EXAM 4: Chapter 13 The Nervous System II: The Central Nervous System (CNS) Part 1単語カード | Quizlet
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
- provides voluntary and involuntary movement
- functions in interpretation and integration of sensation
- provides consciousness and cognitive functions
- involved in innervation of the head through the cranial nerves
What are the functions of the brain?
- cerebrum
- diencephalon
- brain stem
- cerebellum
What are the 4 basic parts of the brain?
gray matter of brain
mostly cell bodies of neurons; some short unmyelinated axons and dendrites; some neuroglia
located in outer brain cortex
white matter of brain
mostly myelinated axons of neurons
located in inner brain cortex
brain stem
Connects the brain and spinal cord
white matter external to central gray matter
cerebrum and cerebellum
additional external cortex of gray matter
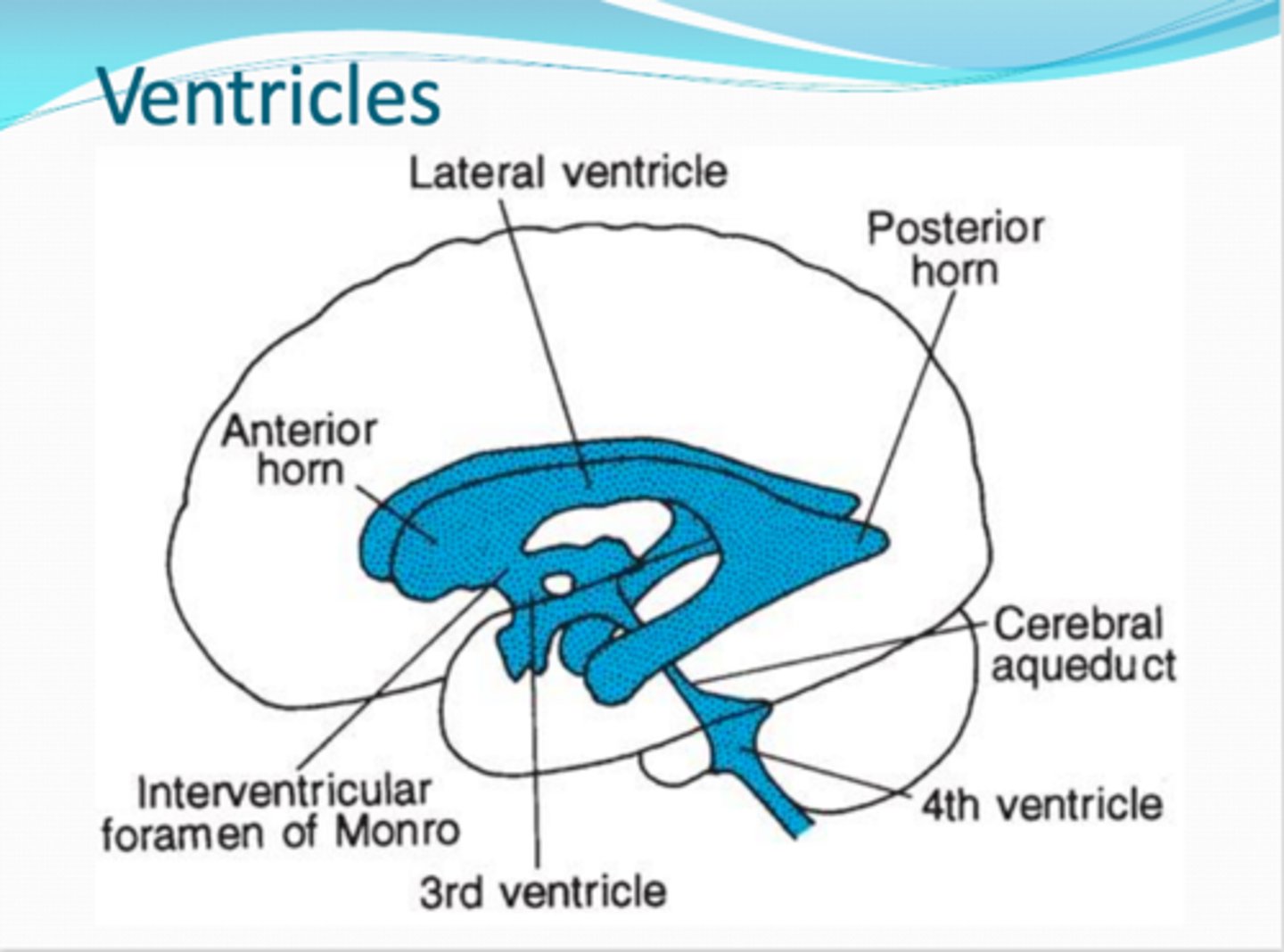
ventricles
expansions of the brain's central cavity
filled with CSF and lined with ependymal cells
floating and cushioning the brain and spinal cord
What is the function of CSF?
lateral ventricles
x2
span both the cerebral hemispheres, separated by the septum pellucidum
third (3rd) ventricle
ventricle that is enclosed by the diencephalon
- cutting the brain in half destroys this ventricle
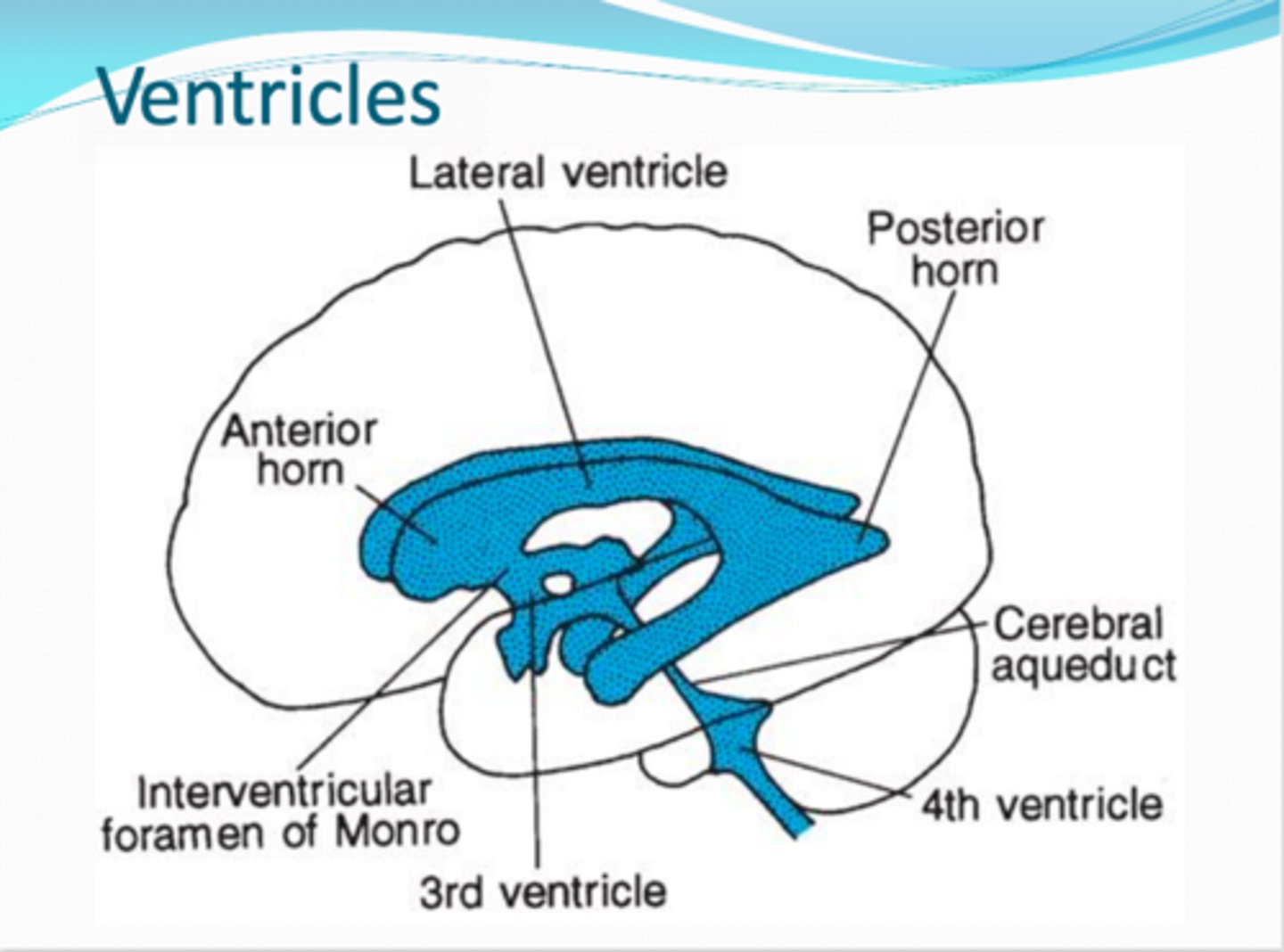
fourth (4th) ventricle
located in the hindbrain (dorsal to pons and superior half of medula)
- continues to inferiorly as the central cavity in the spinal cord
choroid plexus
part of ventricles of the brain
vascular complex in the roofs of the 3rd and 4th ventricles; responsible for CSF production
fissures
deepest grooves, separates major portions of the brain
transverse cerebral fissure
fissure that separates cerebrum from cerebellum inferiorly
longitundinal fissure
fissure that separates the right and left cerebral hemispheres
sulci (sulcus)
"furrow"
the many grooves on the surface of the brain
gyri (gyrus)
"twister"
twisted ridges of brain tissue (lumpy bumps)
primary motor cortex
conscious control of skeletal muscles
function of frontal lobe
primary sensory cortex
conscious perception of touch, pressure, vibration, pain, temperature, and taste
function of parietal lobe
visual cortex
perception of visual stimuli
function of occipital lobe
auditory cortex and olfactory cortex
function of temporal lobe
- cerebral cortex of gray matter (superficial)
- cerebral white matter (internal)
- basal nuclei (basal ganglia) (deep in white matter)
What are the three largest regions within the cerebrum?
cerebral cortex
site of conscious sensory perception, voluntary movements and higher though functions
1. motor areas
2. sensory areas
3. association areas
What are the 3 functional areas of the Cerebral Cortex? (cerebrum)
- primary motor cortex
- premotor cortex
- frontal eye field
- Broca's area
What are the motor areas of the cerebral cortex?
primary motor cortex
a motor cortex that controls precise or skilled voluntary movements of the body
(esp forearms, fingers, and facial muscles)
contralateral projection
R and L motor cortices control muscles on the L and R sides of the body, respectively
motor homunculus
the body map on the motor cortex
(feet to face)
face and hand are represented large
somatotopy
general principle of "body mapping"
premotor cortex
a motor cortex that controls more complex movements than does the primary motor cortex
frontal eye field
a motor area that controls voluntary eye movements
Broca's area
a motor area in the Left hemisphere only that manages speech production
frontal lobe area
Where are the motor areas of the cerebral cortex located?
parietal, temporal and occipital lobes
Where are the sensory areas of the cerebral cortex located?
primary somatosensory cortex
a sensory cortex that functions in
conscious awareness of general somatic senses
spatial discrimination
contralateral projections
sensory homunculus
a body map of the sensory cortex
(feet to face)
lips and hands are large
somatosensory association cortex
a sensory cortex that integrates different sensory inputs (touch, pressure) into a understanding of WHAT IS BEING FELT
visual (striate) cortex
a sensory cortex that receives visual info that originates on the retina of the eye
visual association area
a sensory area that communicates with the visual (striate) cortex by making sense of what is seen
continues processing of visual info by analyzing color, form and movement
auditory cortex
a sensory cortex that function in conscious awareness of sound
auditory association area
a sensory area that permits evaluation of a sound
located in the Left hemisphere, center of Wenicke's Area
gustatory cortex
a sensory cortex that function in conscious awareness of taste stimuli
vestibular (equilibrium) cortex
a sensory cortex that function in conscious awareness of the sense of balance
olfactory cortex
a sensory cortex that function in conscious awareness of smell
cerebral cortex (cerebrum)
Where do higher-order functions perform?
association areas
Higher-order processing areas
- tie together the different kinds of sensory information received
prefrontal cortex
large region of frontal lobe, anterior to motor areas
- MOST complicated cortical region
- performs many COGNITIVE FUNCTIONS
general interpretation area
part of the cortex that functions in integrating ALL different types of sensory information
language area
a complex of functional areas that surround the lateral sulcus in the left hemisphere
- involved in various functions related to language
Broca's area
speech production (motor)
Wernicke's area
speech comprehension (sensory)
cerebral white matter
comprised of many axons (or fibers) through which different areas of the cerebral cortex communicate
most of the fibers are myelinated and bundles into large tracts
commissure fibers
composed of fibers that run BETWEEN the two hemispheres
interconnect R and L hemispheres
corpus callosum
largest commissure; superior to lateral ventricles, deep within the longitudinal fissure
association fibers
connect different cortical areas within the SAME hemispheres
projection fibers
fibers that run vertically to and from the brain stem and spinal cord
basal nuclei (basal ganglia)
paired masses of gray matter embedded deep within the cerebral white matter;
coordinates with the cerebral cortex to control complex movements
1. caudate nucleus
2. amygdaloid body or nucleus (amygdala)
3. claustrum
What are the 3 nuclear groups of the basal nuclei (basal ganglia)?
Diencephalon
forms the central core of the forebrain;
connects the cerebrum to the brain stem structurally and functionally
thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus
What are the three structures of the diencephalon?
subconscious
Functions that occur in the diencephalon are almost exclusively ___________.
Epithalamus
part of the diencephalon that controls the circadian rhythm
Pineal gland is found here - secretes melatonin (sleep-wake cycle)
thalamus
part of the diencephalon that is a relay center (processing center) for sensory information
hypothalamus
part of the diencephalon that controls
autonomic functions; thirst, hunger, sexual desire,
sets emotional states
integrates with endocrine system
suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN)
a pair of cell clusters in the hypothalamus that regulates daily (circadian) rhythms
body's biological clock
autonomic centers
region found in hypothalamus that control heart rate and blood pressure via regulation of autonomic centers in the medulla oblongata
mamillary bodies
region found in hypothalamus that control feeding reflexes (licking, swallowing)
- mesencephalon (midbrain)
- pons
- medulla oblongata
What are the 3 structures of the brain stem?
Mesencephalon (midbrain)
lies between the diencephalon and the pons
coordinate visual and auditory reflexes
corpora quadrigemina
located in mesencephalon (midbrain)
act in the "startle response" - process visual and auditory information and generate reflexive responses to these stimuli
superior colliculi
part of the corpa quadrigemina located in mesencephalon (midbrain)
visual reflex
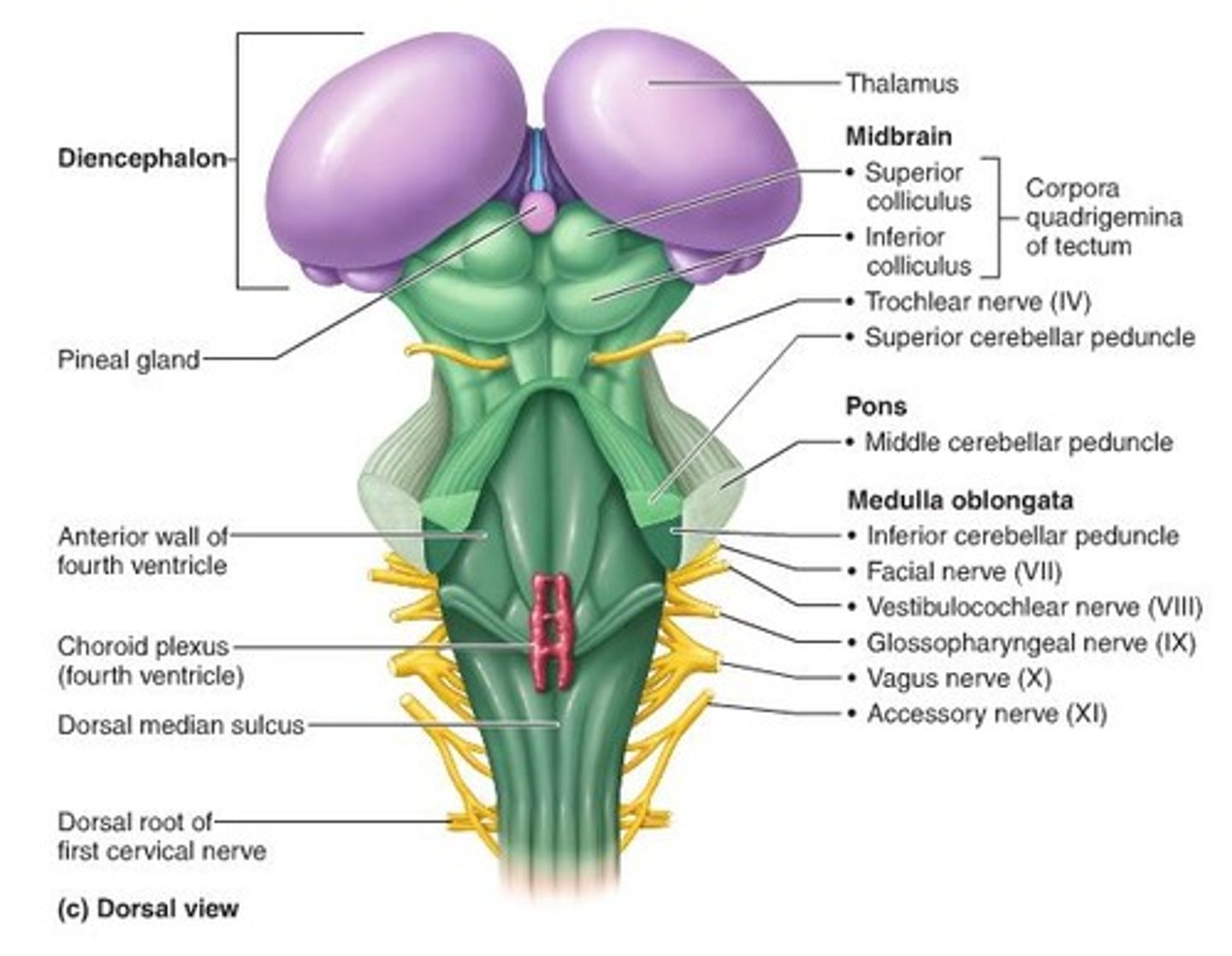
inferior colliculi
part of the corpa quadrigemina located in mesencephalon (midbrain)
auditory reflex
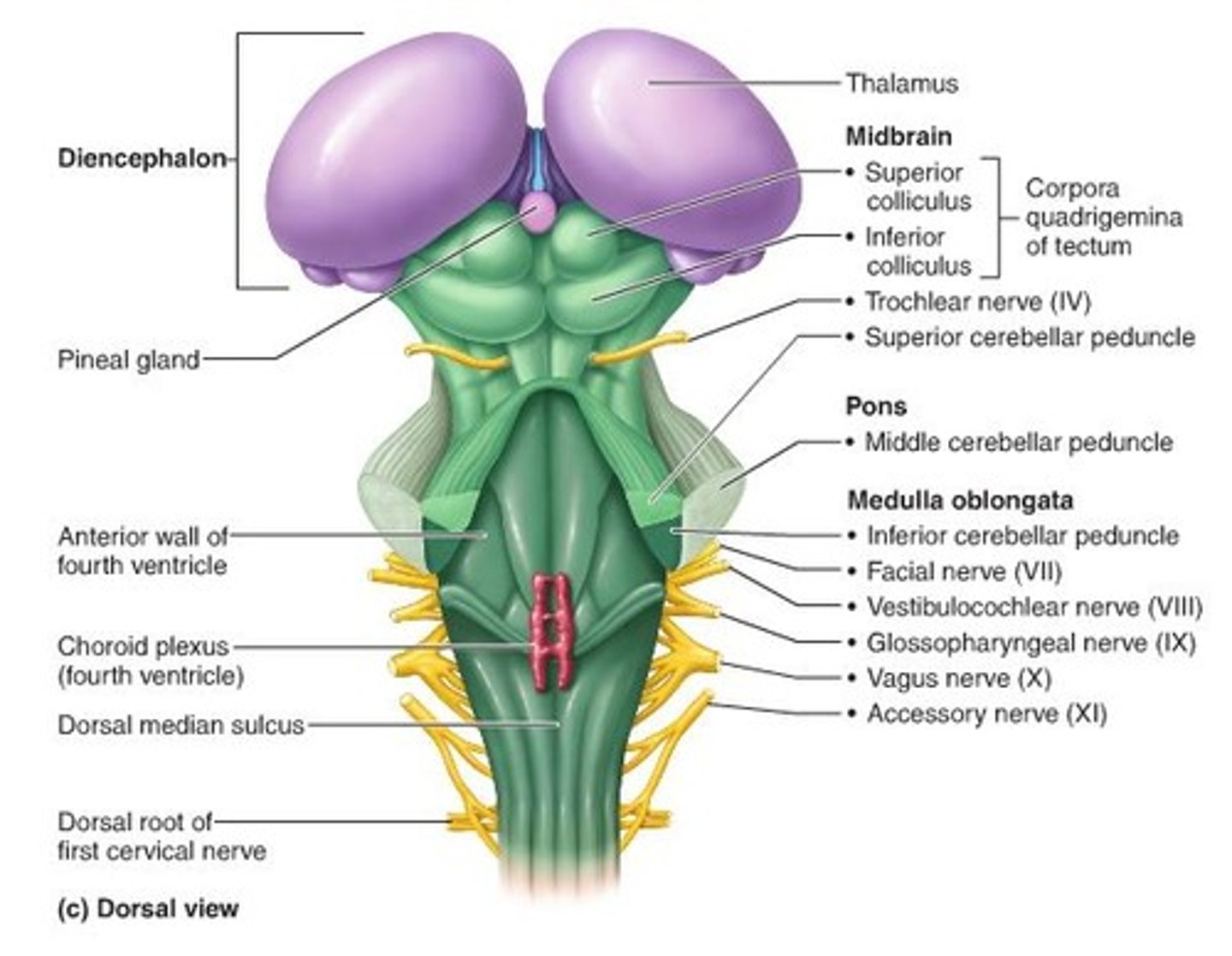
pons
structure on brain stem
HELPS REGULATE RESPIRATION, coordinate involuntary skeletal muscle movements and muscle tone, relays info to and from the brain/spinal cord
apneustic center and pneumotaxic center
What are the two centers of the pons that are concerned with the involuntary control of respiration?
medulla oblongata
Connects the brain and spinal cord
a relay station & controls visceral functions like blood pressure, breathing, and heart rate
cardiovascular center
part of the medulla that regulates blood flow and heart rate
respiratory rhythmicity center
part of the medulla that set pace for respiratory movements
works together with pons
Cerebellum
functions in:
smooth and coordinates body movements (unconsciousness)
helps maintain posture and equilibrium
"muscle memory"
vermis
Connects the two hemispheres of the cerebellum
"worm-like strx"
Purkinje cells
part of internal structure of cerebellum
contains large, highly branched type of cells
functions in subconscious coordination and control of ongoing movements of body parts