ecology exam 3: communities
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
community
all populations of various species living together in a particular area that interact or could potentially interact (boundaries are not always rigid and may cover small or larger areas, geographically in the same place)
community apporach
understands the diversity and interactions of organisms living together in the same place
is type of interaction static
no could have 2 species competing for a long time and living conditions change, a species can be introduced or resources change that competition can turn to predation
how are communities often characterized
dominant organisms or by physical conditions that affect the distribution of species
how are aquatic habitats defined
the structure of the aquatic habitat (lake or stream) and physical conditions than organism expect for coral reefs
when there are definite differences in environmental conditions on one side of something vs the other the division is what
ecotone (treeline of a forest, interior difference from the medow)
ectone
boundary created by sharp changes in environmental condition over a relatively short distance, accompanied by a major change in the composition of species
ecological transition zones
talking about ecotone
what do ectones generally support
a larger number of species than in either adjacent community (constitutes the fundamental niche of both species)
ecological release
ability of individuals to exploit broader niches
why is niche bigger in new areas
new habitat and other small critters can rapidly adapt because changing how much melanin to produce is not a big stretch
how is community defined in ecology
an assemblage of species found together in a specific place at a specific time. they interact or have the potential to interact and scale varies widely with species within it being or not being interdependent
scale of ecological communties
can have one tree or take a portion of the united states
how much of australia is a threat in ecological community
1/3
interdependence
reliance on another species to exist in a community
what did Fredric Clements propose
most communities are interdependent and act as a superorganisms (organisms within the community all have a role and all work together)
what did henry gleason propose
most communities consist of species with independent distribution (no dependency every thing in the community was independent)
which biologist was right
it depends typically on abiotic conditions but is typically not interdependent
what guidelines wound there be if species distributions are independent
they should depend only on individual habitat requirements and there should be gradual changes in species along a line transpect (rise and fall in abundance based on conditions not species)
you will see a gradual change over indepedent species expect for when
ecotone which is a larger change
based on Robert Whittaker’s plant species in the Great Smoky Mountains was it interdependent or independent
independent: different tree species appeared and disappeared at different elevations corresponding to changes in moisture (elevation)
problem with observational studies
cohorts of species may also be evidence for similar biotic or abiotic requirements, and species may be linked by correlations with a 3rd(4th or 5th) variable and not have any interdependencies with one another at all
what can experimental manipulation provide evidence for
support causation
experiment test of interdependency
if species are interdependent then removing a species should cause other species to decline, if changes are neutral or positive species are independent
what conditions do species frequently exhibit interdependence
species living under harsh environmental conditions (high elevation)
why might harsher environments result in greater facilitation
neighboring plants reduce stress by buffering wind, cold, and herbivory and by creating more favorable microhabitats
species richness
the number of spcies in a community
relative abundance
the proportion of individuals in a community represented by each species
species evenness
a comparison of the relative abundance of each species in a community
rank-abundance curve
a curve that plots the relative abundance of each species in a community in rank order from the most abundant species to the least abundant species
what communties have higher diversity
communities with higher species richness and greater evenness
diversity
implies high number of species and abundance of species
flat abundance curve
high evenness
titled abundance curve
low evenness
Two communities each have four species. One community is dominated by a single species, while the other has all species at similar abundances. What does this tell you about their diversity?
Both communities have the same species richness (4 species), but they differ in evenness.The community dominated by one species has low evenness.The community with similar abundances has high evenness.
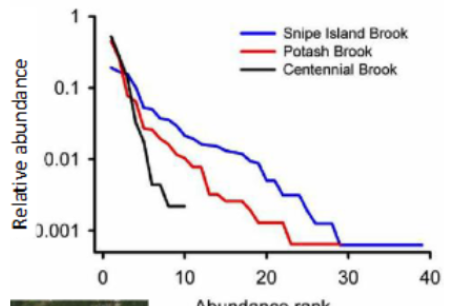
Which stream has the highest species richness? Eveness?
blue has the highest species richness (goes further down the x axis and blue is flattest so most evenness
what does species diversity depend on
resources available, habitat diversity, influential species, frequency or intensity of disturbances
to understand the influnece of resources ecologist examined what relationship
productivity and species richnness
productivity
approximation of available resources
Research can conduct a meta-analysis to identify broad patterns what is meta-analysis
statistical technique in which data from many studies are combined to test a particular question
what is the curve that might be the general pattern that we are looking for across all different communties
hump shape curve because at very low levels and high levels of productivity going to see fewer species
Why lower species at lower level productivity
each propulation probably has lower carrying capacity meaning population smaller
why few species at high level
some species are just really good competitors they finish resources up very quickly leaving nothing for other species in the community
CSR triangle
idea of how species specialize and jacks of all traits
competitors in CSR triangle
throw all their available resources into traits that allow them to be good competitors
stress tolerators in CSR
some species throw all their resources and developmental efforts into becoming really good stress tolerators (low water, low resources)
ruderal
needy, species that put all their life history strategy effort into being really good reproducers, they reproduce really quickly and can recover well after disturbance
most species exist where in the CSR triangle
center, combination of those things but when talking about a limited number of resources in the lifetime (life history trade offs) have to figure out how to allocate stuff
hump shape curve
high level of productivity: competitors, no stress in the environment, implying things are great because no other species are left, low level of productivity: component of the population more likely to go extinct but also have ton of stress and so stress tolerators will be seen, middle of curve are species that have a combination of traits because environments are not so extreme
which community is most species rich
medium productity
park grass experiment showed what
An area already starting with some resources adding resources caused a decline in species richness (diversity) of producers so not hump shape (rare)
what does fertilization do
make competitors more competitive
habitat diversity and species richness
not a situation where you see a hump shape curve (tree height)
influential species and species richness
influential species often increase species richness by preventing competitive dominance or by creating habitat that supports more species
keystone species
a species that substantially affects the structure of communities although species might not be particularly numerous
example of keystone species
starfish keep muscles in check without them muscle take over and nothing else can use substrate
ecosystem engineers
A keystone species that affects communities by influencing the structure of a habitat
difference in ecosystem enginners
impact on their community because building structures that other species will use
disturbance and species richness
based on intermediate disturbance hypothesis
intermediate disturbance hypothesis
more species are present in a community that experiences occasional disturbance than in a community with either frequent or rare disturbances (mowing lawn, forest fires or landslides)
Why do you not see many species if the disturbance are not very frequent or intense
those species that are good competitors or ruderals tend to do well
where do you see high level of diversity
at the intermediate of disturbances, whether the intensity of frequency, no one has an advantage and lots of species can coexist
food chain
a linear representation of how different species in a community feed on each other
food web
a complex and realistic representation of how species feed on each other in a community
tertiary consumers
eat secondary consumers
primary consumers
eat producers
secondary consumer
eat primary consumers
what does the trophic levels (level in a food web) start off as
primary producers
Communities can be organized by guilds which are
based on specifically what/how they eat (leaf eaters, root chewers, nectar sippers)
how can communities also be organized
when the abundance of trophic groups is determined by the existence of predators at the top of the food web or the energy available from producers
direct effect
an interaction between 2 species that does not involve other species but can set off a chain of events affecting other species in the community
indirect effect
an interaction between 2 species that involves one or more intermediate species
trophic cascade
indirect effects in a community that are initiated by a predator (cod→herring→zooplankton→phytoplankton→water quality)
density-mediated indirect effect
indirect effect caused by changes in the density of the intermediate species
trait-mediated indirect effect
indirect effect caused by changes in a trait of the intermediate species
community stability
the ability of a community to maintain a particular structure
resistance
how much a community changes when disturbed
resilience
the time it takes after a disturbance to return to its orginal state
a more diverse community means what
it is more stable
alternative stable states
when a community is disturbed so much that the species composition and relative abundance of populations in the community change, the new community structure is resistant to further change