social psych final
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
social exchange theory
- to minimize costs and maximize rewards (almost an economic theory)
norm theory
- consists of the reciprocity norm and the social responsibility norm
reciprocity norm
- we are obliged to help people who have helped us in similar ways
- ex. if you help lend me $5 i'll lend you $10 but not $50K so some level of parody here
social responsibility norm
- if we have the ability to help someone, we have the responsibility to do so
- universal across cultures and religions
evolutionary theory
consists of reciprocity and kin selection
kin selection
- much more likely to help someone who is closely genetically related to you
- rationale: much more likely to carry out/propagate our genes by helping parents, siblings, kids
reciprocity
- historically homo sapiens needed other people to survive
- if you were rejected by the group you couldn't survive
- too selfish = steal too many resources from others
- too giving = easy to be exploited
- reciprocity is MUTUAL EXCHANGE
kitty genovese incident (bystander effect)
- kitty genovese was a young woman who was stabbed in an open area near her house
- people were awake & windows opened
- no one called the police so she was raped and stabbed for 45 minutes
bystander effect
- the more people are present, the less likely any one of them is likely to get involved
- textbook definition: the likelihood of a given individual helping is reduced in the presence of bystanders
bystander effect STUDY
more bystanders/people in the room -> time it took to get help increase
factors impacting the bystander effect
more likely to happen when:
- situation = ambiguous
- there's a high # of ppl
- bystanders are strangers
- other's ppl's reactions are hard to interpret
latane & darley's "decision tree" model of situational influence
- noticing the problem
- interpreting the incident as a need for help
- assuming responsibility for giving help
diffusion of responsibility
- the more people there are, each person feels less responsible in the situation
- suspected issue in the kitty genovese incident
- relates directly to the third link in the decision tree
pluralistic ignorance
the belief that if others are not responding, it must not be an emergency
darley & batson's "good samaritan" seminarians
- only some of the priests who were on time constraints actually helped while 100% of the priests who had time helped
- takeaway: amount of spare time is a major factor in determining whether someone would help
- religiosity leads to more helping behavior than religious ppl but only IN PUBLIC
negative state relief hypothesis
- the more sadness one experiences/reduced self-esteem -> more helping behavior exhibited
mcMillen & austin's liars
- person who lies to experimenter gives 2x as much, on average, than ppl who were asked to tell the truth to the experimenter
- takeaway: affective state of potential helper (ex. guilt) can greatly influence helping behavior
gender of helper
- men help more than women do in experimental studies
- men more likely to help in heroic ways
- women more likely to help in long-term ways
empathy in the population
- empathy distributed in the population like a bell curve
- some ppl have very lil and others have loads
carol wheelchair study
?? (idk what this is)
prosocial behavior
- like aggression can be increased by viewing others engaged in it
- ex. experimenter showed lassie (dog show) helping video, regular lassie video, and brady bunch
- takeaway: watching helping behavior increased the time spend helping over other two shows
prosocial behavior schnall, roper, & fessler (2010) STUDY
- experimenter showed 3 grps of ppl 3 shows: open ocean, faulty towers, or oprah helping episode
- ppl who watched oprah helping episode increased time helping
- takeaway: demonstrating helping behavior more effective than just putting ppl in a good mood
cognitive factors of prosocial STUDY
- observational learning
- priming pro-social schemas
affective factors of prosocial STUDY
"moral elevation of mood"
neurological factors of prosocial STUDY
- activating mirror neurons (shown to be effective in rhesus monkeys)
- increase in befriending hormones (higher levels of oxytocin in those who help)
prejudice
- a negative attitude toward a socially defined group and any person perceived to be a member of that group
- key words: attitude, socially defined, perceived
cheat sheet for social biases
- prejudice = affective
- stereotype = cognitive
- discrimination = affective
stereotypes
- cognitive component of biases
- beliefs ppl have abt social groups used to make inferences, predictions, and attributions abt individuals
- even if wrong, ppl tend to believe these strongly
- stereotypes = schemas (help bc we're cognitive misers)
stereotypic info
- beliefs abt groups but only used when there's no individuating info
individuating information
- specific info abt a person that may or may not fit w/ a group
- ppl use this when available -> resort to stereotypes when its not
- ex. believe on average that women are worse at math but wouldn't believe that a woman is dumb if she has an 800 math SAT
discrimination
- differential treatment based on perceived group membership
- behavioral component of bias
- feelings, beliefs, and actions have a great deal of congruency
- consists of treating the ingroup > outgroup
swim (1994) STUDY
- gender stereotypes are generally accurate
- when not, ppl usually underestimate gender differences
- generally accurate abt magnitude of differences
metanalysis STUDY of gender differences
- most stereotypes accurate
- only stereotypes that are inaccurate are national stereotypes
- ex. italians are mobsters, germans are uptight
evaluative tone
- positive vs negative stereotypes
- are you perceived as being better at smth or worse
unequal status
- prejudice as a justifying ideology
- has to do w/ cognitive dissonance
- "ppl face unequal suffering bc they are acc below us"
institutional supports
- segregation (happens naturally but leads to lack of knowledge abt other groups)
- education
- language (using slurs will make you more prejudiced; self-perception/cognitive dissonance)
- media (sometimes ppl's only source of info on other groups)
social identity theory (Tajfel)
- group identity serves self-esteem needs (part of your self worth)
- ex. if we identified even/odd number seats in class & give rewards to random ppl -> give rewards to ppl in your ingroup
- view in-group members as extensions of ourselves
in-group bias (wilder)
- minimal group paradigm necessary to produce in-group bias
- ex. "overestimators" v. "underestimators"
- even if groups are inane/inconsequential -> still produces discerning behavior
hovland & sears scapegoating STUDY
- when the price of cotton is low -> less lynching but opposite if crop price is high
- takeaway: frustration is a sufficient cause for scapegoating behavior
realistic group conflict theory
- the theory that prejudice arises from competition between groups for scarce resources
- evolutionary basis bc dangerous to stray from tribe & need to compete w/ other tribes to survive
- also considered "adaptive xenophobia"
- personality factors can impact this
status needs (pratto & sidanius) STUDY
- basically just developed social dominance orientation & authoritarian personality tests
outgroup homogeneity effect
- all ppl in the outgroup are similar to each other physicall/mentally
- "they all look the same to me"
accentuation
- overestimate between group differences
ultimate attribution error
- inclination that outgroup success is external and outgroup failures are internal
- ties to social identity theory (ingroup is successful bc of personal qualities -> we have good personal qualities)
- self-fulfilling prophecy component
clark and clark's doll preference STUDY
- young black kids asked to pick between white and black dolls -> many picked the white dolls and called black dolls ugly
- takeaway: continued discrimination can lead to internalization of negative stereotypes
modern racism scale
- identifies 3 key components of racism
- denial of continued discrimination ("discrimination against blacks is not a problem in the US")
- antagonism towards demands ("blacks are too demanding for equal rights")
- resentment abt special favor ("blacks have gotten more economically than they deserve")
different attitudes
- implicit (non-conscious) attitudes
- explicit (conscious) attitudes
- weak positive correlation btwn the two
- takeaway: you can't tell implicit attitudes from explicit attitudes
devine (1989) stereotypes STUDY
- activation of stereotypes is the same in high/low prejuediced individuals
- takeaway: clocking a stereotype is an automatic process
fazio et. al implicit biases STUDY
- interested in how fast ppl responded to bad/good words based on the race shown
- ppl classified good word faster if followed by white face & classified bad word faster if followed by a black face
- no correlation btwn scores on modern racism scale and facilitation effects
dovidio et. al implicit biases STUDY
- basically the fazio study but instead of supraliminal faces it's subliminal faces (flashed before conscious can process)
- priming effects found for positive and negative words related to race of price
- no relation to self-reported prejudice
related concepts of dovidio STUDY
- self report related to jury decisions bc it's a conscious process so necessary to check before assembling a jury
- priming related to non-verbal indicators of arousal (it's the feeling you can't quite grasp but it's uncomfortable)
dovidio & gardner (2000) hiring STUDY
- when applicants are strongly/weakly qualified, little to no difference in hiring decisions
- small difference favoring black ppl but not statistically significant
- when candidate ambiguously qualified, white ppl hired more than black ppl
- takeaway: schemas are used when there is no individuating information
situational factors of stereot
- more likely to stereotype when:
- highly ambigious situtation
- excessive cognitive demands (law of least effort)
- situational excuses (scapegoats) present
- when self-esteem threatened/reduced
- emotional arousal high
- group v individual interactions (more stereotypes btwn 2 diff groups v 2 diff ppl)
- when there is low familiarity (no individuating info)
eyewitness mistakes
- erroneous eyewitness testimony is the most frequent cause of wrongful convictions
- investigators can (un)knowingly influence eyewitness testimony
buckhout's "staged assault on prof" STUDY
- Ss asked 6-7 weeks later to identify assaulter from a lineup of 6 photos
- 60% misidentification rate
loftus misinformation effect
-occurs when post-event info get erroneously intertwined w/ memory of the event itself
- results in false memories
- follows the lost in the mall experiment where they planted a false memory of ppl being lost in the mall in childhood
- takeaway: person's subjective feelings abt an event is not an accurate guide to whether it's real or not
- memory is reconstructive/malleable
source monitoring error
- when you remember the info but not where and when you encountered it
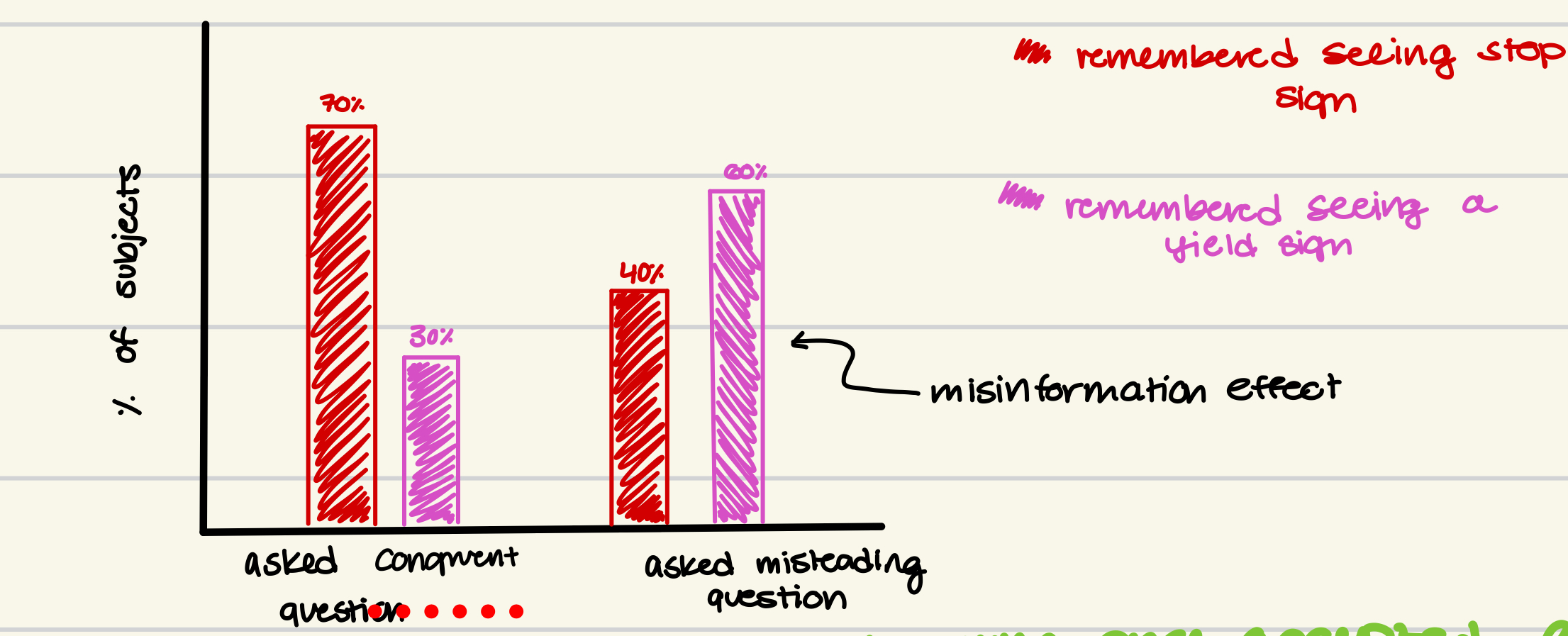
car and sign questions STUDY
- all Ss saw car stop @ stop sign & asked a question -> asked weeks later where car stopped
- congruent question: what happened after the car stopped at the stop sign
- misleading question: what happened after the car stopped at the yield sign
false memories
- recalling events that in fact never occurred
- individuals who once accepted as true certain memories that they now believe to be false ???
reality monitoring error
- misattributing memories to the wrong source of experience
- neither witnesses nor experts can distinguish fake from accurate memory
- jurors not good @ identifying a lying witness
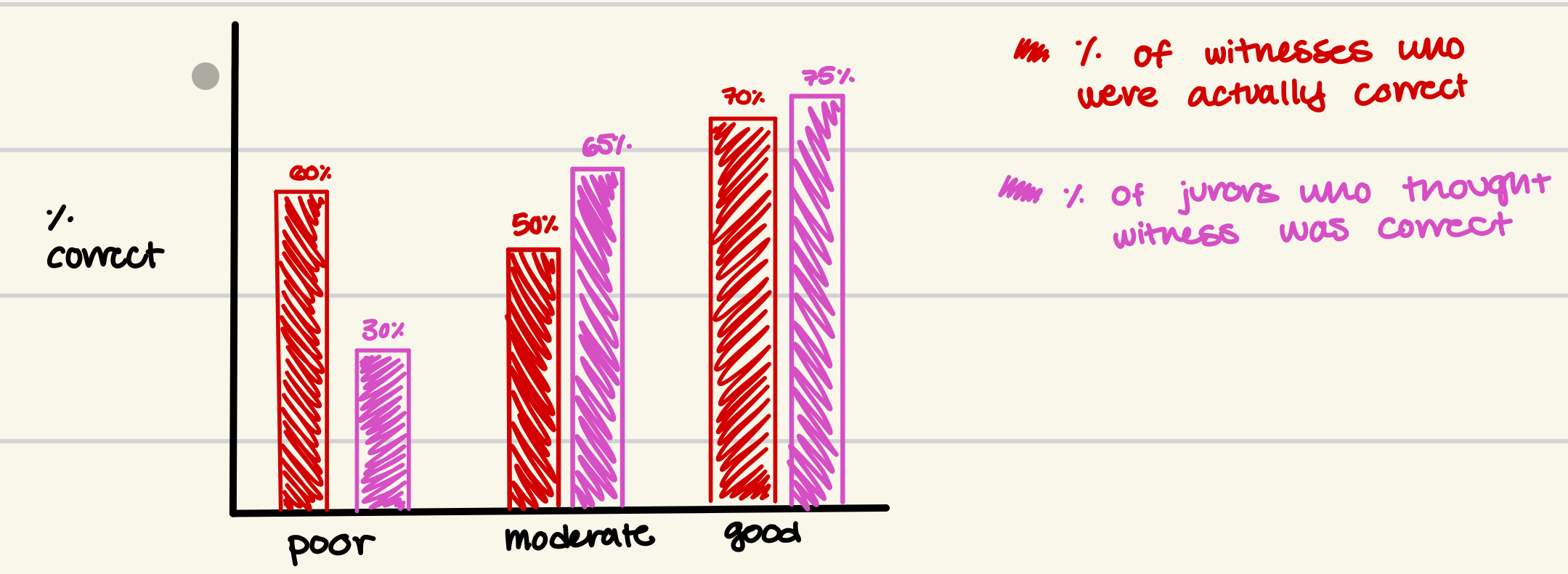
juror study
- shows juror reliance on eyewitness testimony and perception of accuracy
- poor viewing conditions -> not full frontal view, bad lighting, further
- good viewing conditions -> full frontal view, good lighting, close to them
eyewitness mistakes 2
- eyewitness testimony increases the jury's rate of conviction even when the witness is LEGALLY BLIND !!
- human observors have no ability to discern eyewitnesses who have mistakenly identified an innocent person
- those who attend more closely to other details are more likely to misidentify another subject
lineup procedures to be used for accuracy
- foils should "resemble" suspect
- foils should be presented sequentially to avoid best guess problem (most important)
- use double-blind method to avoid self-fulfilling prophecy
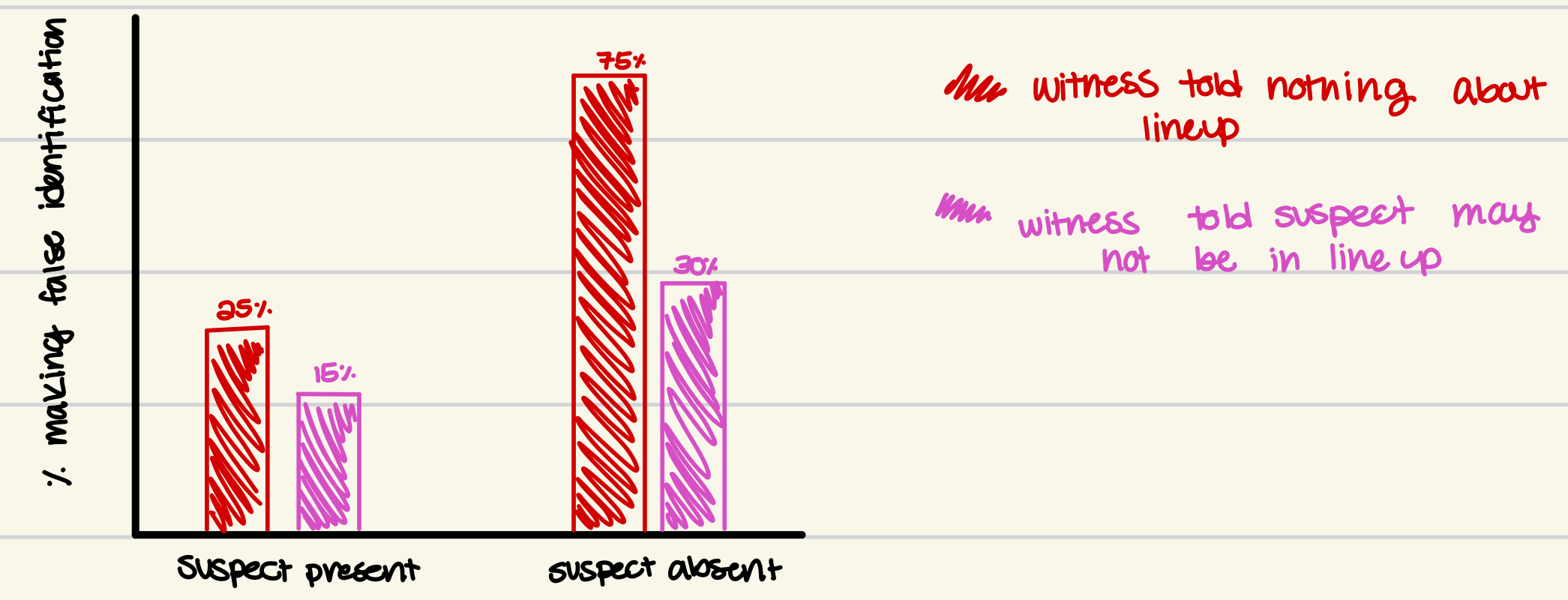
effects of false identification STUDY
- when witnesses given info abt the lineup, much less likely to make a false identification
- especially helpful when the suspect isn't in the lineup
- takeaway: informed decisions abt whether suspect is in the lineup helps decisionmaking
defendant characteristic - attractiveness
- higher physical attractiveness -> less likely to get a conviction
defendant characteristics - similarity to jurors
- similarity attraction
- false consensus effect
- getting a jury similar to defendant is a benefit
- ex. if an indicated sex criminal seems like you -> "not likely to do it"
defendant characteristic - race
- matching principle in conviction/sentencing by race
- ex. convict more white ppl for white collar crimes & black ppl for property damage/violence
- disparity in death penalty cases (race of victim/defendant important)
defendant characteristics impact
- effects occur when evidence/case is ambiguous or too complex for full comprehension
judges' instruction
- lay person translation of the actual law/crime defendant is accused of
- "ignore what has been said; it's inadmissible"
judges' instructions - testimony
- disregarding inadmissible testimony and pretrial publicity
- v important for ppl to focus on what's acc happening inside court
judges' instructions - legal definitions
- need instruction when legal definitions often fail to match juror "prototypes" of crimes
- ex. rape not j an aggresive stranger physically forcing someone to have sex -> can also be a relative, husband, etc.
judges' instructions - burden of proof
- subjective determinations of "preponderance" or "beyond reasonable doubt"
- once again ppl have diff definitions
schematization
- creating a plausible story for the jury
- narrative story abt what happened
- opening statements used for this (focused on emotions not facts)
personality factors on sentencing
- ppl high in authoritarianism -> much more likely to convict/give harsher sentences
- smth v punitive abt them (tend to perceive anyone different as a threat so must treat them punitively)
what is the best predictor of a jury verdict?
- the quality of evidence
- may be exceptions to this but legal scholars made this determination from large samples (unbiased)
group related phenomena - minority influence
- consider how do they help change minds? (ex. 12 angry men)
- however, the most likely scenario when there's only one dissenter is that they'll agree w/ the majority decision
group related phenomena - behavior
- in 12 angry men many jurors willing to capitulate to normative influence
- "i don't know why i just believe he's guilty" after everyone expressed that opinion
benefits of a jury (why not a judge)
- forcing deliberation requires in-depth thinking
- more central route (systematic processing) is increased
- representativeness/diversity of perspectives (each person brings a special knowledge/info to jury room)
- attention focused on all of the evidence rather than selective pieces
- group recall > individual memory (transactive memory almost always superior)