PHAR 202 Amino Acids
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
this only has the basics of the 20 standard α-amino acids (no optical activity, fischer conventions, CIP system, or prochirality yet because i need to watch the lecture again cause i don't understand it yet ;-; )
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What are proteins made up of?
20 standard amino acids called α-amino acids
they are called this because the nitrogen atom is attached to the alpha carbon
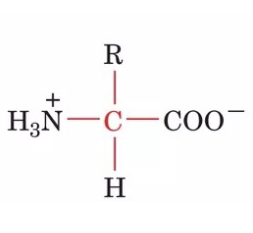
Standard α-amino acid general structure
contains 20 different R groups that yield distinct physicochemical characteristics
amphoteric/can act as either an acid or a base
this is because the carboxylic acid and the amino group of the amino acid are completely ionized in the physiological pH range
zwitterions (bear charged groups of opposite polarity)
COOH → COO- which acts as the base component
H2N → H3N+ which acts as the acid component
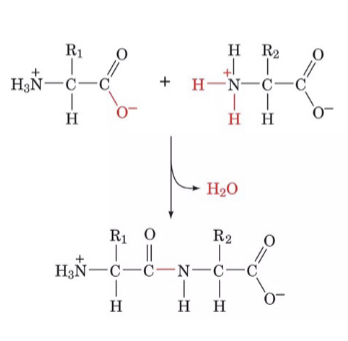
How do peptide bonds form?
two α-amino acids undergo a condensation reaction to form a dipeptide
How to calculate the chemical sequence space for polypeptides?
general formula when considering all 20 distinct α-amino acids: 20^n, where n is the number of building blocks
formula for considering x number of α-amino acids: x^n, where x is the number of total possible amino acids and n is the total possible positions for a building block to go
How are the standard α-amino acids categorized?
They are distinguished by their R groups and the characteristic interactions of their R groups
What are the nonpolar amino acids?
Glycine
Alanine
Valine
Leucine
Isoleucine
Methionine
Proline
Phenylalanine
Tryptophan
What are the uncharged polar amino acids?
Serine
Threonine
Asparagine
Glutamine
Tyrosine
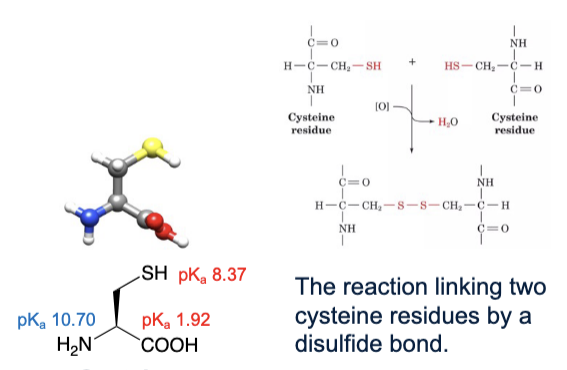
Cysteine
What are the negatively-charged polar amino acids?
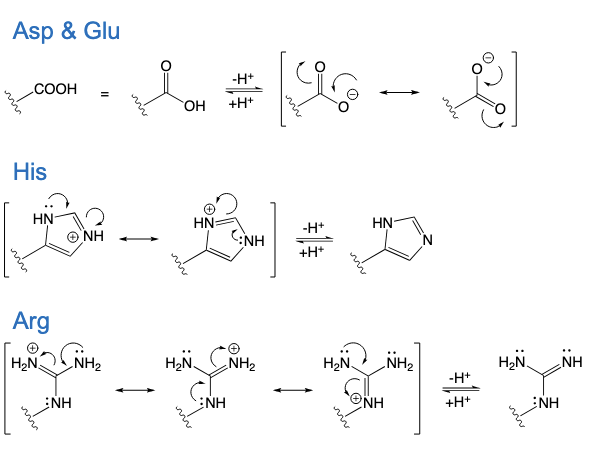
Aspartic acid
Glutamic acid
What are the positively-charged polar amino acids?
Histidine
Lysine
Arginine
Glycine
abbreviations: Gly, G
smallest amino acid as its R group is a hydrogen atom
Alanine
abbreviations: Ala, A
R group for alanine is a methyl group
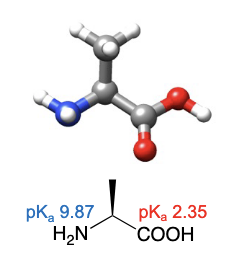
Valine
abbreviations: Val, V
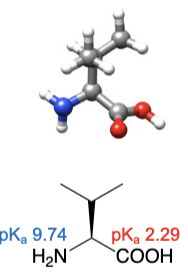
Leucine
abbreviations: Leu, L
same number of carbons as isoleucine, but different atom arrangement
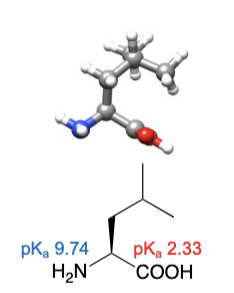
Isoleucine
abbreviations: Ile, I
same number of carbons as isoleucine, but different atom arrangement
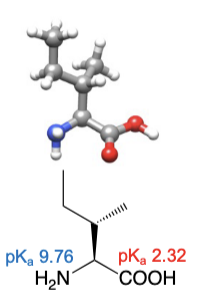
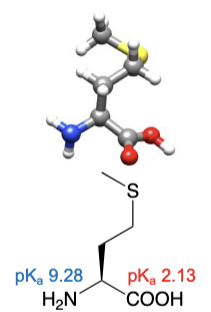
Methionine
abbreviations: Met, M
thiol ether side chain resembles an n-butyl group in physical resemblance and chemical properties
C and S have nearly equal electronegativities and S is about the size of a methylene group
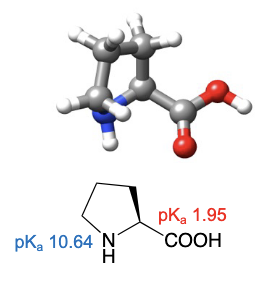
Proline
abbreviations: Pro, P
only amino acid that makes a tertiary amide linkage due to the single hydrogen on linkage point
cyclic secondary amino acid, which is unique among the 20 standard amino acids
cyclic nature of pyrrolidine side chain provides conformational constraints in 3D space
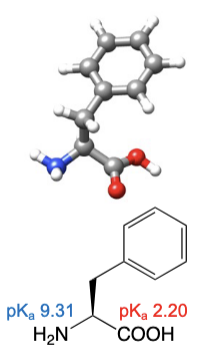
Phenylalanine
abbreviations: Phe, F
alanine with a phenyl group attached, hence the name
Tryptophan
abbreviations: Trp, W
lone pair of electrons on Trp are in a pi orbital so within the aromatic ring, it means it will be flat
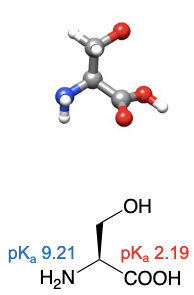
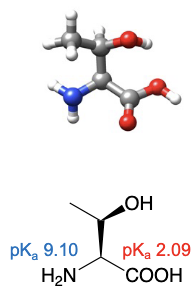
Serine
abbreviations: Ser, S
R group can have favourable interactions with water
Threonine
abbreviations: Thr, T
R group can have favourable interactions with water
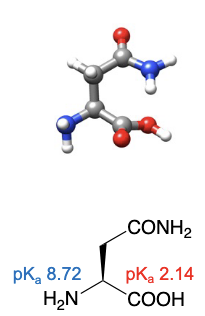
Asparagine
abbreviations: Asn, N
R group can have favourable interactions with water
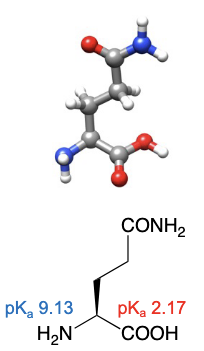
Glutamine
abbreviations: Gln, Q
R group can have favourable interactions with water
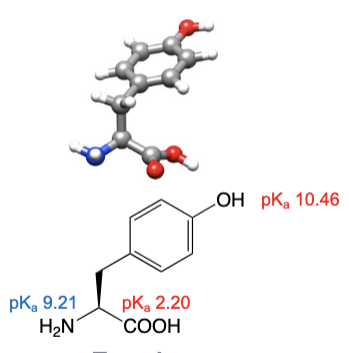
Tyrosine
abbreviations: Tyr, Y
R group can have favourable interactions with water
Cysteine
abbreviations: Cys, C
R group can have favourable interactions with water
SH is an ionizable group but due to its pKa being higher than the physiological pH, the entire molecule is considered an uncharged polar amino acid
two cysteine residues can link via a condensation reaction to form a disulfide bond
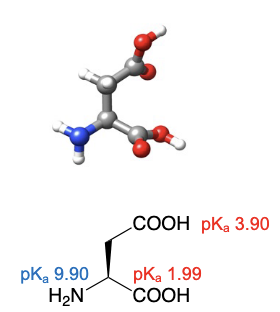
Aspartic acid
abbreviations: Asp, D
similar structure to aspargine, but on the gamma carbon, the attached NH2 is swapped for OH to become its current COOH
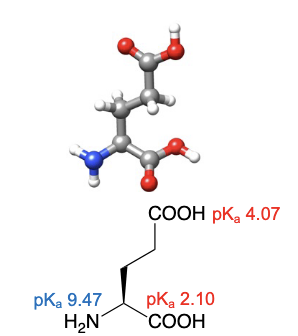
Glutamic acid
abbreviations: Glu, E
similar structure to glutamine, but on the delta carbon, the attached NH2 is swapped for OH to become its current COOH
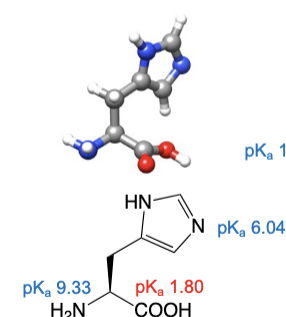
Histidine
abbreviations: His, H
indol ring appended to the beta carbon
indol component of the molecule can act as a base
Lysine
abbreviations: Lys, K
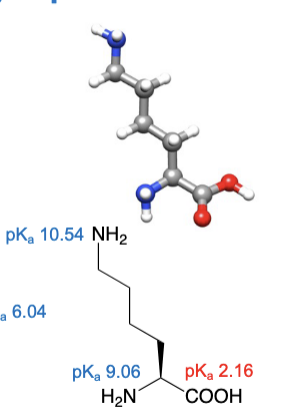
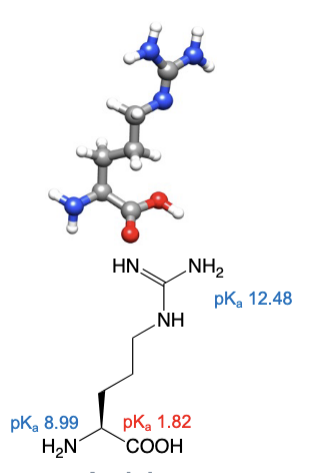
Arginine
abbreviations: Arg, R
Which amino acids have charged polar amino sidechains?
Asp and Glu
His
Arg