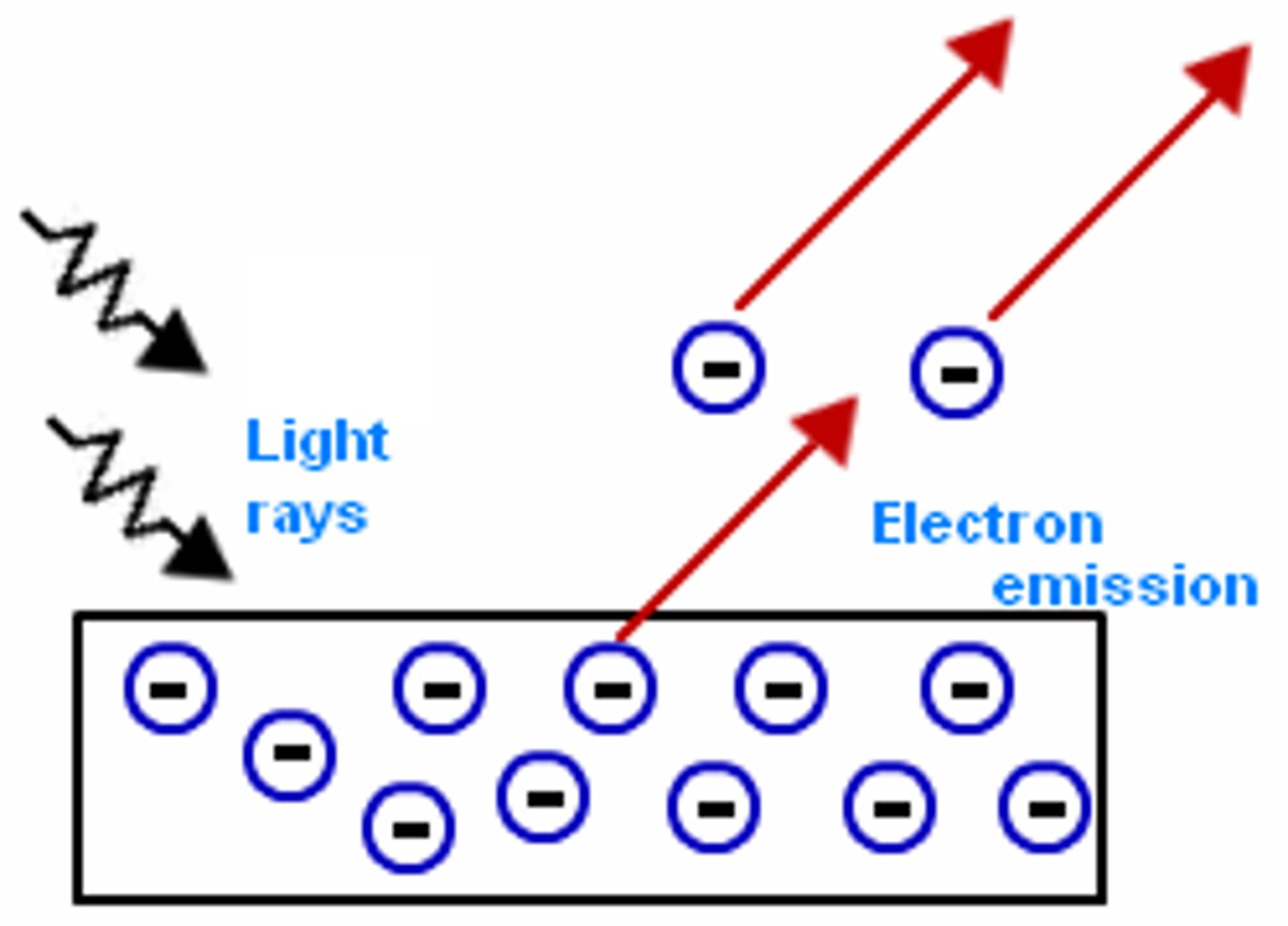
When are electrons emitted from a surface?
Electrons are only emitted from. surface if the light is above the threshold frequency
What happens when you increase intensity of light?
Maximum kinetic energy remains the same
The number of photoelectrons emitted increases
Define a one to one interaction.
One photon can cause the emission of ONE electron.
Photoelectric Effect and Particle Theory
The photoelectric effect shows that light behaves as particles (photons). Only light above a certain frequency can eject electrons from a metal, no matter how bright the light is.This can't be explained by wave theory, but it supports the idea that light delivers energy in packets (photons) instead of sustained oscillations, proving its particle-like behaviour.
Threshold Frequency
The lowest frequency of light that causes electrons to be emitted from the surface of a metal
Work Function
Minimum amount of energy needed to release an electron from the surface of a metal
Threshold frequency equation
f = Φ / h
Calculating maximum photoelectric energy
E = hf - Φ
This can also be expressed as:
1/2mv^2 = hf - Φ
Converting ev to J
Multiply by 1.6 x 10^-19 (elementary charge)
the number should get smaller
Converting J to eV
Divide by 1.6 x10^-19 (elementary charge)
The number should get bigger