Antimicrobial in Equine Medicine
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
What are pros of beta-lactams?
safe in horses
high efficacy
low cost
what is the mechanism of action of beta-lactams?
interfere with bacterial cell wall production —> cell lysis
What do we use beta-lactams for?
gram positive bacteria
best choice for streptococci infection
most anaerobic infections
what other antimicrobial can we use with beta-lactams for a better effect?
aminoglycosides
fluoroquinolones
what are cons of beta-lactams?
limited efficacy with abscesses (which are common with streptococci infection)
what are the routes of administration of beta-lactams in horses?
Na and K penicillin - IV
Procaine penicillin - IM
oral absorption is too poor in horses
what are adverse effects of beta-lactams?
type I immune reactions - anaphylaxis
type II immune reactions - haemolytic anaemia, thrombocytopenia
what do we need to be aware of when administering procaine penicillin?
horse tests positive in dope test for next 6 weeks (important for race horses)
if bottle not shaken properly to mix - can administer pure procaine —> overdose
if given IV instead of IM - CNS effects
what is the effect of beta-lactams on the bacteria?
bactericidal - kill the bacteria
what is the mechanism of action of cephalosporins?
interfere with bacterial cell wall production —> cell lysis
(same as beta-lactams)
why might cephalosporins be a better choice than beta-lactams?
same mechanism of action - however cephalosporins more resistant to bacterial defences
what are the main differences between the generations of cephalosporins?
the higher the generation (4th gen highest) the more effective they are against gram negative bacteria
what is the effect of cephalosporins on the bacteria?
bactericidal - kill the bacteria
what is the mechanism of action of aminoglycosides?
penetrate bacteria
bind to ribosomal subunit —> cause misreading of genetic code —> inhibit production of proteins
what would we use aminoglycosides for?
gram negative bacteria
especially effective for pseudomonas infection
what is the route of administration for aminoglycosides?
poor oral absorption
good via injection
what are adverse effects of aminoglycosides?
nephrotoxicity
when would we avoid using aminoglycosides?
dehydrated animals
if other nephrotoxic drugs are being used
animals with any sign of renal damage
what is the effect of aminoglycosides on the bacteria?
bactericidal - kill the bacteria
what is the mechanism of action of chloramphenicol?
bind to ribosomal subunit
inhibit protein synthesis
what is the effect of chloramphenicol on the bacteria?
bacteriostatic - don’t kill the cell, just damage it and inhibit growth
when would we not use chloramphenicol?
in immunosuppressed animals - as only inhibits growth of bacteria, doesn’t kill it (relies on immune system)
can chloramphenicol be used in food producing animals?
no - if giving to horses, make sure to sign them off the food chain
what are routes of administration of chloramphenicol?
good oral absorption
not given IV due to short half life
not given IM as very painful
what are adverse effects of chloramphenicol?
colitis
aplastic anaemia in humans - so not given to food producing animals
what can we not administer chloramphenicol with?
beta-lactams
aminoglycosides
fluoroquinolones
macrolides
what are potentiated sulphonamides?
combination of sulphonamide and diaminopyrimidine
what is the mechanism of action of potentiated sulphonamides?
inhibit folic acid pathway —> block nucleic acid synthesis
bacteria cannot produce genetic material
what is the effect of potentiated sulphonamides on the bacteria?
sulphonamide is bacteriostatic - don’t kill bacteria, just inhibit growth
when combined with diaminopyrimidine (potentiated sulphonamide) —> bactericidal
what are cons of potentiated sulphonamides?
ineffective in pus and necrotic tissue
ineffective against most anaerobes
what would we use potentiated sulphonamides for?
strep
staph
some gram negative - E. coli, Salmonella
how do we administer potentiated sulphonamides?
good oral absorption
rapid IV admin causes collapse
what are adverse effects of potentiated sulphonamides?
anaemia, thrombocytopenia
crystalluria
if given IV with detomidine —> fatal dysrhythmias
What is the mechanism of action of tetracyclines?
bind to ribosomal subunit —> inhibit protein synthesis
what is the effect of tetracyclines on the bacteria?
bacteriostatic
what would we use tetracyclines for?
gram positive and negative
some anaerobes
chlamydia
mycoplasma
ehrlichia
can be used to treat contracted tendons in foals
how are pros of tetracyclines?
very lipid soluble so can be used for abscesses
how do we administer tetracyclines?
IV - tetracycline
rapid IV can lead to collapse
oral - doxycycline
what are adverse effects of tetracyclines?
fatal colitis
discolouration of teeth
what is the mechanism of action of fluoroquinolones?
inhibit bacterial DNA gyrase
abnormal configuration of DNA
autolysis
what is the effect of fluoroquinolones on the bacteria?
bactericidal
what are fluoroquinolones used for?
most aerobic gram negative
some aerobic gram positive
mycoplasma
chlamydia
best choice for salmonella
what are the routes of administration for fluoroquinolones?
good oral absorption
can be injected aswell
what are pros of fluoroquinolones?
very lipid soluble - can be used for abscesses
what are adverse effects of fluoroquinolones?
cartilage lesions in foals
what antimicrobials should we not use fluoroquinolones with?
antimicrobials that inhibit bacterial protein synthesis
what is the mechanism of action of macrolides?
binds to ribosomal subunit —> inhibit protein synthesis
what is the effect of macrolides on the bacteria?
bacteriostatic
what is a con of macrolides?
resistance develops quickly
what age of horses would we never use macrolides in?
adult horses - causes colitis
what would we use macrolides for?
treatment of Rhodococcus equi in foals
can give in very small IV dose as a prokinetic (only time we can use in adult horses) - colitis is still a concern
what is the route of administration of macrolides?
oral most common - via tablets
can be injected
what are adverse effects of macrolides?
colitis and diarrhoea in adult horses
hyperthermia
what is the mechanism of action of rifampin?
inhibit bacterial RNA polymerase
decreases RNA synthesis
what are cons of rifampin?
rapid development of resistance - so we use in combination with other antimicrobials
what are pros of rifampin?
good penetration - can be used for abscesses
what do we use rifampin for?
staph
Rhodococcus equi
mycobacteria
some viruses and fungi
what is the best treatment of Rhodococcus equi?
rifampin + erythromycin
what is the route of administration of rifampin?
can be given oral
can be injected
what are adverse effects of rifampin?
stains everything red - urine, faeces, tears, saliva, etc.
what is the mechanism of action of metronidazole?
anaerobic bacteria take it up and break into small free radicals
causes DNA damage
what is metronidazole used for?
anaerobic bacteria
protozoa (but rare in horses)
what is the route of administration of metronidazole?
can be given oral - but not very palatable, and makes you feel unwell
can be given rectally - good absorption but needs increased dose
what are adverse effects of metronidazole?
mutagenic - problems with the foetus if used in pregnant animals
neurotoxicity
depression
decreased appetite
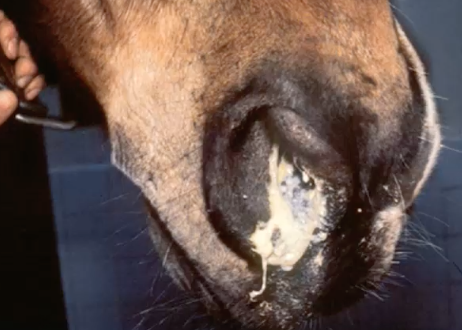
what is the most likely bacteria causing this?
streptococci