RxPrep/UWorld - Human Immunodeficiency Virus
1/175
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
176 Terms
Define HIV
HIV is a single stranded RNA retrovirus that uses the machinery in host CD4 T-helper cells (T cells) to replicate
How is AIDS diagnosed?
AIDS is diagnosed when the CD4 count falls below 200 cells/mm or the patient develops an AIDS defining condition
body can no longer ward off opportunistic infections and aids-specific malignancies
How can HIV be transmitted?
body fluids ( blood, semen, vaginal secretion, rectal secretion and breast milk)
mucus membranes
open wounds
sharing drug needles
unprotected sex
vertical transmission (mom to baby via preg, childbirth, or breastfeeding)
True or False: Most infections are caused by unprotected vaginal and rectal sex and sharing injection drug equipment, including needles
True
How do vertical transmission occur?
Vertical transmission (from mother to child) may occur, either during pregnancy, at birth or through breastfeeding
HIV screening recommedations:
everyone
high-risk (+ what are high risk)
Once for all patients
Annual testing:
hx of stis
hx of hepatitis
hx of TB
multiple sexual partners
sharing drug needles

What symptoms will a person with acute HIV infection experience?
how long do sx last?
non specific flu like symptoms, such as fever, fatigue/malaise, myalgia/arthralgias, lymphadenopathy and rash
few days to weeks

Criteria for AIDS diagnosis

HIV wasting syndrome treatment
stimulate appetite w/
dronabinol (cannabis-related drug)
megestrol (progestin)
When can HIV antibodies be detected?
4-12 weeks post-infection
initial HIV screening includes testing for what?
p24 antigens
and/or hiv1/hiv2 antibodies
after a positive initial screening for hiv antibodies, what must be done next?
confirmatory testing to differentiate b/t hiv 1 and hiv 2
if hiv confirmatory test to distinguish between hiv 1 and hiv 2 is...what comes next?
intermediate
negative (non reactive)
positive (reactive)
intermediate, negative: hiv 1 nucleic acid test to quantify viral load. if viral load undetectable, prob no hiv. if viral load +, then hiv
positive: HIV dx and subtype confirmed

What over the counter HIV test detects the presence of HIV antibodies and provides immediate results?
The OraQuick In Home HIV Test
When should the otc hiv test oraquick be done?
>3 months
if earlier may have false neg d/t lag in antibody production
HIV lifecycle
binding&attachment
, fusion,
reverse transcription, integration,
replication,
assembly,
budding
Define Stage 1: Binding/Attachment
HIV attaches to a CD4 receptor and the co-receptors (CCR5 and/or CXCR4) on the surface of the CD4+ host cell. The virus must bind/ attach to both a CD4 receptor and a co-receptor for the next step of viral replication to occur.
Define Stage 2: Fusion
The HIV viral envelope fuses with the CD4 cell membrane. HIV enters the host cell and releases HIV RNA, viral proteins and enzymes needed for replication.
Define Stage 3: Reverse Transcription
HIV RNA is converted to HIV DNA by reverse transcriptase. HIV DNA can then enter the CD4 cell nucleus
Define Stage 4: Integration
Once inside the CD4 cell nucleus, integrase is released and used to insert HIV DNA into the host cell DNA
Define Stage 5: Replication
Host cell machinery is used to transcribe and translate HIV DNA into HIV RNA and long chain proteins
Define Stage 6: Assembly
New HIV RNA, proteins and enzymes moves to the cell surface and assemble into immature HIV
Define Stage 7: Budding and Maturation
Immature HIV pushes out of the CD4 cell and protease breaks up the long viral protein chain, creating mature virus that can infect other cells
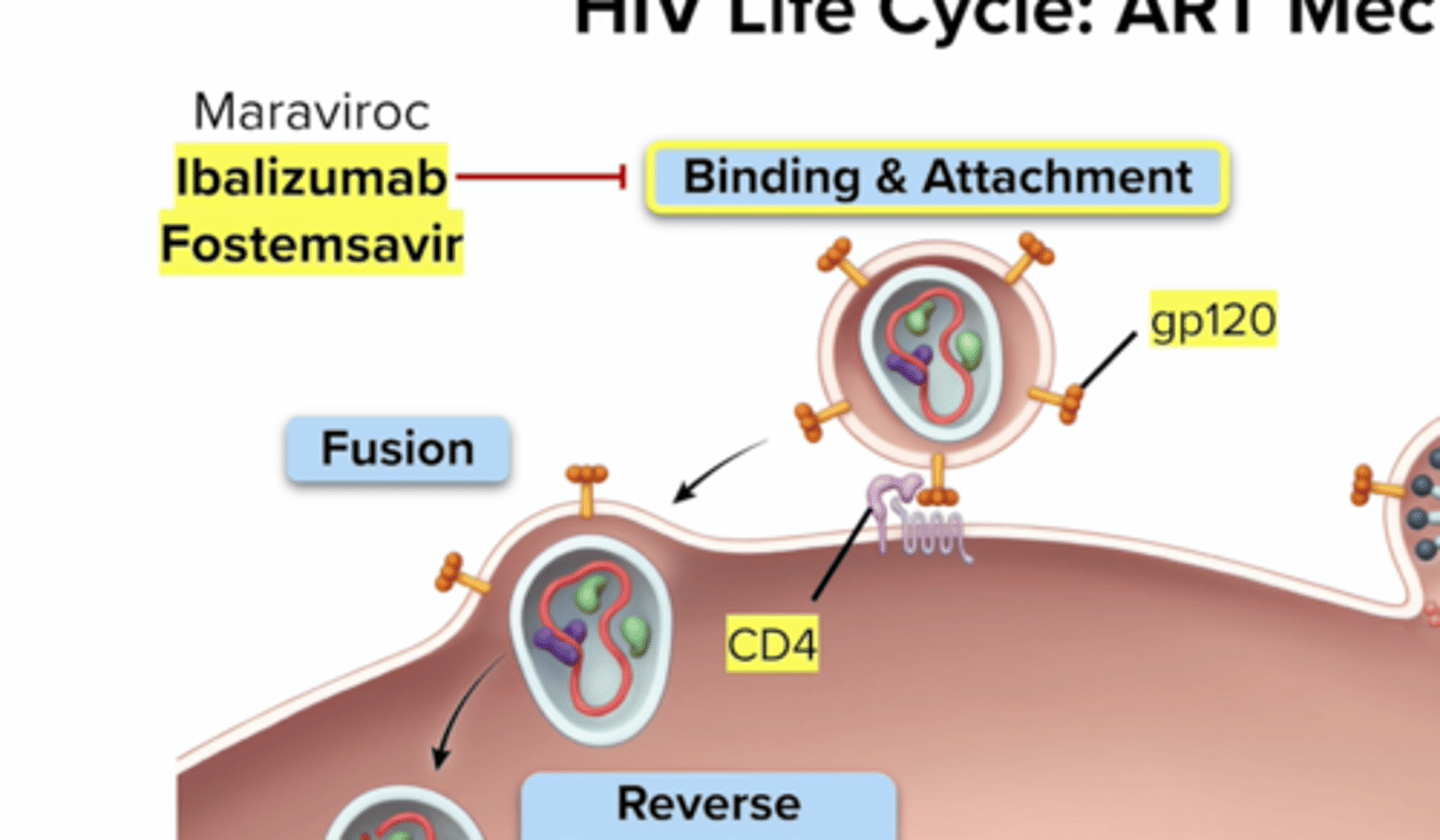
What drug class target Stage 1: Binding/Attachment?
step: Hiv attaches to CD4 receptor and Coreceptor CCR5 and or CXCR4
CCR5 Antagonist: Maraviroc (Selzentry) - tropism test prior to use
Post Attachment Inhibitors: Ibalizumab-uiyk (Trogarzo) - cd4 diected
Attachment Inhibitor: Fostemsavir (Rukobia) - blocks gp120
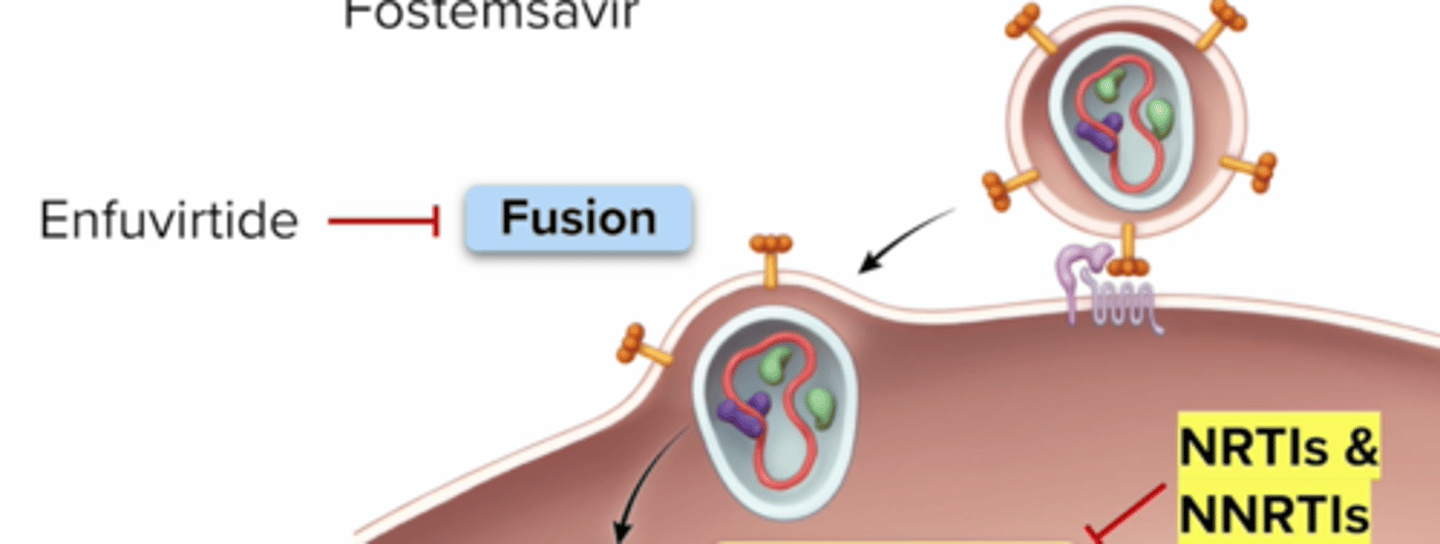
What drug class target Stage 2: Fusion?
step: HIV viral envelope fuses with cell membrane
Fusion Inhibitors: Enfuvirtide (Fuzeon)
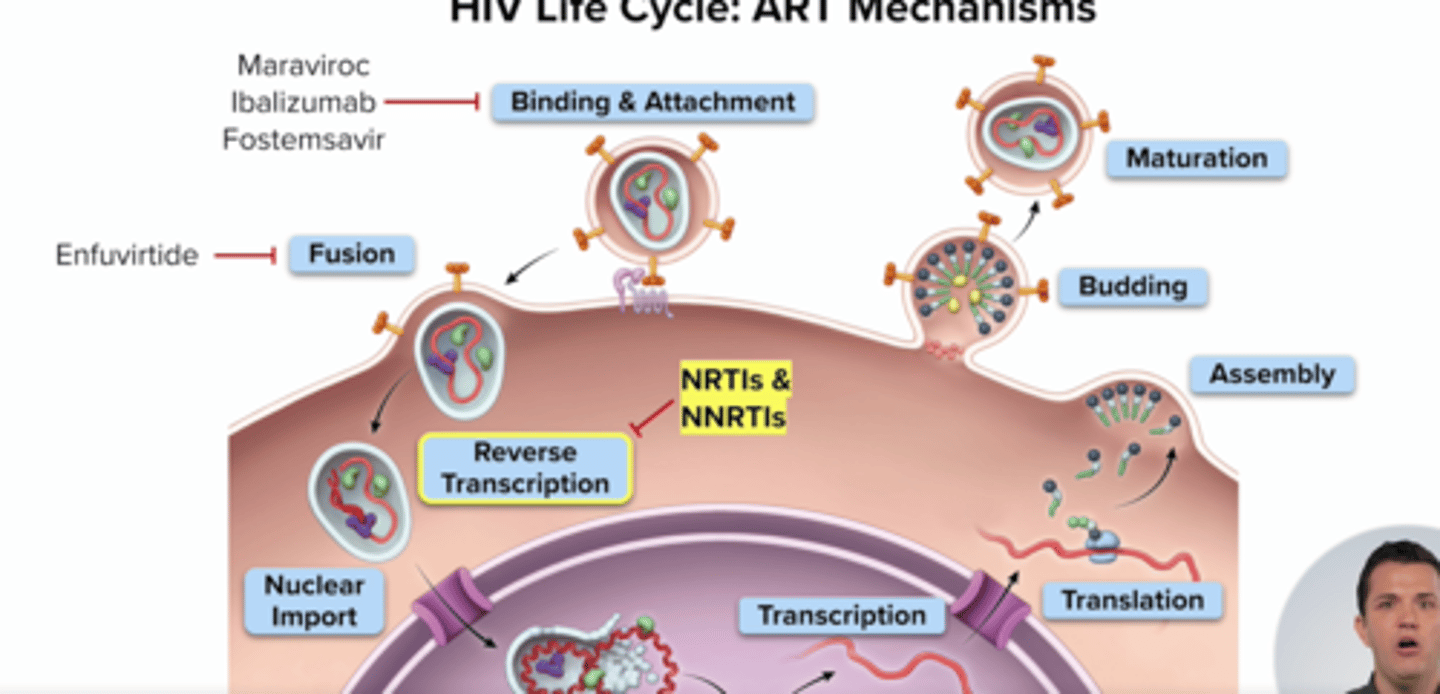
What drug class target Stage 3: Reverse Transcription?
step: Hiv rna converted to hiv dna via reverse transcriptase (hiv enzyme)
Nucleoside/Nucleotide Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs) (eg. emcitritabine) - compete w nucleosides for active site on RT causing chain termination and stop hiv replicaiton
Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NNRTIs) (eg. riplivirine)
- bind allosteric site to conformational change that prevents conversion hiv rna to hiv dna
What drug class target Stage 5: Integration?
step: Integrase (hiv enzyme) inserts hiv dna into host cell dna
Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibitors (INSTIs): Bictegravir (Biktarvy), Dolutegravir (Tivicay) , Raltegravir (Isentress)
block action of integrase so hiv dna cant enter host cell dna
What drug class target Stage 8: Budding and Maturation?
step 8: Immature virus pinches off the cell protease (hiv enzyme) breaks up viral protein chains to form mature virus that can infect other cells
Protease Inhibitors (PIs): Atazanavir (Reyataz), Darunavir (Prezista)
block maturation of HIV by inh protease
Capsid inhibitors
disrupt hiv capsid
work on
nuclear import (step 4) budding/maturation (step 8), and assembly (step 7)
lenacapavir
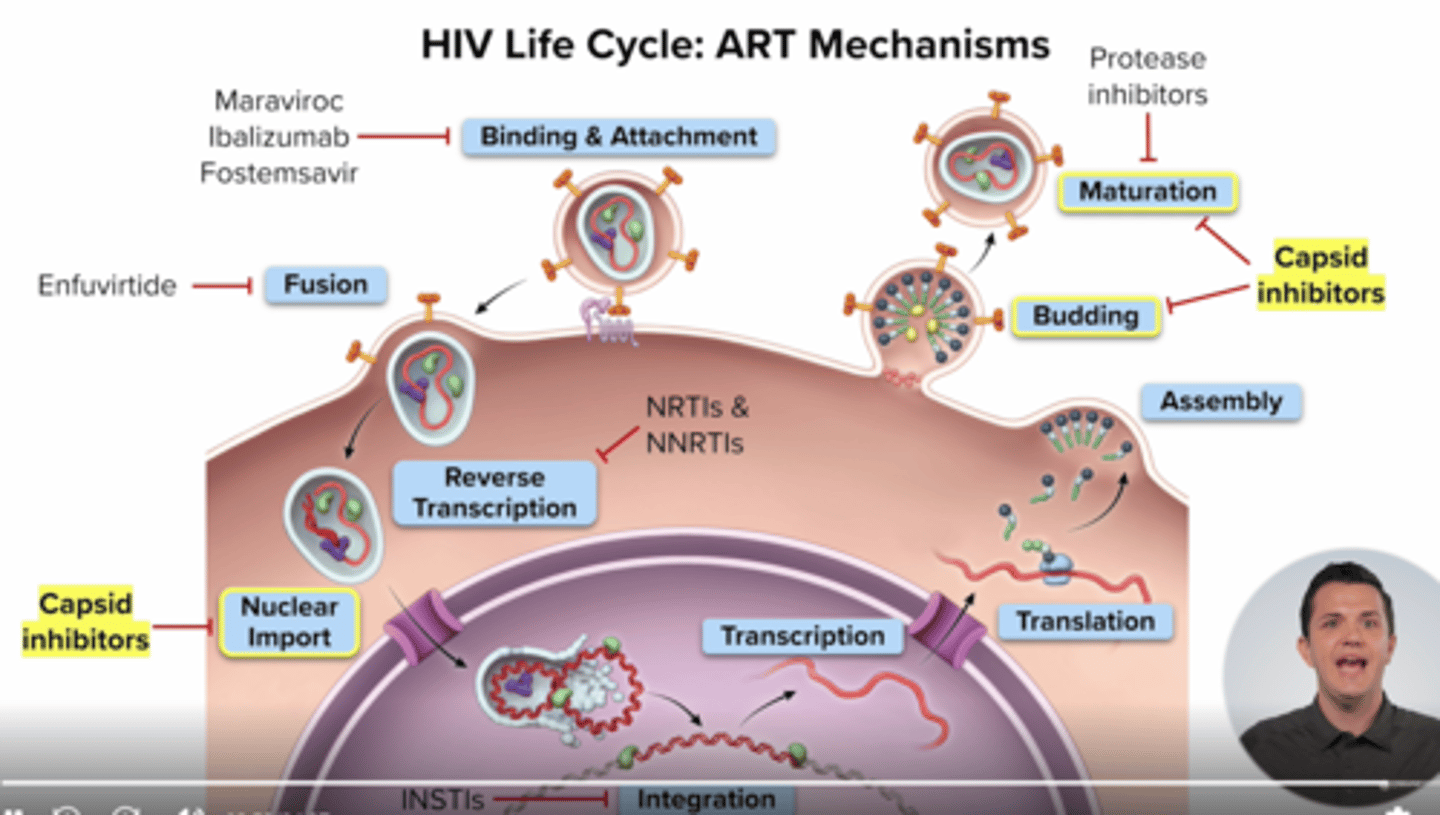
in which step in the hiv lifecyle do no drugs work?
step 6: Transcription and translation
host cell machinery is used to transcribe and translate HIV DNA into HIV RNA and long chain proteins
What are the routine lab tests for initial evaluation in monitoring of HIV?
CD4 count
Hiv viral load
Hiv genotypic testing
CMP
Hepatitis B and C screening pregnancy test
HLAB*5701 allele (abacavir)
ccr5 tropism test (maraviroc)
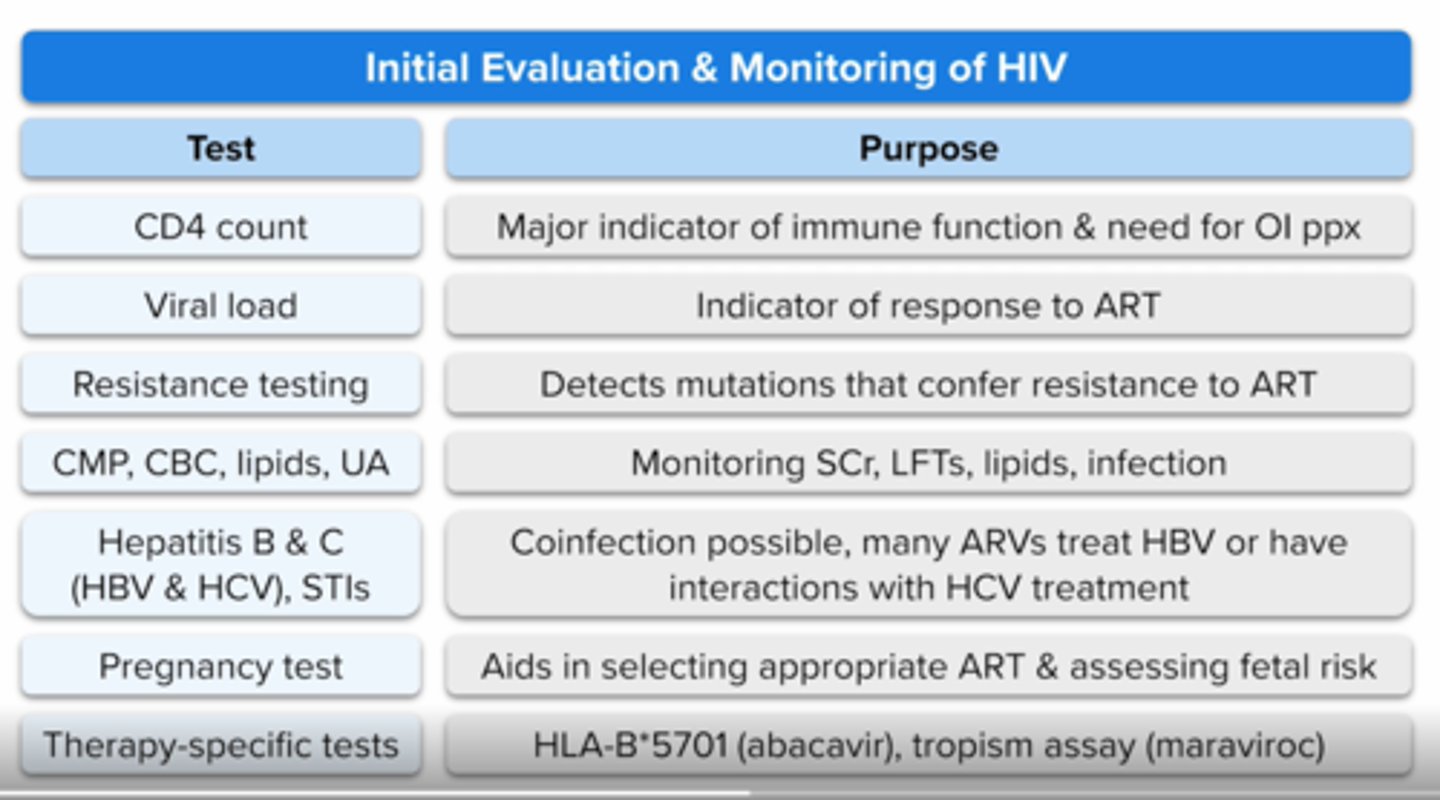
HIV evaluation and monitoring:
what does a cd4 count indicate?
indicates the need for?
does it increase or decrease with treatment?
Indicator of immune function
Determines the need for OI prophylaxis
CD4 count increases with ART
HIV evaluation and monitoring:
hiv viral load indicates what?
If a patient is being treated, what does a high viral load indicate?
Antiretroviral therapy response
If still high after starting treatment, may be d/t Medication non adherence or drug resistance
Guidelines recommend initial treatment with what class of HIV medications for most patients with newly diagnosed HIV?
INSTI based regimens for most pts
Most preferred HIV regimens for treatment naive patients contain what?
2 NRTIs + 1 INSTI
What two drugs in their components make up the NRTI backbone in most HIV regimens?
emtricitabine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (truvada)
emtricitabine/tenofovir alfenamide (descovy)
which two drugs in NRTI are interchangeable? can they be used together, why or why not?
emcitritabine and lamuvidine
no, Both are cytosine analogs and would be antagonistic if taken together
Preferred initial art regimen in most treatment naive adults - hiv:
generic, brand, pill burden
+ what class do they contain
all contain an integrase inhitor With a high barrier to resistance (bictegravir or dolutegravir)
plus 2 nrtis (emcitritabine + taf or tdf
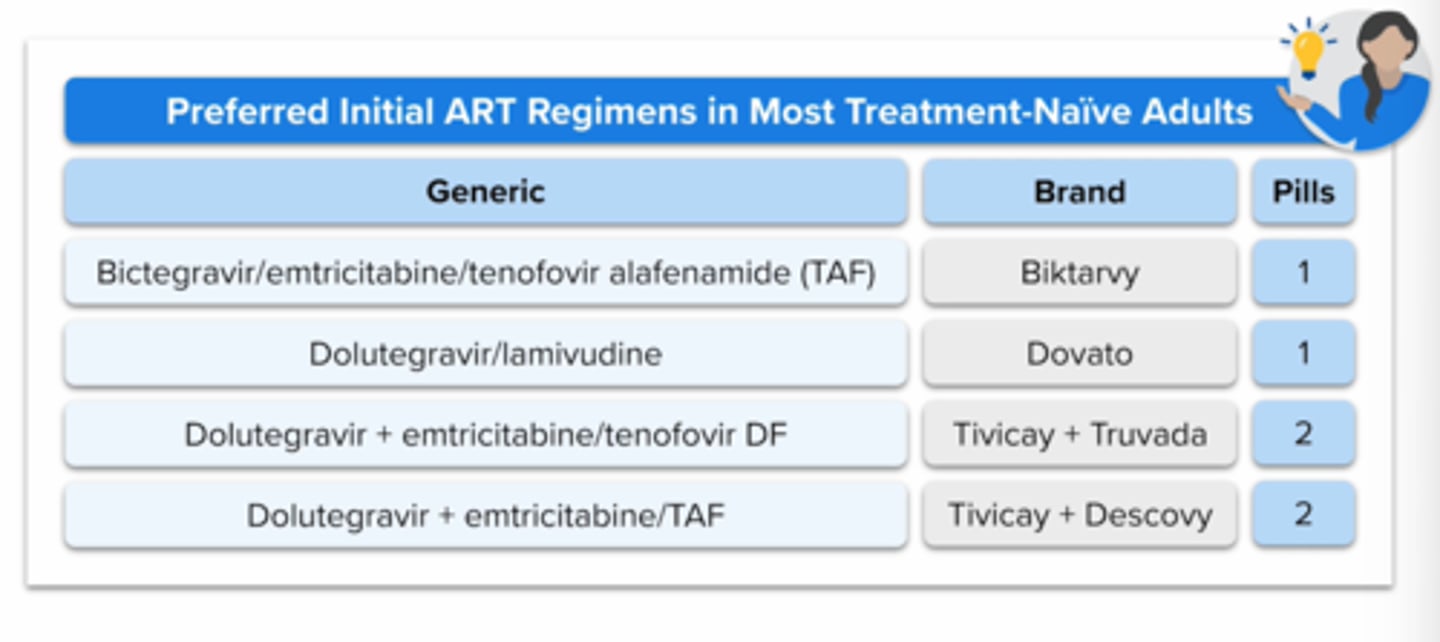
Preferred initial art regimen in most treatment naive adults - hiv:
how are they all dosed?
renal impairment?
all qd
biktarvy, triumeq, dovato, tivicay, descovy: CI if crcl <30
all except biktarvy can be given components separately to allow for renal adjustment (so larger pill burden)
Which of the following is consider first line treatment regimen for a patient with newly diagnosed HIV (one pill)?
Biktarvy (Bictegravir/ Emtricitabine/ Tenofovir Alafenamide)
Triumeq (Dolutegravir/ Abacavir/ Lamivudine)
Dovato (Dolutegravir/ Lamivudine)
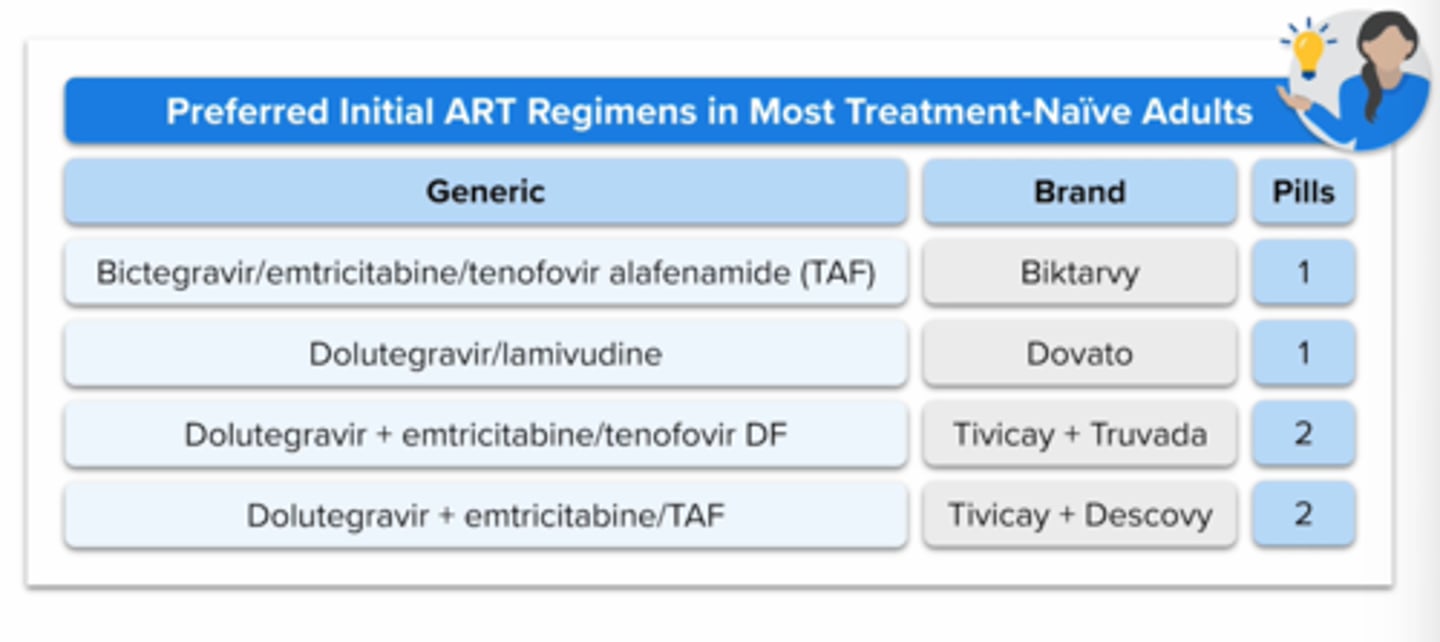
when can dolutegravir/lamivudine (dovato) be used 1st line for Treatment naive patients?
do not use if
viral load >500,000
hep b coinfection or unknown
hiv genotype not done OR resistance to either drug

Which of the following antiretroviral therapy should not be started in patients if HIV RNA >500,000 copies/mL or if a hepatitis B confection is present or HIV genotypic testing not yet available?
Dovato (Dolutegravir/ Lamivudine)
Which of the following antiretroviral therapy requires testing for the HLA-B*5701 allele before using?
Triumeq (Dolutegravir/ Abavacir/ Lamivudine)
Epzicom (Abavacir/ Lamivudine)
Trizivir (Abavacir/ Lamivudine /Zidovudine)
Which of the following antiretroviral therapy should not be used if CrCl <30 mL/min?
Biktarvy (Bictegravir/ Emtricitabine/ Tenofovir Alafenamide)
Triumeq (Dolutegravir/ Abacavir/ Lamivudine)
Dovato (Dolutegravir/Lamivudine)
Truvada (Emtricitabine/ Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate)
Descovy (Emtricitabine/ Tenofovir Alafenamide)
Biktarvy
Bictegravir/ Emtricitabine/ Tenofovir Alafenamide
Triumeq
Dolutegravir/ Abacavir/ Lamivudine
Dovato
Dolutegravir/ Lamivudine
Tivicay + Truvada
Dolutegravir + Emtricitabine/ Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate
Tivicay + Descovy
Dolutegravir + Emtricitabine/ Tenofovir Alafenamide
Isentress + Truvada
Raltegravir + Emtricitabine/ Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate
Isentress + Descovy
Raltegravir + Emtricitabine/ Tenofovir Alafenamide
Alternative Complete hiv antiretroviral regimens contain
(aka 2nd line treatments for treatment naive pts)

ART in pregnancy:
if pt already on art
newly diagnosed while pregnant
continue art regimen
new: 3 components rec'd
dolutegravir (insti) or boosted darunavir (PI) PLUS
dual nrti backbone (eg. emcit/tenofovir)

ART in pregnancy:
perinatal transmission prophylaxis
IV zidovudine near time of delivery to mother and newborn

What is the mechanism of action for NRTIs?
Competitively inhibit the reverse transcriptase enzyme, preventing the conversion of HIV RNA to HIV DNA in stage 3 of the HIV life cycle
Match the generic name with the correct brand name NRTIs (hint: Z Loves LATTE
Zidovudine (Retrovir)
Lamivudine
(Epivir)
Abacavir (Ziagen)
Tenofovir disoproxil
fumarate (Viread)
Tenofovir alafenamide (Vemlidy brand is for hep b only)
Emtricitabine (Emtriva)
Which NRTIs are dosed once daily?
Tenofovir (both formulations)
Abacavir (Ziagen)
Lamivudine (Epivir)
Which NRTIs are dosed twice daily?
Zidovudine (Retrovir)
Which NRTIs requires renal dose adjustment?
All NRTIs except Abacavir requires DECREASE dose with renal impairment
Which NRTI is administered IV during labor and delivery in women with HIV RNA >1,000 copies/mL?
Zidovudine (Retrovir)
ALL NRTIs have a warning for what?
all: lactic acidosis, hepatomegaly with steatosis (fatty liver)
Which nrtis have BBW for reactivation of HBV if dc'd?
emcitritabine
lamivudine
tenofovir products
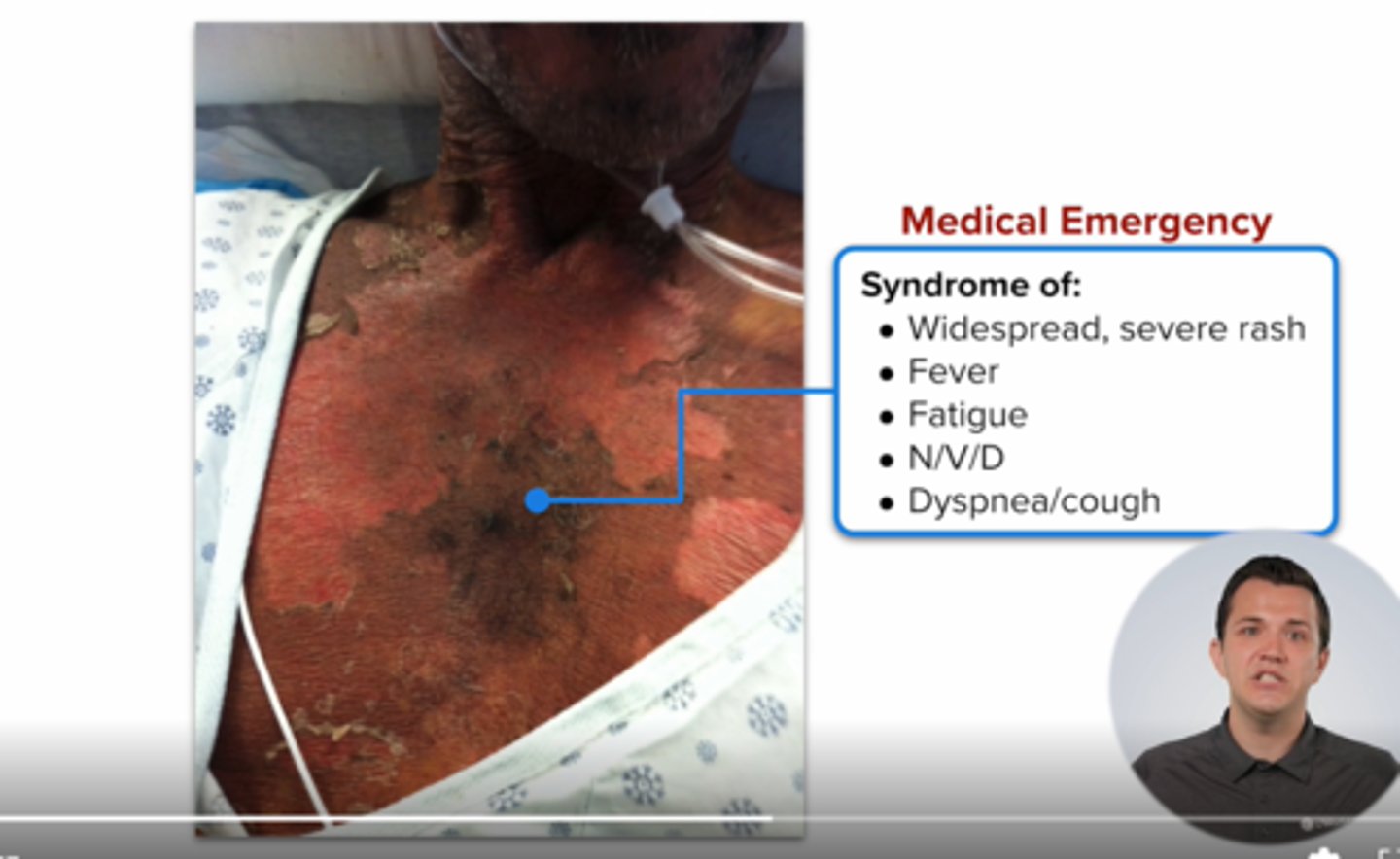
what is the BBW for abacavir?
risk for hypersensitivity reaction (HSR)
must test prior for
hlab5701
pts must carry card indicating HSR (fever, rash, nvd, dyspnea, cough) are emergency
never rechallenge pts with hsr symptoms
what is the BBW for zidovudine?
lactic acidosis and hepatomegaly with steatosis
What are the common side effects of NRTIs?
Nausea
Diarrhea
Headache
Increase LFTs
Which NRTI can cause hyperpigmentation of the palms of the hands or soles of the feet?
Emtricibine (Emtriva)
Which NRTI decrease bone mineral density?
Tenofovir Formulations - consider calcium/vitamin D supplementation and DEXA scan if at risk
higher risk with tdf v taf
NRTIs:
what are specific side effects/warning for tenofovir products?
which is higher risk?
tdf higher risk v taf
renal impairment (aki, fanconi syndrome)
decreased bone mineral density
NRTIs:
what monitoring must be done if switching from tdf to taf?
monitor lipids
taf is associated with lipid abnormalities
Which NRTI can cause hematologic toxicity (neutropenia and anemia)?
Zidovudine (Retrovir), prolonged use has been associated with symptomatic myopathy
Which NRTIs can cause pancreatitis and peripheral neuropathy?
Didanosine (Videx, Videx EC)
Stavudine (Zerit)
Testing for the HLA-B 5701 allele is required before prescribing which medication?
Abacavir (Ziagen)
Which NRTI has a boxed warning for the risk of serious hypersensitivity reaction?
Abacavir (Ziagen)
Which of the following NRTIs should patients with CVD avoid due to a potential increase risk for MI?
Abacavir (Ziagen)
What is the mechanism of action for INSTIs?
Block the integrase enzyme preventing HIV DNA from inserting into the host cell DNA in stage 4 of the HIV life cycle
Match the generic name with the correct brand name INSTIs (hint: BCRED)
Bictegravir only in combination drug (Bikatarvy)
cabotegravir (apretude, cabenuva -combo)
Raltegravir (Isentress, Isentress HD)
Elvitegravir only in combination drugs (Genvoya and Stribild)
Dolutegravir (Tivicay, triumeq & dovato-combos)
names end in -tegravir
Which INSTIs are dose once daily?
Biktarvy
Raltegravir (Insentress HD onlyw)
Elvitegravir (Stribild)
Elvitegravir (Genvoya)
Dolutegravir (Tivicay, triumeq, dovato)

which INSTI is twice daily?
Raltegravir (Insentress)
isentress hd (high dose) is ONCE daily

Do not start Stribild in which of the following conditions?
CrCl of <70 mL/min

Discontinue Stribild in which of the following conditions?
CrCl of <50 mL/min

Do not start Bictegravir (Bikatarvy) and Elvitegravir (Genvoya) in which of the following conditions?
CrCl of <30 mL/min

Which INSTIs increase Scr?
Bictegravir (Biktarvy)
Dolutegravir (Tivicay)
what is cabotegravir (apretude) used for?
er IM injection used for post exposure prophylaxis ONLY
What are the most common side effects associated with Raltegravir (Isentress, Isentress HD)?
Increase CPK
Myopathy
Rhabdomyolysis
What is the most common side effect associated with Elvitegravir (Genvoya and Stribild) ?
Proteiniuria
Which of the following statements are true concerning Dolutegravir (Tivicay)?
Hypersensitivity reaction with severe rash and organ dysfunction including hepatotoxicity
Small risk of neural tube defects in women (though still a preferred drug for treatment of HIV during pregnancy)
INCREASE CPK
Myalgia
All INSTIs can cause
Insomnia,
depression &suicidal ideations in patients with pre existing psychiatric condition
weight gain
diarrhea

INSTI drug interactions + counseling
polycalent cations decrease insti absorption ->
separate INSTIs from polyvalent cations (eg. antacids, supplements (ca, iron))
take INSTI 2 hours before or 6 hours after products containing Al, Ca, Mg, Fe
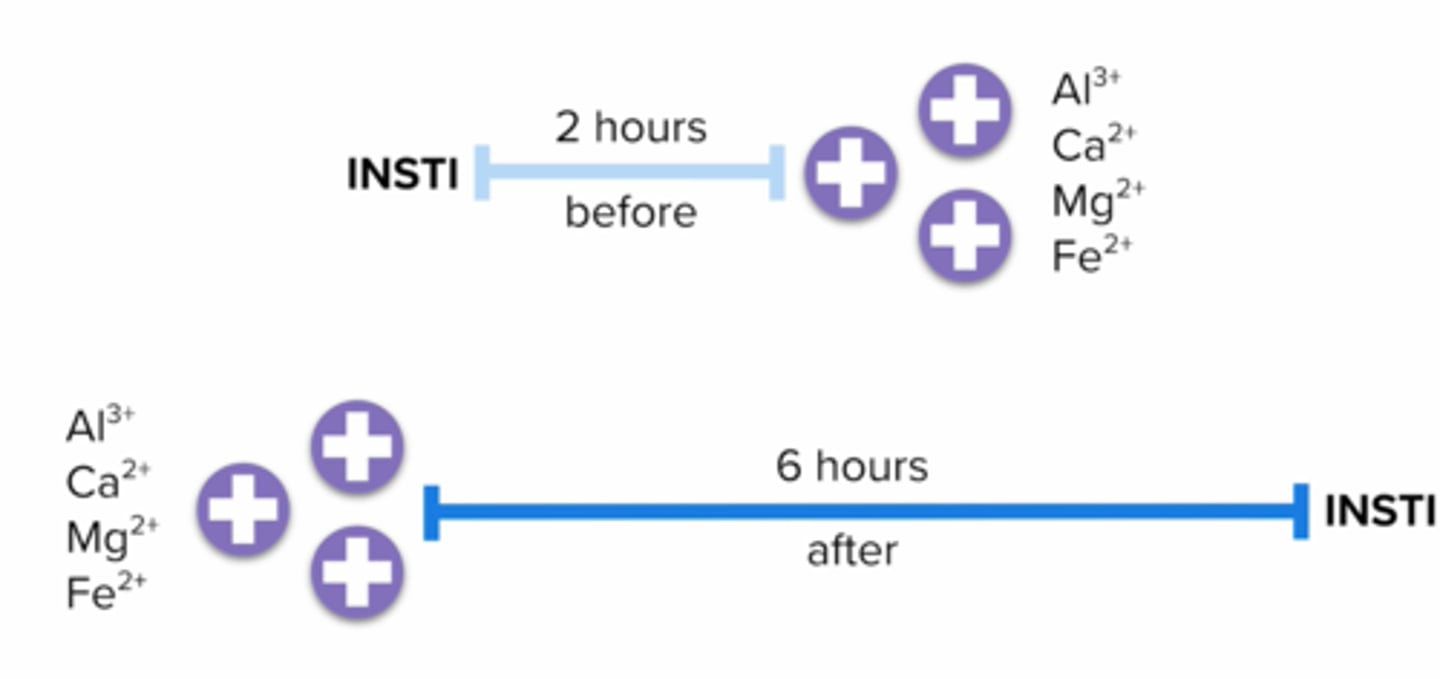
Which antiretroviral class should be administered separately from antacids?
Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibitors
eltegravir drug interactions
coformulated with cobicistat
strong cyp 3a4 inh
which INSTIs may be taken with oral calcium or iron if also taken with food
Dolutegravir (Tivicay) and Bictegravir
What is the mechanism of action for NNRTIs?
Non competitively inhibit the reverse transcriptase enzyme, preventing the conversion of HIV RNA to HIV DNA in stage 3 of the HIV life cycle
Match the generic name with the correct brand name NNRTIs (hint: REDEN)
Rilpivirine (combo: complera, odefsey, cabenuva)
Efavirenz
Doravirine
Etravirine
Nevirapine
why are NNRTIs not first line?
have lower barrier to resitance (easier to gain resistance) than instis or PIs
How must ripivirine (complera, odefsey, cabenuva (im)) PO be administered?
Take with a meal and water do not substitute with a protein drink
Which NNRTIs needs an acidic gut for absorption? why is this important? (think drug interactions)
rilpivirine (complera, odefsey, cabenuva (im))
requires acidic environment for absorption; can not be used with PPIs
what is the IM version of rilpiverine?
cabenuva - cabotegravir/rilpivirine
a pt with heartburn that is taking rilpivirine (complera, odefsey, cabenuva (im)) should to not take which medication class?
CI with PPis
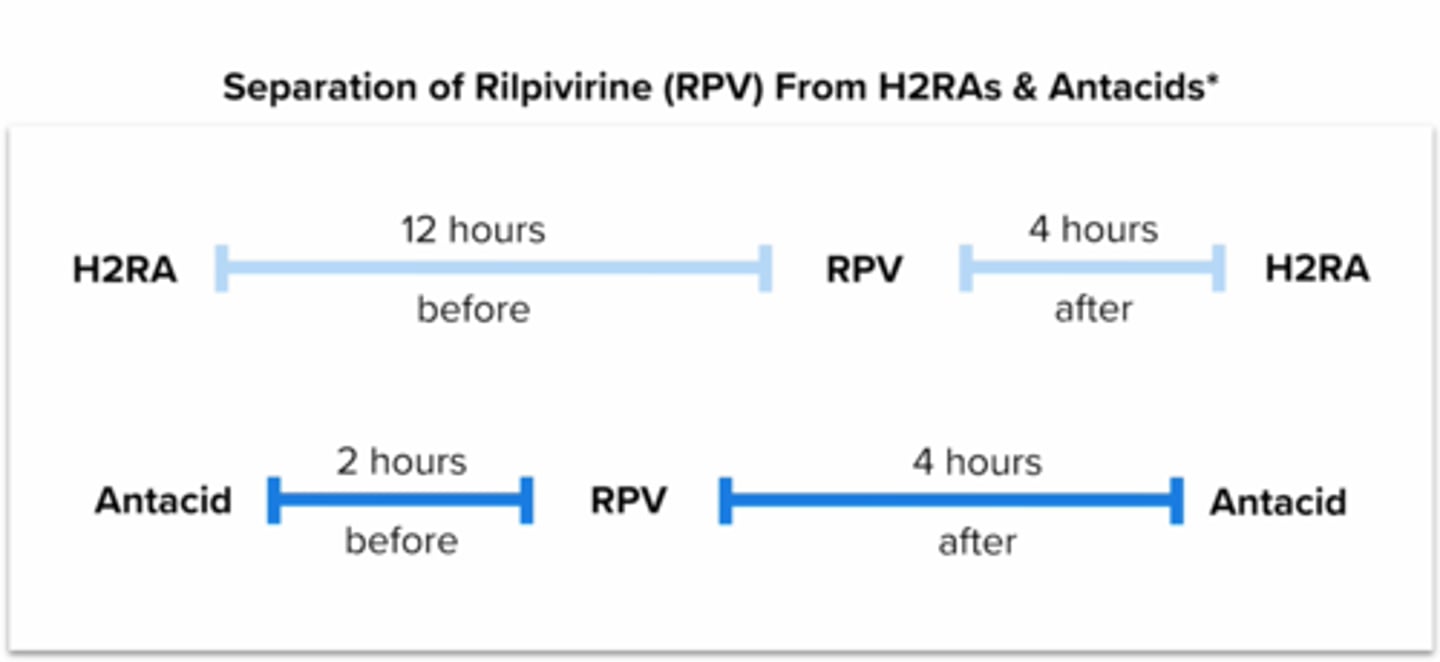
How should a pt on H2RAs be counseled to take rilpivirine (complera, odefsey, cabenuva (im)?
should be taken at least 12 hours before or 4 hours after Rilpivirine (Edurant)
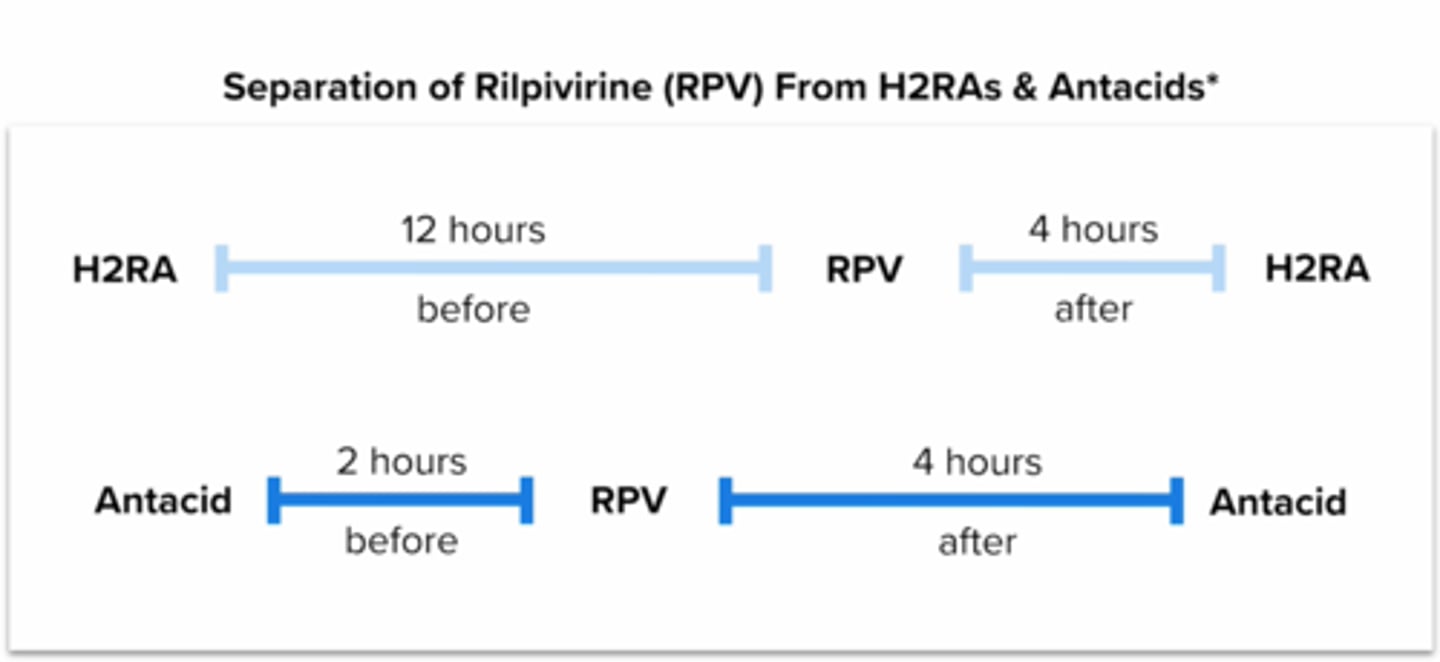
how should a pt on rilpivirine (complera, odefsey, cabenuva (im) be counseled on how to take Antacids?
should be taken at least 2 hours before or 4 hours after rilpivirine (complera, odefsey, cabenuva (im))