Cellular Energy and Respiration: Key Processes and Pathways
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What is the primary energy currency of the cell?
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
What are the products of ATP hydrolysis?
ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and a phosphate group (P)
How is ATP resynthesized in cells?
ADP and P are combined to form ATP.
What is the main fuel source for ATP synthesis in most cells?
Glucose, in the presence of oxygen (O2).
What are the products of cellular respiration?
Carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O), along with ATP.
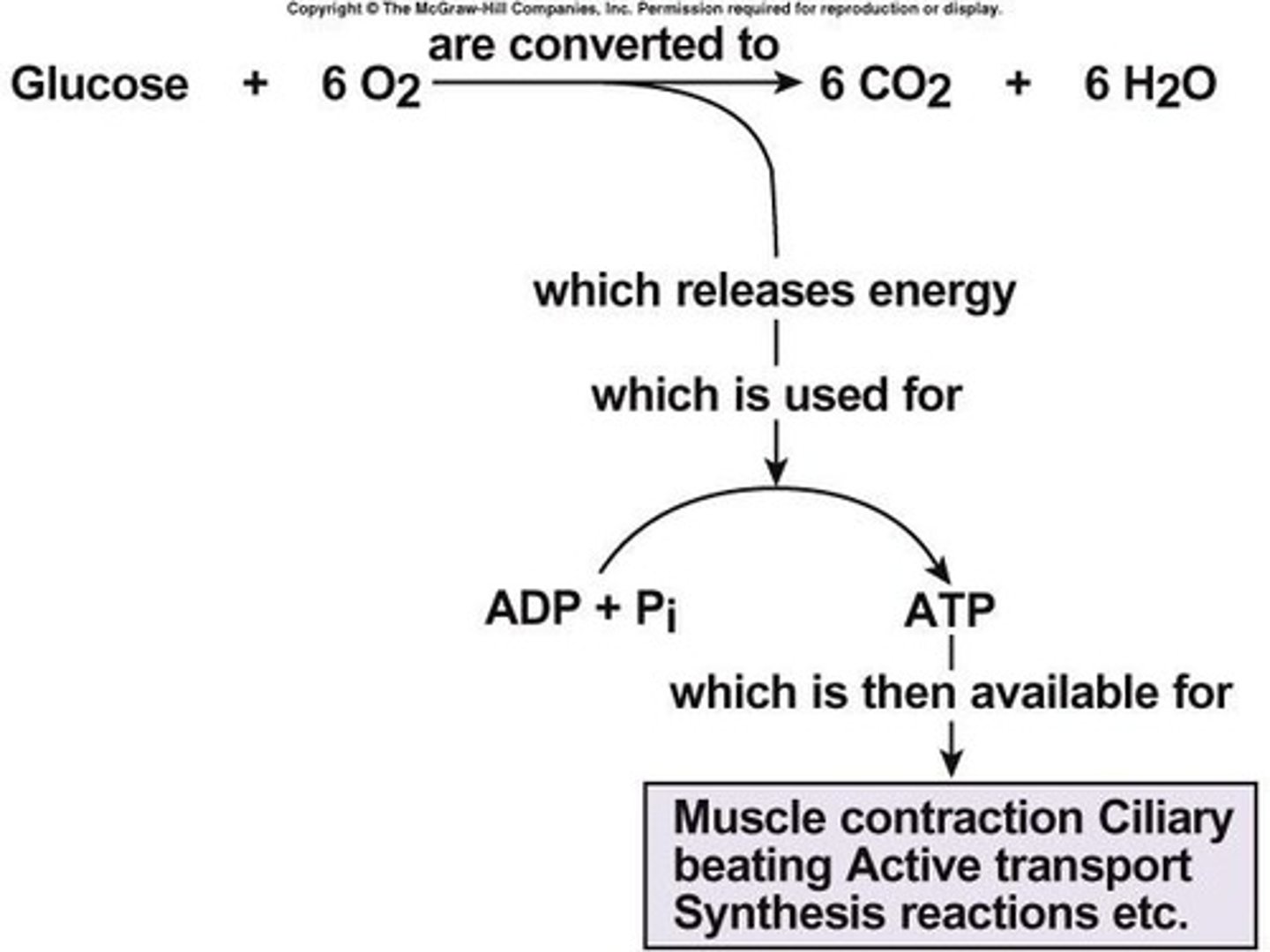
What is the overall equation for cellular respiration?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 38 ADP + 38 P → 6H2O + 6CO2 + 38 ATP.
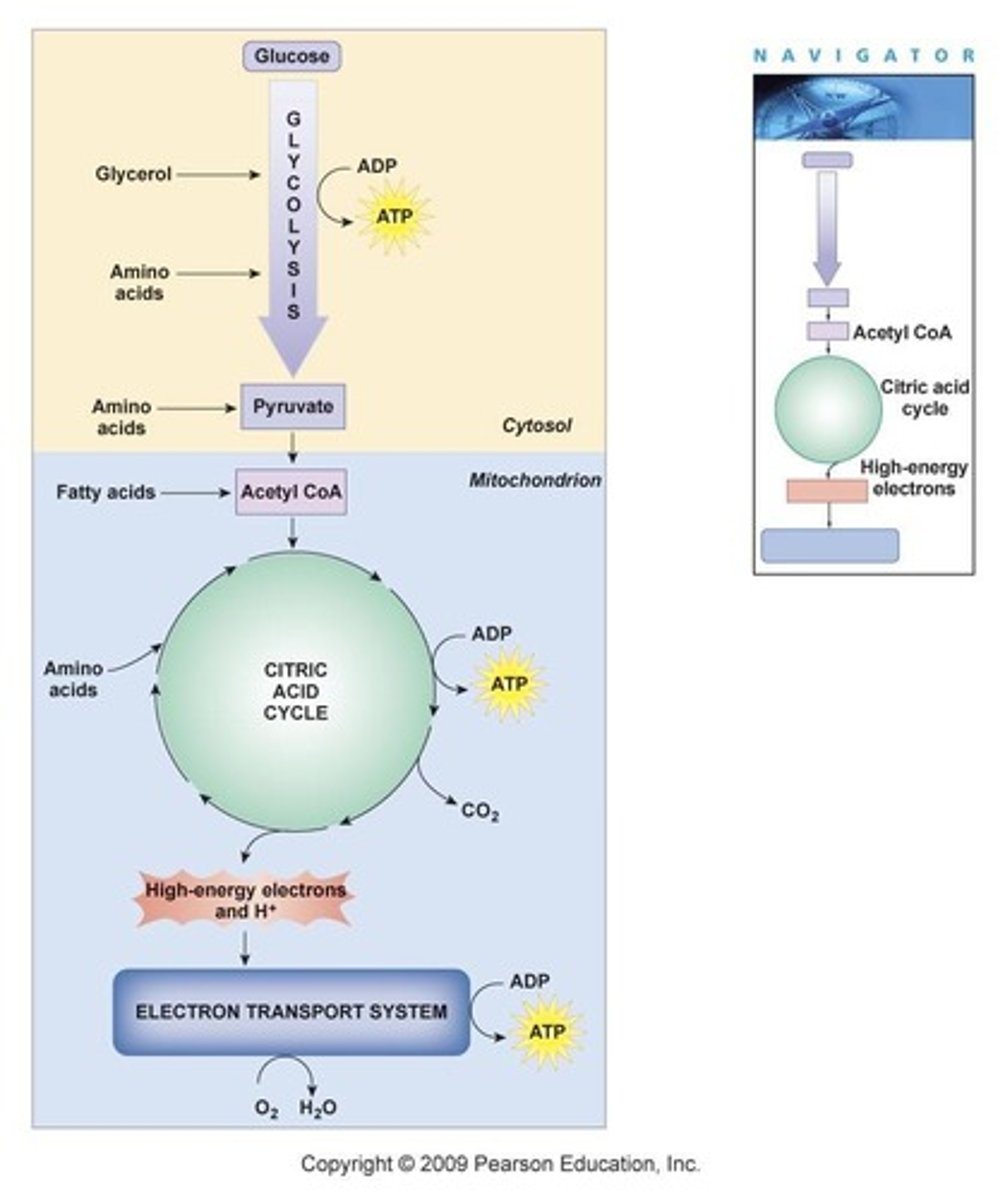
What are the three phases of cellular respiration?
Glycolysis, Krebs cycle (Citric acid cycle), and the electron transport chain.
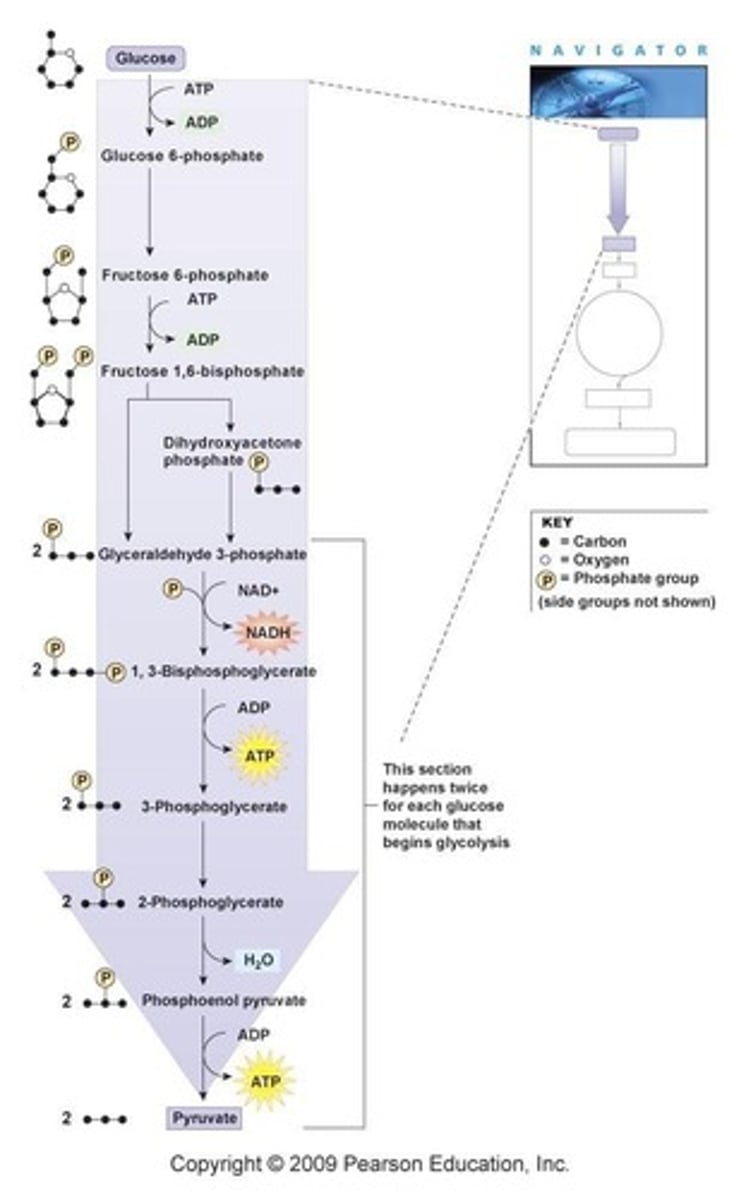
Where does glycolysis occur?
In the cytoplasm of the cell.
Where does the Krebs cycle take place?
In the mitochondrial matrix.
What is the role of the electron transport chain?
It synthesizes ATP using the H+ gradient created during glycolysis and the Krebs cycle.
What are the products of glycolysis?
2 molecules of ATP, 2 molecules of pyruvic acid, and 2 molecules of NADH.
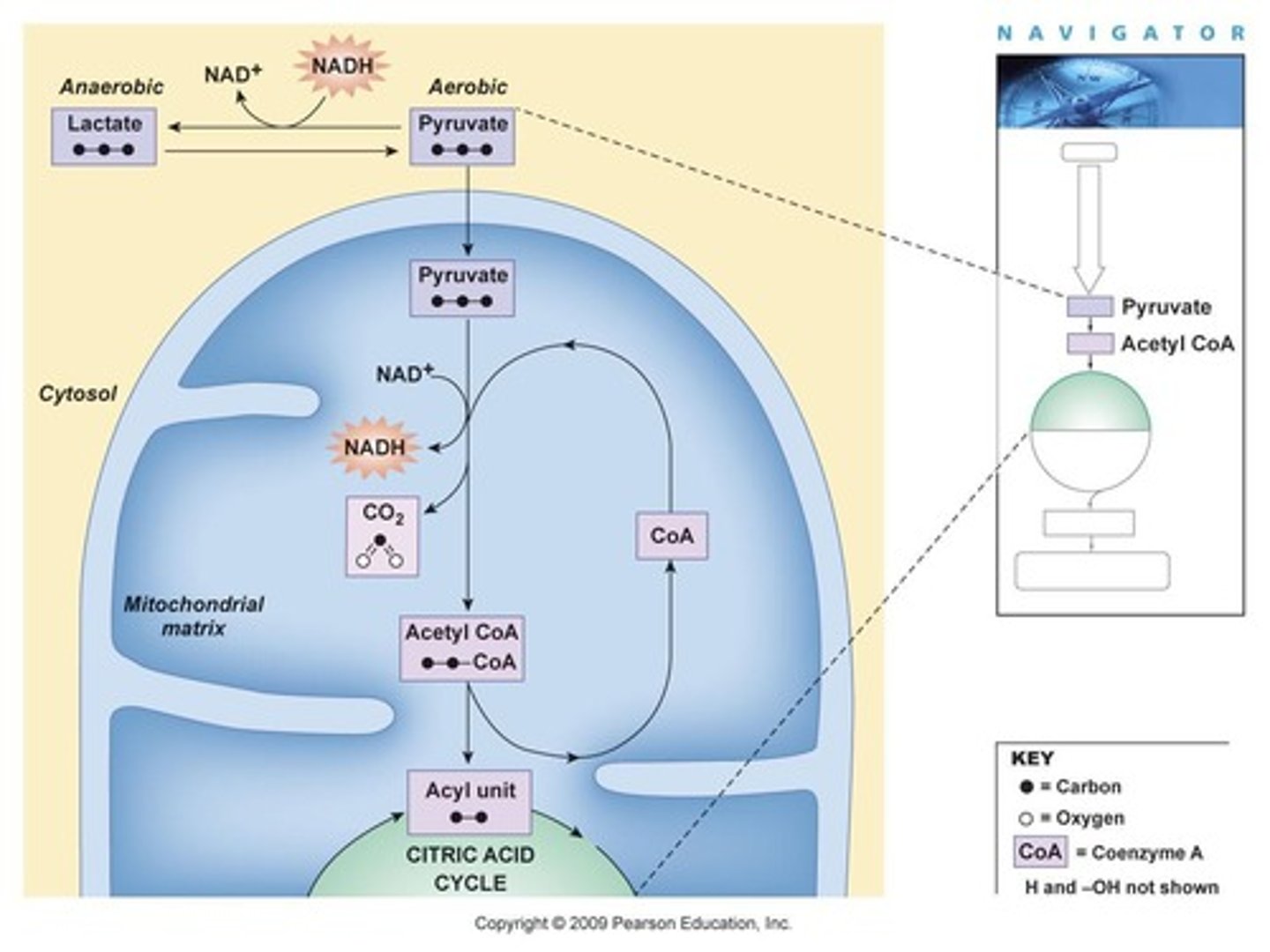
What happens to pyruvic acid in the presence of oxygen?
It is converted into Acetyl Coenzyme A (Acetyl CoA) for aerobic respiration.
What occurs during anaerobic respiration (fermentation)?
Pyruvic acid is converted into lactic acid, producing no additional ATP.
What is the consequence of lactic acid accumulation in muscles?
It causes muscle fatigue and soreness.
What is the process of converting pyruvic acid to Acetyl CoA called?
Decarboxylation.
What is produced during the conversion of pyruvic acid to Acetyl CoA?
2 molecules of CO2, 2 molecules of NADH, and 2 molecules of Acetyl CoA.
What is glycolysis often referred to as?
Sugar breaking.
How many ATP molecules are synthesized during glycolysis?
4 ATP are synthesized, but 2 are used, resulting in a net gain of 2 ATP.
What is the significance of the H+ gradient in cellular respiration?
It is used by the electron transport chain to synthesize ATP.
What is the main function of NAD+ in cellular respiration?
It accepts hydrogen atoms during oxidation, becoming reduced to NADH.
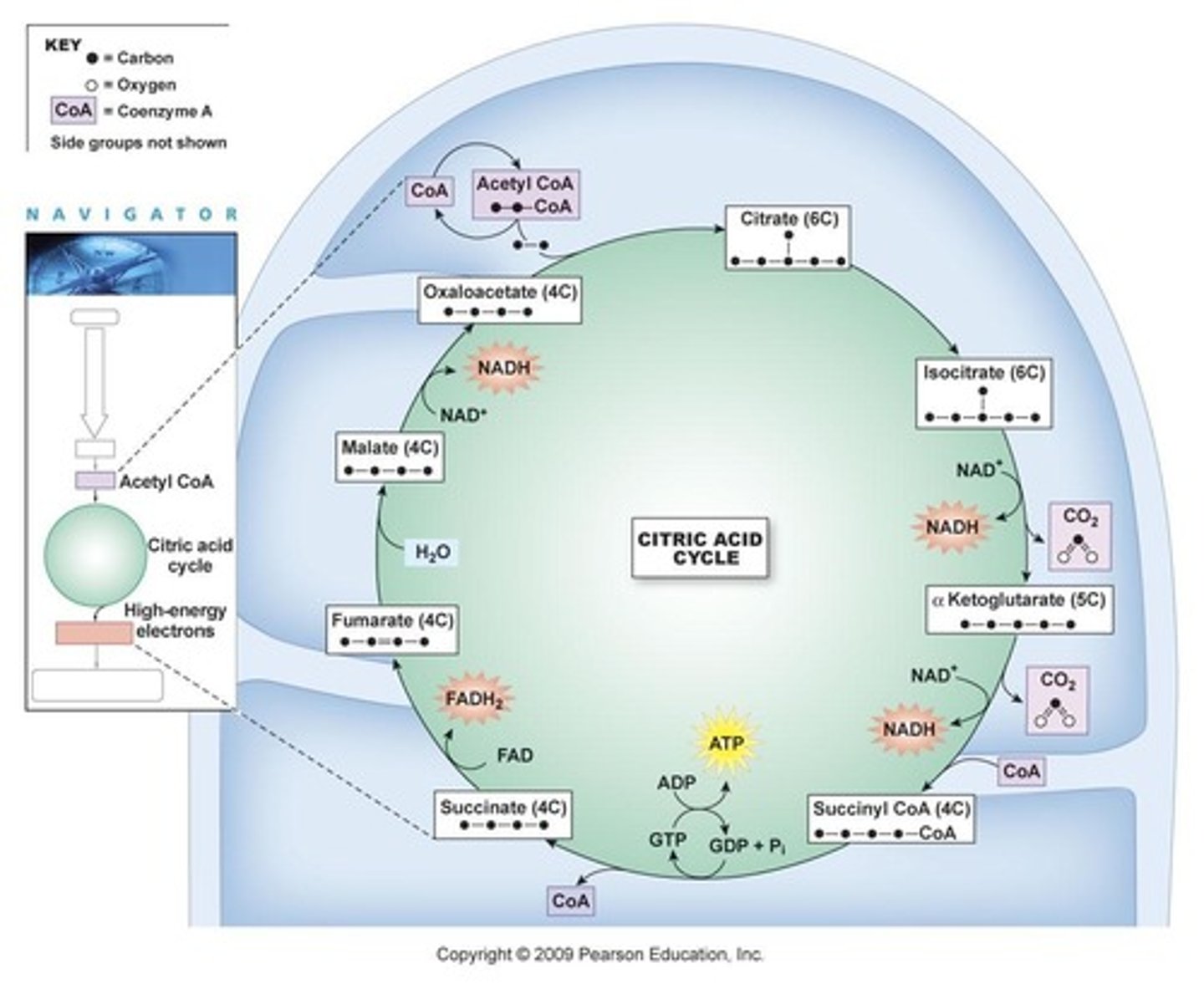
What is the Krebs Cycle?
A series of 10 biochemical reactions that begins and ends with a molecule of citric acid.
What molecule is formed when acetic acid combines with oxaloacetic acid in the Krebs Cycle?
Citric acid (6 carbons).
What are the main products of one turn of the Krebs Cycle?
3 NADH, 1 FADH2, 2 CO2, 1 ATP, and 1 oxaloacetic acid.
How many NADH molecules are produced from two turns of the Krebs Cycle?
6 NADH.
What is the role of NAD+ and FAD in the Krebs Cycle?
They are reduced to NADH and FADH2, contributing to the H+ gradient in the mitochondria.
What is the net ATP yield from glycolysis and the Krebs Cycle combined?
4 ATP (2 from glycolysis and 2 from Krebs).
What is the function of the Electron Transport Chain (ETC)?
To create a H+ gradient between the intermembrane space and the mitochondrial matrix.
How does NADH contribute to the proton gradient in the ETC?
NADH is oxidized by Enzyme complex 1, pumping 3 protons into the intermembrane space.
What is the difference in proton pumping between NADH and FADH2 in the ETC?
NADH pumps 3 protons, while FADH2 pumps 2 protons.
What is the role of ATP synthase in ATP production?
It allows H+ to diffuse down its gradient and uses the energy to synthesize ATP from ADP and P.
How many ATP molecules are synthesized from one NADH during oxidative phosphorylation?
3 ATP molecules.
How many ATP molecules are synthesized from one FADH2 during oxidative phosphorylation?
2 ATP molecules.
What is the total ATP yield from the oxidation of one glucose molecule?
34 of the 38 ATP molecules are synthesized by oxidative phosphorylation.
What happens to electrons at the end of the Electron Transport Chain?
They are transferred to oxygen atoms, forming water (H2O) in the mitochondrial matrix.
What is the significance of the proton (H+) gradient in the mitochondria?
It is the source of energy used to synthesize ATP as protons diffuse back into the matrix.
What is the starting molecule for the Krebs Cycle?
Oxaloacetic acid.
What is the end product of the Krebs Cycle that re-enters the cycle?
Oxaloacetic acid.
What are the two main phases of cellular respiration discussed?
The Krebs Cycle and the Electron Transport Chain.
What is oxidative phosphorylation?
The process of ATP synthesis that requires the oxidation of NADH and FADH2.