N2NN3 - A Bit Out of Sorts: Mood Disorders
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
RNAO - Delirium, Dementia, and Depression in Older Adults: Assessment and Care (pp. 15, 70-73, 76-77)
Recommendations Related to Depression
Assessment:
- Assess for depression during assessments and ongoing observations when risk factors or signs and symptoms of depression are present . Use validated, context specific screening or assessment tools, and collaborate with the older adult, his/ her family/care partners, and the interprofessional team
- Assess for risk of suicide when depression is suspected or present
- Refer older adults suspected of depression for an in-depth assessment by a qualified health-care professional . Seek urgent medical attention for those at risk for suicide and ensure their immediate safety
Planning:
- Develop an individualized plan of care for older adults with depression using a collaborative approach . Where applicable, consider the impact of co-morbid dementia
Implementation:
- Administer evidence-based pharmacological and/or non-pharmacological therapeutic interventions for depression that are tailored to the person’s clinical profile and preferences
- Educate older adults with depression (and their families/care partners, if appropriate) about depression, self-management, therapeutic interventions, safety, and follow-up care
Evaluation:
- Monitor older adults who are experiencing depression for changes in symptoms and response to treatment using a collaborative approach . Document the effectiveness of interventions and changes in suicidal risk
Risk Factors & Signs of Depression
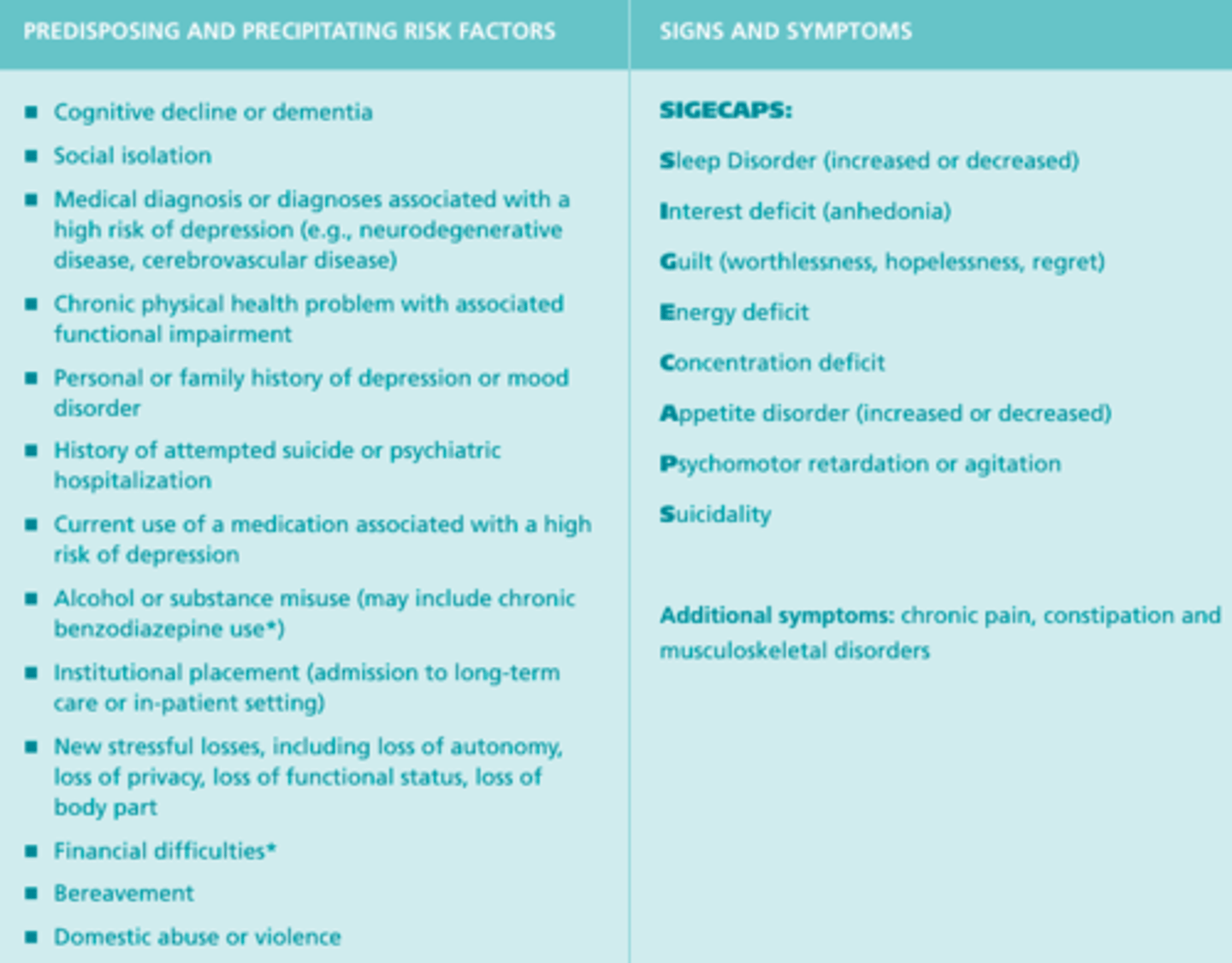
Assessment for Depression
- A detailed assessment for depression should occur when risk factors are present or when depression is suspected
- A variety of tools and approaches have been validated for depression screening and assessment in older adults—for example, depression scales for older adults, scales for self-report and proxy report, tools for assessing depression in people with dementia, tools for those with significant language or communication difficulties, and tools for assessing suicide
- Other aspects of an assessment may include a history and physical exam, diagnostic testing, an assessment of contributing factors, tests to rule out alternative diagnoses, and an assessment of functional impairment
Screening for Depression
- Three clinical guidelines suggest that organizations consider screening processes, and one recommends screening upon admission to long-term care and at regular intervals or after significant changes
- Assess for depression when risk factors or signs and symptoms of depression are present
Other Words for Suicide
- Harming yourself
- Wishing away your life
- Wishing you weren't living
- Ending your life
- Hastening death
Steps for Active Suicidal Ideation
- Call a crisis line, crisis team, or local emergency phone number, or take the person to the emergency department
- Determine whether the person has access to a means or has the ability to end his/her life
- Maintain safety: do not leave the person alone, and consider warning others who may be at risk
Actions to Support a Person Who is at Risk for Suicide
- Assess whether the person has adequate social support
- Provide the person with information regarding sources of help/support
- Consider a referral to specialized mental health services
- Increase the level of support (ex. more frequent phone contact)
- Assess the potential toxicity in overdose if an antidepressant is prescribed or the person is taking other medication that could be used to end one's life, and, in collaboration with the person and his/her prescribing practitioner, explore the possibility of limiting the dose
Non-Pharmalogical Therapies for Depression
- Reminiscence
- Mindfulness
- Behavioral activation
- Music therapy
*Nurses should reinforce the benefits of, advocate for, and support the use of such therapies
Psychotherapy Interventions for Depression

Exercise Interventions for Depression

Psychological & Social Interventions for Depression

Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) Interventions for Depression

Pharmalogical Interventions

RNAO - Nursing Best Practice Guideline: Assessment and Care of Adults at Risk for Suicidal Ideation and Behaviors (pp. 12, 19-32, 94-95)
Practice Recommendations - Part #1
- The nurse will take seriously all statements made by the client that indicate, directly or indirectly, a wish to die by suicide, and/or all available information that indicates a risk for suicide
- The nurse works toward establishing a therapeutic relationship with clients at risk for suicidal ideation and behaviour
- The nurse works with the client to minimize the feelings of shame, guilt and stigma that may be associated with suicidality, mental illness and addictions
- The nurse provides care in keeping with the principles of cultural safety/cultural competence
- The nurse assesses and manages factors that may impact the physical safety of both the client and the interdisciplinary team
- The nurse recognizes key indicators that put an individual at risk for suicidal behaviour, even in the absence of expressed suicidality. For individuals who exhibit risk indicators, the nurse conducts and documents an assessment of suicidal ideation and plan
- The nurse assesses for protective factors associated with suicide prevention
- The nurse obtains collateral information from all available sources: family, friends, community supports, medical records and mental health professionals
- The nurse mobilizes resources based upon the client's assessed level of suicide risk and associated needs
Practice Recommendations - Part #2
- The nurse ensures that observation and therapeutic engagement reflects the client's changing suicide risk
- The nurse works collaboratively with the client to understand his/her perspective and meet his/her needs
- The nurse uses a mutual (client nurse) problem-solving approach to facilitate the client's understanding of how they perceive his/her own problems and generate solutions
- The nurse fosters hope with the suicidal client
- The nurse is aware of current treatments to provide advocacy, referral, monitoring and health teaching interventions, as appropriate
- The nurse identifies persons affected by suicide that may benefit from resources and supports, and refers as required
- The nurse may initiate and participate in a debriefing process with other health care team members as per organizational protocol
- The nurse seeks support through clinical supervision when working with adults at risk for suicidal ideation and behaviour to become aware of the emotional impact to the nurse and enhance clinical practice
Stigma of Mental Illness
- The negative attitude based on prejudice and misinformation that is triggered by a marker of illness (ex. odd behaviour, or the mention of psychiatric treatment in a curriculum vitae)
Stigma of Suicide
- A negative attitude based on prejudice and misinformation that is triggered by a suicide or suicidal ideation or behaviour
- Suicide, and suicidal ideation and behaviour is sometimes, but not always, linked to a mental illness
- The presence of stigma is problematic because it leads to ongoing discrimination and marginalization with detrimental effects for clients, families and communities of people, including decreased self-esteem, increased isolation and vulnerability and, in the presence of a mental illness, a higher probability of relapse
Suicide
- An abrupt ending to life and the most extreme way in which people respond to overwhelming distress
Goal of Suicide Related Interventions
- The goal of intervention is to reduce the risk of suicidal ideation and behaviour, and to promote the safety of the client, staff and others
Treatment Planning for Suicide
- The nurse considers factors that support mental health and wellbeing, keeping in mind determinants of health, including social and cultural factors
- It is important to support internal strengths and self-esteem, and the development of emotional coping and life skills needed for stress management
Risk Factors for Suicide - Demographic or Social Factors
- Being an older adult
- Being male
- Poverty
- Being Aboriginal, especially youth ages 14-24
- White race
- Gay, lesbian or bisexual orientation - association. with attempts
- Being single (widow, divorced, separated, single)
- Social isolation, including new or worsening estrangement, and rural location
- Economic or occupational stress, loss, or humiliation
- New incarceration
- History of gambling
- Easy access to firearms
Assessment & Care of Adults at Risk for Suicidal Ideation & Behaviour
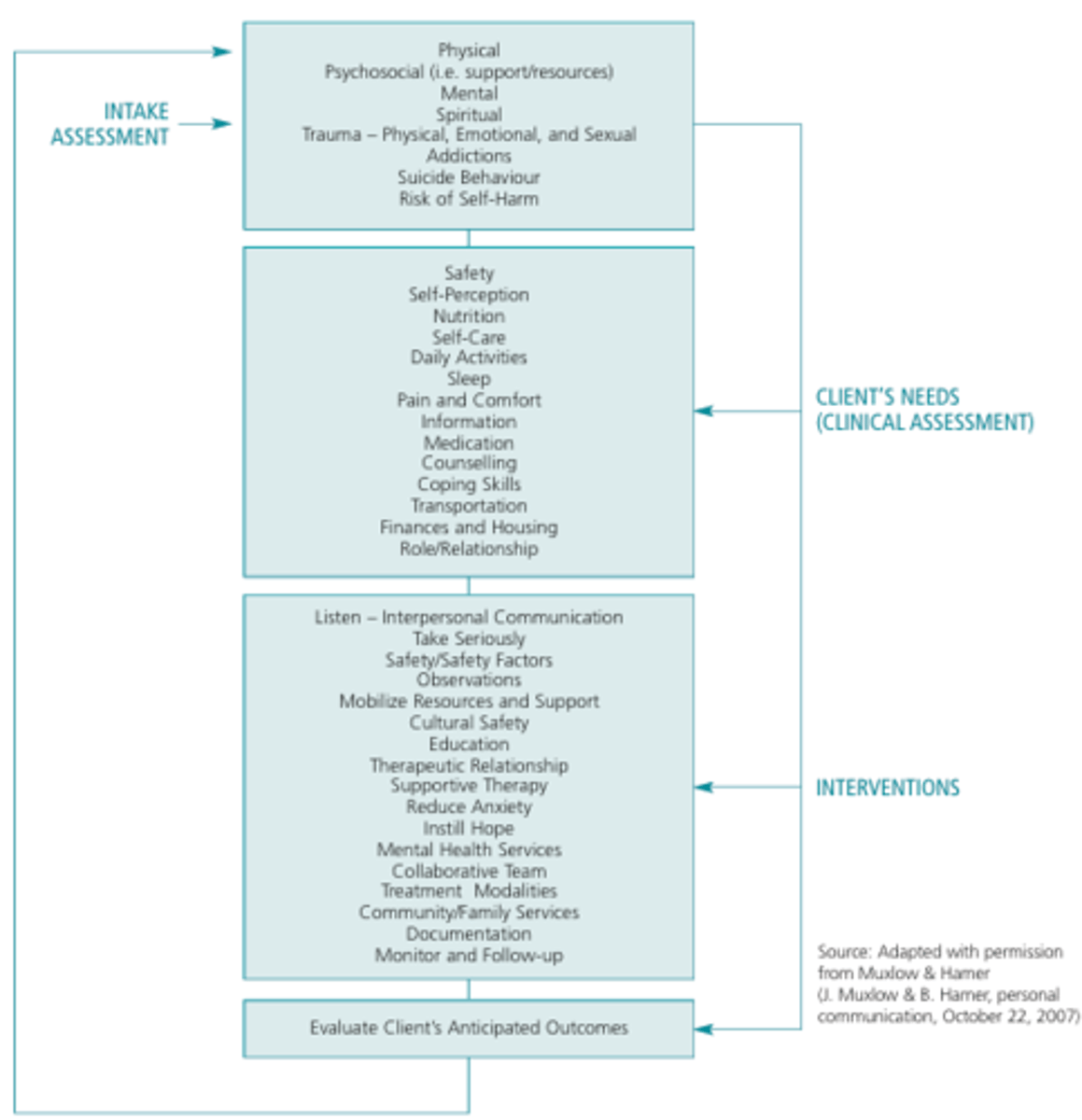
Expressions of Suicide
- Clients express suicidal ideation overtly with statements such as 'I am going to kill myself', and through indirect statements or behaviours
- Indirect statements, such as 'I can't take it anymore', are significant, as a person's willingness to overtly disclose thoughts about suicide may be restricted for many reasons (i.e. cultural or religious beliefs and/or a desire for concealment in order to limit intervention by others
"Taking Seriously"
- To conduct a suicide risk assessment, to document the assessment, to discuss the assessment with other members of the client's health care team and create a plan for safety and care as determined by the outcome of the assessment
- If there is any uncertainty about suicidal intent and risk, the case should be discussed as soon as possible with appropriate health care providers or consultants, and the client's status should be considered a potential emergency until assessed otherwise by clinicians
- Includes being sensitive to, and aware of, the constellation of social situations such as sudden losses, and emotional states such as depression, that combine to increase the risk factors for suicide

Nurses & Patients with Suicide
- To minimize the effect of the nurse's own potentially negative reactions to the client, it is essential that nurses engage in reflective practice and obtain support to address such challenges
- Beware of your own negative attitudes, beliefs and behaviours, which may have negative impact on the client
Cultural Safety, Nurse, & Patient
- Cultural safety is more than recognizing and respecting "difference" - it is a relational concept that demands engagement with policies and practices that impact health care and health
- The nurse demonstrates acceptance and respect for the 'culture' of the client and for the associated differences, in addition to advocating for change in response to policies and practices that may be experienced as 'unsafe' by the client
- Cultural safety is safe service as defined by those who receive the service
Physical Safety of the Nurse & Patient
- Before intervening to enhance the client's safety, the nurse needs to ensure her/his own safety first
- Attending to the physical safety of the client is an ongoing priority when providing nursing care and should be initiated before a thorough clinical assessment of suicide risk is completed
- The nurse should be alert to the physical setting and any item in it that may pose a threat to safety
- It is also suggested that external stimuli, such as noise and commotion, may increase agitation and aggression
- Life threatening injuries should be addressed immediately
- Considerations of emotional and psychological safety should be balanced with ensuring physical safety
Potentially Hazardous Items for Suicidal Patient

Risk Factors for Suicidal Ideations
- Being male
- Being elderly
- Hopelessness
- Previous suicide attempts
- Past and current psychiatric illness
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Substance use
- Intoxication
- Access to lethal means
- Engaging in risky behaviour (ex. increased use of alcohol or substances, reckless driving)
- Self-neglect (ex. change in appearance, including changes in weight and appetite)
- Change in personality
- Change in mood (ex. depression, anxiety, agitation)
- Social withdrawal and isolation, including a loss of enjoyment in activities

Psychiatric/Psychosocial Assessment
- Presenting problem and/or current mental status
- History of present illness
- Past psychiatric history
- Past medical/surgical history
- Current and recent past medication
- Drug allergies
- Substance use history
- Forensic history
- Family history
- Psychosocial history
- Nursing diagnosis

Comprehensive Assessment Regarding Suicidal Ideation & Plan
- Presence of risk factors
- Lack or presence of protective factors (ex. spirituality, hope, future orientation, cultural and/or spiritual factors)
- Suicidal intent
- Plan
- Lethality
- Access to means
- Timeframe
- Hope
- Previous attempts
Risk Factors for Suicide - Clinical Factors
- Past and current major psychiatric illness, including bipolar, schizophrenia and major depressive disorder (especially depression)
- Personality disorder (borderline, narcissistic, antisocial)
- Impulsive or violent traits by history
- Current medical illness
- Family history of suicide
- Previous suicide attempts or other self-injurious or impulsive acts
- Current anger, agitation, or constricted preoccupation
- Current abuse of alcohol or drugs (including solvents)
- Easy access to lethal toxins (including prescribed medication)
- Formulated plan, preparations for death or suicide note
- Low ambivalence about dying versus. living
- Childhood trauma (sexual abuse, physical abuse)
- Suicidal ideas (current or previous)
- Suicidal intent
- Hopelessness
- Severe or unremitting anxiety
- Panic attacks
- Impulsiveness
- Aggression
Risk Factors for Suicide - Precipitants
- Recent stressors (especially losses of emotional, social, physical, or financial security)
Protective Factors for Suicide
- Intact social supports
- Active religious affiliation or faith (may also be a risk factor if shame/guilt about behaviour is involved)
- Marriage and presence of dependent children
- Ongoing supportive relationship with a caregiver
- Positive therapeutic relationship
- Absence of depression or substance abuse
- Access to medical and mental health resources
- Impulse control
- Proven problem-solving and coping skills
- Pregnancy
- Life satisfaction
- Relief about not completing suicide
- Sense of 'unfinished business'
- Good self-esteem, self-confidence
- Awareness of significant others about their suicidal thoughts
- Sense of belonging
National Guidelines for Seniors Mental Health: The Assessment of Suicide Risk and Prevention of Suicide (pp. 66-68)
Self-Harm Behaviour
- The literature indicates that any expression of a wish to die and any self-harm behaviour increases the risk for death by suicide and so must be regarded seriously
- It should also be noted that suicidal intent is not equivalent to the lethality of the means used, necessitating explicit assessment of both intent to die and the lethality of self-harm behaviour
- Older adults might downplay thoughts of suicide owing to guilt, stigma, and fear of hospitalization
Therapies for Older Adults
- The Prevention of Suicide in Primary Care Elderly Collaborative Trial (PROSPECT), found that combined antidepressant (citalopram) and psychotherapeutic treatment (interpersonal psychotherapy) provided in a collaborative care context helped resolve depression and reduce suicide ideation among older primary care patients
- Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) may be of value in treating depressed and suicidal patients, there have been no studies to date of ECT for the amelioration of suicidal ideation or behaviour in older adults
- Thoughtful risk management strategies,attending to client safety and to the well-being of both clients and providers,may help reduce clients'suicide risk and provider burnout
Table #1

Table #2

Table #3

Table #4

Table #5

Medication Administration
