Korean Art History Midterm
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
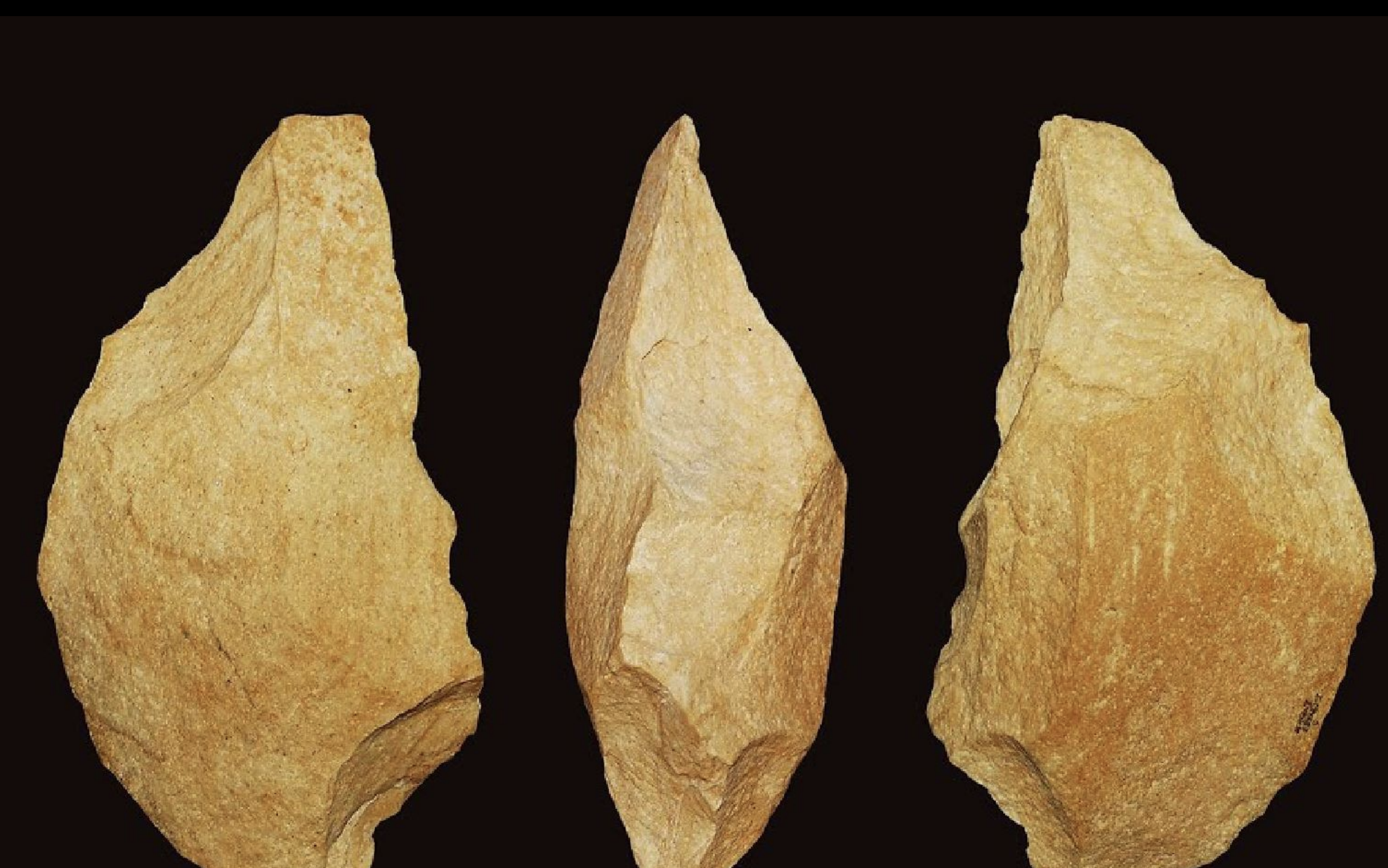
Handaxe
Time: Paleolithic Period/Ice Age (600,000-ca. 8,000 BCE)
Found in Gyeonggi (경기) Province by Greg Bowen in 1978

Paleolithic Period (600,000-ca. 8,000 BCE)
The earliest part of the Stone Age, characterized by the development of primitive stone tools and human survival tactics - 1st period
Neolithic Period (8000 BCE to 1000 BCE)
The final stage of the Stone Age, marked by the advent of agriculture, pottery, and permanent settlements, led to significant social and technological advancements; first attempt of farming since they were settling in one area - 2nd period
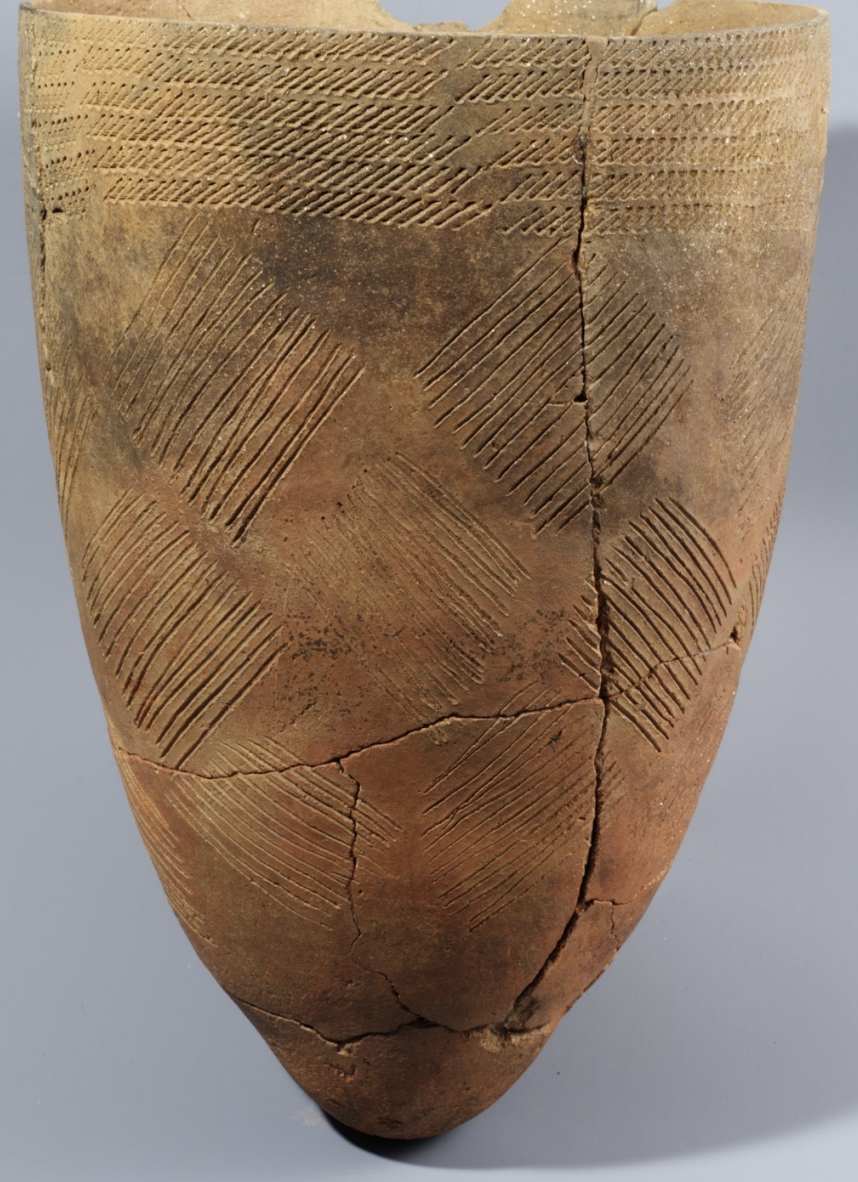
Comb-Patterned Pottery
Time: Neolithic Period (8000 BCE to 1000 BCE)
Found in Amsa-dong, Seoul (암사동, 서울)
Unique to Korea, patterns are debated to have meaning related to agriculture. (Mountains, Waves)

Bronze Age (1000 BCE - 300 BCE)
The period that followed the Neolithic, characterized by the use of bronze tools and weapons, advancements in art, and the emergence of social hierarchies in ancient Korean society - 3rd period
Red-Burnished Jar
Time: Bronze Age (1000 BCE - 300 BCE)
Found: various archaeological sites in Korea
Known for its smooth surface and red coloring, often used for storage or burial purposes.

Black-Burnished Jar
Time: Bronze Age (1000 BCE - 300 BCE)
Found: various archaeological sites in Korea
Known for its smooth surface and red coloring, often used for storage or burial purposes.
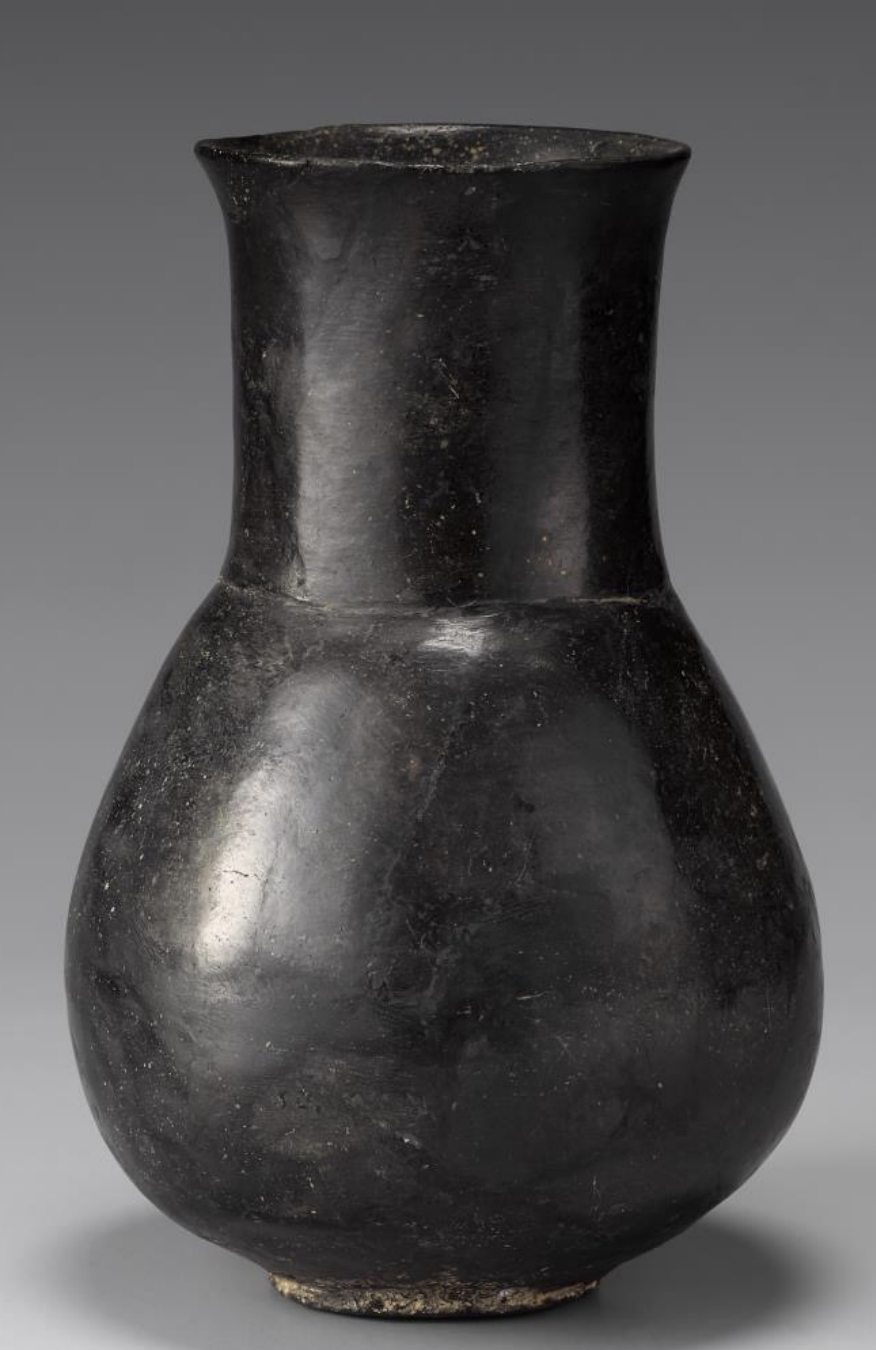

Burnished
(Bronze Age) a technique used to create a smooth, shiny surface on pottery by polishing the clay before firing
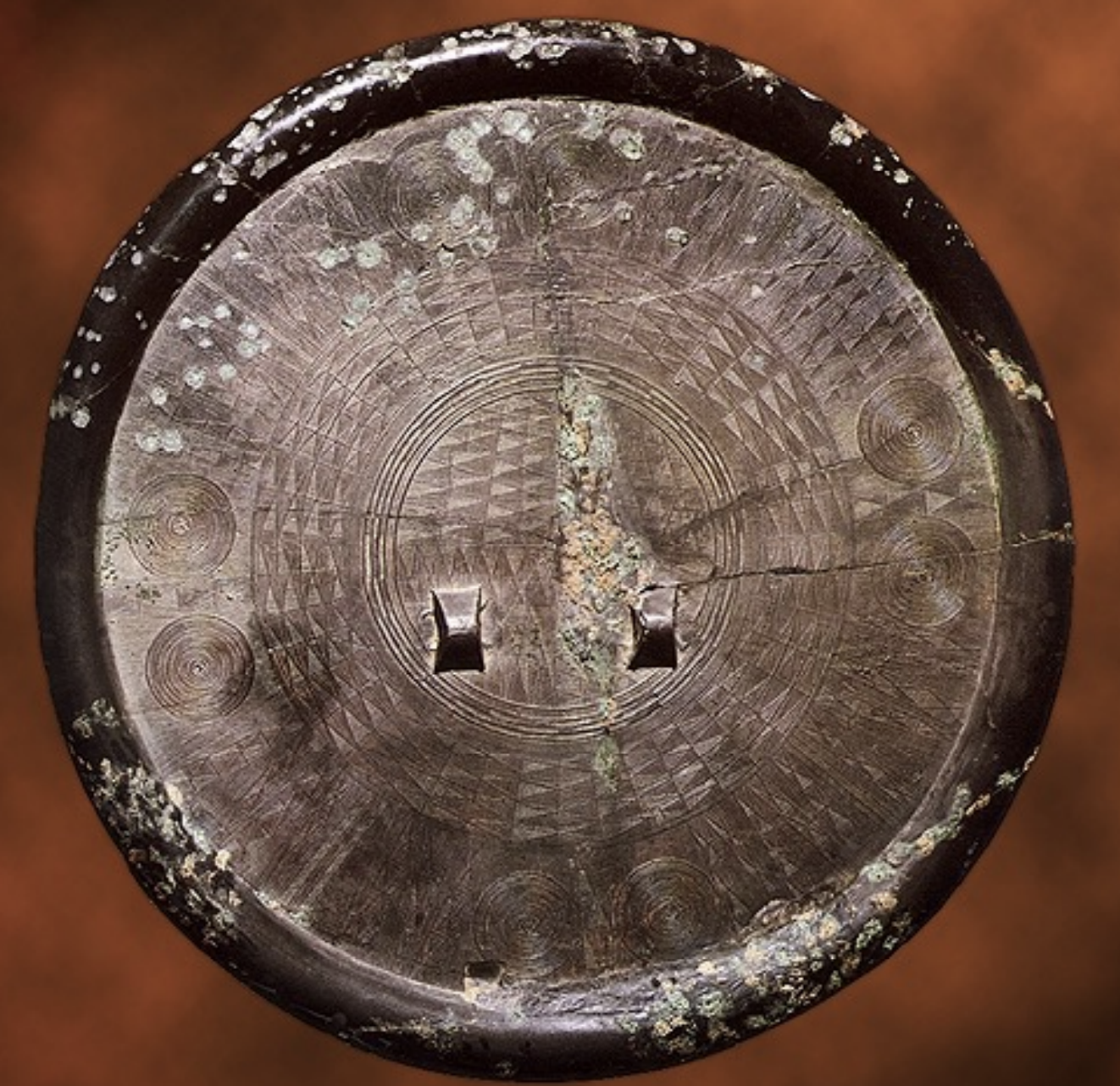
Bronze Mirror
Time: Bronze Age (1000 BCE - 300 BCE)
Found: various archaeological sites in Korea, particularly in Asan-si, South Chungcheong (아산시, 충청남도)
Unique to Korea, so intricate that even scholars now are unsure how they were made.

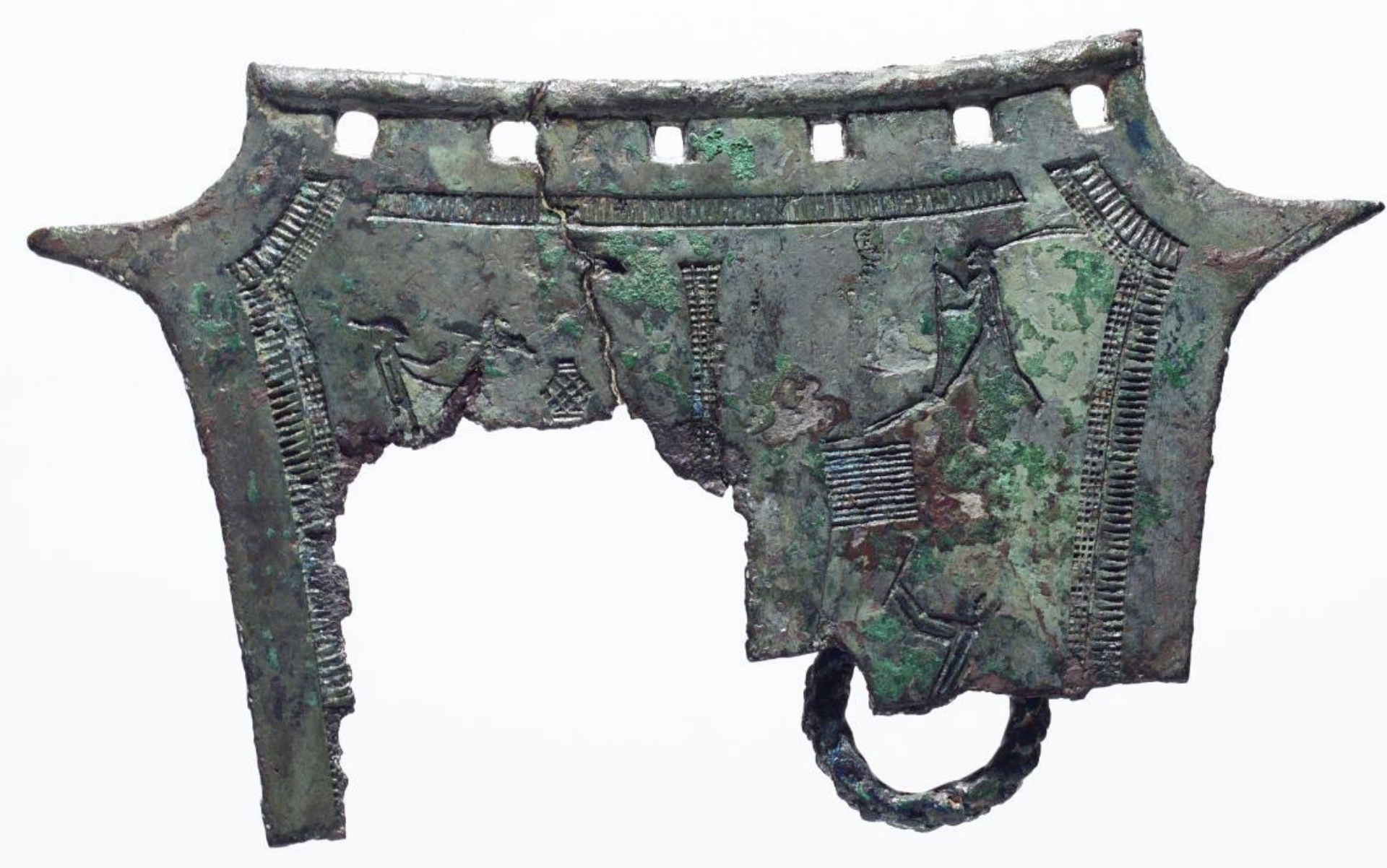
Bronze Ritual Artifact
Time: Bronze Age (1000 BCE - 300 BCE)
Found: Daejeon, South Chungcheong (대전, 충청남도)
Used in religious ceremonies, these artifacts often feature elaborate designs of daily farming activities; the holes on top indicate they were often suspended on walls for display during rituals.

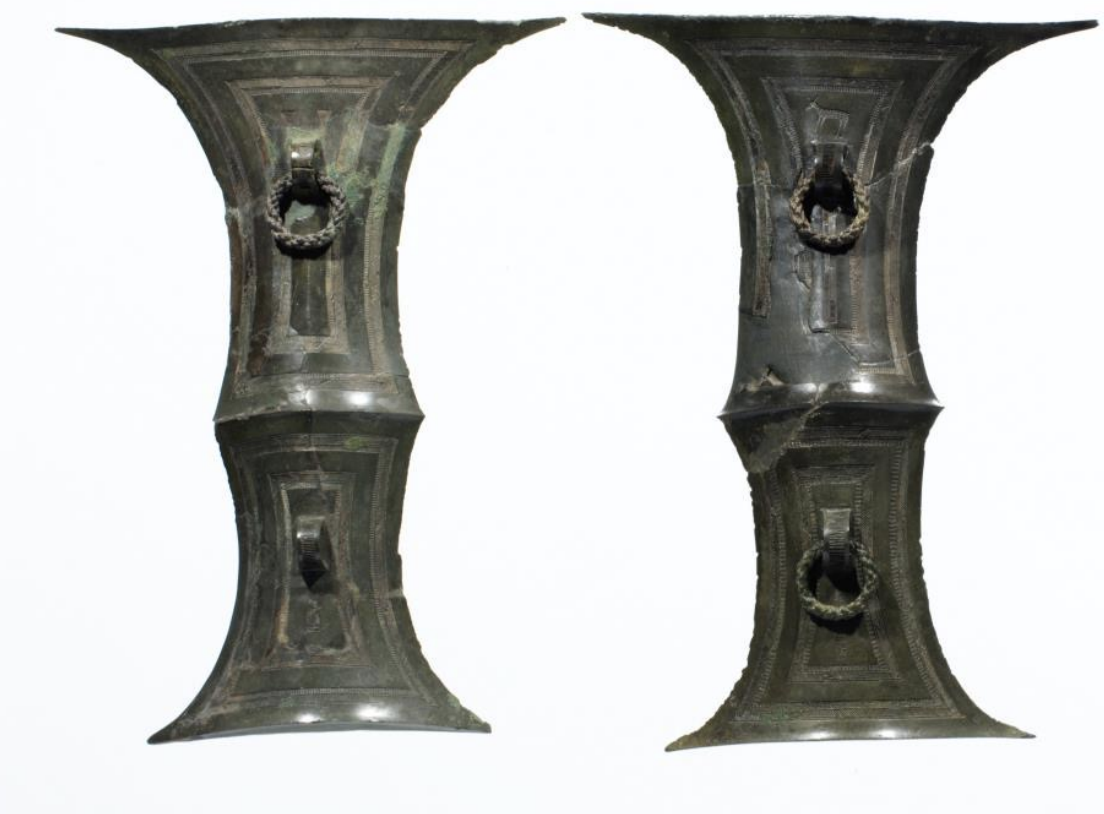
Bronze Split Bamboo-Shaped Artifact
Time: Bronze Age (1000 BCE - 300 BCE)
Found: Asan-si, South Chungcheong (아산시, 충청남도)
Rings allowed for them to be hung from walls; Used to signify the state of the owners. The design of the deer symbolizes shamanism; this artifact gives clues of cultural exchange between Korea and Siberian shamanism and a Theocratic society in Korea

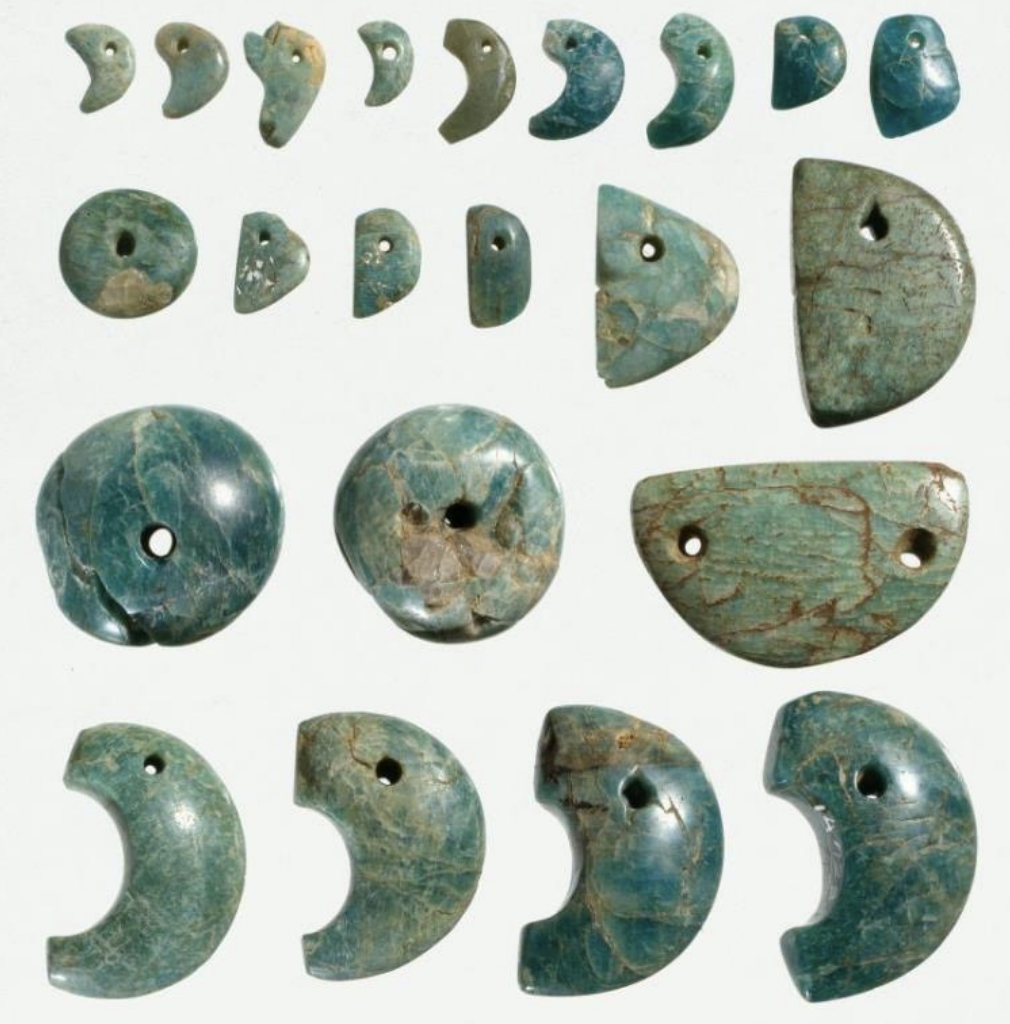
Comma-Shaped Jades/Magatama (Gogok/곡옥)
Time: From Bronze Age (1000 BCE - 300 BCE) to late 6th century
Found: Siberia and Northeast Asia
Korea - Daejeon, South Chungcheong (대전, 충청남도)
These artifacts are made of Jade and characterized by their unique comma shape. The composition of jade does not change over time, thus, the Chinese would use it for burials because of its believed powers for elite people.

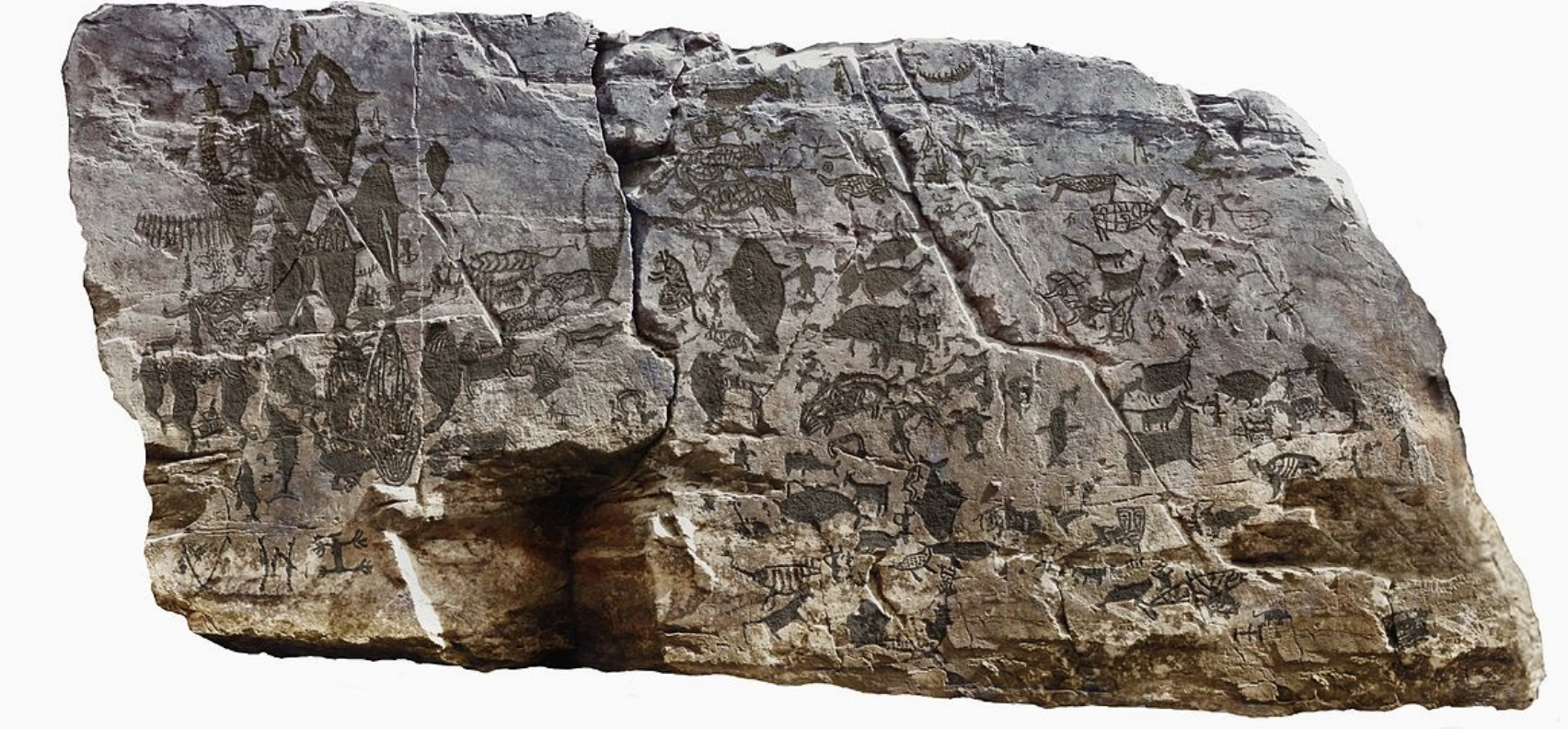
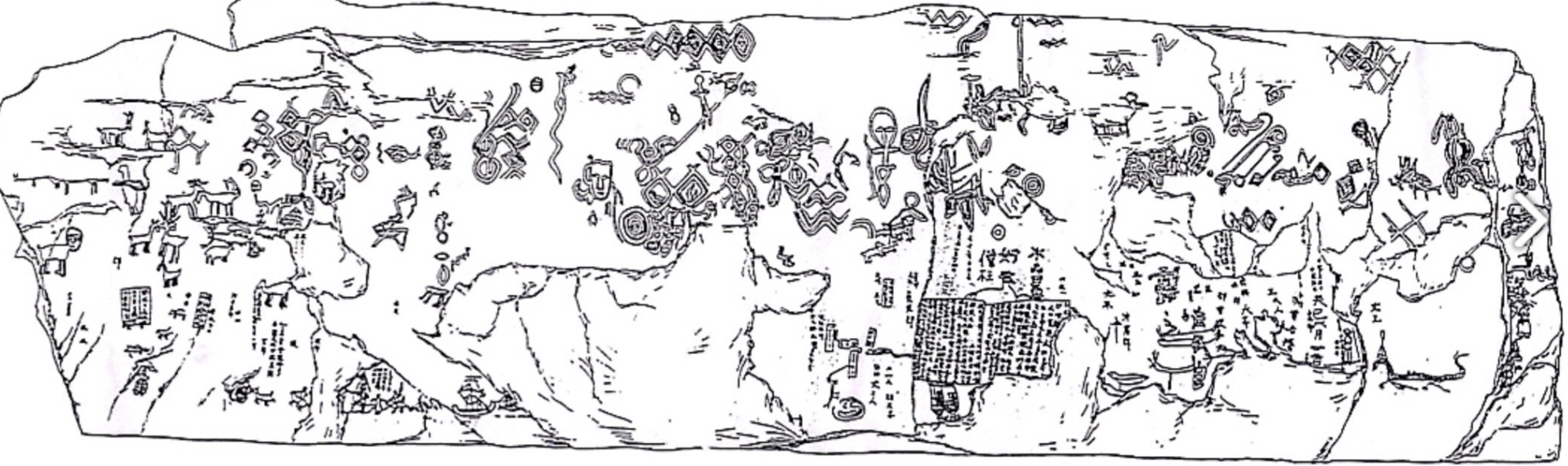
Bangudae (반구대) Petroglyphs
Time: Late Neolithic (8000 BCE to 1000 BCE) to early Bronze age (1000 BCE - 300 BCE)
Found: Ulju-gun (Western Ulsan), South Gyeongsang Province (울주군 - 울산, 경상남도)
These ancient rock carvings depict hunting scenes; uncover the hunting culture of whales during the time.

Cheonjeon-ri (천전리) Petroglyphs
Time: Late Neolithic (8000 BCE to 1000 BCE) to early Bronze Age (1000 BCE - 300 BCE)
Found: Pohang, North Gyeongsang Province (포항, 경상북도)
These petroglyphs feature various animal motifs and are believed to provide insight into ancient spiritual beliefs and practices; said to be tailsman reflecting shamanism.
Bird-shaped Vessel
Time: Proto-Three Kingdoms Period (a. late 2nd–3rd century CE)
Vessel for wine; bird-shaped vessels are usually associated with funerary ceremonies as birds were seen as vehicles carrying souls to the land of the immortals
“[Eastern tribes] use the feathers of a large bird to help the spirit of the deceased fly [into heaven].” – “Accounts of the Eastern Tribes,” in Sanguozhi (“Records of the Three Kingdoms”)
![<p>Time: Proto-Three Kingdoms Period (a. late 2nd–3rd century CE)<br></p><p>Vessel for wine; bird-shaped vessels are usually associated with funerary ceremonies as birds were seen as vehicles carrying souls to the land of the immortals<br><br>“[Eastern tribes] use the feathers of a large bird to help the spirit of the deceased fly [into heaven].” – “Accounts of the Eastern Tribes,” in Sanguozhi (“Records of the Three Kingdoms”)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/00f85fff-34f4-4043-83e3-b272e332bd43.png)
Baekje Kingdom (백제)
An ancient Korean kingdom that existed from 18 BCE to 660 CE, known for its advanced culture, art, and architecture, particularly during the Three Kingdoms period; located in southwestern Korea; lots of trade with South China and Japan through the Yellow Sea; Buddhism and Daoism
Silla Kingdom (신라)
An ancient Korean kingdom that lasted from 57 BCE to 668 CE, renowned for its cultural achievements, including advanced metallurgy, Buddhist art, and architectural developments, particularly during the Unified Silla Period; located in the southerneast region.
Koguryo Kingdom (고구려)
An ancient Korean kingdom that existed from 37 BCE to 668 CE, noted for its military power, extensive wall art, and cultural influence during the Three Kingdoms period; located in the northern region.
Kaya Federation (가야)
A federation of ancient Korean states that existed from approximately 42 CE to 562 CE, known for its advanced metalwork, including gold and silver craftsmanship, as well as its maritime trade; located in the southern part of the Korean peninsula.
Kyongjil (경질) Pottery
Time: 6th-7th Century
From: Baekje Kingdom (Mongchon Earthen Fortification)
Brought/influenced by Southern China from trade through the Yellow Sea
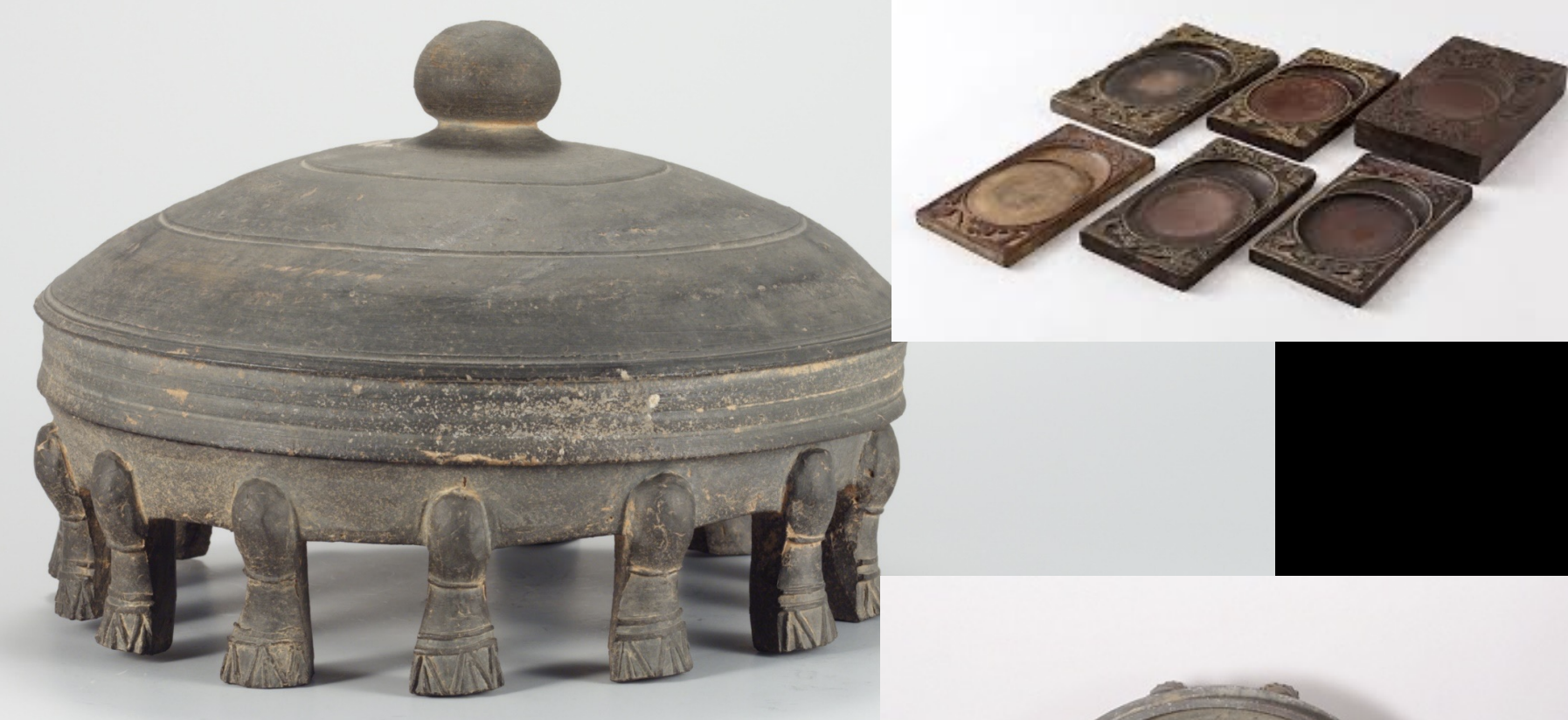

Mongchon Earthen Fortification (몽촌토성)
A major fortress of the Baekje Kingdom that lots of Atifacts were found at. This fortification features earthen walls and served as a military base, reflecting the architectural styles influenced by interactions with Southern China.
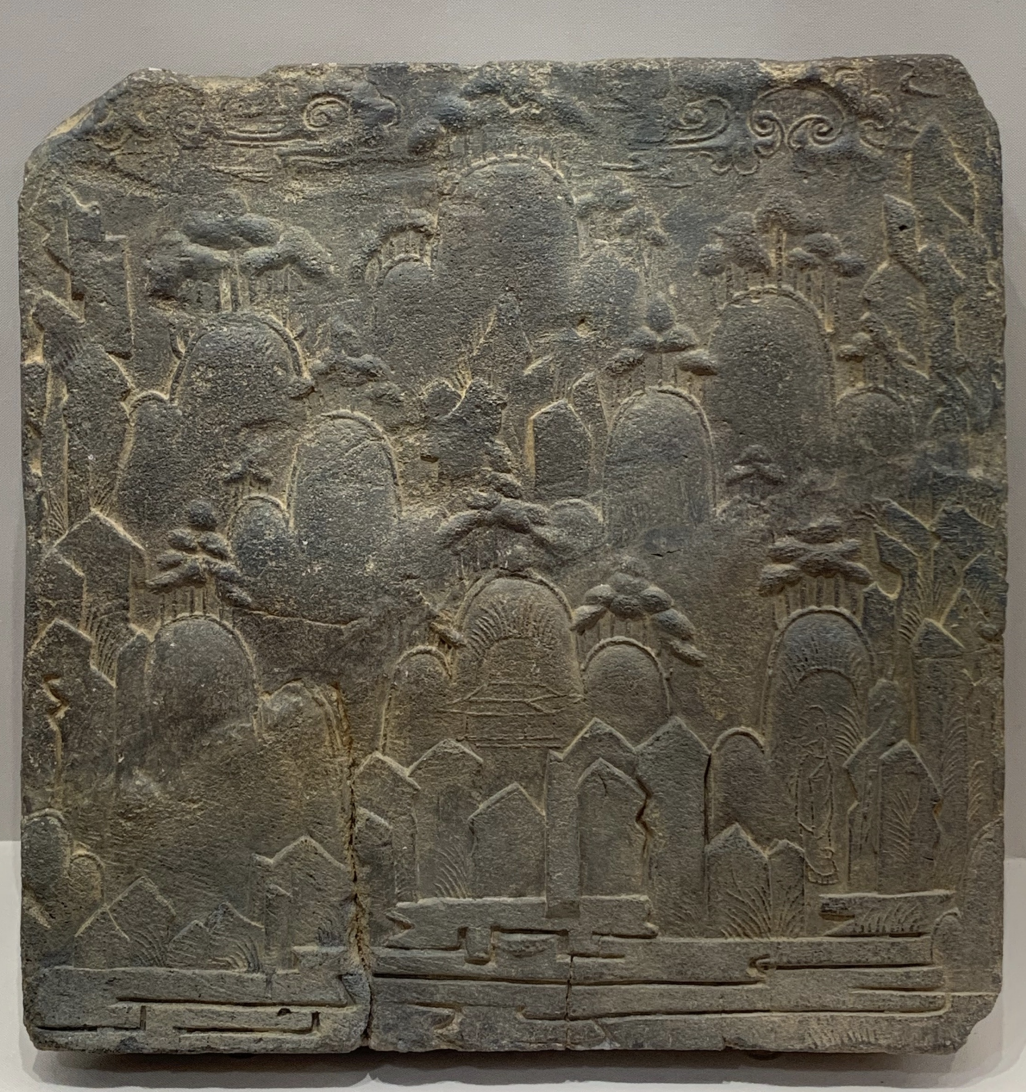
Earthenware Tile with Landscape Design
Time: 7th Century
Found: Baekje Kingdom in Buyeo, Chungcheong Province (부여군, 충청)
The tiles depict Mt. Peng-lai, which is a mythical place in Chinese mythology, symbolizing paradise and longevity; in Korea, it’s called 삼신산 (Samshin Mountain) and it’s the ideal dwelling place in Daoist or Buddhist.
8 tiles have been extracted.

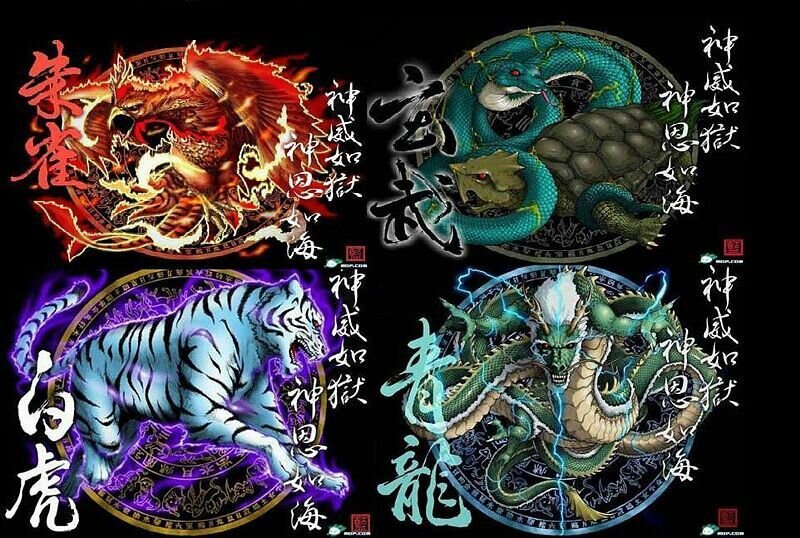
Cardinal Directions
Phoenix (Red) - South
Dragon (Yellow or Blue) - East
Black Turtle/Snake - North
Tiger - West
Folk religion; influenced by Chinese beliefs

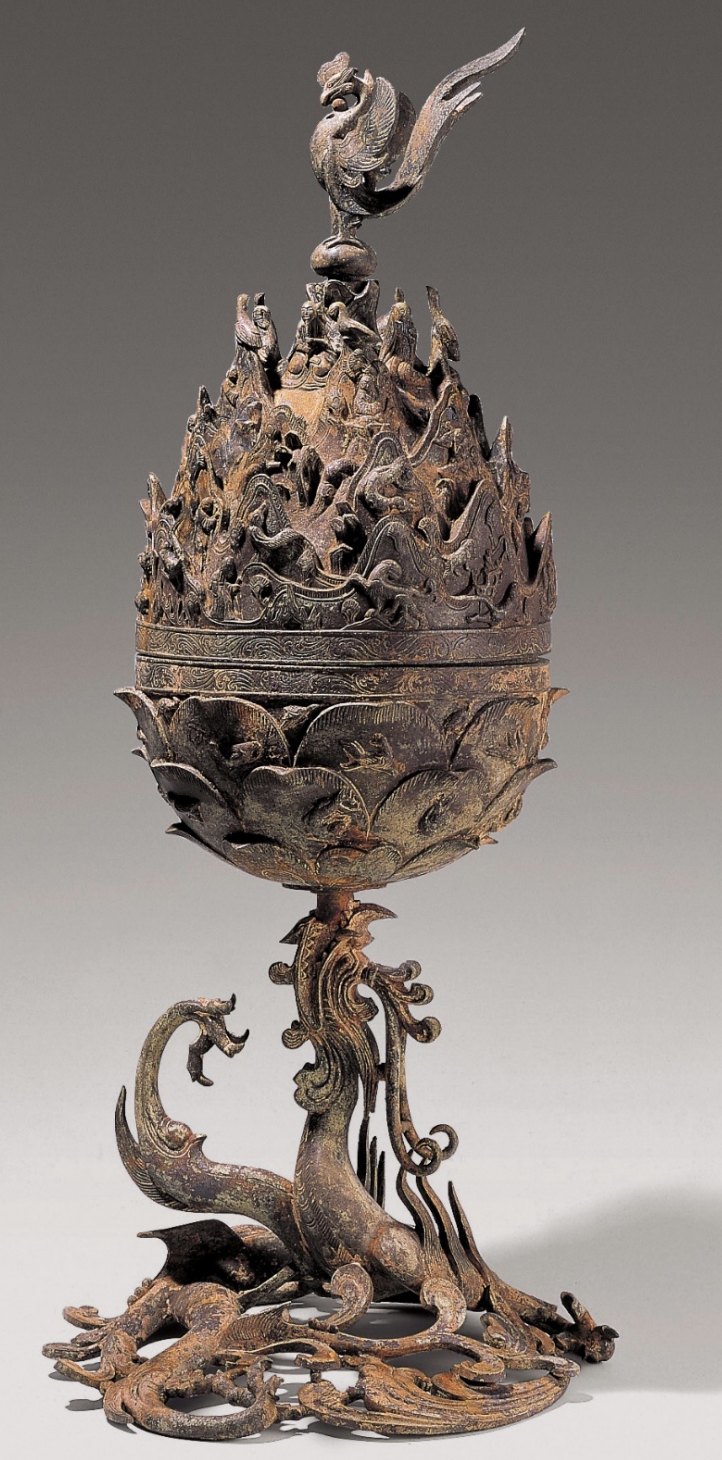
Great Gilt-bronze Incense Burner
Time: 6th - 7th Century
Found: Baekje Kingdom in Buyeo, Chungcheong Province (부여군, 충청)
A ceremonial artifact used in rituals, elaborately designed with intricate motifs, showcasing the sophistication of Baekje metalwork and both Deoist and Buddhist influence.

Golden Crown
Time: 5th Century
Found: Silla Kingdom; from Tomb 88, The Great Tomb at Hwangnam, Gyeongju (황남, 경주)
A crown made of gold and jade
3 treelike vertical forms linking heaven and the earth, representing how shamans move between the two realms using trees
2 antler-like prongs representing antlers of a reindeer to symbolize the fertility of the earth;
comma-shaped jade pieces, fruit hanging from a tree, further representing fertility
crown is similar to headgear found in Russian tombs, further showing a connection to Siberian connections.
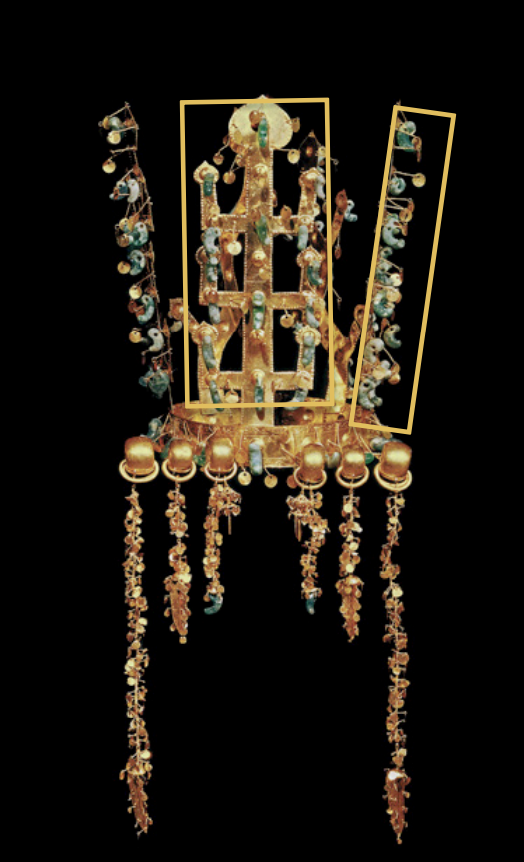
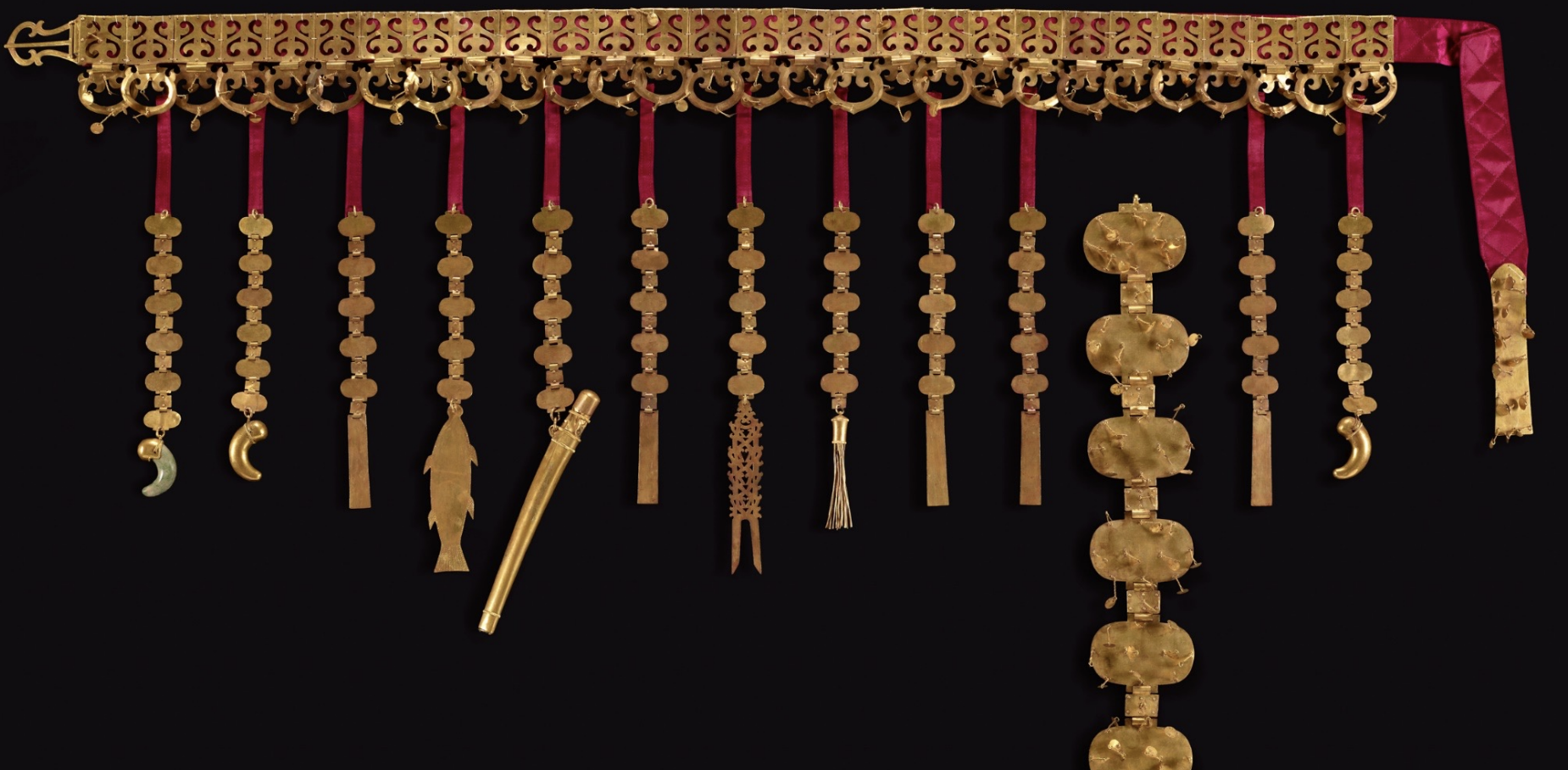
Gold Waist Belt
Time: 5th Century
Found: Silla Kingdom; North Mound of Hwangnamdaechong Tomb (황남대총)
Further shows Siberian connection

Gold Earrings
Time: 6th Century
Found: Silla Kingdom; Bubuchong Tomb (부부총)
shows lots of granulation
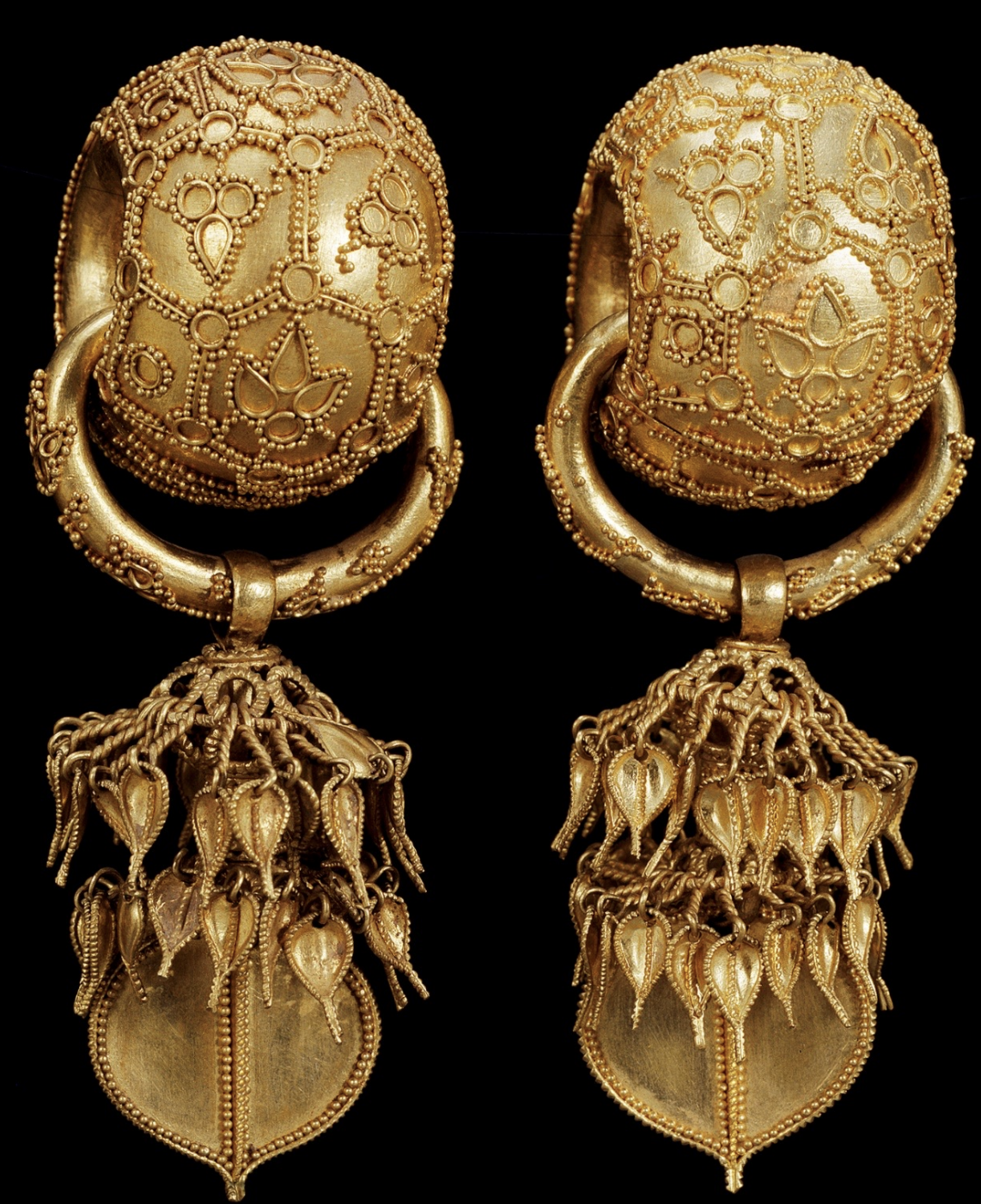

Granulation
A decorative technique used in jewelry making, involving the application of tiny metal beads to create intricate patterns. Granulation is often found in ancient artifacts, including those from the Silla Kingdom.
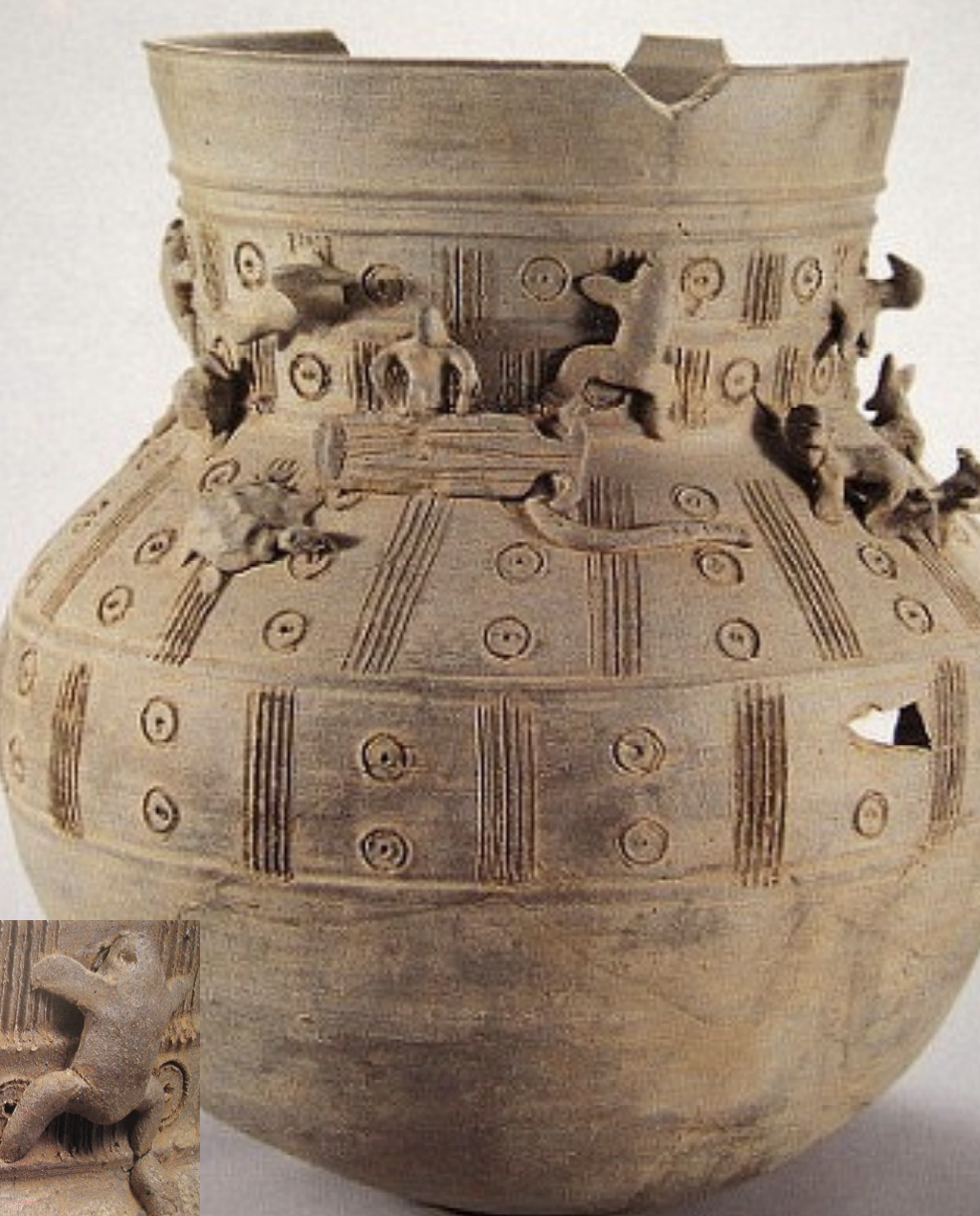
Large Jar with Applied Figures
Time: 5th-6th Century
Found: Silla Kingdom, Gyeongju (경주)
Depicts figures playing Korean Zither

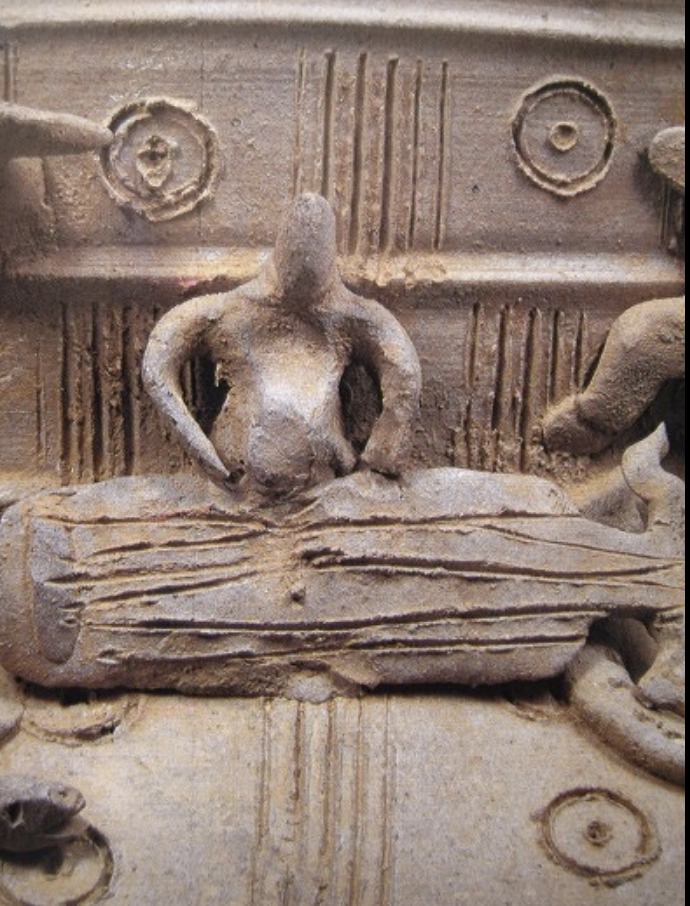
Korean Zither
A traditional Korean stringed instrument known as the gayageum (가야금), characterized by its long, rectangular shape and the use of movable bridges to change pitch.

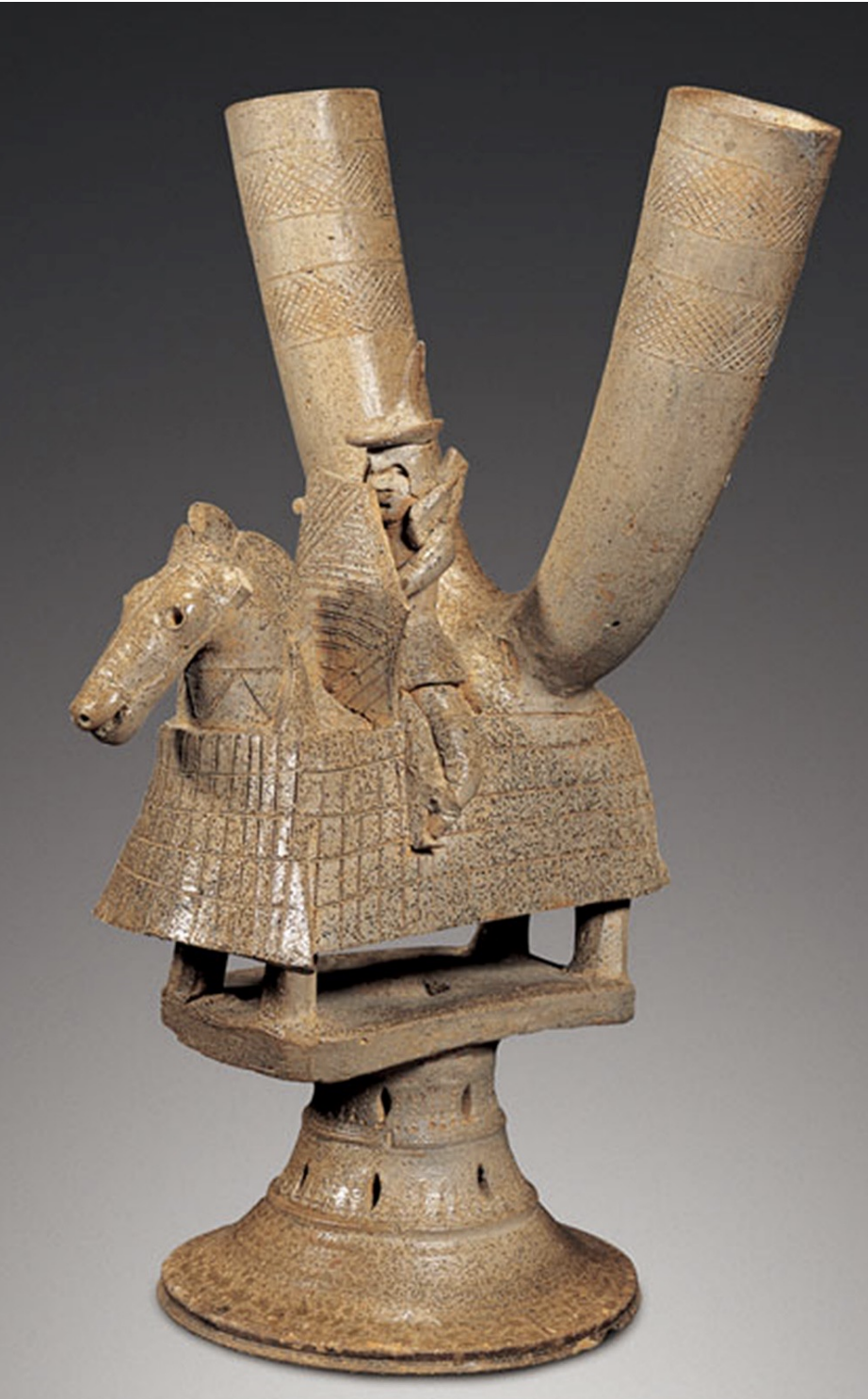
Vessel in the shape of a mounted warrior
Time: 5th-6th Century
Found: Gaya Kingdom; Gimhae, Geyongsang Province (김해, 경상)
Depicts a warrior on horseback, symbolizing military strength and cultural significance; scale armor using leather strings; (different warrior scultures showed class at this time because some showed elaborate clothes while others shows less elaborate clothes)

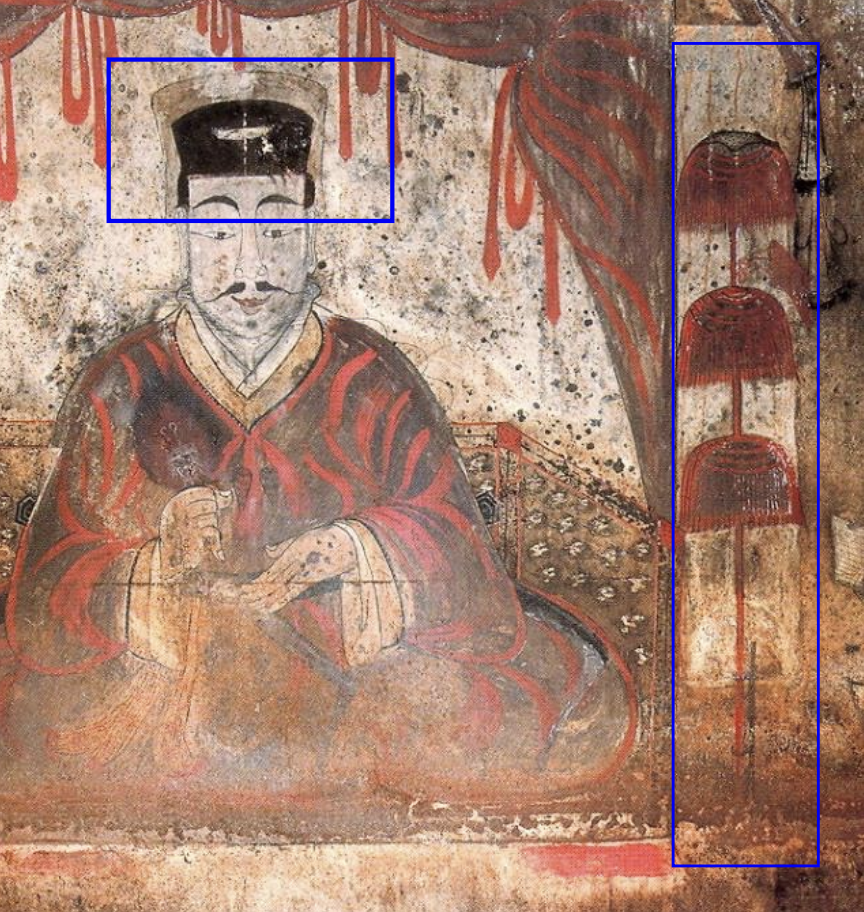
Baekna (백나)
white silk; usually used for white silk crowns depicted on a deceased masters head (with a black inner headdress) in traditional burial tombs of nobles in Korean history.
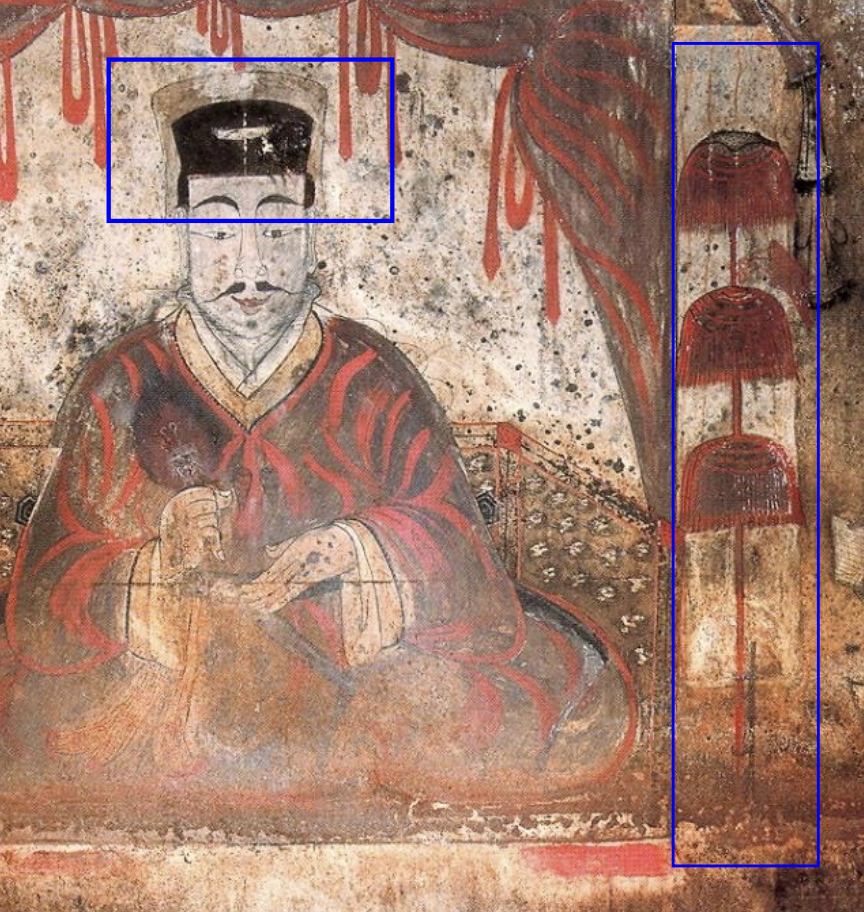

Zhuwei Fan
A traditional Chinese folding fan often decorated with intricate designs, used in various cultural ceremonies and performances, influencing Korean art and aesthetics; shown in tombs of nobles in images of them holding this in their right hand.

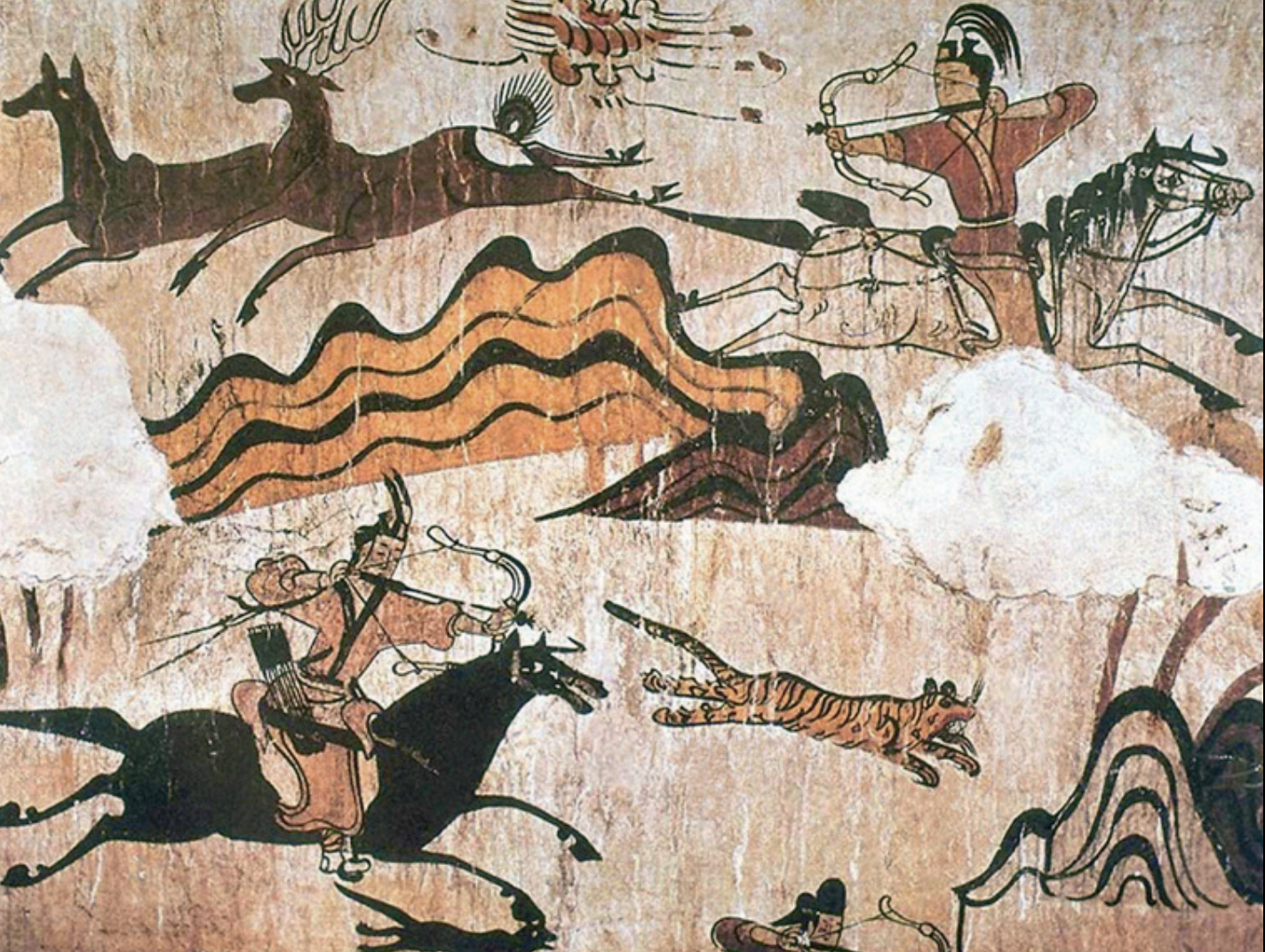
Parthian Shot
A military tactic where a mounted archer shoots at pursuers while riding away, exemplifying strategic skill and mobility in warfare, including influence on East Asian military tactics; shown on western walls of tombs

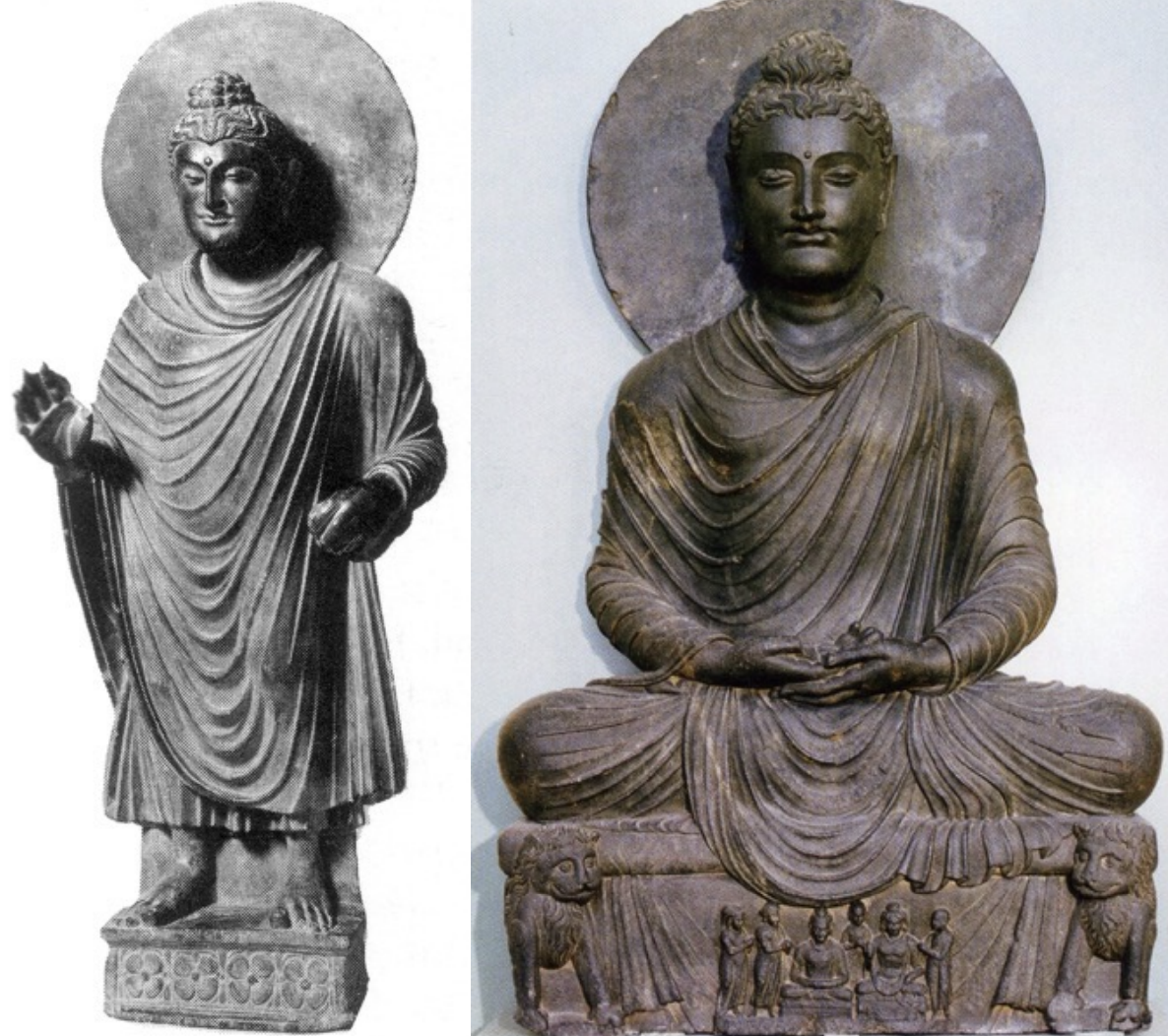
Gandhara Style
An ancient artistic style originating from the Gandhara region in present-day Pakistan and Afghanistan, characterized by a fusion of Hellenistic (influence of Greco-Roman style) and Indian influences, particularly in Buddhist art and sculpture; 2-3rd century CE; made with gray schist

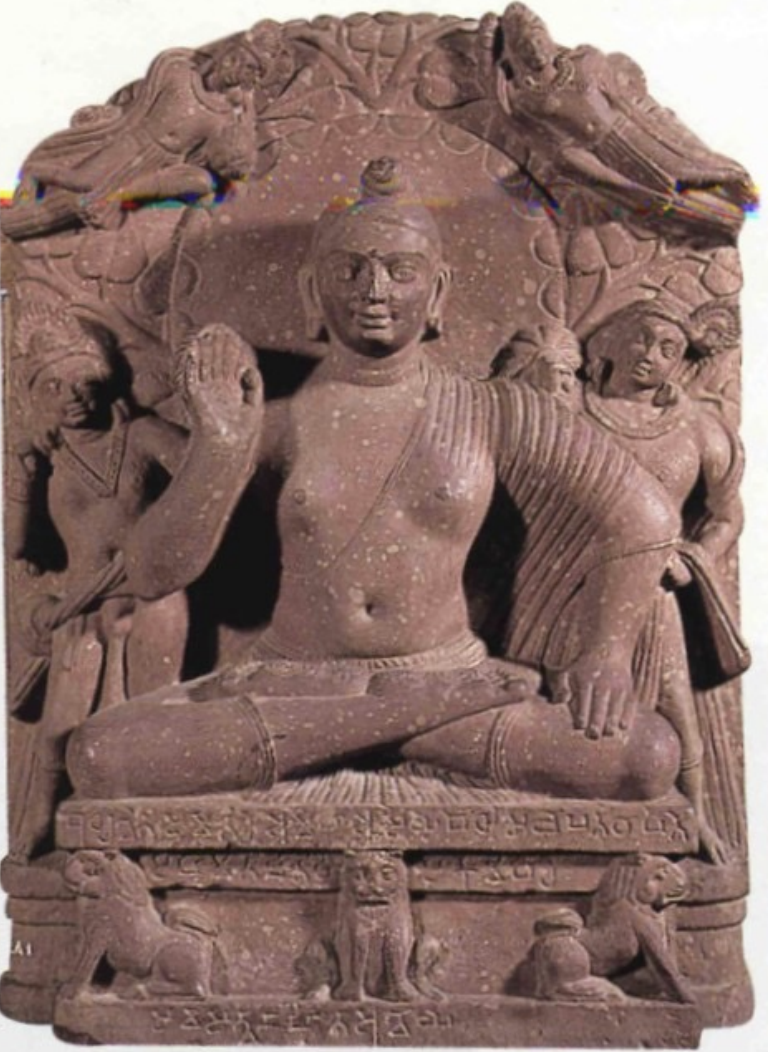
Mathura Style
An ancient artistic style originating from the Mathura region in India, known for its distinctive representation of Hindu and Buddhist deities, characterized by an emphasis on lyrical forms and emotional expression in sculpture; around 1st century CE; made with red sandstone

Preaching the First Sermon at Sarnath Tan Sandstone
Time: 4th Century
Sculture shows Buddha sitting in a yoga posture; with the mudra of “turning the wheel of the law”; with a halo that signifies Buddha’s radiance; Urna (third eye) on the forehead to show wisdom; Ushnisha (bony bumps on his head) to further show his wisdom
significant Buddhist artistic representation depicting the Buddha delivering his first sermon to his disciples after achieving enlightenment
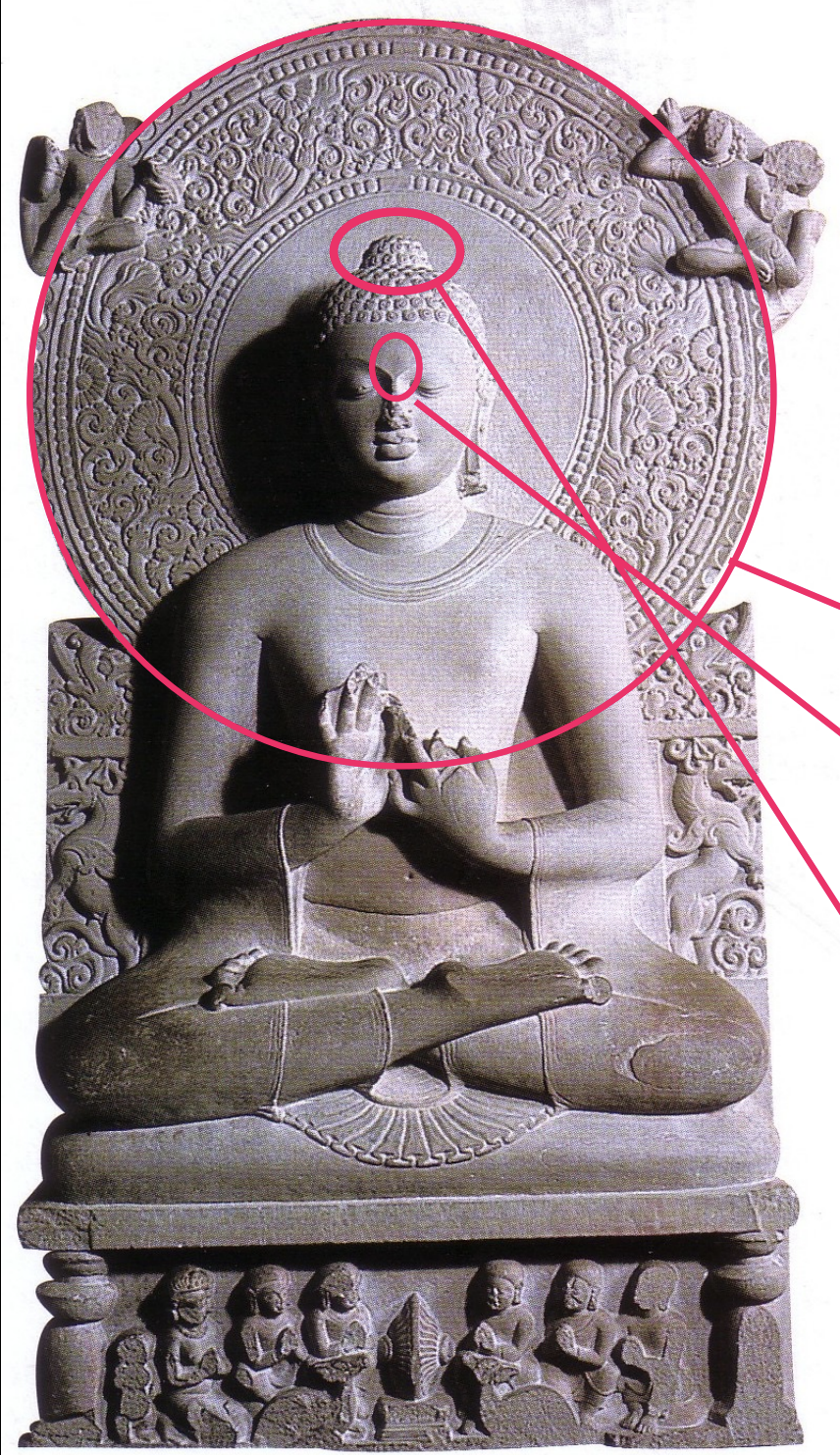
Urna
third eye on the forehead to show enlightenment and wisdom
Ushnisha
bony bumps on head; to show his wisdom
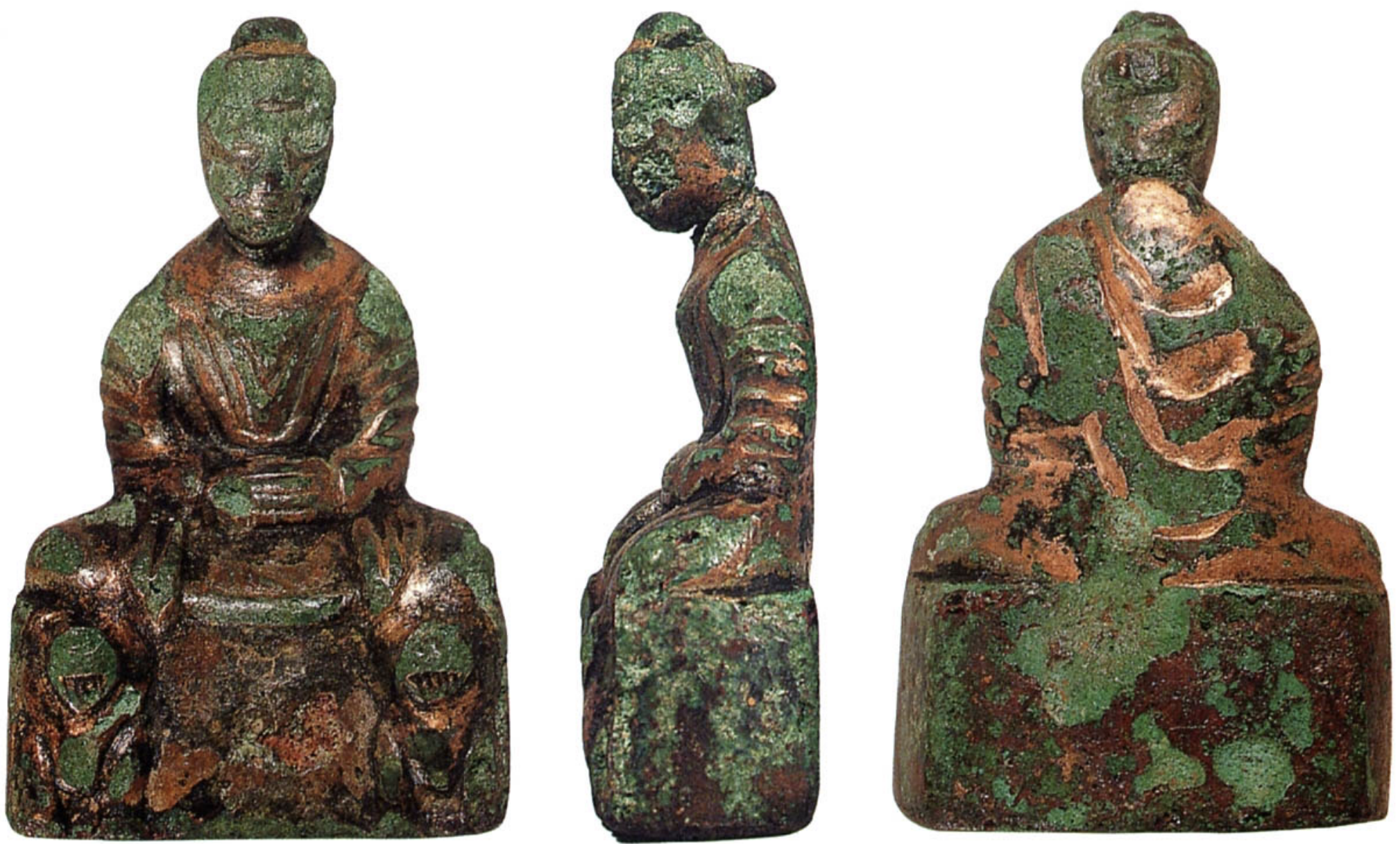
Seated Buddha
Time: 5th Century
Found: Goguryeo or Baekje Kingdom; Ttuksom, Seoul (뚝섬, 서울)
shows a meditating Buddha with hands in a meditative pose; often depicted with elaborate clothing and a serene expression, symbolizing his enlightenment and the calm of meditation; more Gandhara Style than Mathura Style.

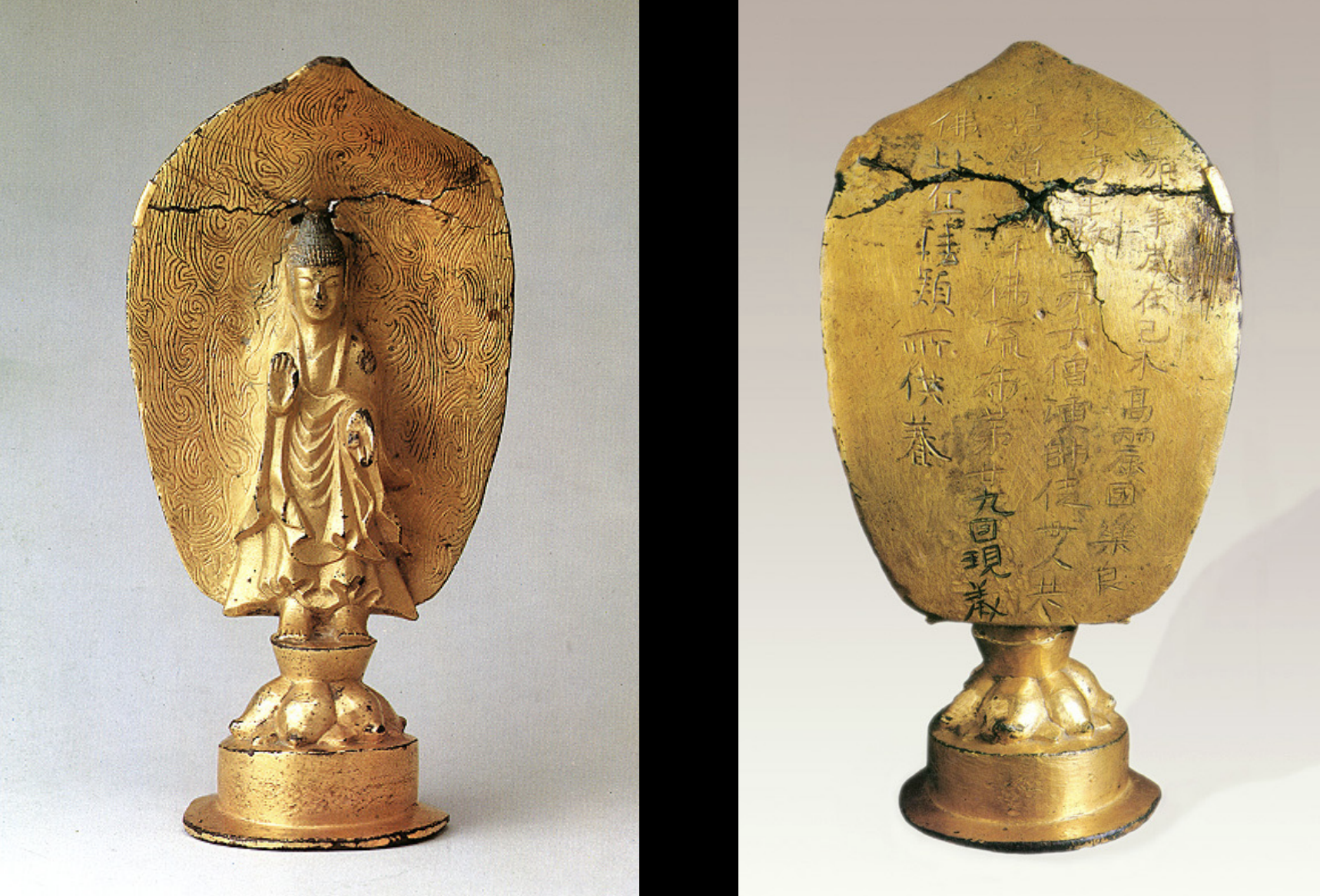
Standing Buddha
Time: 539
Found: Goguryeo Kingdom; South Kyongsang Province (경상남도)
Made of gilt bronze, has exact date and location written on the back; depicts a standing Buddha with a teaching mudra

Mudra
a symbolic hand gesture used in Buddhist and Hindu traditions that conveys specific meanings and intentions
Siddhartha Gautama
the historical figure known as the Buddha, who achieved enlightenment and founded Buddhism; real name of the Buddha
Shakyamuni
Original Buddha; characterized by elongated ear and meditiation mudra (simple hands overlapping each other)
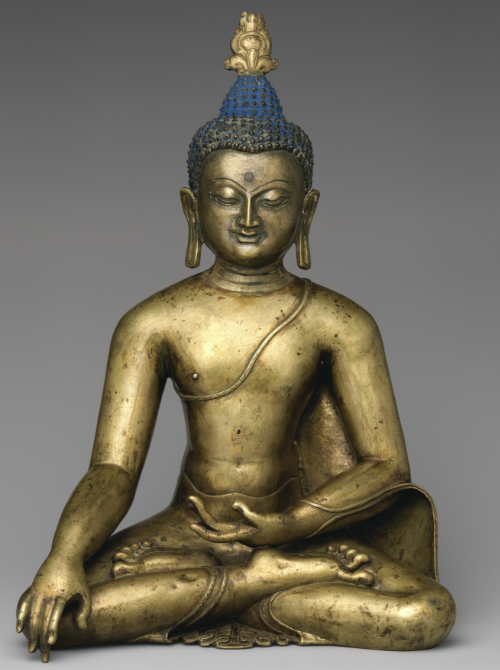

Meditation Mudra
Simple hands overlapping each other; often depicts original Buddha (Shakyamuni)

Queen Maya
Buddha's mother, who died shortly after his birth, often depicted in art as a symbol of purity and devotion; gave birth to the Buddha from her armpits; had an elephant related birth-dream

The Four Encounters
The significant events in the Buddha's life that led him to renounce worldly life; they include encountering an old man, a sick man, a dead man, and a holy man; lead to the conculsion that there are four univeral sufferings: birth, life/aging, sickness, and death (life = suffering)
Amitabha
The Buddha of Infinite Light, associated with the Pure Land sect of Buddhism. He represents compassion and the promise of rebirth in his Pure Land for those who invoke his name; 9 gestures (main is the mudra with index figure touching thumb with both hands and the two hand facing up and touching each other on the lap); also depicted with the color red a lot; represents Western Paradise (after enlightenment)

Bodhisattva
closer to us(human begins) and secular worlds; reached enlightenment but denies the end of rebirth in order to save others that are not enlightened here on Earth; wears jewelry and clothes

Avalokitesvara
A Bodhisattva of compassion known for helping those in suffering. Often depicted with multiple arms to assist many beings simultaneously and associated with both male and female forms
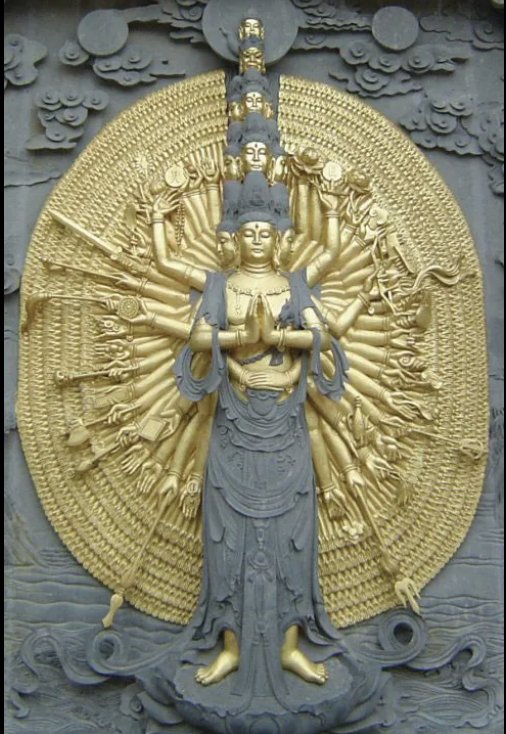

Vairocana
The celestial Buddha representing the concept of enlightenment and the principle of cosmic truth; Vairocana is often depicted at the center of the mandala and symbolizes the illumination that dispels ignorance; mudra shows Buddha holding right index finger with left fist
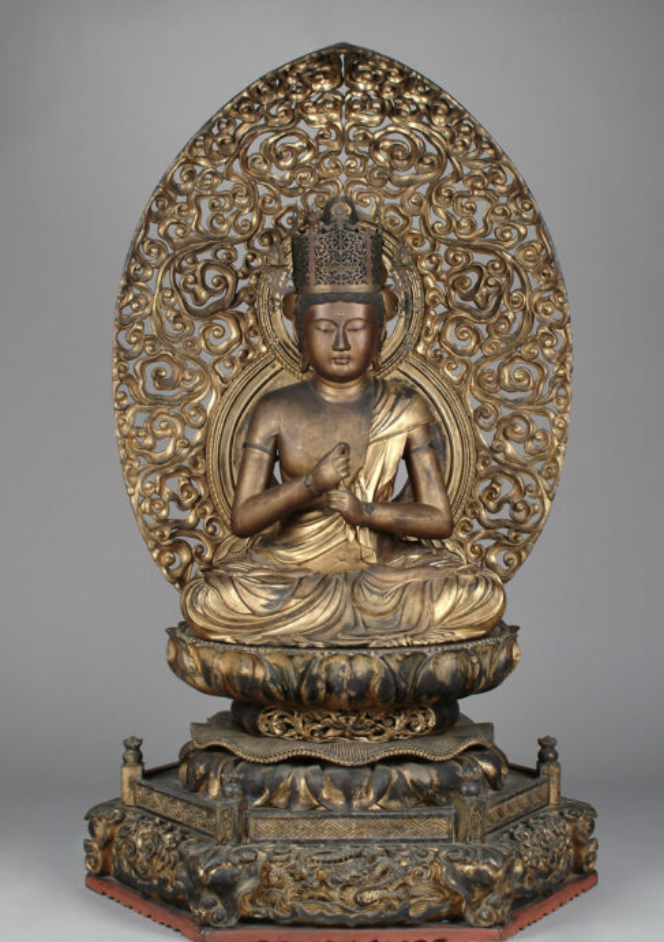

Hinayana
A school of Buddhism emphasizing individual enlightenment and personal discipline, often seen as more conservative and focused on monastic life compared to Mahayana
Mahayana
A major branch of Buddhism that emphasizes the collective salvation of all beings and the pursuit of enlightenment for others, promoting compassion and altruism
Chakra Dharma
The principle of the "Wheel of Dharma," representing the teachings of Buddha and the path to enlightenment, symbolizing the cycle of birth, life, death, and rebirth; often depicted as a wheel with eight spokes,
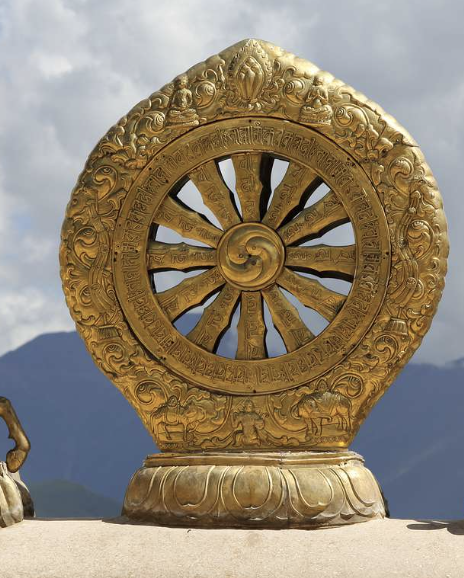

Jeon’gok-ri Site
An archaeological site in South Korea that dates back to the Neolithic period, known for its large stone tools and evidence of early human settlements
Amsadong Site
An archaeological site in South Korea notable for its dolmens and evidence of ancient burial practices, dating back to the Bronze Age
Goindol (Dolmen Tombs)
Prehistoric burial structures found in Korea, known for their large stone configurations
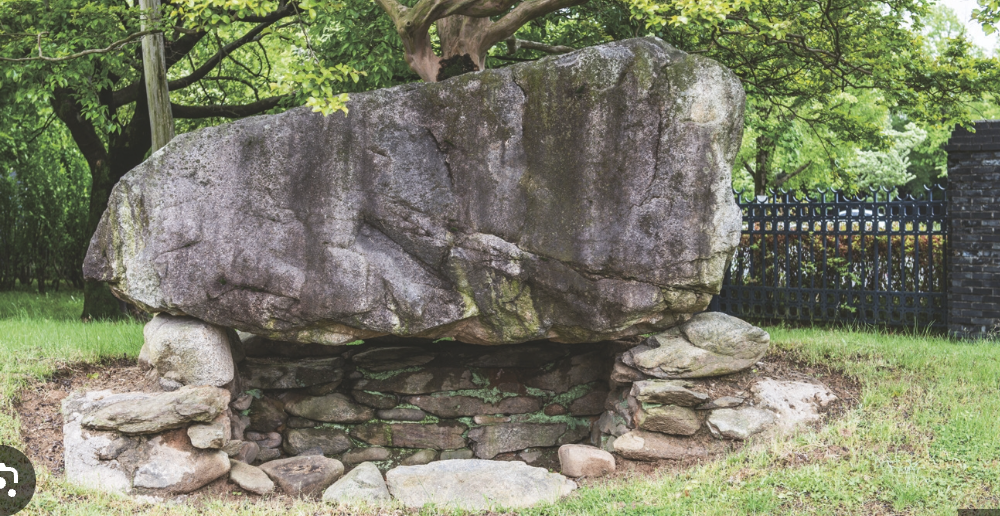

The Silk Road
An ancient trade route that connected the East and West, facilitating the exchange of goods, culture, and ideas; Buddhism was brought to China by monks and travelers from India; Mahayana Buddhism was spread into Central and Eastern Asia
Dunhuang Buddhism
A significant branch of Buddhism that flourished in the Dunhuang region (China), known for its art and manuscripts, serving as a cultural crossroads along the Silk Road.
Yungang Grottoes, Northern Wei
A series of ancient Chinese rock-cut Buddhist cave temples located near Datong, known for their impressive sculptures and carvings that reflect the cultural exchange along the Silk Road; these sculptures were brought to Korea and influenced heavily